一、k折交叉验证:让模型评估告别"一次性偏见"
核心原理
k折交叉验证(k-fold Cross Validation)是一种可靠的模型评估方法,核心逻辑是把训练集平均分成k份,轮流用其中k-1份训练模型,剩下1份做验证集,重复k次后取k次评估结果的平均值作为最终得分。这就像多轮模拟考试,避免了单次拆分数据导致的"运气成分",让模型性能评估更客观。
实战应用(基于信用卡欺诈检测)
文档中针对信用卡交易数据(正常交易为多数类,欺诈为少数类),用k折交叉验证做了逻辑回归模型的参数调优:
-
先将数据拆分训练集和测试集(测试集占30%),聚焦训练集做交叉验证;
-
设定参数C的候选范围(0.01~100),针对每个C值,用8折交叉验证(cv=8)评估模型召回率(scoring='recall')------因为欺诈检测的核心是"不漏掉欺诈交易",召回率比准确率更关键;
-
计算每轮交叉验证的平均召回率,选择得分最高的C作为最优参数,再用全量训练集训练最终模型。
代码
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
#绘制混淆矩阵
def cm_plot(y,yp):
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cm=confusion_matrix(y,yp)
plt.matshow(cm,cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.colorbar()
for x in range(len(cm)):
for y in range (len(cm)):
plt.annotate(cm[x,y],xy=(y,x),horizontalalignment='center',verticalalignment='center')
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
return plt
#数据预处理
data = pd.read_csv("./creditcard.csv", encoding='utf8')
scaler = StandardScaler()
data['Amount'] = scaler.fit_transform(data[['Amount']]) #对Amount列标准化
data = data.drop(['Time'], axis=1) #丢弃Time无关列
X = data.drop('Class', axis=1) #分X,y特征
y = data['Class']
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
#切分训练集、测试集
#8折交叉验证
scores = [] #存放
c_param_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100] #遍历的参数列表
#每一个参数都要进行8折交叉验证
for i in c_param_range:
lr = LogisticRegression(C=i, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000)
score = cross_val_score(lr, x_train, y_train, cv=8, scoring='recall') #评分标准是召回率
score_mean = sum(score)/len(score) #求8次的平均值
scores.append(score_mean)
print(score_mean)
best_c = c_param_range[np.argmax(scores)] #argmax找到最大召回率所属参数的下标
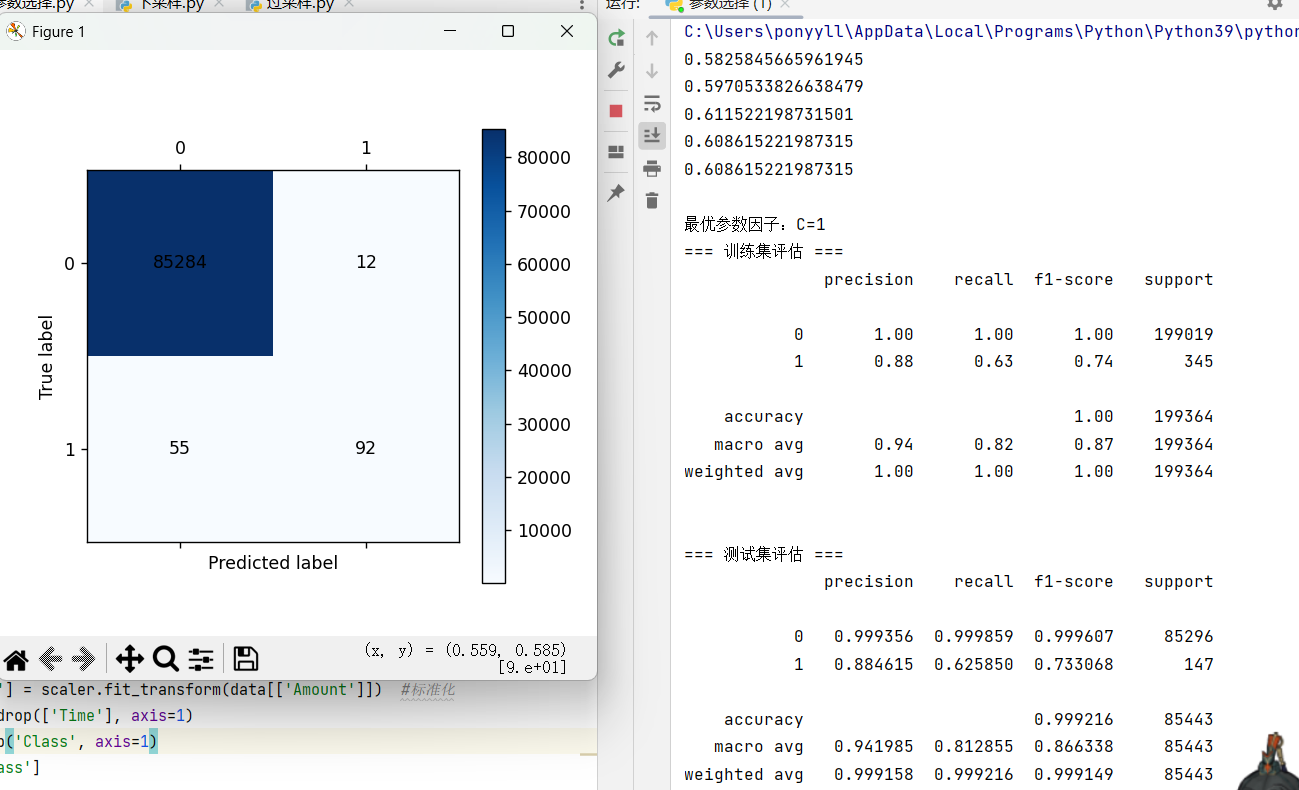
print(f"\n最优参数因子:C={best_c}")
#训练最优模型
