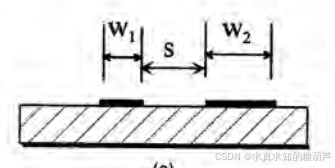
图1 不对称耦合微带线
这里讨论的是如图1剖面不对称,在图2中左右1和3端口、2和4端口满足对称条件
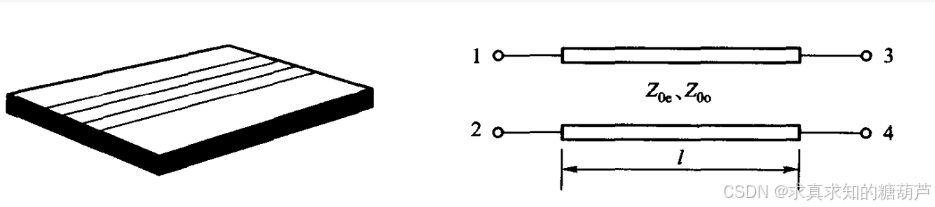
图2 端口顺序定义
参考前面的5篇文章中我们推出了如下公式
U1U2\]=\[11k−1k\]\[UeIUoI\](1) \\left\[\\begin{array}{l} U_{1} \\\\ U_{2} \\end{array}\\right\]=\\left\[\\begin{array}{cc} 1 \& 1 \\\\ k \& -\\frac{1}{k} \\end{array}\\right\]\\left\[\\begin{array}{l} U_{\\mathrm{e}}\^{I} \\\\ U_{\\mathrm{o}}\^{I} \\end{array}\\right\] \\quad(1) \[U1U2\]=\[1k1−k1\]\[UeIUoI\](1) \[U3U4\]=\[11k−1k\]\[UeIIUoII\](2) \\left\[\\begin{array}{l} U_{3} \\\\ U_{4} \\end{array}\\right\]=\\left\[\\begin{array}{cc} 1 \& 1 \\\\ k \& -\\frac{1}{k} \\end{array}\\right\]\\left\[\\begin{array}{l} U_{\\mathrm{e}}\^{II} \\\\ U_{\\mathrm{o}}\^{II} \\end{array}\\right\] \\quad(2) \[U3U4\]=\[1k1−k1\]\[UeIIUoII\](2) \[IeIIoI\]=kk2+1\[1k1k−1\]\[I1I2\](3) \\left\[\\begin{array}{l} I_{\\mathrm{e}}\^{I} \\\\ I_{\\mathrm{o}}\^{I} \\end{array}\\right\]=\\frac{k}{k\^{2}+1}\\left\[\\begin{array}{cc} \\frac{1}{k} \& 1 \\\\ k \& -1 \\end{array}\\right\]\\left\[\\begin{array}{l} I_{1} \\\\ I_{2} \\end{array}\\right\] \\quad(3) \[IeIIoI\]=k2+1k\[k1k1−1\]\[I1I2\](3) \[IeIIIoII\]=kk2+1\[1k1k−1\]\[I3I4\](4) \\left\[\\begin{array}{l} I_{\\mathrm{e}}\^{II} \\\\ I_{\\mathrm{o}}\^{II} \\end{array}\\right\]=\\frac{k}{k\^{2}+1}\\left\[\\begin{array}{cc} \\frac{1}{k} \& 1 \\\\ k \& -1 \\end{array}\\right\]\\left\[\\begin{array}{l} I_{3} \\\\ I_{4} \\end{array}\\right\] \\quad(4) \[IeIIIoII\]=k2+1k\[k1k1−1\]\[I3I4\](4) 传输线ABCD矩阵可以由如下二式表示 \[Ue1Ie1\]=\[cosθejZ0esinθejY0esinθecosθe\]\[UeIIIeII\](5) \\begin{bmatrix} U_e\^1 \\\\ I_e\^1 \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} \\cos \\theta_e \& j Z_{0e} \\sin \\theta_e \\\\ j Y_{0e} \\sin \\theta_e \& \\cos \\theta_e \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} U_e\^{II} \\\\ I_e\^{II} \\end{bmatrix}\\qquad(5) \[Ue1Ie1\]=\[cosθejY0esinθejZ0esinθecosθe\]\[UeIIIeII\](5) \[Uo1Io1\]=\[cosθojZ0osinθojY0osinθocosθo\]\[UoIIIoII\](6) \\begin{bmatrix} U_o\^1 \\\\ I_o\^1 \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} \\cos \\theta_o \& j Z_{0o} \\sin \\theta_o \\\\ j Y_{0o} \\sin \\theta_o \& \\cos \\theta_o \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} U_o\^{II} \\\\ I_o\^{II} \\end{bmatrix}\\qquad(6) \[Uo1Io1\]=\[cosθojY0osinθojZ0osinθocosθo\]\[UoIIIoII\](6) (这里 Y0e=1/Z0e,Y0o=1/Z0oY_{0e} = 1/Z_{0e}, Y_{0o} = 1/Z_{0o}Y0e=1/Z0e,Y0o=1/Z0o) 分析思路:下面我们需要将去耦后的传输线ABCD参数转换为二端口的Z参数矩阵。