定义
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或
Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路
径会比其他路径长出俩倍,因而是接近平衡的。
性质
1.左根右:左根的值小于根节点的值小于右节点的值
2.根叶黑:根节点和叶子(定义空节点为叶子节点)为黑色
3.不红红:不会出现两个连续的红色的节点
4.黑路同:从根节点到叶子节点的的任意一条路径的黑色节点的数量都相等
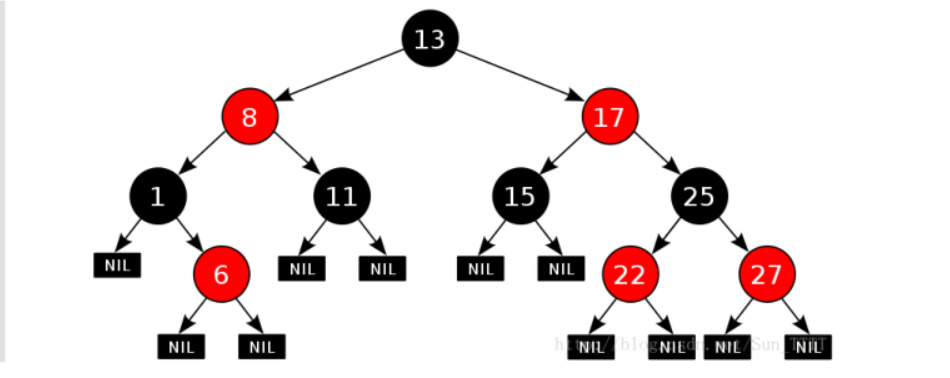
比如下面的
节点的定义
cpp
enum Col
{
RED
,BLACK
};
template<class T>
class AVLTreeNode
{
public:
AVLTreeNode(const T& data=T(),Col col=RED)
:_val(data)
,_col(col)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
}
T _val;
Col _col;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _left;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _right;
AVLTreeNode<T>* _parent;
};插入操作
对于红黑树来说,最重要的就是插入操作,其他的都基本上和AVL树和二叉树差不多
关于插入有一下几种情况:在这之前,需要确定一下,新插入的节点必须是红色节点,因为如果是黑色节点的话,就会导致违反黑路同的原则,导致一条路上多一个黑色节点,虽然插入红色节点可能会导致违反不红红的原则,但是,这个东西比违反黑路同处理问题来更加简单,况且,也是可能违反不红红的原则,黑路同那是必然违反的
以parent为grandfather节点的左节点为例
1.插入一个红色节点:父亲是黑色节点,不用处理,什么都不原则都不违反
2.插入一个红色节点:父亲是红色节点,需要处理,有以下几种情况:
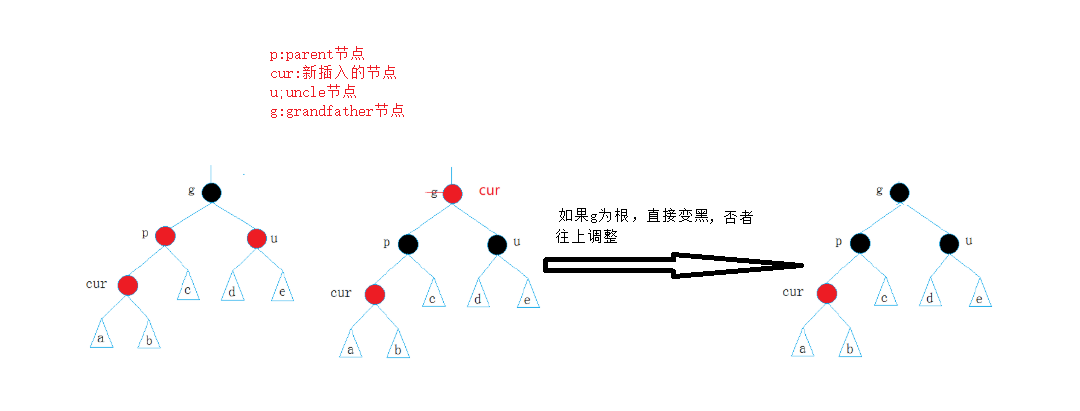
(a)叔叔是红色节点:父亲和叔叔变成黑色节点,祖父节点变成红色,继续往上调整(如果祖父节点是根节点,就变成黑色)
(b)叔叔是黑色节点或空节点:
(i)cur为parent节点的左子树,将grandfather节点右单旋转,将parent变成黑色,grandfather变成红色
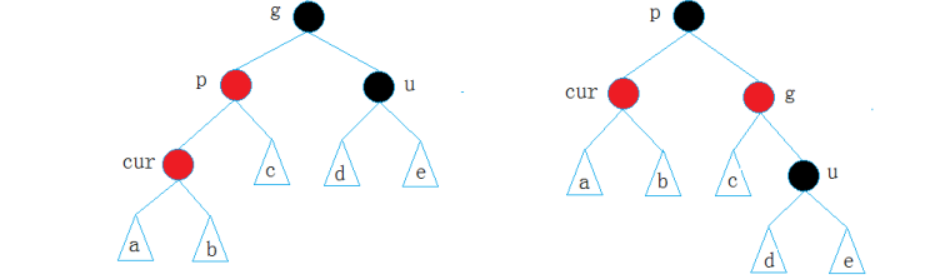
但是有人会说,万一g为根节点嘞?这是不可能的,如果g为根节点,在插入节点的时候,p和u必然为黑色节点,所以这种情况必然是由第一种情况变来的,比如下面的
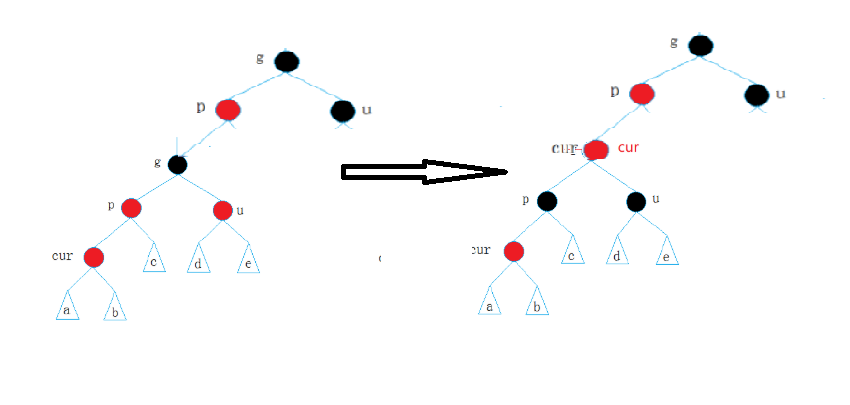
(ii)cur为parent节点的右子树
对p进行左单旋转,让它变成上面的那种情况,然后按照上面的那种进行处理
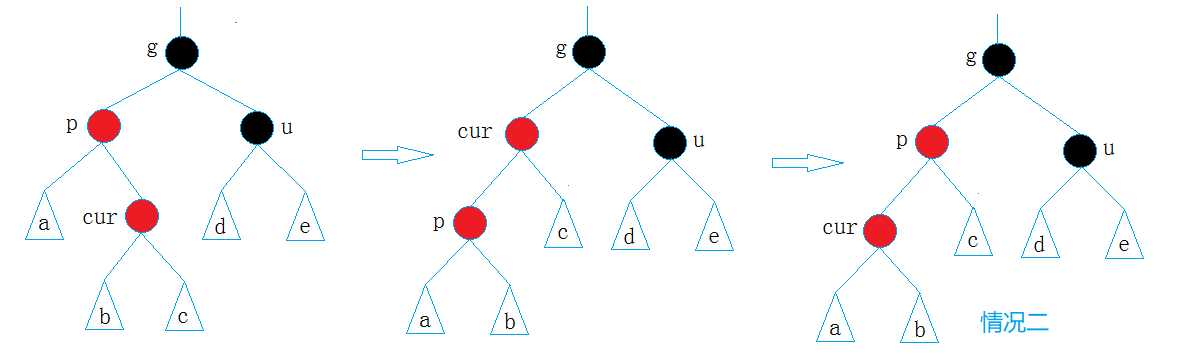
注意:如果parent在grandfather的右边分析方法和上面的一样
代码实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
enum Col
{
RED
,BLACK
};
template<class T>
class RBTreeNode
{
public:
RBTreeNode(const T& data=T(),Col col=RED)
:_val(data)
,_col(col)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{
}
T _val;
Col _col;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
};
template<class T>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
