
一、题目描述
二、算法原理
思路:使用队列实现层序遍历 + 让节点绑定一个下标 pair< TreeNode* , unsigned int>
例如:
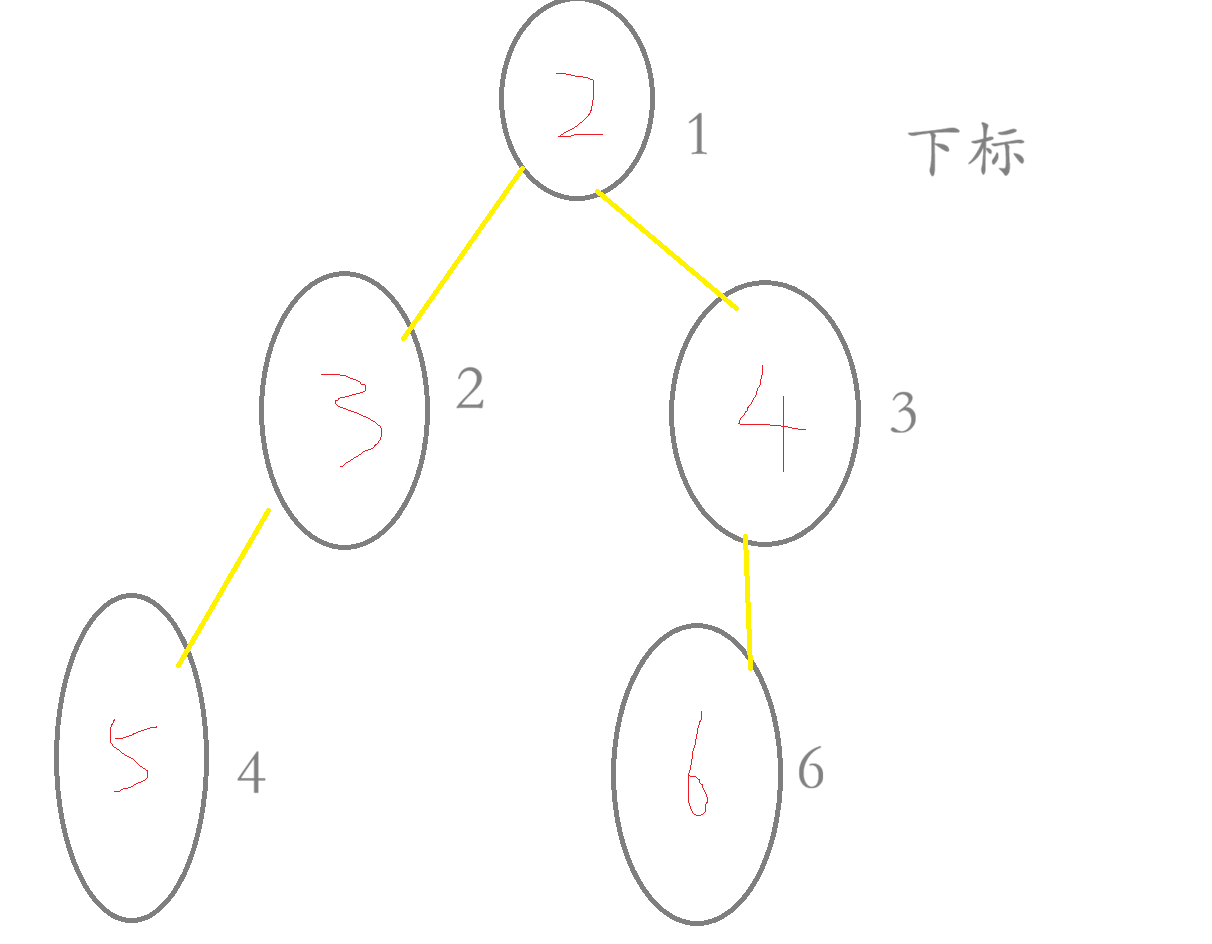
计算左节点的下标的公式:父亲节点 * 2
计算右节点的下边的公式:父亲节点 * 2 + 1
第一层的宽度:1
第二层的宽度:3 - 2 + 1 = 2
第三层的宽度:6 - 4 + 1 = 3
故而最大的宽度位3
为什么使用 unsigned int 因为数值溢出了也不报错。
当使用 int 时,即使一个数溢出了:
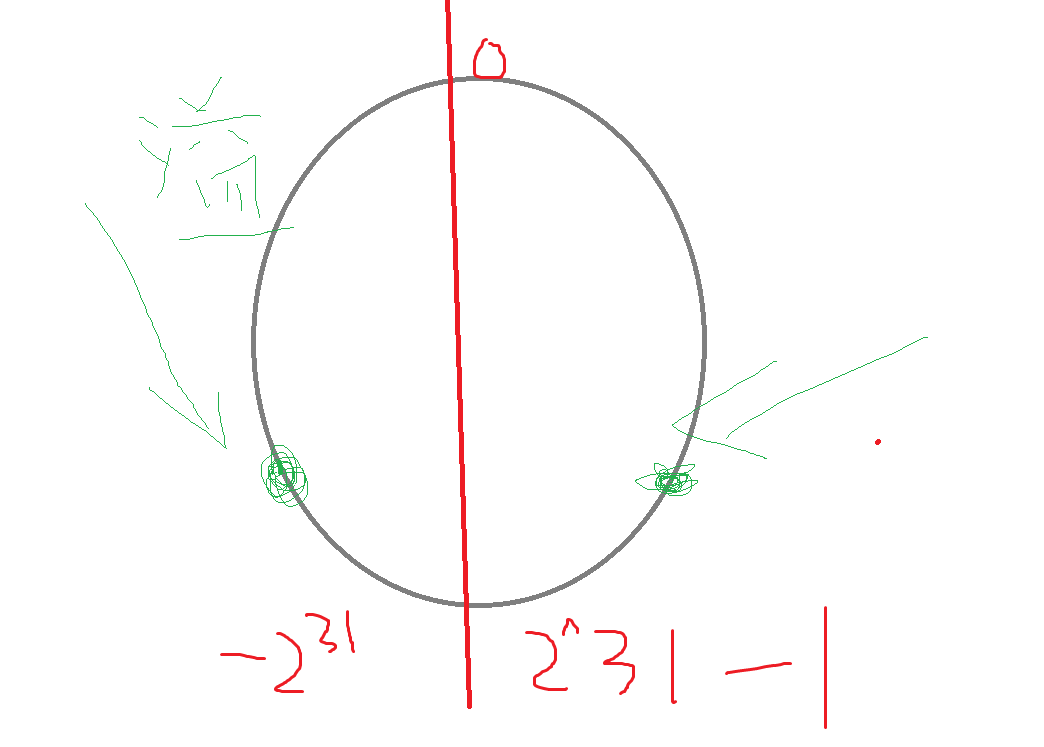
此时这两个数其中一个溢出了,但是相减出来的值是正确的,不过这样编译器会报错,所以使用 unsigned int
三、代码实现
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int>> que;//给每个节点绑定一个下标
que.push({root,1});//让 root 绑定 1 下标
unsigned int maxi = 0;//记录最大的宽度
while(!que.empty())
{
int popnum = que.size();
unsigned int l = que.front().second;//左边的节点的下标
unsigned int r = 0;
while(popnum--)
{
pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int> node = que.front();
que.pop();
unsigned int index = node.second;
if(node.first->left != nullptr)
{
que.push({node.first->left,2 * index});
}
if(node.first->right != nullptr)
{
que.push({node.first->right,2 * index + 1});
}
if(popnum == 0) r = index;//最右节点的下标
}
maxi = max(maxi, r - l + 1);
}
return maxi;
}
};