通过**奇偶模分解法,**将四端口网络分解为偶模和奇模两个独立的二端口网络,然后通过**前后两个变换矩阵**组合得到整体Z参数。 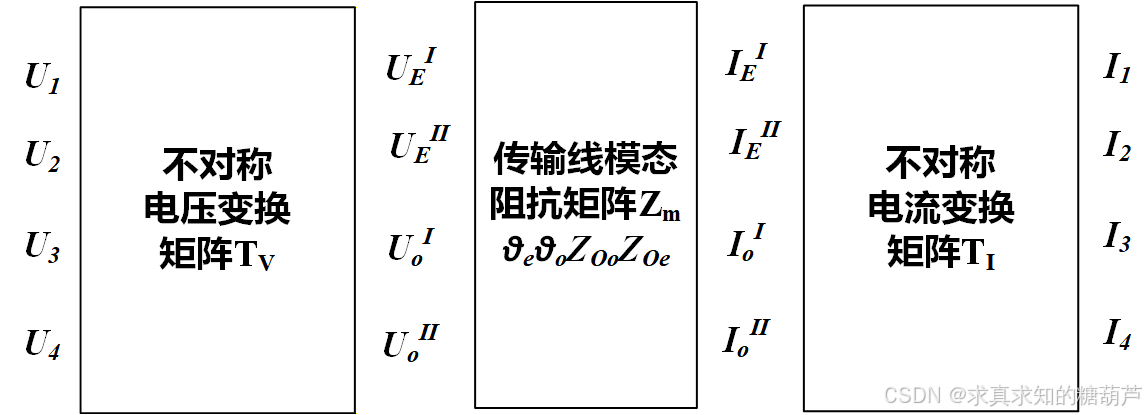 图3 变换矩阵Z参数求解思路 #### 1. 变量定义与变换关系 设四端口网络的端口电压和电流(定义所有电流流入网络为正)为: Vp=\[U1,U2,U3,U4\]T,Ip=\[I1,I2,I3,I4\]T. \\mathbf{V}_p = \[U_1, U_2, U_3, U_4\]\^T, \\quad \\mathbf{I}_p = \[I_1, I_2, I_3, I_4\]\^T. Vp=\[U1,U2,U3,U4\]T,Ip=\[I1,I2,I3,I4\]T. 奇偶模电压、电流定义为: Vm=\[UeI,UeII,UoI,UoII\]T,Im=\[IeI,IeII,IoI,IoII\]T. \\mathbf{V}_m = \[U_e\^I, U_e\^{II}, U_o\^I, U_o\^{II}\]\^T, \\quad \\mathbf{I}_m = \[I_e\^I, I_e\^{II}, I_o\^I, I_o\^{II}\]\^T. Vm=\[UeI,UeII,UoI,UoII\]T,Im=\[IeI,IeII,IoI,IoII\]T. 根据式(1)-(4),变换关系为: \[U1U2\]=M\[UeIUoI\],\[U3U4\]=M\[UeIIUoII\],M=\[11k−1/k\]. \\begin{bmatrix} U_1 \\\\ U_2 \\end{bmatrix} = \\mathbf{M} \\begin{bmatrix} U_e\^I \\\\ U_o\^I \\end{bmatrix}, \\quad \\begin{bmatrix} U_3 \\\\ U_4 \\end{bmatrix} = \\mathbf{M} \\begin{bmatrix} U_e\^{II} \\\\ U_o\^{II} \\end{bmatrix}, \\quad \\mathbf{M} = \\begin{bmatrix} 1 \& 1 \\\\ k \& -1/k \\end{bmatrix}. \[U1U2\]=M\[UeIUoI\],\[U3U4\]=M\[UeIIUoII\],M=\[1k1−1/k\]. \[IeIIoI\]=N\[I1I2\],\[IeIIIoII\]=N\[I3I4\],N=kk2+1\[1/k1k−1\]=M−1. \\begin{bmatrix} I_e\^I \\\\ I_o\^I \\end{bmatrix} = \\mathbf{N} \\begin{bmatrix} I_1 \\\\ I_2 \\end{bmatrix}, \\quad \\begin{bmatrix} I_e\^{II} \\\\ I_o\^{II} \\end{bmatrix} = \\mathbf{N} \\begin{bmatrix} I_3 \\\\ I_4 \\end{bmatrix}, \\quad \\mathbf{N} = \\frac{k}{k\^2+1} \\begin{bmatrix} 1/k \& 1 \\\\ k \& -1 \\end{bmatrix} = \\mathbf{M}\^{-1}. \[IeIIoI\]=N\[I1I2\],\[IeIIIoII\]=N\[I3I4\],N=k2+1k\[1/kk1−1\]=M−1. 根据以上关系,整体**电压变换矩阵 TV\\mathbf{T}_VTV和电流变换矩阵 TI\\mathbf{T}_ITI**满足: Vp=TVVm,Im=TIIp. \\mathbf{V}_p = \\mathbf{T}_V \\mathbf{V}_m, \\quad \\mathbf{I}_m = \\mathbf{T}_I \\mathbf{I}_p. Vp=TVVm,Im=TIIp. 具体表达式如下: TV=\[1010k0−1/k001010k0−1/k\],TI=Tv−1=1k2+1\[1k00001kk2−k0000k2−k\] \\mathbf{T}_V = \\begin{bmatrix} 1 \& 0 \& 1 \& 0 \\\\ k \& 0 \& -1/k \& 0 \\\\ 0 \& 1 \& 0 \& 1 \\\\ 0 \& k \& 0 \& -1/k \\end{bmatrix}, \\quad \\mathbf{T}_I = \\mathbf{T}_v\^{-1} = \\frac{1}{k\^2+1} \\begin{bmatrix} 1 \& k \& 0 \& 0 \\\\ 0 \& 0 \& 1 \& k \\\\ k\^2 \& -k \& 0 \& 0 \\\\ 0 \& 0 \& k\^2 \& -k \\end{bmatrix} TV= 1k00001k1−1/k00001−1/k ,TI=Tv−1=k2+11 10k20k0−k0010k20k0−k #### 2. 模态阻抗矩阵 偶模和奇模二端口网络(均为传输线段)的ABCD参数如式(5)(6)所示。