best_lr = LogisticRegression(C=best_c, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000, random_state=0)
best_lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 训练集评估
y_train_pred = best_lr.predict(x_train)
print("=== 训练集评估 ===")
print(classification_report(y_train, y_train_pred))
# 测试集评估
y_pred = best_lr.predict(x_test)
print("\n=== 测试集评估 ===")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, digits=6))
# 绘制测试集混淆矩阵
plt = cm_plot(y_test, y_pred)
plt.show()演示结果:
二、下采样:给多数类"瘦身",快速平衡数据
核心逻辑
下采样(Undersampling)是处理不平衡数据的"减法策略":当多数类样本数量远多于少数类时,从多数类中随机抽取部分样本,让其数量与少数类持平,最终得到类别平衡的数据集。
实战实现
文档中信用卡数据的下采样步骤清晰明了:
-
先对交易金额(Amount)做标准化处理,删除无关特征(Time);
-
拆分训练集和测试集后,在训练集中分离多数类(正常交易,Class=0)和少数类(欺诈交易,Class=1);
-
对多数类样本随机抽样,抽样数量等于少数类样本数;
-
将抽样后的多数类与少数类拼接,得到平衡的训练集,再用于逻辑回归模型训练。
代码:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
#绘制混淆矩阵
def cm_plot(y,yp):
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cm=confusion_matrix(y,yp)
plt.matshow(cm,cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.colorbar()
for x in range(len(cm)):
for y in range (len(cm)):
plt.annotate(cm[x,y],xy=(y,x),horizontalalignment='center',verticalalignment='center')
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
return plt
#数据预处理
data = pd.read_csv("./creditcard.csv", encoding='utf8')
scaler = StandardScaler()
data['Amount'] = scaler.fit_transform(data[['Amount']])
data = data.drop(['Time'], axis=1)
X = data.drop('Class', axis=1)
y = data['Class']
x_train_w,x_test_w,y_train_w,y_test_w=train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
#下采样
x_train_w['Class']=y_train_w #把y特征加入到训练集的X特征
data_train=x_train_w
positive_eg=data_train[data_train['Class']==0] #分别筛选出y为0和1的特征
negative_eg=data_train[data_train['Class']==1]
positive_eg=positive_eg.sample(len(negative_eg)) #从y=0中采样使样本数量与y=1的一样多
