本篇技术博文摘要 🌟
- 文章开篇简要回顾了系列先前内容,随后系统性地拆解了项目完整工作流 。在"环境准备"部分,详述了所需工具库(如PyTorch、TorchText、SpaCy)的安装与可能的依赖问题解决方案。
- 继而,在"数据准备"环节,介绍了情感分析常用数据集,并给出了数据预处理的具体代码示例 。核心的"模型构建"部分,展示了LSTM的架构图与完整的PyTorch实现代码 。"模型训练"章节则提供了超参数设置、训练循环的详细示例;
- 而"模型评估"部分阐述了评估函数与准确率计算方法 。文章还通过"模型应用"演示了如何对新文本进行情感预测,并提供了预测示例。
- 最终,汇总了全部项目代码,并对训练结果进行了可视化展示,旨在为读者提供一个从理论到实践、可复现的完整项目蓝本。
引言 📘
- 在这个变幻莫测、快速发展的技术时代,与时俱进是每个IT工程师的必修课。
- 我是盛透侧视攻城狮,一名什么都会一丢丢的网络安全工程师,也是众多技术社区的活跃成员以及多家大厂官方认可人员,希望能够与各位在此共同成长。

上节回顾
目录
[本篇技术博文摘要 🌟](#本篇技术博文摘要 🌟)
[引言 📘](#引言 📘)
[1.PyTorch 实例 - 文本情感分析项目](#1.PyTorch 实例 - 文本情感分析项目)

1.PyTorch 实例 - 文本情感分析项目
- 文本情感分析是自然语言处理(NLP)中的一项基础任务,旨在判断一段文本表达的情感倾向(正面/负面)。
- 本项目将使用PyTorch构建一个深度学习模型,实现对电影评论的情感分类。
1.1情感分析的应用场景
- 产品评论分析
- 社交媒体舆情监控
- 客户服务反馈分类
- 市场趋势预测

2.环境准备
2.1所需工具和库
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchtext.data import Field, TabularDataset, BucketIterator
import spacy
import numpy as np2.2安装依赖
python
pip install torch torchtext spacy
python -m spacy download en_core_web_sm
2.2.1安装中出现的问题
解决方案如下:
首先
*
bash# 查看当前目录下有哪些文件 dir # Windows # 或 ls # Linux/Machttps://github.com/explosion/spacy-models/releases/tag/en_core_web_sm-3.7.0
- 下载到当前目录后
bashpip install en_core_web_sm-3.7.0.tar.gz
bash
# 在 Anaconda 环境中执行
conda activate cpu1
# 卸载当前版本
pip uninstall torch torchtext torchvision torchaudio -y
#安装兼容版本
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
# 安装可用的最新版本
pip install torchtext==0.18.0
#安装其他依赖
pip install spacy==3.7.2 pandas==2.2.0 numpy==1.26.4


3.数据准备
3.1数据集介绍
- 使用IMDB电影评论数据集,包含50,000条带有情感标签(正面/负面)的评论。
3.2数据预处理及示例
python
# 定义字段处理
TEXT = Field(tokenize='spacy',
tokenizer_language='en_core_web_sm',
include_lengths=True)
LABEL = Field(sequential=False, use_vocab=False)
# 加载数据集
train_data, test_data = TabularDataset.splits(
path='./data',
train='train.csv',
test='test.csv',
format='csv',
fields=[('text', TEXT), ('label', LABEL)]
)
# 构建词汇表
TEXT.build_vocab(train_data,
max_size=25000,
vectors="glove.6B.100d")
4.模型构建
4.1LSTM模型架构图
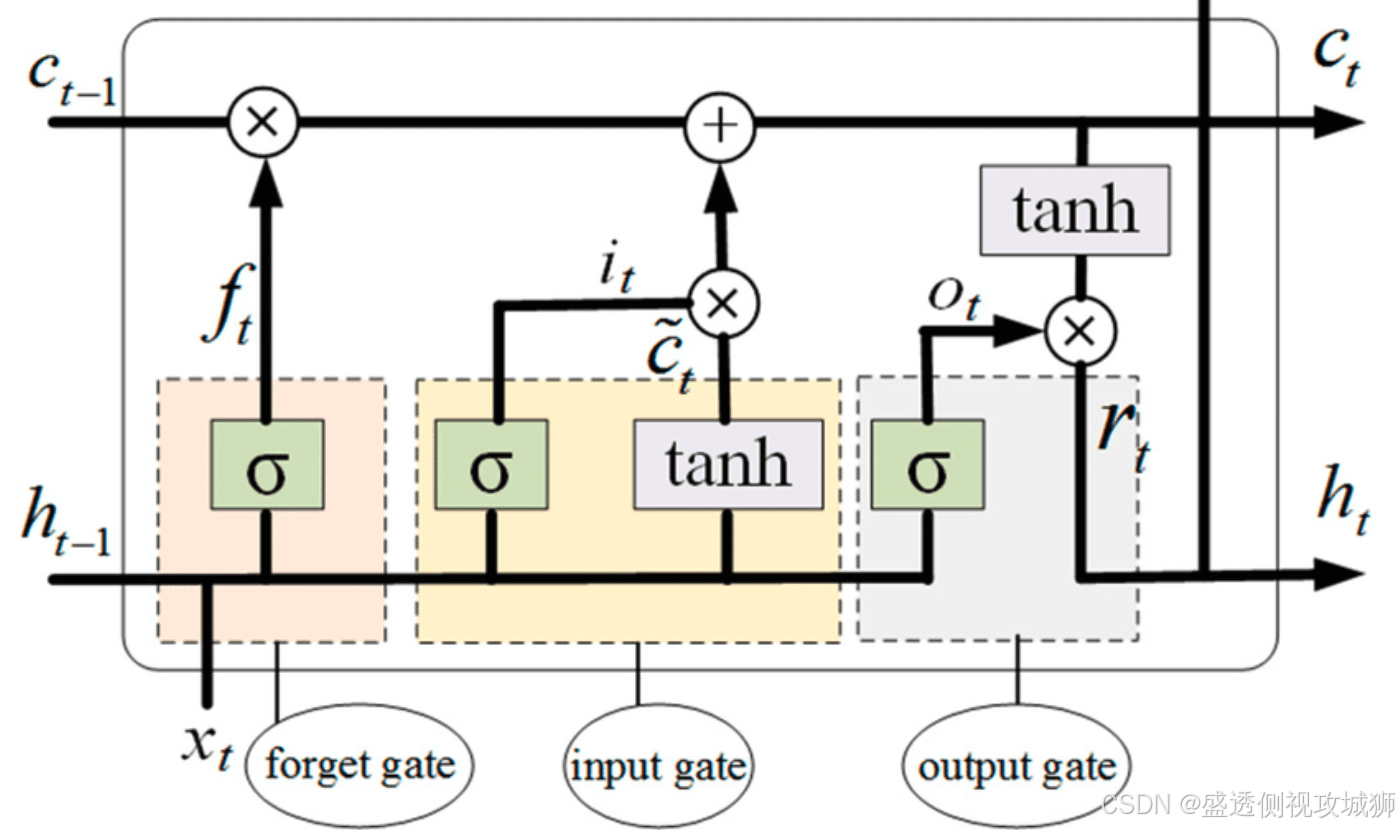
4.2LSTM模型实现代码示例
python
class SentimentLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim, n_layers):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim,
hidden_dim,
num_layers=n_layers,
bidirectional=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 2, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
def forward(self, text, text_lengths):
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(text))
