
前言:
在上一篇文章中我们讲到了异常,但由于这个异常的概念当我们new一些对象时就会碰到释放不完全以及创建不成功的样例,为了解决这一问题C++中增加智能指针这一概念,那么今天带大家来了解一下智能指针。
一.RAII
RAII(Resource Acquisition Is Initialization)是一种利用对象生命周期来控制程序资源(如内
存、文件句柄、网络连接、互斥量等等)的简单技术。
在对象构造时获取资源,接着控制对资源的访问使之在对象的生命周期内始终保持有效,最后在
对象析构的时候释放资源。借此,我们实际上把管理一份资源的责任托管给了一个对象。这种做
法有两大好处:
不需要显式地释放资源。
采用这种方式,对象所需的资源在其生命期内始终保持有效
下面我们根据RAII思想来完成一下我们的smart_ptr
cpp
template<class T>
class smart_ptr {
public:
smart_ptr(T*ptr):_ptr(ptr){ cout << "smart_ptr" << endl; }
~smart_ptr()
{
delete _ptr;
cout << "~smart_ptr" << endl;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};
int main()
{
int* a = new int;
smart_ptr<int> s1(a);
return 0;
}
在C++库中的智能指针大概也是利用的这一个原理,不过肯定是更加的复杂一点。比如重载了*和
->。
二.auto_ptr
在C++11之前C++委员会为了防止内存泄漏的情况采用了auto_ptr。不过auto_ptr有着严重的设计缺陷。
cpp
class Date {
public:
Date(int year,int month,int day):_year(year),_month(month),_day(day){}
~Date()
{
cout << "~Date" << endl;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date* a = new Date(1,2,3);
auto_ptr<Date> ap1(a);
auto_ptr<Date> ap2(ap1);
ap1->_year++;
return 0;
}这段代码设计到管理权限的丢失,当ap2拷贝ap1之后ap1便不可以使用了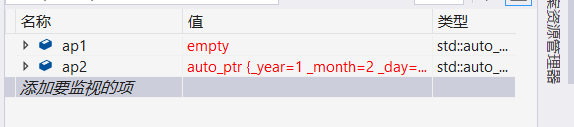
为此C++委员会在C++11中新增了unique_ptr(不支持拷贝)和share_ptr(支持拷贝)。
三.unique_ptr
其实在C++11之前,C++委员会的一位大佬就发现了这一个问题,不过因为C++标准库中的内容并不能够随意的修改,所以便创建了boost库。也称为伪标准库
而我们的unique_ptr的前身就是来自于boost库中的的scoped_ptr。包括share_ptr以及weak_ptr同样也是来自与boost库。
在模拟实现unique_ptr之前我们看一下unique_ptr中使用的一些小细节。
cpp
class Date {
public:
Date(int year=1, int month=1, int day=1) :_year(year), _month(month), _day(day) {}
~Date()
{
cout << "~Date" << endl;
}
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date* d1 = new Date(1, 1, 1);
Date* d2 = new Date[5];
unique_ptr<Date> up1(d1);
unique_ptr<Date> up2(d2);
return 0;
}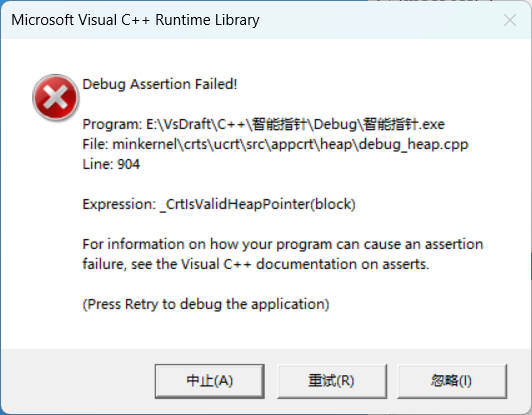
可以看到如果像模板中传入的是一个数组则会导致程序的崩溃,那么我们应该要怎么去解决这一个问题呢?这时我们有两个方法可以选择1.仿函数2.使用库中提供的特化版本。
cpp
template<class T>
class DelateArray
{
public:
void operator()(T* ptr)
{
delete[] ptr;
}
};
int main()
{
Date* d1 = new Date(1, 1, 1);
Date* d2 = new Date[5];
Date* d3 = new Date[5];
unique_ptr<Date> up1(d1);
//仿函数
unique_ptr<Date,DelateArray<Date>> up2(d2);
//特化版本
unique_ptr<Date[]> up3(d3);
return 0;
}
不过特化版本只有对数组有效像关闭文件夹等一些其他的操作仍需要写其对应的仿函数。
四.share_ptr
share_ptr和unique_ptr最大的区别就是share_ptr支持了拷贝,其他与unique_ptr相差不大,像仿函数以及特化的性质也都是有的。