data_c=pd.concat([positive_eg,negative_eg]) #拼接两类样本
x_train = data_c.drop('Class', axis=1) #分开训练集的x,y特征
y_train = data_c['Class']
#8折交叉验证
scores = []
c_param_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100]
for i in c_param_range:
lr = LogisticRegression(C=i, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000)
score = cross_val_score(lr, x_train, y_train, cv=8, scoring='recall')
score_mean = sum(score)/len(score)
scores.append(score_mean)
print(score_mean)
best_c = c_param_range[np.argmax(scores)]
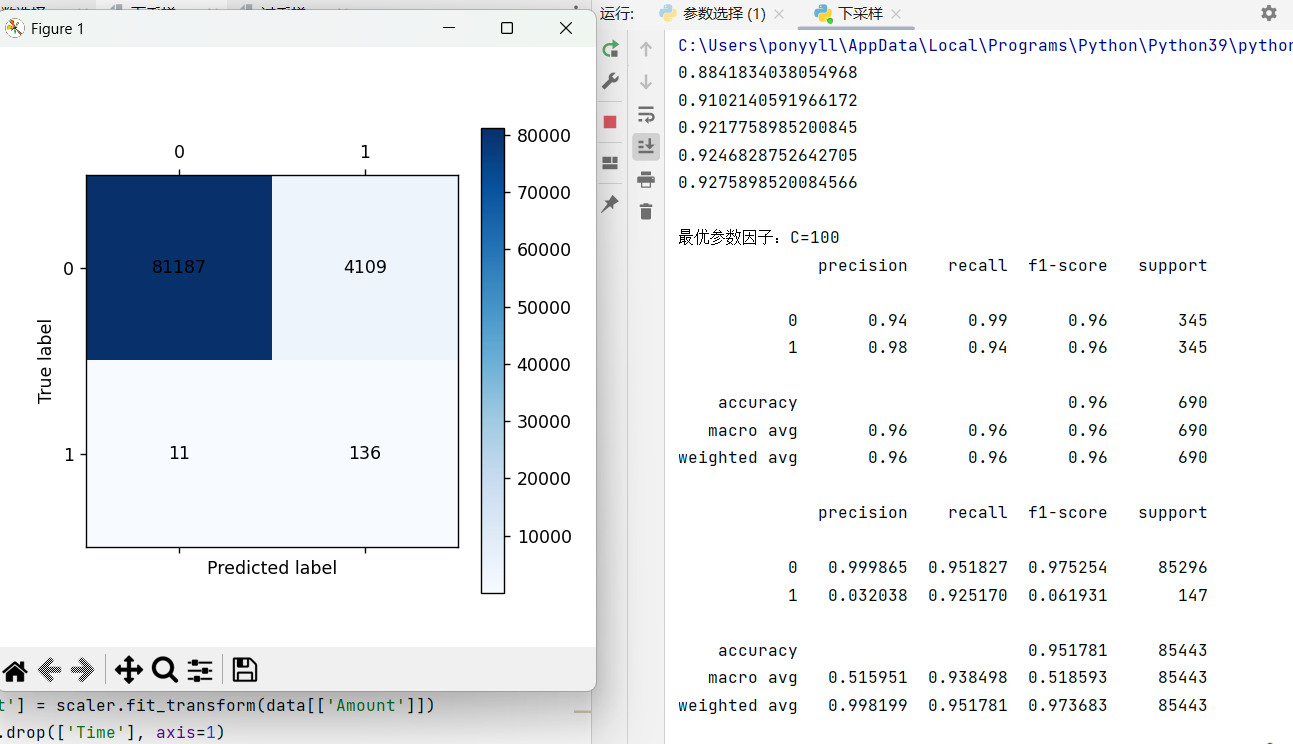
print(f"\n最优参数因子:C={best_c}")
best_lr = LogisticRegression(C=best_c, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000, random_state=0)
best_lr.fit(x_train, y_train)
y_pred = best_lr.predict(x_train)
print(classification_report(y_train, y_pred))
y_pred = best_lr.predict(x_test_w)
print(classification_report(y_test_w, y_pred,digits=6))
plt = cm_plot(y_test_w, y_pred)
plt.show()演示结果:
优缺点
-
优点:实现简单、计算效率高,不增加数据量;
-
缺点:会丢失多数类中的有效信息(文档注释也提到"很多数据没训练到"),可能导致模型泛化能力下降。
三、过采样(SMOTE):给少数类"扩容",智能合成新样本
核心原理
过采样(Oversampling)是"加法策略",但普通随机过采样会导致少数类样本重复,容易过拟合。SMOTE(合成少数类过采样技术)是更优方案,原理是:
-
对每个少数类样本,计算它与其他少数类样本的欧氏距离,在随机两个点间生成一个新点,补充少数类样本;
-
用原样本与选中的近邻做线性插值(new = 原样本 + 随机数×|距离|),合成新的少数类样本,最终让两类样本数量平衡。
实战实现
-
同样先做数据预处理(标准化、删无关特征)和数据集拆分;
-
调用imblearn库的SMOTE类,对训练集做过采样拟合,自动生成平衡的训练集(os_x_train, os_y_train);
-
后续流程与k折交叉验证、下采样一致:用8折交叉验证调优参数C,训练逻辑回归模型,最后用测试集评估召回率等指标。
代码:
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, classification_report
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def cm_plot(y,yp):
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cm=confusion_matrix(y,yp)
plt.matshow(cm,cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.colorbar()
for x in range(len(cm)):
for y in range (len(cm)):