packed_embedded = nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(
embedded, text_lengths.to('cpu'))
packed_output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(packed_embedded)
hidden = self.dropout(torch.cat((hidden[-2,:,:], hidden[-1,:,:]), dim=1))
return self.fc(hidden)
5.模型训练
5.1训练参数设置及示例
python
# 模型参数
INPUT_DIM = len(TEXT.vocab)
EMBEDDING_DIM = 100
HIDDEN_DIM = 256
OUTPUT_DIM = 1
N_LAYERS = 2
# 初始化模型
model = SentimentLSTM(INPUT_DIM, EMBEDDING_DIM, HIDDEN_DIM, OUTPUT_DIM, N_LAYERS)
# 优化器和损失函数
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()5.2训练循环及示例
python
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.train()
for batch in iterator:
text, text_lengths = batch.text
predictions = model(text, text_lengths).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
6.模型评估
6.1评估函数及示例
python
def evaluate(model, iterator, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in iterator:
text, text_lengths = batch.text
predictions = model(text, text_lengths).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)6.2准确率计算
python
def accuracy(preds, y):
rounded_preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds))
correct = (rounded_preds == y).float()
acc = correct.sum() / len(correct)
return acc
7.模型应用
7.1预测新文本及示例
python
def predict_sentiment(model, sentence):
tokenized = [tok.text for tok in nlp.tokenizer(sentence)]
indexed = [TEXT.vocab.stoi[t] for t in tokenized]
length = [len(indexed)]
tensor = torch.LongTensor(indexed).to(device)
tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(1)
length_tensor = torch.LongTensor(length)
prediction = torch.sigmoid(model(tensor, length_tensor))
return prediction.item()7.2示例预测
python
positive_review = "This movie was fantastic! I really enjoyed it."
negative_review = "The film was terrible and boring."
print(f"Positive review score: {predict_sentiment(model, positive_review):.4f}")
print(f"Negative review score: {predict_sentiment(model, negative_review):.4f}")
8.文本情感分析项目代码汇总
8.1代码汇总:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import spacy
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from collections import Counter
import os
import warnings
import sys
import re
# 忽略警告
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 检查 torchtext 版本并决定使用哪个 API
try:
import torchtext
torchtext_version = torchtext.__version__
print(f"torchtext 版本: {torchtext.__version__}")
