文章目录
宽度优先搜索的过程中,每次都会从当前点向外扩展⼀层,所以会具有⼀个最短路的特性。因此,宽搜不仅能搜到所有的状态,⽽且还能找出起始状态距离某个状态的最⼩步数。
但是,前提条件是每次扩展的代价都为 1,或者都是相同的数。宽搜常常被⽤于解决边权相同的最短路问题。 宽度优先搜索适用于以下情况:
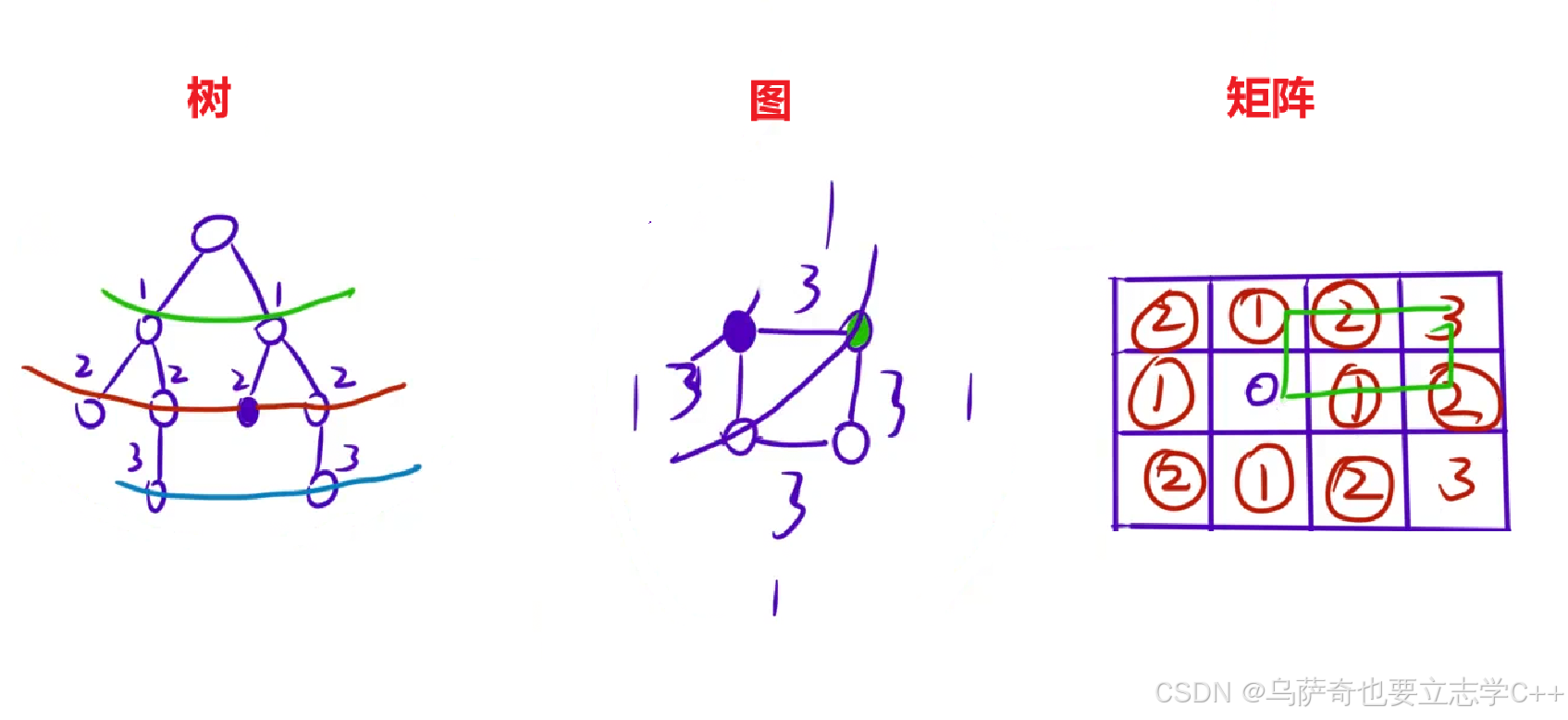
小编提醒一下,BFS不是递归,所以一般BFS函数不用传参。
马的遍历
题目描述
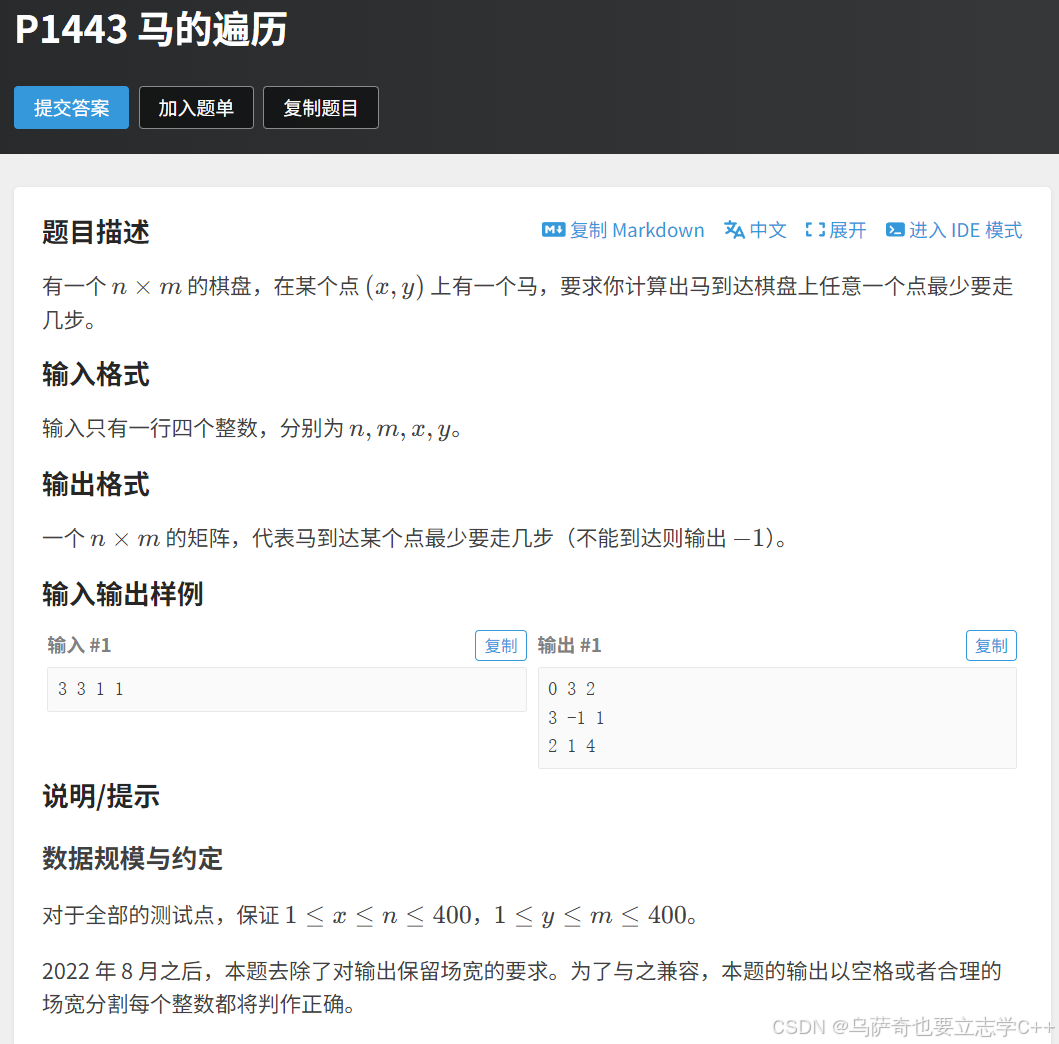
题目解析
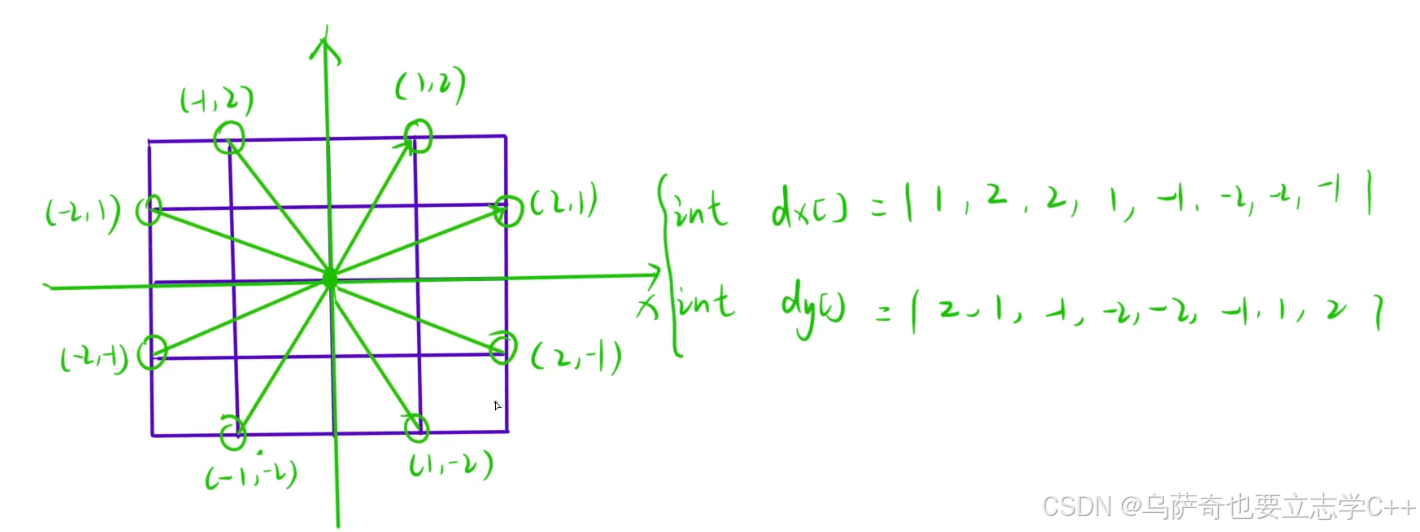
先介绍一下象棋中马的走法,马是走日的对角线,如下图所示,一共有8中可能,我们枚举要把8种可能全部枚举一边,还是用方向向量表示偏移量:
本题用层序遍历,步数改变表示状态改变,步数相同表示同一层:
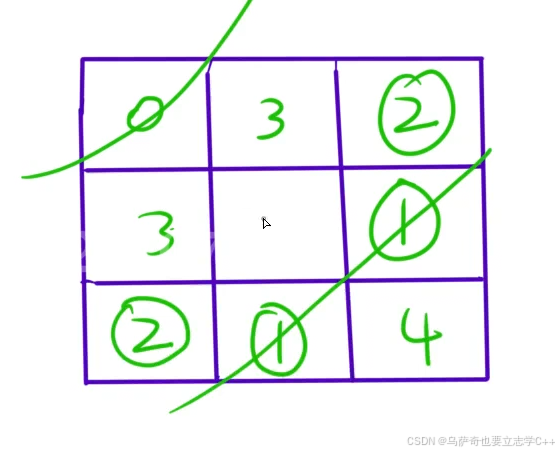
本题有两个可行性剪枝,第一个是数组越界剪枝,第二个是不能枚举已经枚举过的格子,所以一开始全为0的二维数组要初始化为-1,不让就无法区分格子为0是初识格子步数为0还是没有遍历枚举过,二维数组初始化为-1后-1就表示没有枚举过的格子。
代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 410;
int n, m, x, y;
int a[N][N]; //存储步数
//方向向量
int dx[8] = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
int dy[8] = {2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
void bfs()
{
//将a初始化为-1,避免混淆未递归格子的0和起始格子的0
memset(a, -1, sizeof(a));
a[x][y] = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x, y });