plt.annotate(cm[x,y],xy=(y,x),horizontalalignment='center',verticalalignment='center')
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
return plt
#数据预处理
data = pd.read_csv("./creditcard.csv", encoding='utf8')
scaler = StandardScaler()
data['Amount'] = scaler.fit_transform(data[['Amount']])
data = data.drop(['Time'], axis=1)
X = data.drop('Class', axis=1)
y = data['Class']
x_train_w,x_test_w,y_train_w,y_test_w=train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
#使用SMOTE方法进行过采样
oversampler=SMOTE(random_state=0)
os_x_train,os_y_train=oversampler.fit_resample(x_train_w,y_train_w) #新生成的训练集x,y特征
scores = []
c_param_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100]
for i in c_param_range:
lr = LogisticRegression(C=i, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000)
score = cross_val_score(lr, os_x_train, os_y_train, cv=8, scoring='recall')
score_mean = sum(score)/len(score)
scores.append(score_mean)
print(score_mean)
best_c = c_param_range[np.argmax(scores)]
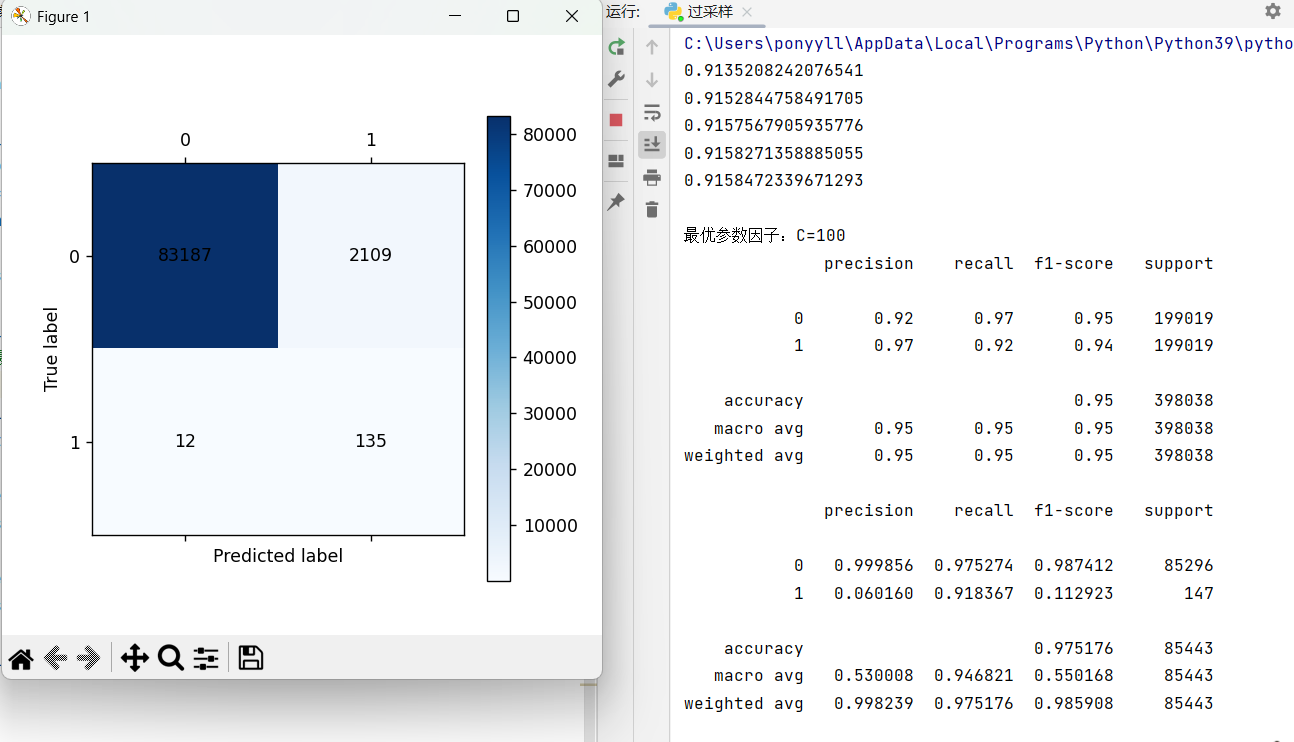
print(f"\n最优参数因子:C={best_c}")
best_lr = LogisticRegression(C=best_c, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000, random_state=0)
best_lr.fit(os_x_train, os_y_train)
y_pred = best_lr.predict(os_x_train)
print(classification_report(os_y_train, y_pred))
y_pred = best_lr.predict(x_test_w)
print(classification_report(y_test_w, y_pred,digits=6))
plt = cm_plot(y_test_w, y_pred)
plt.show()演示结果:
优缺点
-
优点:不丢失多数类信息,通过合成新样本丰富少数类特征,泛化能力更优;
-
缺点:可能生成噪声样本(如合成的样本与多数类边界模糊),计算量比下采样略大。
四、三者对比与选型建议
| 技术 | 核心作用 | 适用场景 | 关键注意点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| k折交叉验证 | 客观评估模型性能 | 所有机器学习场景,尤其数据量有限时 | 匹配业务需求选择评分指标 |
| 下采样 | 快速平衡数据,降低计算量 | 多数类数据冗余、追求训练效率时 | 避免过度丢失多数类有效信息 |
| 过采样(SMOTE) | 丰富少数类特征,平衡数据 | 少数类样本极少、需保留多数类信息时 | 控制采样倍率,避免生成过多噪声样本 |