二叉树
目录
一、二叉树的性质
1.根节点层数为1,一颗非空二叉树的第i层上最多有2^(i-1)个节点
2.根节点层数为1,深度为h的二叉树的最大节点数是2^h - 1
3.任何二叉树,度为0的叶节点个数为n(0),度为2的分支节点个数为n(2),则有n(0) = n(2) + 1
4.根节点层数为1,有n个节点的满二叉树深度h = log(2)(n + 1)
二、二叉树的遍历
子树不断被拆解为根和子树
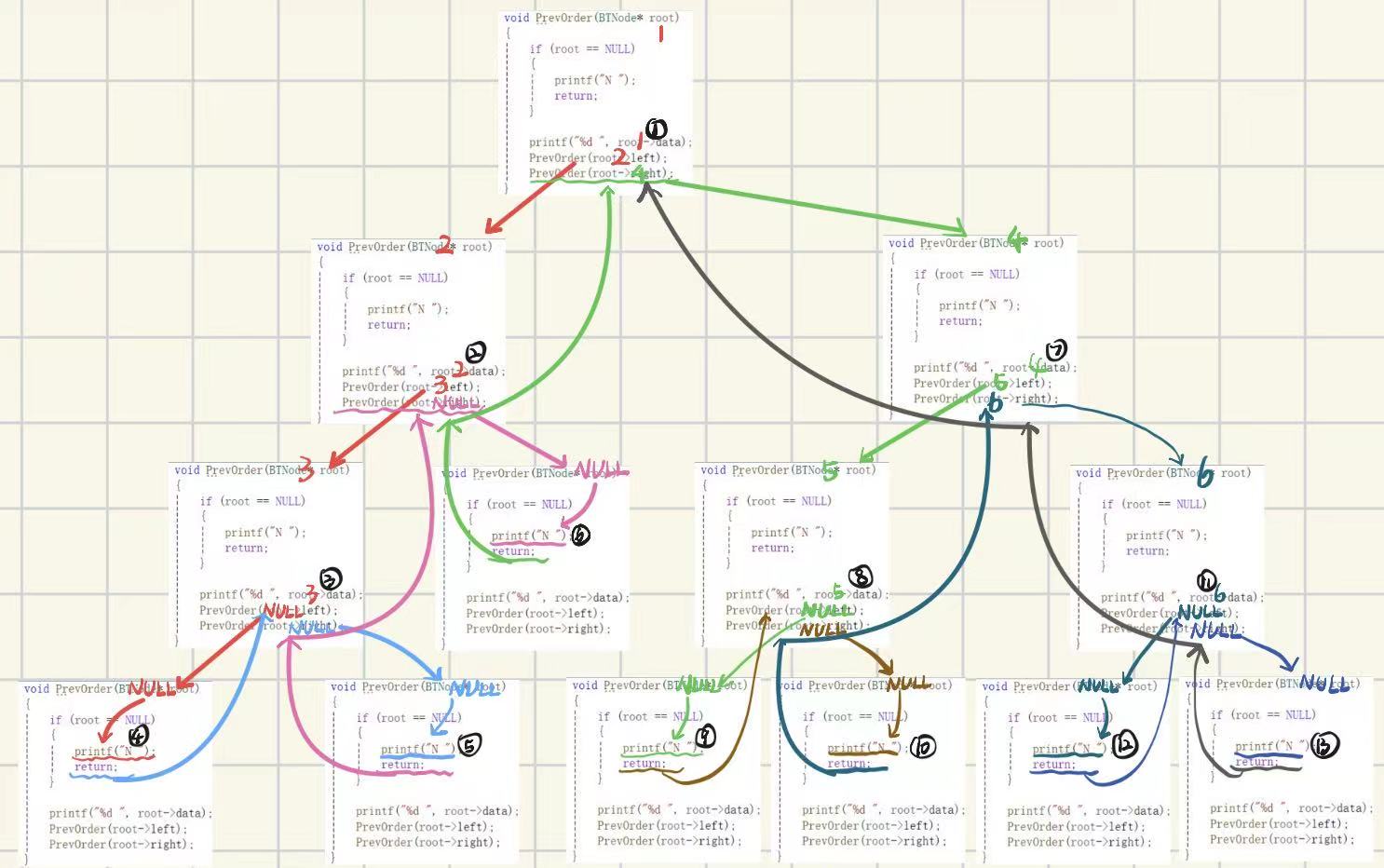
**前序遍历:**根 左子树 右子树
访问根节点的操作发送在遍历其左右子树之前
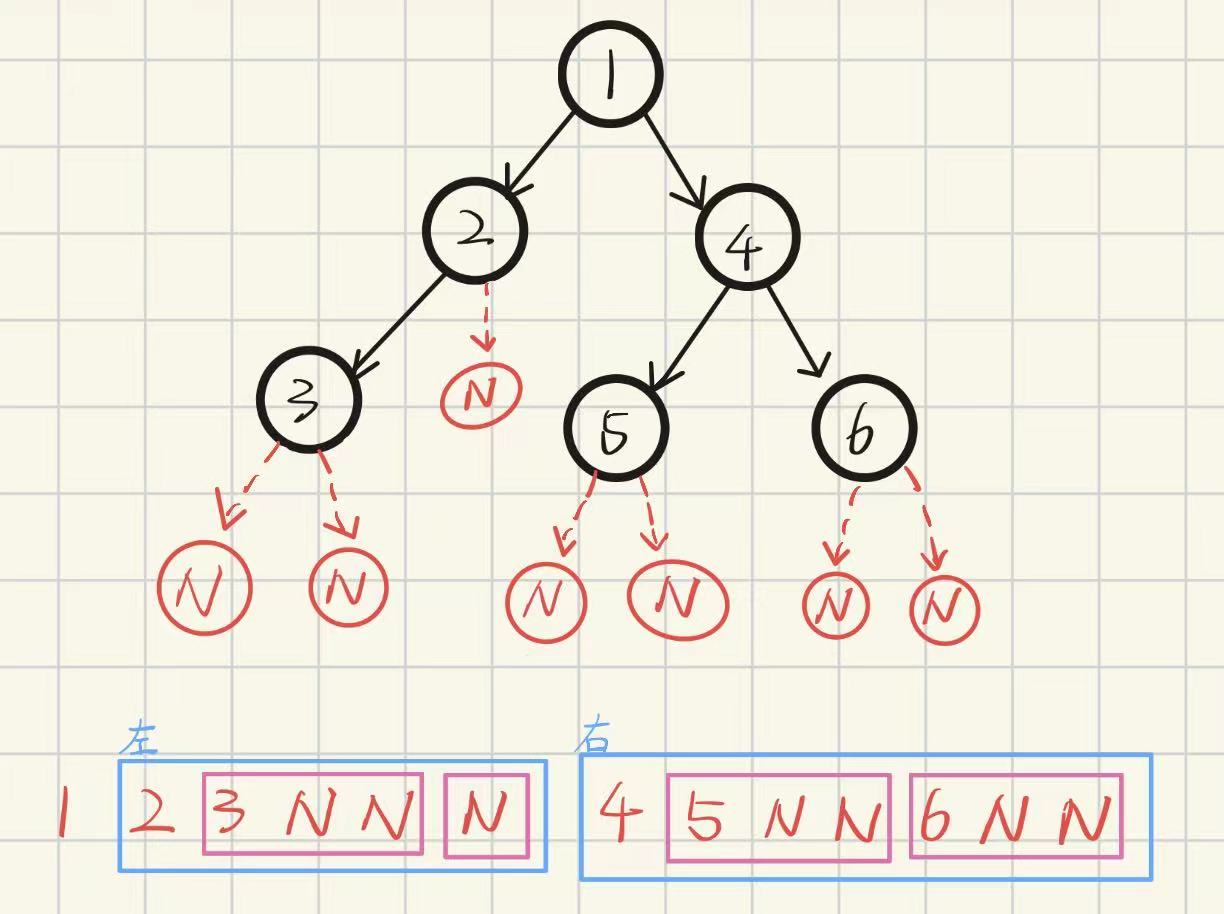
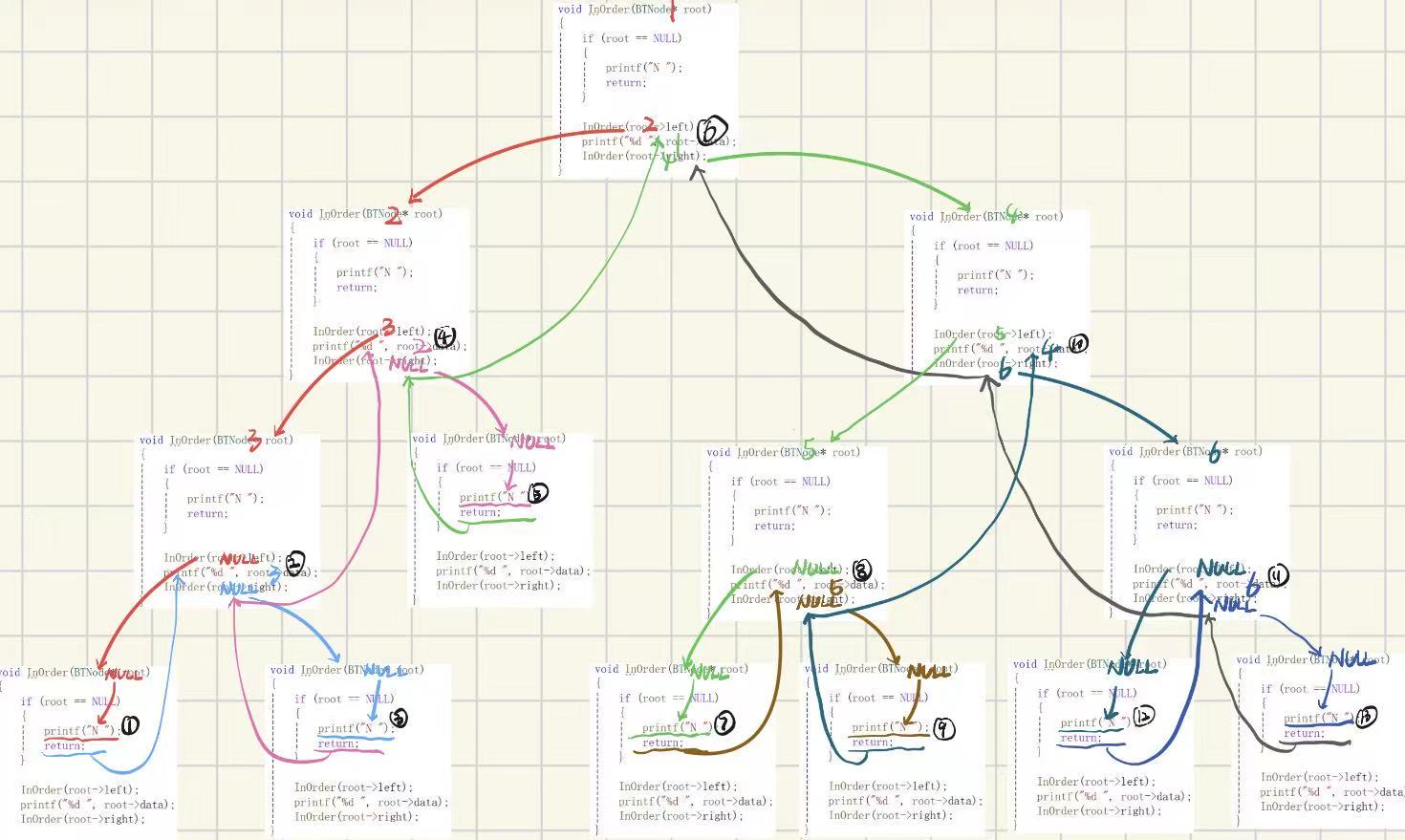
**中序遍历:**左子树 根 右子树
访问根节点的操作发送在遍历其左右子树之间
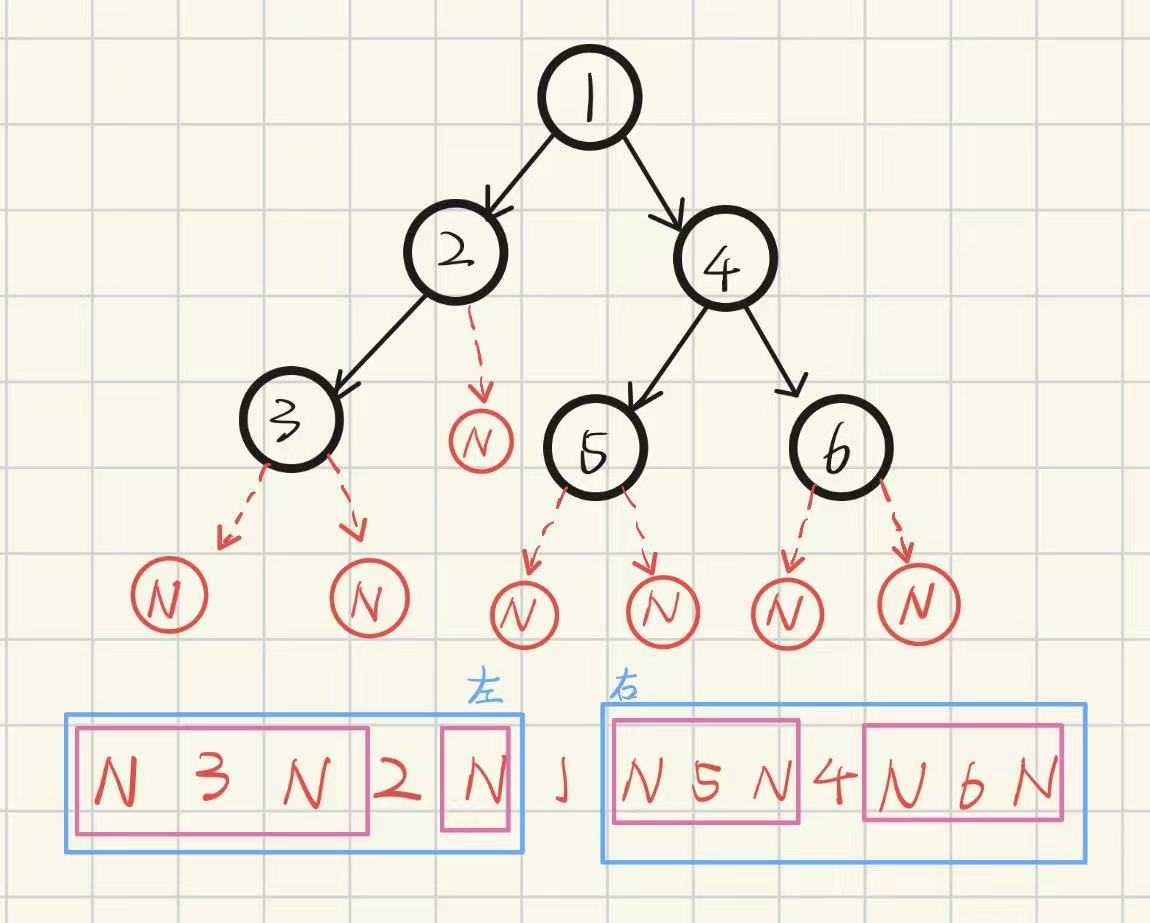
**后序遍历:**左子树 右子树 根
访问根节点的操作发送在遍历其左右子树之后
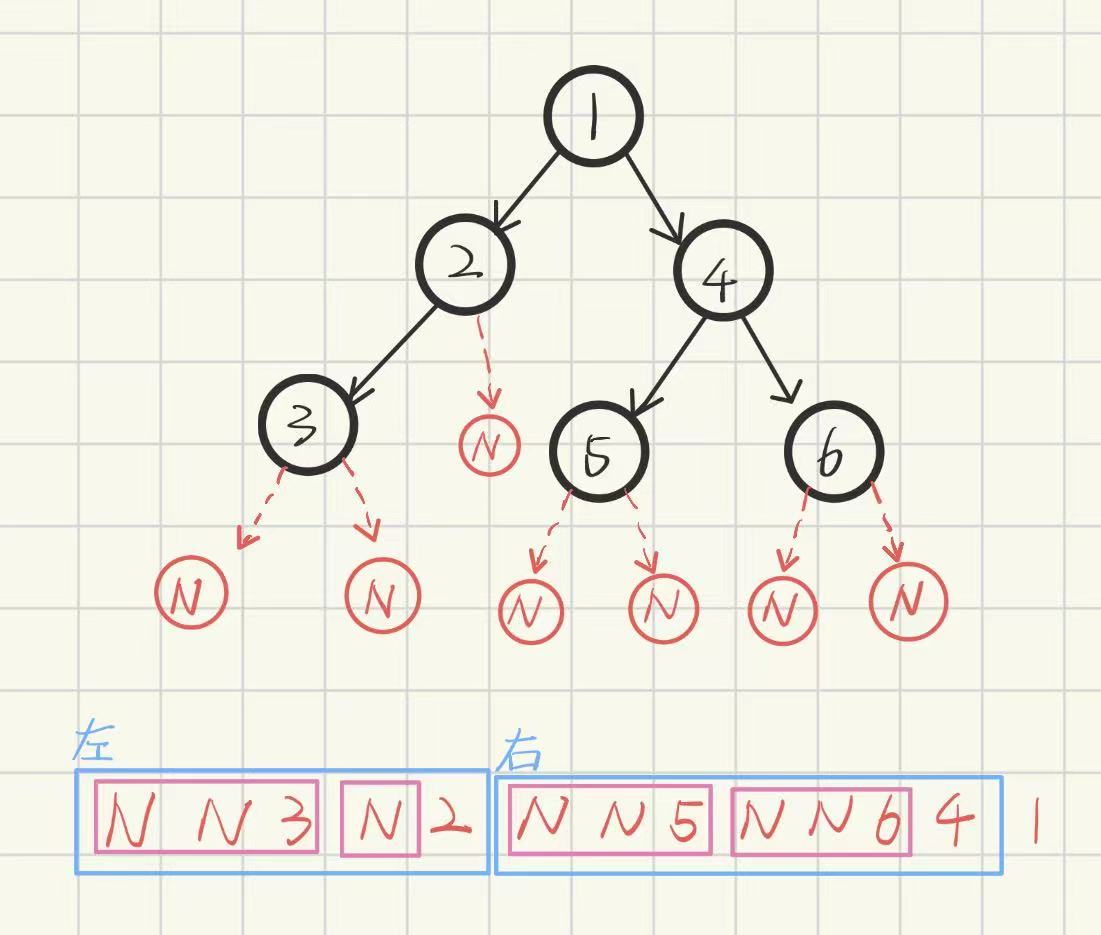
创建一颗二叉树,并且前序遍历
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
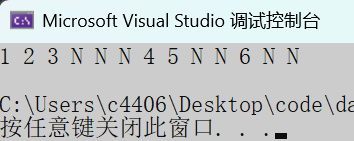
PrevOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
 创建一颗二叉树,并且中序遍历
创建一颗二叉树,并且中序遍历
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("N ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
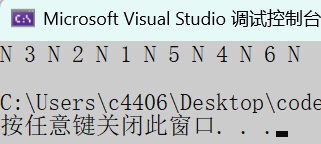
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