# 检查版本并设置标志
if torchtext_version >= '0.12.0':
# 使用新版 API
try:
from torchtext.data.utils import get_tokenizer
from torchtext.vocab import build_vocab_from_iterator
USE_NEW_API = True
print("使用新版 torchtext API")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"新版 API 导入失败: {e}")
USE_NEW_API = False
else:
# 使用旧版 API
try:
from torchtext.data import Field, TabularDataset, BucketIterator
USE_NEW_API = False
print("使用旧版 torchtext API")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"旧版 API 导入失败: {e}")
USE_NEW_API = False
except ImportError as e:
print(f"导入 torchtext 失败: {e}")
print("将使用纯 PyTorch 实现...")
USE_NEW_API = False
# 设置设备
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f"使用设备: {device}")
# 下载 spacy 英文模型(如果未安装)
try:
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
print("spaCy 英文模型加载成功")
except OSError:
print("下载 spaCy 英文模型...")
import subprocess
result = subprocess.run([sys.executable, '-m', 'spacy', 'download', 'en_core_web_sm'],
capture_output=True, text=True)
if result.returncode == 0:
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
print("spaCy 英文模型下载并加载成功")
else:
print("spaCy 模型下载失败,使用简单分词器")
nlp = None
# 自定义分词器
def tokenizer(text):
"""文本分词器"""
if nlp is not None:
return [token.text for token in nlp.tokenizer(text)]
else:
# 简单分词器作为备选
text = text.lower()
# 移除非字母字符,保留基本标点
text = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z\s\.,!?]', '', text)
return text.split()
# 自定义数据集类
class TextDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, texts, labels, vocab, max_length=100):
self.texts = texts
self.labels = labels
self.vocab = vocab
self.max_length = max_length
def __len__(self):
return len(self.texts)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
text = self.texts[idx]
label = self.labels[idx]
# 分词
tokens = tokenizer(text)
# 转换为索引
if isinstance(self.vocab, dict):
# 纯 PyTorch 实现的词汇表
indices = [self.vocab.get(token, self.vocab.get('<unk>', 1)) for token in tokens[:self.max_length]]
else:
# torchtext 词汇表
indices = [self.vocab[token] for token in tokens[:self.max_length]]
# 填充到固定长度
if len(indices) < self.max_length:
indices += [self.vocab['<pad>']] * (self.max_length - len(indices))
else:
indices = indices[:self.max_length]
return {
'text': torch.tensor(indices, dtype=torch.long),
'label': torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.float32)
}
def load_and_prepare_data():
"""加载和准备数据"""
print("加载数据...")