while (q.size())
{
//取出队头元素,并将它弹出
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
//将队列中的pair对象转化为矩阵中的坐标信息
int i = t.first;
int j = t.second;
//枚举8个位置
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
//可行性剪枝
if (x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m)
continue;
if (a[x][y] != -1)
continue;
a[x][y] = a[i][j] + 1;
q.push({ x, y });
}
}
}
int main()
{
//初始化数据
cin >> n >> m >> x >> y;
bfs();
//输出结果
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}kotori和迷宫
题目描述
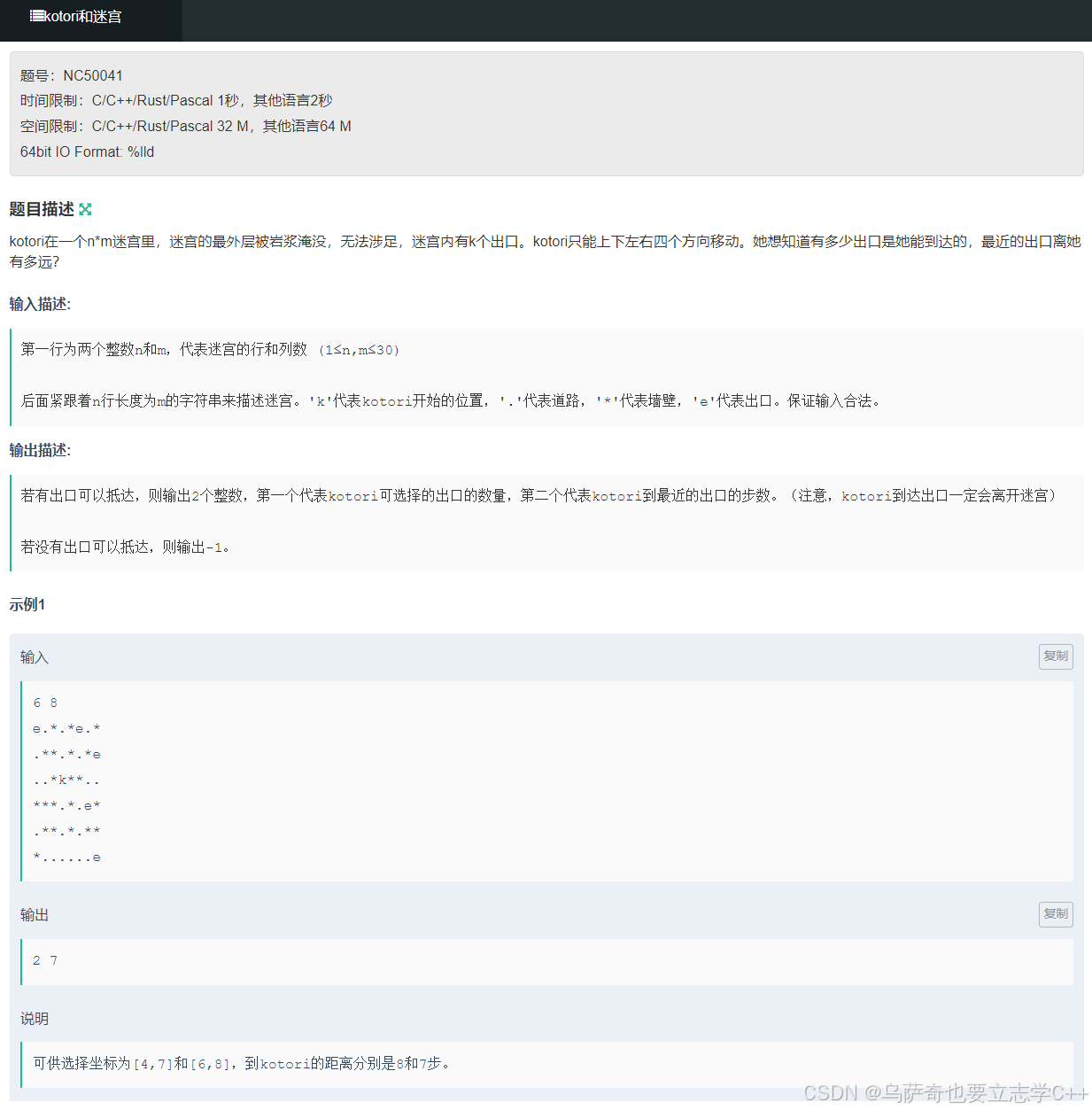
题目解析
本题依旧用BFS枚举递归路径,本题需要两个棋盘,一个字符棋盘a存储迷宫,一个整型棋盘dict存储从起始位置到各个格子的步数。
当坐标越界或者走到墙或者走到已经走过的位置直接剪掉,除了上述的情况还剩两种情况,一种是走到-1格子,需要继续push该格子进队列然后后面继续上下左右枚举,一种是走到e,此时枚举结束,不用继续push该格子进队列。
本题需要注意一点,不能在bfs的时候统计结果:
cpp
void bfs()
{
memset(dict, -1, sizeof(dict));
dict[x][y] = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x, y });
while (q.size())
{