可以根据ABCD到Z参数二端口转换公式转换为Z参数(电流均定义为流入)得: 偶模二端口Z参数矩阵: Ze=\[Z11eZ12eZ21eZ22e\]=\[−jZ0ecotθe−jZ0ecscθe−jZ0ecscθe−jZ0ecotθe\]. \\mathbf{Z}_e = \\begin{bmatrix} Z_{11}\^e \& Z_{12}\^e \\\\ Z_{21}\^e \& Z_{22}\^e \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} -jZ_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e \& -jZ_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e \\\\ -jZ_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e \& -jZ_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e \\end{bmatrix}. Ze=\[Z11eZ21eZ12eZ22e\]=\[−jZ0ecotθe−jZ0ecscθe−jZ0ecscθe−jZ0ecotθe\]. 奇模二端口Z参数矩阵: Zo=\[Z11oZ12oZ21oZ22o\]=\[−jZ0ocotθo−jZ0ocscθo−jZ0ocscθo−jZ0ocotθo\]. \\mathbf{Z}_o = \\begin{bmatrix} Z_{11}\^o \& Z_{12}\^o \\\\ Z_{21}\^o \& Z_{22}\^o \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} -jZ_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o \& -jZ_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o \\\\ -jZ_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o \& -jZ_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o \\end{bmatrix}. Zo=\[Z11oZ21oZ12oZ22o\]=\[−jZ0ocotθo−jZ0ocscθo−jZ0ocscθo−jZ0ocotθo\]. 由于**两模态独立** ,整个模态域的4×4阻抗矩阵为分块对角阵: Zm=\[Ze00Zo\]. \\mathbf{Z}_m = \\begin{bmatrix} \\mathbf{Z}_e \& \\mathbf{0} \\\\ \\mathbf{0} \& \\mathbf{Z}_o \\end{bmatrix}. Zm=\[Ze00Zo\]. #### 3. 四端口Z参数矩阵 由 Vm=ZmIm\\mathbf{V}_m = \\mathbf{Z}_m \\mathbf{I}_mVm=ZmIm和上述变换,得: Vp=TVZmTIIp. \\mathbf{V}_p = \\mathbf{T}_V \\mathbf{Z}_m \\mathbf{T}_I \\mathbf{I}_p. Vp=TVZmTIIp. 故四端口Z参数矩阵为: Zp=TVZmTI. \\mathbf{Z}_p = \\mathbf{T}_V \\mathbf{Z}_m \\mathbf{T}_I. Zp=TVZmTI. 代入 TV\\mathbf{T}_VTV、Zm\\mathbf{Z}_mZm、TI\\mathbf{T}_ITI 并进行矩阵乘法,可得各Z参数表达式。 Z11=1k2+1\[Z11e+k2Z11o\]=−jk2+1(Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθo),Z12=kk2+1\[Z11e−Z11o\]=−jkk2+1(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo),Z13=1k2+1\[Z12e+k2Z12o\]=−jk2+1(Z0ecscθe+k2Z0ocscθo),Z14=kk2+1\[Z12e−Z12o\]=−jkk2+1(Z0ecscθe−Z0ocscθo),Z22=1k2+1\[k2Z11e+Z11o\]=−jk2+1(k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo),Z23=kk2+1\[Z12e−Z12o\]=Z14,Z24=1k2+1\[k2Z12e+Z12o\]=−jk2+1(k2Z0ecscθe+Z0ocscθo),Z33=Z11,Z34=Z12,Z44=Z22. \\begin{aligned} Z_{11} \&= \\frac{1}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ Z_{11}\^e + k\^2 Z_{11}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j}{k\^2+1}\\left( Z_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e + k\^2 Z_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{12} \&= \\frac{k}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ Z_{11}\^e - Z_{11}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j k}{k\^2+1}\\left( Z_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{13} \&= \\frac{1}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ Z_{12}\^e + k\^2 Z_{12}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j}{k\^2+1}\\left( Z_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e + k\^2 Z_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{14} \&= \\frac{k}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ Z_{12}\^e - Z_{12}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j k}{k\^2+1}\\left( Z_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e - Z_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{22} \&= \\frac{1}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ k\^2 Z_{11}\^e + Z_{11}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j}{k\^2+1}\\left( k\^2 Z_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e + Z_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{23} \&= \\frac{k}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ Z_{12}\^e - Z_{12}\^o \\right\] = Z_{14}, \\\\ Z_{24} \&= \\frac{1}{k\^2+1}\\left\[ k\^2 Z_{12}\^e + Z_{12}\^o \\right\] = -\\frac{j}{k\^2+1}\\left( k\^2 Z_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e + Z_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o \\right), \\\\ Z_{33} \&= Z_{11}, \\quad Z_{34} = Z_{12}, \\quad Z_{44} = Z_{22}. \\end{aligned} Z11Z12Z13Z14Z22Z23Z24Z33=k2+11\[Z11e+k2Z11o\]=−k2+1j(Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθo),=k2+1k\[Z11e−Z11o\]=−k2+1jk(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo),=k2+11\[Z12e+k2Z12o\]=−k2+1j(Z0ecscθe+k2Z0ocscθo),=k2+1k\[Z12e−Z12o\]=−k2+1jk(Z0ecscθe−Z0ocscθo),=k2+11\[k2Z11e+Z11o\]=−k2+1j(k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo),=k2+1k\[Z12e−Z12o\]=Z14,=k2+11\[k2Z12e+Z12o\]=−k2+1j(k2Z0ecscθe+Z0ocscθo),=Z11,Z34=Z12,Z44=Z22. 其余元素由互易性和对称性确定:Zij=ZjiZ_{ij} = Z_{ji}Zij=Zji,且由于结构对称(端口1与3、2与4在几何上对称),有Z33=Z11Z_{33}=Z_{11}Z33=Z11、Z44=Z22Z_{44}=Z_{22}Z44=Z22、Z34=Z12Z_{34}=Z_{12}Z34=Z12、Z13=Z31Z_{13}=Z_{31}Z13=Z31 等。 Z=−jk2+1\[Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)Z0esinθe+k2Z0osinθok(Z0esinθe−Z0osinθo)k(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθok(Z0esinθe−Z0osinθo)k2Z0esinθe+Z0osinθoZ0esinθe+k2Z0osinθok(Z0esinθe−Z0osinθo)Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k(Z0esinθe−Z0osinθo)k2Z0esinθe+Z0osinθok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo\] Z = \\frac{-j}{k\^2+1} \\begin{bmatrix} Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e + k\^2 Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o \& k (Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o) \& \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} + k\^2 \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \& k \\left( \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} - \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \\right) \\\\\[8pt\] k (Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o) \& k\^2 Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e + Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o \& k \\left( \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} - \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \\right) \& k\^2 \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} + \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \\\\\[8pt\] \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} + k\^2 \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \& k \\left( \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} - \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \\right) \& Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e + k\^2 Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o \& k (Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o) \\\\\[8pt\] k \\left( \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} - \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \\right) \& k\^2 \\dfrac{Z_{0e}}{\\sin\\theta_e} + \\dfrac{Z_{0o}}{\\sin\\theta_o} \& k (Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o) \& k\^2 Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_e + Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_o \\end{bmatrix} Z=k2+1−j Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)sinθeZ0e+k2sinθoZ0ok(sinθeZ0e−sinθoZ0o)k(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθok(sinθeZ0e−sinθoZ0o)k2sinθeZ0e+sinθoZ0osinθeZ0e+k2sinθoZ0ok(sinθeZ0e−sinθoZ0o)Z0ecotθe+k2Z0ocotθok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k(sinθeZ0e−sinθoZ0o)k2sinθeZ0e+sinθoZ0ok(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo)k2Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo #### 小结一下 当k=1k=1k=1(对称耦合微带线)时,上述结果退化为经典对称耦合线Z参数: Z11=Z22=Z33=Z44=−j2(Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo),Z12=Z21=Z34=Z43=−j2(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo),Z13=Z31=Z24=Z42=−j2(Z0ecscθe+Z0ocscθo),Z14=Z41=Z23=Z32=−j2(Z0ecscθe−Z0ocscθo). \\begin{aligned} Z_{11} \&= Z_{22} = Z_{33} = Z_{44} = -\\frac{j}{2}(Z_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e + Z_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o), \\\\ Z_{12} \&= Z_{21} = Z_{34} = Z_{43} = -\\frac{j}{2}(Z_{0e}\\cot\\theta_e - Z_{0o}\\cot\\theta_o), \\\\ Z_{13} \&= Z_{31} = Z_{24} = Z_{42} = -\\frac{j}{2}(Z_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e + Z_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o), \\\\ Z_{14} \&= Z_{41} = Z_{23} = Z_{32} = -\\frac{j}{2}(Z_{0e}\\csc\\theta_e - Z_{0o}\\csc\\theta_o). \\end{aligned} Z11Z12Z13Z14=Z22=Z33=Z44=−2j(Z0ecotθe+Z0ocotθo),=Z21=Z34=Z43=−2j(Z0ecotθe−Z0ocotθo),=Z31=Z24=Z42=−2j(Z0ecscθe+Z0ocscθo),=Z41=Z23=Z32=−2j(Z0ecscθe−Z0ocscθo). 参数模比系数(ke=k,ko=1/kk_e=k, k_o=1/kke=k,ko=1/k 1、2端口偶模电压比例系数) kkk 表征了不对称程度,k≠1k \\neq 1k=1 时,端口1与2、3与4的阻抗不再相同. 这种推导方法通过**模态分解与变换,将复杂的不对称耦合线四端口网络分析转化为两个独立传输线模型的组合,**是分析耦合线结构的有效手段,**相比四端口矩阵直接相互直接转换要简单很多** 。前面第(四)节中(参考梁老师简明微波书2-12节)我们用该方法推导出了**耦合微带线的A参数矩阵** ,同时在**RF and Microwave Coupled-Line Circuits** 书中第四章也用该方法推出了四端口耦合线的**S参数矩阵** 。 **当对称均匀时(k=1k=1k=1,θe=θo\\theta_e = \\theta_oθe=θo),矩阵将大幅简化**,可退化为上一节(五)中我们推出来的均匀对称耦合线节的Z参数形式。 Z=−j2sinθ\[cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)Z0e+Z0oZ0e−Z0ocosθ(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)Z0e−Z0oZ0e+Z0o(Z0e+Z0o)(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)(Z0e−Z0o)(Z0e+Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)\] \\boxed{ Z = \\frac{-j}{2\\sin\\theta} \\begin{bmatrix} \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \& Z_{0e}+Z_{0o} \& Z_{0e}-Z_{0o} \\\\ \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \& Z_{0e}-Z_{0o} \& Z_{0e}+Z_{0o} \\\\ (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \& (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \\\\ (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \& (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}-Z_{0o}) \& \\cos\\theta (Z_{0e}+Z_{0o}) \\end{bmatrix} } Z=2sinθ−j cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)(Z0e+Z0o)(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e+Z0o)(Z0e−Z0o)(Z0e+Z0o)Z0e+Z0oZ0e−Z0ocosθ(Z0e+Z0o)cosθ(Z0e−Z0o)Z0e−Z0oZ0e+Z0ocosθ(Z0e−Z0o)cosθ(Z0e+Z0o) ### 应用:如何应用?