本节目标:
1 . 多叉树型结构扩展
2 . 加深哈希思想与熟练运用
题目介绍
Trie (发音类似 "try")或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补全和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie()初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word)向前缀树中插入字符串word。boolean search(String word)如果字符串word在前缀树中,返回true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回false。boolean startsWith(String prefix)如果之前已经插入的字符串word的前缀之一为prefix,返回true;否则,返回false。

提示:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000word和prefix仅由小写英文字母组成insert、search和startsWith调用次数 总计 不超过3 * 104次
代码片段:
cpp
class Trie {
public:
Trie() {
}
void insert(string word) {
}
bool search(string word) {
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
}
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/解析
1 . 仔细读题:能了解何为"前缀树" ------ 给你一个字符串,能利用"前缀树"这个结构返回存在树里的完整字符串------常用于 自动填充 和 拼写检查
2 . 再看接口设计:初始化Trie() 插入单词insert() 搜索单词search() 通过前缀查找单词startsWith()
3 . 总的来说:就是上层用户传来前缀作为键,返回值
哈希
1 . 对于已知键,要快速得到对应的值;我们应该形成条件反射------哈希
2 . 但是哈希也有两种结构 : unordered_set 、 unordered_map
3 . 那此时再问自己:我们要存储的是否是一对关系呢 ?
答:其实没必要,这里的接口都是返回bool 或 void。
换句话说:我们只需要快速搜索目标字符串是否存在,那么首当其冲的结构是unordered_set
4 . 那哈希表中每个格子存的,就是std::string
cpp
class Trie {
public:
Trie() {
// stl容器(此处的hash)会默认调用它自己的默认构造。此处代码不必添加什么
}
void insert(string word) {
}
bool search(string word) {
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
}
private:
std::unordered_set<std::string> hash;// 结构
};5 . insert接口里,要求在Trie里插入指定字符串------能吃现成就吃
cppvoid insert(string word) { if(!hash.count(word)) // 检查word是否是已经存在?如果不存在,则插入word { hash.insert(word); } }6 . search接口同样,不就是搜索指定字符串是否在哈希表里存在? count接口
cppbool search(string word) { return hash.count(word) == 1; // unordered_set的count接口,若查到了返回1 ;没查到返回0 }7 . 给定前缀,要求查找------ 现在无法直接拿着prefix直接查找;但我们可以遍历哈希表里存储的所有字符串,然后一个一个比对前缀
8 . 怎么比对,这是关键
a) 我们遍历哈希表时,拿到的元素是string -> 那就试试想字符串相关接口
b) 有接口能在当前字符串查找前缀嘛? 查找前缀不知道,反正有在当前字符串查找一个子串的接口 find
c) 至于是否是前缀,就要看find的返回值是否是0(find的返回值:
那代码跃然纸上:
cpp
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
for(const string& word:hash)
{
if(word.find(prefix) == 0)
return true;
}
return false;
}完整代码:
cpp
class Trie {
public:
Trie() {
}
~Trie()
{
}
void insert(string word) {
if(!hash.count(word))
hash.insert(word);
}
bool search(string word) {
return hash.count(word) == 1;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
for(const string& word:hash)
{
if(word.find(prefix) == 0)
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
std::unordered_set<string> hash;
};树型结构
1 . 此方法为本章核心目标
2 . 我们实现的当真是前缀树否? 非也,只是个带了前缀搜索的哈希表(苦笑)
3 . 还记得树得天独厚的结构:比如二叉树查找时间复杂度O(logN)
4 . 我们要想办法实现一个树结构+前缀搜索功能------>前缀树
1 . 谈到"树",不免想到树结点 、递归 、前中后序等等回忆2 . 首先是结构:
树 : 一棵树往往是给出它的根节点代表 一棵树
细看,树 : 由根节点和孩子结点们组成
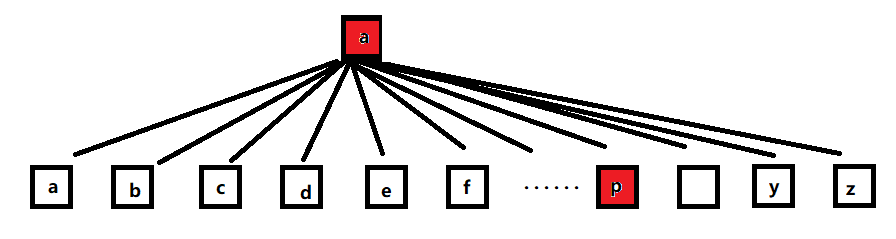
3 . 此处的结点如何设计?(缺乏想象力,那就先画一点
如图:这是一棵树,它的根节点是'a',它的孩子有36个
a) 如果找单词:app ; 那么首先找到root的 a字符所在树,即找到图上这棵
b) 接下来找p , 顺着a(当前root为a )找到p字符所在树,即红色p那棵
4 . 相信你有点启示,但不够清晰;接下来代码会有点陡,但看懂了就会加深多叉树构建能力
cpp
// 结点结构
struct TrieNode
{
TrieNode()
:_children(26,nullptr) // 初始化为26个空槽位
{}
~TrieNode() // 析构:成员变量为含指针,手动析构->暗含递归
{
for(auto* child:_children)
{
delete child;
}
_isEnd = false;
}
std::vector<TrieNode*> _children; // 该结点存的是孩子们,只会有26种情况------所以大小为26,存的是孩子结点的指针
}5 . 是有点抽象------这是在干嘛:Trie 树的结点本身并不直接存储字符,字符是通过「结点在数组中的索引位置」来隐含表示的。
a) 即 0 下标表示 'a'
b) 而 _children[0] 则是'a'这棵树,即找到'a'的孩子们
c) 整棵树你想象出来,应该是:本结点有26个槽位(vector大小),每个非空的槽位都会指向一个新的、同样有 26 个槽位的节点
i) TrieNode本质是不是一个大小为26的数组? 是的
ii) 那26个槽位中其中一个元素存储的是什么 ?是TrieNode的地址
iii) 所以其中一个槽位能指向新的 26 个槽位
6 . 有结点,那就组织起来成为树:
cppclass Trie { public: using TrieNode = struct TrieNode;//取别名,少打点字 Trie() { _root = new TrieNode();// 初始化 } ~Trie() { delete _root; } void insert(string word) { } bool search(string word) { } bool startsWith(string prefix) { } private: TrieNode* _root; // 用该树的根节点表示整棵树 };