pair<int, int> t = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = t.first;
int j = t.second;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
//可行性剪枝
if (nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m || a[nx][ny] == '*' || dict[nx][ny] != -1)
continue;
if (a[nx][ny] == 'e')
{
e++;
b = min(b, dict[i][j] + 1);
continue;
}
dict[nx][ny] = dict[i][j] + 1;
q.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
}如果在bfs的时候统计可能会有多条路径到达同一个出口,如下图所示,可选择的出口数量就会被多统计。
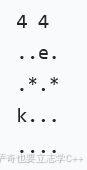
所以需要bfs搜索完后对dict数组进行统计。
代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 35;
int n, m;
char a[N][N]; //存储原数据
int dict[N][N]; //存储步数信息
int x, y; //k的坐标
int e; //出口数
int b = 1000; //距离最近出口的步数
//方向向量
int dx[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int dy[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
void bfs()
{
memset(dict, -1, sizeof(dict));
dict[x][y] = 0;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x, y });
while (q.size())
{
pair<int, int> t = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = t.first;
int j = t.second;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int nx = i + dx[k];
int ny = j + dy[k];
//可行性剪枝
if (nx < 1 || nx > n || ny < 1 || ny > m || a[nx][ny] == '*' || dict[nx][ny] != -1)
continue;
dict[nx][ny] = dict[i][j] + 1;
if (a[nx][ny] != 'e')
{
//a[nx][ny]不为e,继续往后BFS
q.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> a[i][j];
if (a[i][j] == 'k')
{
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
bfs();
//统计结果
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if (a[i][j] == 'e' && dict[i][j] != -1)
{
e++;
b = min(b, dict[i][j]);
}
}
}
//输出结果
if (e)
{
cout << e << " " << b << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
return 0;
}CatchThatCowS
题目描述
题目解析
本题大家可能最先想到用贪心解决,要走到一个比自己大的数先二倍,当超过目标数字再减,但是这个方法有时并不会得到最优结果,如下图所示。

所以本题需要将所有情况枚举出来,采用bfs。
