在对图像进行操作的过程中,经常会遇到要将图像放大或者缩小,从而进行进一步操作的情况。例如将图片放大后察看局部细节,或者将一张大图缩小后作为图标使用。使用 OpenCV 提供的 cv2.resize()函数实现图像的缩放。
原始图像:
代码-1:
python
import cv2
bird = cv2.imread('images/bird.png')
# 获取图片的宽和高
rows,cols = bird.shape[:2]
# 缩放图片大小:将图片缩小到原来的0.5倍
size = (int(cols*0.5),int(rows*0.5))
# 缩放图片 使用INTER_AREA:缩小图片
bird_resize = cv2.resize(bird,size,interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
cv2.imshow('bird',bird)
cv2.imshow('bird_resize',bird_resize)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()执行结果:
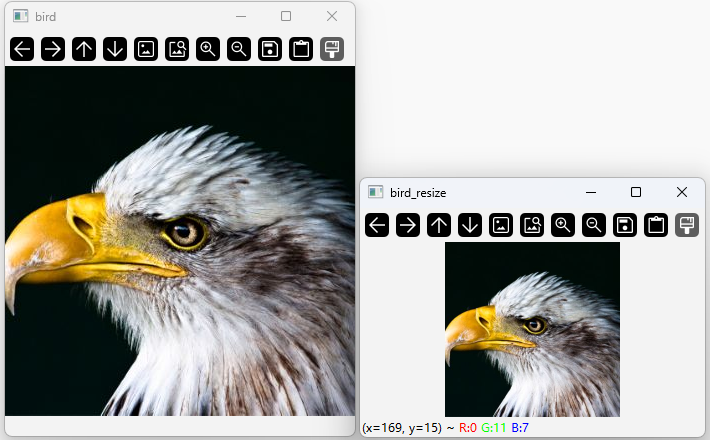
代码-2:
python
import cv2
bird = cv2.imread('images/bird.png')
# 获取图片的宽和高
rows,cols = bird.shape[:2]
# 缩放图片 fx:缩放比例,fx为x轴缩放比例,fy为y轴缩放比例
bird_resize = cv2.resize(bird,None,fx=0.5,fy=0.5,interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
cv2.imshow('bird',bird)
cv2.imshow('bird_resize',bird_resize)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()执行结果:同上
代码解读:
函数 cv2.resize()
在 OpenCV 中使用函数 cv2.resize()实现对图像的缩放,该函数的具体形式如下所示:
dst=cv2.resize( src,dsize[,fx[,fy,[,interpolation]]])
- src 代表需要缩放的原始图像;
- dst 代表输出的目标图像,该参数的类型与 src 相同;
- dsize 代表缩放后输出图像大小,如果指定了参数 dsize 的值,则无论是否指定了参数 fx 和 fy 的值,都由参数 dsize
来决定目标图像大小。如果参数 dsize 的值是 0,那么目标图像的大小通过参数 fx 和 fy 来决定。 - fx 代表水平方向的缩放比例;
- fy 代表垂直方向的缩放比例;
- interpolation 代表插值方式。