RBTree() = default;
RBTree& operator=(const RBTree<T>& a)
{
swap(_root, a._root);
return *this;
}
RBTree(const RBTree<T>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
bool insert(const T& val)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(val);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_val < val)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_val > val)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else return false;
}
cur = new Node(val);
cur->_col = RED; //新节点定义为红色节点,给黑色违反黑路同
if (val > parent->_val)
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent ==grandfather->_left)
{
// g
// p u
//cur
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//uncle不存在或者为黑色
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
//parent为grandfather的右边
//uncle在左边
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle&& uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//uncle的颜色为黑色或者不存在
// g
// u p
// cur
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
T& root_val()
{
return _root->_val;
}
void inordered()
{
_MidOrdered(_root); //中序遍历,判断是否是二叉搜索树
}
bool IsValidRBTree() //红黑树的检测
{
Node* pRoot = GetRoot();
// 空树也是红黑树
if (nullptr == pRoot)
return true;
// 检测根节点是否满足情况
if (BLACK != pRoot->_col)
{
cout << "违反红黑树性质二:根节点必须为黑色" << endl;
return false;
}
// 获取任意一条路径中黑色节点的个数
size_t blackCount = 0;
Node* pCur = pRoot;
while (pCur)
{
if (BLACK == pCur->_col)
blackCount++;
pCur = pCur->_left;
}
// 检测是否满足红黑树的性质,k用来记录路径中黑色节点的个数
size_t k = 0;
return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot, k, blackCount);
}
bool _IsValidRBTree(Node* pRoot, size_t k, const size_t blackCount)
{
//走到null之后,判断k和black是否相等
if (nullptr == pRoot)
{
if (k != blackCount)
{