不过需要注意的是两个的书写方法是不一样的:
cpp
int main()
{
Date* d1 = new Date(1, 1, 1);
Date* d2 = new Date[5];
Date* d3 = new Date[5];
shared_ptr<Date> sp1(d1);
//仿函数需要写在类的参数中
shared_ptr<Date> sp2(d2,DelateArray<Date>());
shared_ptr<Date[]> sp3(d3);
return 0;
}不过在share_ptr设计之初有一个很致命的错误为循环引用所以C++11又新增了一个新的接口weak_ptr。weak_ptr只可以管理数据不可以访问数据。
五.weak_ptr
weak_ptr是为了防止一个知明错误而产生的,当share_ptr发生循环引用时导致计数器一直不为0,则会导致内存泄漏。
我们详细讲一下weak_ptr中的一些内置方法。
use_count
在weak_ptr中也是有计数器存在的不过他不参与share_ptr中的计数原则。
expired
观察 weak_ptr所指的对象是否消亡。
lock
cpp
class ListNode {
public:
weak_ptr<ListNode> _next;
weak_ptr<ListNode> _prev;
};
int main()
{
weak_ptr<ListNode> w1;
shared_ptr<ListNode> s1;
{
shared_ptr<ListNode> s2(new ListNode());
w1 = s2;
cout << w1.expired() << endl;
//s1 = w1.lock();
}
cout << w1.expired() << endl;
return 0;
}注释后:

注释前:

六.模拟实现share_ptr以及weak_ptr
++share_ptr++
cpp
template<class T>
class share_ptr
{
public:
share_ptr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
, _count(new int) {
*_count = 1;
}
//template<class D>
//share_ptr(T* ptr, D del)
// : _ptr(ptr)
// , _count(new int(1))
// , _del(del)
//{}
template <class K>
share_ptr(T* ptr, K del)
: _ptr(ptr)
, _del(del)
, _count(new int)
{
*_count = 1;
}
//_ptr=ptr
share_ptr(const share_ptr<T>& ptr)
:_ptr(ptr._ptr)
, _count(ptr._count)
{
++(*_count);
}
//_ptr=ptr
share_ptr<T>& operator=(const share_ptr<T>& ptr)
{
if (_ptr != ptr._ptr)
{
reverse();
_ptr = ptr._ptr;
_count = ptr._count;
++(*_count);
}
return *this;
}
void reverse()
{
if (-- * _count == 0)
{
//delete _ptr;
_del(_ptr);
delete _count;
_ptr = nullptr;
_count = nullptr;
}
}
T& operator*()
{
return _ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
~share_ptr()
{
reverse();
}
T* get()const
{
return _ptr;
}
int get_count()
{
return *_count;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
int* _count = 1;
function<void(T* ptr)> _del = [](T* ptr)
{
delete ptr;
};
};++weak_ptr++
cpp
template<class T>
class weak_ptr
{
public:
weak_ptr()
{}
weak_ptr(const share_ptr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp.get())
{}
weak_ptr<T>& operator=(const share_ptr<T>& sp)
{
_ptr = sp.get();
return *this;
}
private:
T* _ptr = nullptr;
//T* _pcount
};注:这种方法实现的接口不可以作为程序的开发,跟标准库中的原有接口有很大差距,这种实现方法。