# 尝试加载数据文件
try:
train_df = pd.read_csv('./data/train.csv')
test_df = pd.read_csv('./data/test.csv')
print("从文件加载数据成功")
except FileNotFoundError:
print("未找到数据文件,创建示例数据...")
# 创建示例数据
sample_texts = [
"This movie was fantastic! I really enjoyed it.",
"The film was terrible and boring.",
"A wonderful experience from start to finish.",
"I would not recommend this movie to anyone.",
"Excellent acting and a compelling storyline.",
"Waste of time and money.",
"One of the best films I've seen this year.",
"Poor direction and weak performances.",
"I was captivated from beginning to end.",
"Disappointing and predictable."
]
sample_labels = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]
train_df = pd.DataFrame({
'text': sample_texts[:8],
'label': sample_labels[:8]
})
test_df = pd.DataFrame({
'text': sample_texts[8:],
'label': sample_labels[8:]
})
# 保存示例数据
os.makedirs('./data', exist_ok=True)
train_df.to_csv('./data/train.csv', index=False)
test_df.to_csv('./data/test.csv', index=False)
print("示例数据已创建并保存")
# 构建词汇表
all_texts = list(train_df['text']) + list(test_df['text'])
if USE_NEW_API:
# 使用 torchtext 构建词汇表
print("使用 torchtext 构建词汇表...")
def yield_tokens(text_list):
for text in text_list:
yield tokenizer(text)
vocab = build_vocab_from_iterator(
yield_tokens(all_texts),
specials=['<unk>', '<pad>'],
max_tokens=10000
)
vocab.set_default_index(vocab['<unk>'])
else:
# 使用纯 PyTorch 构建词汇表
print("使用纯 PyTorch 构建词汇表...")
counter = Counter()
for text in all_texts:
tokens = tokenizer(text)
counter.update(tokens)
# 创建词汇表
vocab = {'<pad>': 0, '<unk>': 1}
for word, _ in counter.most_common(10000 - 2): # 保留位置给特殊标记
if word not in vocab:
vocab[word] = len(vocab)
print(f"词汇表大小: {len(vocab)}")
# 创建数据集
train_dataset = TextDataset(
list(train_df['text']),
list(train_df['label']),
vocab
)
test_dataset = TextDataset(
list(test_df['text']),
list(test_df['label']),
vocab
)
# 创建 DataLoader
train_loader = DataLoader(
train_dataset,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=True
)
test_loader = DataLoader(
test_dataset,
batch_size=4,
shuffle=False
)
return train_loader, test_loader, vocab, len(vocab)
# 情感分析模型
class SentimentLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim, n_layers, dropout=0.5):
super().__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, padding_idx=0)
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim,
hidden_dim,
num_layers=n_layers,
bidirectional=True,
batch_first=True,
dropout=dropout if n_layers > 1 else 0)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 2, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, text):