cout << "违反性质四:每条路径中黑色节点的个数必须相同" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 统计黑色节点的个数
if (BLACK == pRoot->_col)
k++;
// 检测当前节点与其双亲是否都为红色
Node* pParent = pRoot->_parent;
if (pParent && RED == pParent->_col&& RED == pRoot->_col)
{
cout << "违反性质三:没有连在一起的红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_left, k, blackCount) &&
_IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_right, k, blackCount);
}
Node* GetRoot()
{
return _root;
}
private:
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* ParentParent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (ParentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == ParentParent->_left)
{
ParentParent->_left = subR;
subR->_parent = ParentParent;
}
else
{
ParentParent->_right = subR;
subR->_parent = ParentParent;
}
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* ParentParent = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (ParentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == ParentParent->_left)
{
ParentParent->_left = subL;
subL->_parent = ParentParent;
}
else
{
ParentParent->_right = subL;
subL->_parent = ParentParent;
}
}
}
void RotateRL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
RotateR(parent->_right);
RotateL(parent);
}
void RotateLR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
RotateL(parent->_left);
RotateR(parent);
}
void _MidOrdered(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr) return;
_MidOrdered(root->_left);
cout << root->_val << " ";
_MidOrdered(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};运行代码
cpp
#include"RBTree.h"
#include<vector>
void test01()
{
vector<int> v = { 1,3,4,5,8,3,4,6,3,2};
RBTree<int> R;
for (auto& e : v)
{
R.insert(e);
}
R.inordered();
cout << endl;
cout << R.IsValidRBTree() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}运行效果: