题目
给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
数据范围
1 <= candidates.length <= 30
2 <= candidates[i] <= 40
candidates 的所有元素 互不相同
1 <= target <= 40
测试用例
示例1
bash
输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
输出:[[2,2,3],[7]]
解释:
2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。
7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。
仅有这两种组合。示例2
bash
输入: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
输出: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]示例3
bash
输入: candidates = [2], target = 1
输出: []题解1(博主解法,时间OS,空间OT/M)
bash
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
// 结果集:存放所有符合条件的组合
List<List<Integer>> res;
// 缓存数组长度,避免在循环中重复调用 .length
int len;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
// 优化点 1:使用 ArrayList 代替 LinkedList
// ArrayList 底层是数组,内存连续,CPU 缓存命中率高,读取和尾部操作效率极高
res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
len = candidates.length;
// 建议优化:如果数据量较大,可以在这里先排序:Arrays.sort(candidates);
// 排序后可以在 dfs 循环中提前 break,大幅提升剪枝效率
// 开始 DFS 搜索
// list: 当前路径, 0: 当前和, 0: 从第几个数开始选(防止回头选产生重复组合)
dfs(candidates, target, list, 0, 0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, List<Integer> list, int curr, int start) {
// Base Case 1: 找到目标值
if (curr == target) {
// 必须创建一个新的 ArrayList 进行拷贝 (Deep Copy)
// 如果直接 add(list),存进去的只是引用,后续 list 变化时结果集里的内容也会变
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
return;
}
// Base Case 2: 超过目标值,此路不通 (剪枝)
if (curr > target) {
return;
}
// 核心循环
// int i = start:确保单向搜索。比如当前选了第 2 个数,
// 下一层递归也只能从第 2 个数开始选,不能回头选第 1 个数,避免产生 [2,3,2] 这种重复
for (int i = start; i < len; i++) {
// --- 做选择 (Choose) ---
list.add(candidates[i]);
curr += candidates[i];
// --- 递归 (Recurse) ---
// 关键点:传入 i 而不是 i+1
// 题目允许"元素无限制重复被选取",所以下一层依然可以选当前的 candidates[i]
dfs(candidates, target, list, curr, i);
// --- 撤销选择 (Backtrack / Unchoose) ---
// 优化点 2:ArrayList 删除最后一个元素的标准写法
// list.size() - 1 是最后一个元素的索引
// 这一步是 O(1) 的,因为不需要移动数组中的其他元素
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
curr -= candidates[i];
}
}
}题解2(官解,时空同上)
bash
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> combine = new ArrayList<Integer>();
dfs(candidates, target, ans, combine, 0);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> combine, int idx) {
if (idx == candidates.length) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(combine));
return;
}
// 直接跳过
dfs(candidates, target, ans, combine, idx + 1);
// 选择当前数
if (target - candidates[idx] >= 0) {
combine.add(candidates[idx]);
dfs(candidates, target - candidates[idx], ans, combine, idx);
combine.remove(combine.size() - 1);
}
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/solutions/406516/zu-he-zong-he-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。思路
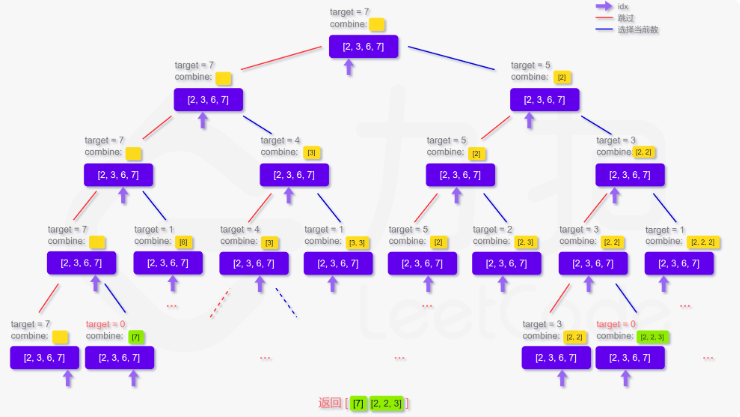
这道题思路依然简单,大体方向就是回溯,不用多思考,但博主的解法与官解存在一些细节上的差异,简单说官解使用的是递归,博主使用的是循环,递归代码简单一些,可读性高,循环代码多一些,但是时间效率高一些,大家仁者见仁智者见智吧。