三、计算节点个数
cpp
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1
}四、计算叶子节点个数
cpp
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}五、计算树的高度
cpp
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}六、计算第k层节点个数
cpp
int TreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
//如果当前节点是空的,说明这颗子树没有节点,返回0
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//如果k等于1,说明要找的就是根节点所在层,返回1
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
//子问题:第k层的节点数 = 左子树的第k-1层节点数 + 右子树的第k-1层节点数
return TreeLevelKSize(root->left, k - 1) + TreeLevelKSize(root->right, k - 1);
}七、查找值为x的节点
cpp
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
//如果当前节点是空的,说明这条路径找不到,返回NULL
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//如果当前节点的值就是x,找到了,直接返回这个节点
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
//去左子树里找
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
//如果左子树找到了,就直接返回找到的节点
if (ret1)
{
return ret1;
}
//左子树没找到,就去右子树里找
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
//如果右子树找到了,也直接返回
if (ret2)
{
return ret2;
}
//左右子树都没有找到,返回NULL
return NULL;
}八、二叉树的销毁
cpp
void TreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreeDestroy(root->left);
TreeDestroy(root->right);
free(root);
}九、层序遍历
广度优先遍历(BFS)
cpp
#include "Queue.h"
void TreeLevelOrder()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
}
if (front->right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}十、完全二叉树判断
层序遍历,空节点也入队
遇到第一个空节点时判断
后面全为空节点就是完全二叉树
cpp
int TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//遇到第一个空,就判断队列中是否还有非空
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
while (!QueueEmty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//如果有非空,就不是完全二叉树
if (front)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}十一、二叉树OJ
试题1:单值二叉树
题目内容:
如果二叉树每个节点都具有相同的值,那么该二叉树就是单值二叉树
只有给定的树是单值二叉树时,才返回true;否则返回false