本题的剪枝策略有三种,第一是越界剪枝,加一和二倍要小于等于上限1e5,减一要大于0,第二是枚举到已经枚举过的格子时要剪掉,具体时间依旧是把数组初始化为-1,格子数据为-1表示没有枚举过,注意本题有多组测试用例,所以每一组开始都需要初始化数组。第三时当枚举的数字等于目标数字时立即停止搜索,return返回,因为BFS 层序特性保证首次找到目标即为最短路径。
代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int r = 1e5; //上限
int z, x, y;
int a[N]; //存储步数
void bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
a[x] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
int i = t + 1;
int j = t - 1;
int k = 2 * t;
//可行性剪枝
if (i <= r && a[i] == -1)
{
a[i] = a[t] + 1;
q.push(i);
}
if (j > 0 && a[j] == -1)
{
a[j] = a[t] + 1;
q.push(j);
}
if (k <= r && a[k] == -1)
{
a[k] = a[t] + 1;
q.push(k);
}
if (i == y || j == y || k == y)
{
return;
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> z;
while (z--)
{
//多组测试用例清空数据
memset(a, -1, sizeof(a));
cin >> x >> y;
bfs();
cout << a[y] << endl;
}
return 0;
}以上就是小编分享的全部内容了,如果觉得不错还请留下免费的赞和收藏
如果有建议欢迎通过评论区或私信留言,感谢您的大力支持。
一键三连好运连连哦~~