# text: [batch_size, seq_len]
embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(text)) # [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim]
# LSTM 前向传播
lstm_output, (hidden, _) = self.lstm(embedded)
# 连接最后时刻的前向和后向隐藏状态
hidden = self.dropout(torch.cat((hidden[-2, :, :], hidden[-1, :, :]), dim=1))
return self.fc(hidden)
# 训练函数
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.train()
for batch in iterator:
text = batch['text'].to(device)
labels = batch['label'].to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
predictions = model(text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, labels)
acc = accuracy(predictions, labels)
loss.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0)
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
# 评估函数
def evaluate(model, iterator, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in iterator:
text = batch['text'].to(device)
labels = batch['label'].to(device)
predictions = model(text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, labels)
acc = accuracy(predictions, labels)
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
# 准确率计算
def accuracy(preds, y):
rounded_preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds))
correct = (rounded_preds == y).float()
acc = correct.sum() / len(correct)
return acc
# 预测情感函数
def predict_sentiment(model, sentence, vocab, device):
model.eval()
# 分词
tokens = tokenizer(sentence)
# 转换为索引
if isinstance(vocab, dict):
# 纯 PyTorch 词汇表
indices = [vocab.get(token, vocab.get('<unk>', 1)) for token in tokens]
else:
# torchtext 词汇表
indices = [vocab[token] for token in tokens]
# 转换为张量
tensor = torch.tensor(indices, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
prediction = torch.sigmoid(model(tensor))
return prediction.item()
# 主函数
def main():
print("=" * 60)
print("PyTorch 情感分析项目")
print("=" * 60)
# 加载数据
train_loader, test_loader, vocab, vocab_size = load_and_prepare_data()
# 模型参数
EMBEDDING_DIM = 100
HIDDEN_DIM = 256
OUTPUT_DIM = 1
N_LAYERS = 2
DROPOUT = 0.5
print(f"\n模型参数:")
print(f"词汇表大小: {vocab_size}")
print(f"嵌入维度: {EMBEDDING_DIM}")
print(f"隐藏层维度: {HIDDEN_DIM}")
print(f"输出维度: {OUTPUT_DIM}")
print(f"LSTM 层数: {N_LAYERS}")
print(f"Dropout: {DROPOUT}")
# 初始化模型
model = SentimentLSTM(vocab_size, EMBEDDING_DIM, HIDDEN_DIM, OUTPUT_DIM, N_LAYERS, DROPOUT)
model = model.to(device)
# 优化器和损失函数
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
# 训练模型
print("\n开始训练模型...")
N_EPOCHS = 10
best_test_acc = 0