示例:
输入:[1,1,1,1,1,null,1]
输出:true
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left && root->left->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
if(root->right && root->right->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}试题2:相同的树
题目内容:
给你两棵二叉树的根节点p和q,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的
示例:
输入:p = [1,2,3],q = [1,2,3]
输出:true
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
//两个都为空
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
//其中一个为空
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
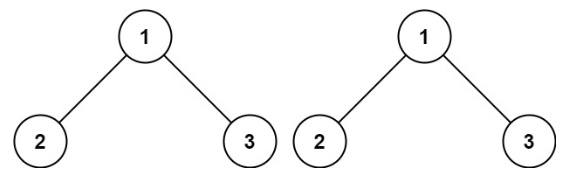
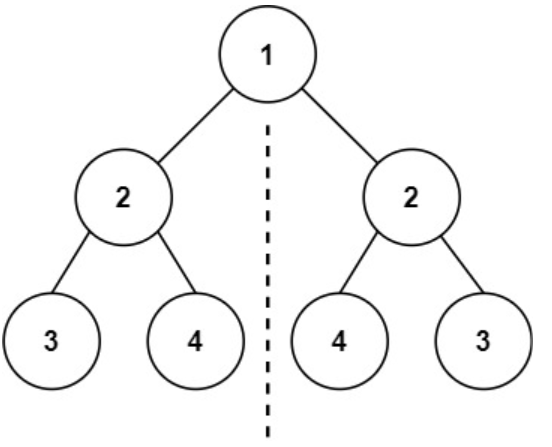
}试题3:对称二叉树
题目内容:
给你一个二叉树的根节点root,检查它是否轴对称
示例:
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* q,struct TreeNode* p)
{
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
return (p->val == q->val) && _isSymmetric(p->left,q->right) && _isSymmetric(p->right,q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right);