类似第五节 从给定的四端口阻抗矩阵ZZZ反求五个参数(Z0eZ_{0e}Z0e、Z0oZ_{0o}Z0o、θe\\theta_eθe、θo\\theta_oθo、kkk)可以按如下方法: #### 提取矩阵独立元素 给定对称的 ZZZ 矩阵,我们取以下六个独立元素: Z11, Z12, Z13, Z14, Z22, Z24 Z_{11},\\ Z_{12},\\ Z_{13},\\ Z_{14},\\ Z_{22},\\ Z_{24} Z11, Z12, Z13, Z14, Z22, Z24 并验证对称性:Z21=Z12Z_{21}=Z_{12}Z21=Z12,Z23=Z14Z_{23}=Z_{14}Z23=Z14,Z33=Z11Z_{33}=Z_{11}Z33=Z11,Z34=Z12Z_{34}=Z_{12}Z34=Z12,Z44=Z22Z_{44}=Z_{22}Z44=Z22。**实际画的版图可能不那么理想。** #### 求解不对称系数 kkk 利用 Z11Z_{11}Z11、Z12Z_{12}Z12、Z22Z_{22}Z22 建立关于kkk 的方程: Z12k2+(Z11−Z22)k−Z12=0 Z_{12} k\^2 + (Z_{11} - Z_{22}) k - Z_{12} = 0 Z12k2+(Z11−Z22)k−Z12=0 解得: k=−(Z11−Z22)±(Z11−Z22)2+4Z1222Z12(7) k = \\frac{-(Z_{11}-Z_{22}) \\pm \\sqrt{(Z_{11}-Z_{22})\^2 + 4Z_{12}\^2}}{2Z_{12}}\\quad{(7)} k=2Z12−(Z11−Z22)±(Z11−Z22)2+4Z122 (7) 选取正实根(通常 k\>0k\>0k\>0),若两根均为正,需结合后续步骤选择合理的解。 #### 计算中间变量A,B,C,DA, B, C, DA,B,C,D 定义: α=1k2+1 \\alpha = \\frac{1}{k\^2+1} α=k2+11 计算: A=12\[(Z11+Z22)+k2+1kZ12\]B=12\[(Z11+Z22)−k2+1kZ12\]C=12\[(Z13+Z24)+k2+1kZ14\]D=12\[(Z13+Z24)−k2+1kZ14\](8) \\begin{aligned} A \&= \\frac{1}{2}\\left\[ (Z_{11}+Z_{22}) + \\frac{k\^2+1}{k} Z_{12} \\right\] \\\\ B \&= \\frac{1}{2}\\left\[ (Z_{11}+Z_{22}) - \\frac{k\^2+1}{k} Z_{12} \\right\] \\\\ C \&= \\frac{1}{2}\\left\[ (Z_{13}+Z_{24}) + \\frac{k\^2+1}{k} Z_{14} \\right\] \\\\ D \&= \\frac{1}{2}\\left\[ (Z_{13}+Z_{24}) - \\frac{k\^2+1}{k} Z_{14} \\right\] \\end{aligned}\\quad{(8)} ABCD=21\[(Z11+Z22)+kk2+1Z12\]=21\[(Z11+Z22)−kk2+1Z12\]=21\[(Z13+Z24)+kk2+1Z14\]=21\[(Z13+Z24)−kk2+1Z14\](8) 其中 A=Z0ecotθeA = Z_{0e} \\cot\\theta_eA=Z0ecotθe,B=Z0ocotθoB = Z_{0o} \\cot\\theta_oB=Z0ocotθo,C=Z0e/sinθeC = Z_{0e}/\\sin\\theta_eC=Z0e/sinθe,D=Z0o/sinθoD = Z_{0o}/\\sin\\theta_oD=Z0o/sinθo。 #### 求解偶模和奇模参数 * **偶模** : Z0e=C2−A2(取正值) Z_{0e} = \\sqrt{C\^2 - A\^2} \\quad (\\text{取正值}) Z0e=C2−A2 (取正值) cosθe=AC,θe=arccos(AC)∈\[0,π\] \\cos\\theta_e = \\frac{A}{C}, \\quad \\theta_e = \\arccos\\left(\\frac{A}{C}\\right) \\in \[0, \\pi\] cosθe=CA,θe=arccos(CA)∈\[0,π
或联合 sinθe=Z0e/C\sin\theta_e = Z_{0e}/Csinθe=Z0e/C确定象限。
- 奇模 :
Z0o=D2−B2(取正值) Z_{0o} = \sqrt{D^2 - B^2} \quad (\text{取正值}) Z0o=D2−B2 (取正值)
cosθo=BD,θo=arccos(BD)∈[0,π] \cos\theta_o = \frac{B}{D}, \quad \theta_o = \arccos\left(\frac{B}{D}\right) \in [0, \pi] cosθo=DB,θo=arccos(DB)∈[0,π]
检查求得的Z0eZ_{0e}Z0e、Z0oZ_{0o}Z0o是否为正实数,θe\theta_eθe、θo\theta_oθo是否为实数。若kkk 有两个正根,需将两组解代入验证,选取使所有参数物理合理(如 Z0e,Z0o>0Z_{0e}, Z_{0o}>0Z0e,Z0o>0,0<θe,θo<π0<\theta_e,\theta_o<\pi0<θe,θo<π)的一组。若 Z12=0Z_{12}=0Z12=0 或Z11=Z22Z_{11}=Z_{22}Z11=Z22(可能退化为对称耦合线或解不唯一)。