for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS):
train_loss, train_acc = train(model, train_loader, optimizer, criterion)
test_loss, test_acc = evaluate(model, test_loader, criterion)
# 保存最佳模型
if test_acc > best_test_acc:
best_test_acc = test_acc
torch.save({
'epoch': epoch,
'model_state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer.state_dict(),
'loss': test_loss,
'vocab': vocab,
'vocab_size': vocab_size,
'embedding_dim': EMBEDDING_DIM,
'hidden_dim': HIDDEN_DIM,
'output_dim': OUTPUT_DIM,
'n_layers': N_LAYERS
}, 'best_sentiment_model.pth')
print(f'Epoch: {epoch + 1:02}/{N_EPOCHS}')
print(f' 训练损失: {train_loss:.3f} | 训练准确率: {train_acc * 100:.2f}%')
print(f' 测试损失: {test_loss:.3f} | 测试准确率: {test_acc * 100:.2f}%')
print(f"\n最佳测试准确率: {best_test_acc * 100:.2f}%")
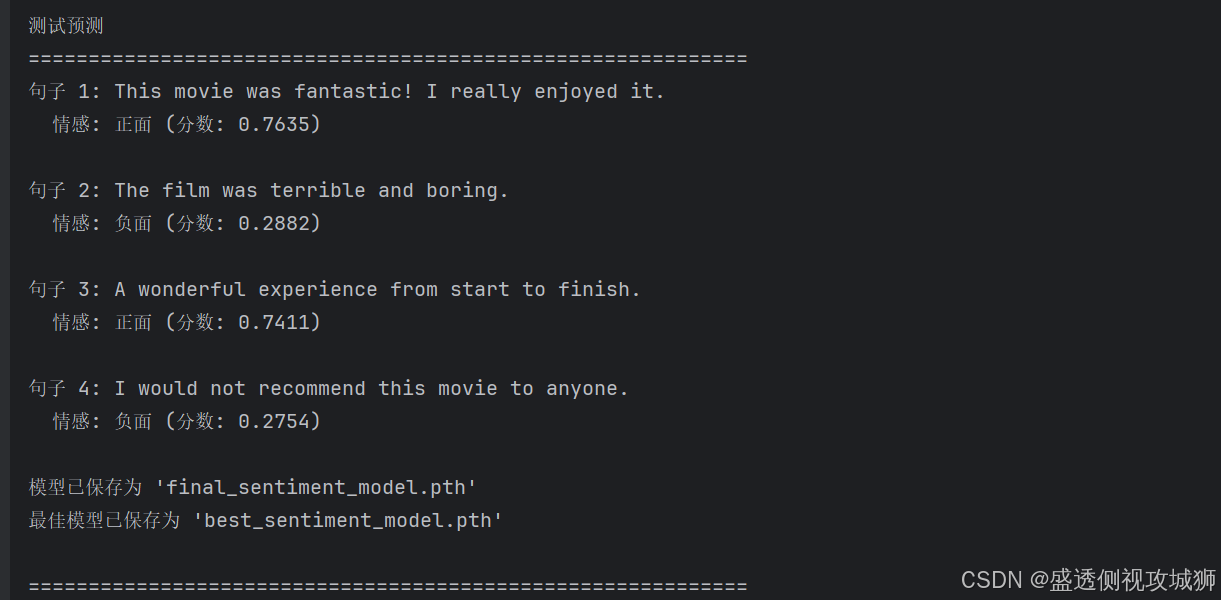
# 测试预测
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("测试预测")
print("=" * 60)
test_sentences = [
"This movie was fantastic! I really enjoyed it.",
"The film was terrible and boring.",
"A wonderful experience from start to finish.",
"I would not recommend this movie to anyone."
]
for i, sentence in enumerate(test_sentences):
score = predict_sentiment(model, sentence, vocab, device)
sentiment = "正面" if score > 0.5 else "负面"
print(f"句子 {i + 1}: {sentence}")
print(f" 情感: {sentiment} (分数: {score:.4f})")
print()
# 保存最终模型
torch.save({
'model_state_dict': model.state_dict(),
'vocab': vocab,
'params': {
'vocab_size': vocab_size,
'embedding_dim': EMBEDDING_DIM,
'hidden_dim': HIDDEN_DIM,
'output_dim': OUTPUT_DIM,
'n_layers': N_LAYERS
}
}, 'final_sentiment_model.pth')
print("模型已保存为 'final_sentiment_model.pth'")
print("最佳模型已保存为 'best_sentiment_model.pth'")
# 加载模型示例
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("模型加载示例")
print("=" * 60)
try:
checkpoint = torch.load('best_sentiment_model.pth', map_location=device, weights_only=True)
loaded_model = SentimentLSTM(
checkpoint['vocab_size'],
checkpoint['embedding_dim'],
checkpoint['hidden_dim'],
checkpoint['output_dim'],
checkpoint['n_layers']
)
loaded_model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['model_state_dict'])
loaded_model.to(device)
loaded_model.eval()
print("模型加载成功!")
# 测试加载的模型
test_sentence = "This is a great movie!"
score = predict_sentiment(loaded_model, test_sentence, checkpoint['vocab'], device)
sentiment = "正面" if score > 0.5 else "负面"
print(f"测试句子: {test_sentence}")
print(f"预测情感: {sentiment} (分数: {score:.4f})")
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型加载失败: {e}")
print("\n" + "=" * 60)
print("项目完成!")