}试题4:二叉树的前序遍历
题目内容:
给你二叉树的根节点root,返回它节点值的前序遍历
示例:
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,2,3]
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
void preOrder(struct TreeNode* root,int* a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;
preOrder(root->left,a,pi);
preOrder(root->right,a,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int i = 0;
preOrder(root,a,&i);
return a;
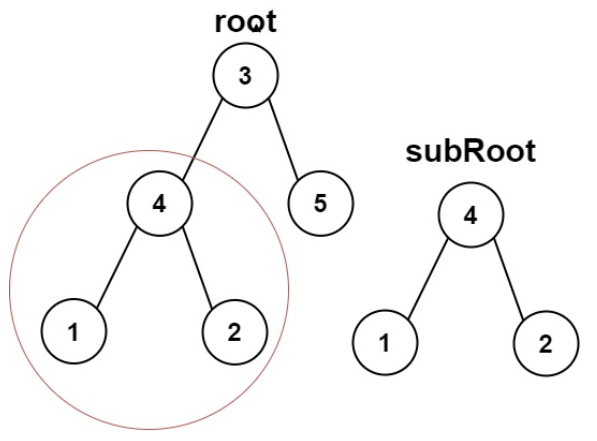
}试题5:另一颗树的子树
题目内容:
给你两棵二叉树root和subRoot,检验root中是否包含和subRoot具有相同结构和节点值的子树,如果存在,返回true,否则,返回false
二叉树tree的一棵子树包括tree的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点
tree也可以看做它自身的一棵子树
示例:
输入:root = [2,4,5,1,2],subRoot = [4,1,2]
输出:true
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p,struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(root->val == subRoot->val && isSameTree(root,subRoot))
{
return true;
}
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}试题6:二叉树的遍历
题目内容:
读入输入的一串先序遍历字符串,用此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)
例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F###
其中"#"表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树
建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果
示例:
输入:abc##de#g##f###
输出:c b e g d f a
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct BinTreeNode
{
char val;
struct BinTreeNode* left;
struct BinTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* CreateTree(char* a,int* pi)
{
if(a[*pi] == '#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
root->val = a[(*pi)++];
root->left = CreateTree(a,pi);
root->right = CreateTree(a,pi);
return root;
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main()
{
char a[100];
scanf("%s",a);
int i = 0;
BTNode* root = CreateTree(a,&i);
InOrder(root);
return 0;
}