print("=" * 60)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
8.2结果图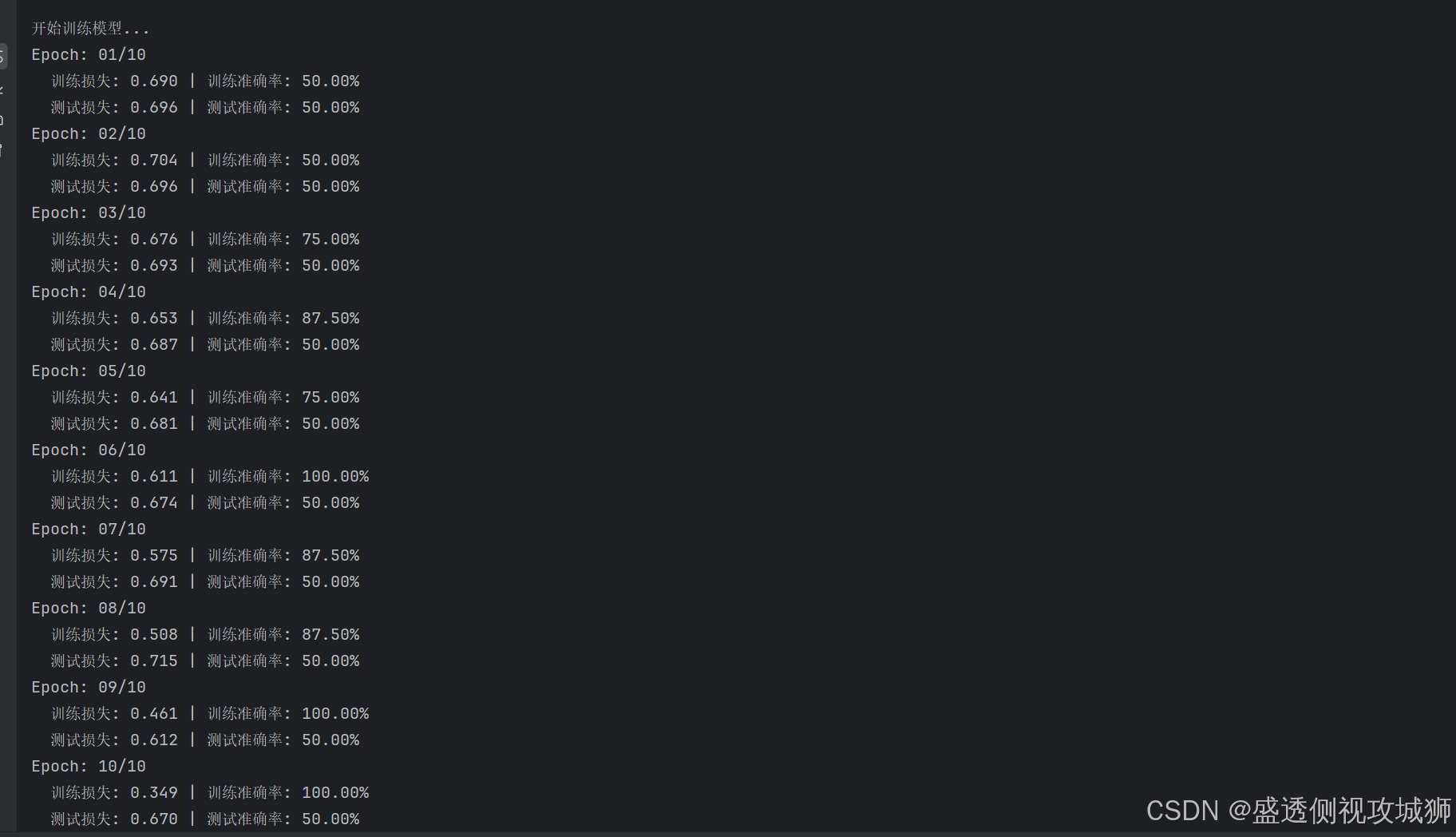


欢迎各位彦祖与热巴畅游本人专栏与技术博客
你的三连是我最大的动力
点击➡️指向的专栏名即可闪现
➡️计算机组成原理****
➡️操作系统
➡️****渗透终极之红队攻击行动********
➡️ 动画可视化数据结构与算法
➡️ 永恒之心蓝队联纵合横防御
➡️****华为高级网络工程师********
➡️****华为高级防火墙防御集成部署********
➡️ 未授权访问漏洞横向渗透利用
➡️****逆向软件破解工程********
➡️****MYSQL REDIS 进阶实操********
➡️****红帽高级工程师
➡️红帽系统管理员********
➡️****HVV 全国各地面试题汇总********