7 . 试着完成insert。设想:遍历word的每个字母然后一个一个存入前缀树------因为TrieNode没必要单独开一个char存储当前结点的字符,所以直接用槽位的下标表示。
cppvoid insert(string word) { for(auto& c : word) { TrieNode* pcur = _root;// 不直接操作_root int idx = c - 'a';//获取到本次字母的下标 if(pcur->_children[idx]) { // 如果pcur->_children[idx]有效,意味着该字母存过 } else { // 如果pcur->_children[idx]无效,意味着该字母没存过 // 没存过 ? 那就存;存该字母,就是"存下标"->让该下标有效->让它有存放孩子的槽位 } } }
cppvoid insert(string word) { TrieNode* pcur = _root for(auto& c : word) { int idx = c - 'a';//获取到本次字母的下标 if(!pcur->_children[idx]) { pcur->_children[idx] = new TrieNode(); } pcur = pcur->_child[idx];// 接下来的字母就应该存在它的槽位中,pcur自然要更新 } }8 . 有个bug需注意
1)我们在后面树的时候,如果插入apple ,app 两个单词后
2)搜索app时,我们该怎么区分apple 和 app呢 ?
3)给结点再加一个标志字段 : _isEnd 用于搜索目标单词时判断是否结尾
i. 如果搜索app ,此时遍历到p最后一个字母,然后再判断该结点是否结束字母即可
ii. 如果搜索apple ,此时遍历到e最后一个字母,然后再判断该结点是否结束字母即可
所以改后的 结点结构 + insert :
cpp
struct TrieNode
{
TrieNode()
:_children(26,nullptr),
_isEnd(false)
{}
~TrieNode() // 析构:成员变量为含指针,手动析构->暗含递归
{
for(auto* child:_children)
{
delete child;
}
_isEnd = false;
}
std::vector<TrieNode*> _children;
bool _isEnd;// 添加字段
}
class Trie {
public:
using TrieNode = struct TrieNode;
Trie() {
_root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root
for(auto& c : word)
{
int idx = c - 'a';//获取到本次字母的下标
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
{
pcur->_children[idx] = new TrieNode();
}
pcur = pcur->_child[idx];
}
pcur->_isEnd = true;// 插入完毕,记得给最后一个结点修改标志位
}9 . 有了insert , 那search就是照猫画虎:
思路:遍历给定的word,在树里挨个搜索:
a)如果遇到某个字母在树里不存在,那么返回false
b) 全部存在,但需要最后判断是否以最后一个字母结尾
cppbool search(string word) { TrieNode* pcur = _root; for(auto& c:word) { int idx = c - 'a'; if(!pcur->_children[idx]) return false; pcur = pcur->_children[idx]; } return pcur->_isEnd == true; }
10 . startsWith 则是需要查找是否存在给定prefix的单词
11 . 放在树型结构里,和search的思路很像------唯一区别是我们只要求这个prefix存在即可,并不要求它是一个单词
cppbool startsWith(string prefix) { TrieNode* pcur = _root; for(auto& c:prefix) { int idx = c - 'a'; if(!pcur->_children[idx]) return false; pcur = pcur->_children[idx]; } return true; }
整合代码:
cpp
struct TrieNode
{
TrieNode()
:_children(26,nullptr),
_isEnd(false)
{}
~TrieNode() // 析构:成员变量为含指针,手动析构->暗含递归
{
for(auto* child:_children)
{
delete child;
}
_isEnd = false;
}
std::vector<TrieNode*> _children;
bool _isEnd;
};
class Trie {
public:
using TrieNode = struct TrieNode;
Trie() {
_root = new TrieNode();
}
~Trie()
{
delete _root;
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c : word)
{
int idx = c - 'a';//获取到本次字母的下标
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
{
pcur->_children[idx] = new TrieNode();
}
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
pcur->_isEnd = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c:word)
{
int idx = c - 'a';
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
return false;
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
return pcur->_isEnd == true;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c:prefix)
{
int idx = c - 'a';
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
return false;
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
return true;
}
private:
TrieNode* _root;
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/总结以及完整参考代码

cpp
class Trie {
public:
Trie() {
}
~Trie()
{
}
void insert(string word) {
if(!hash.count(word))
hash.insert(word);
}
bool search(string word) {
return hash.count(word) == 1;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
for(const string& word:hash)
{
if(word.find(prefix) == 0)
return true;
}
return false;
}
private:
std::unordered_set<string> hash;
};
cpp
struct TrieNode
{
TrieNode()
:_children(26,nullptr),
_isEnd(false)
{}
~TrieNode() // 析构:成员变量为含指针,手动析构->暗含递归
{
for(auto* child:_children)
{
delete child;
}
_isEnd = false;
}
std::vector<TrieNode*> _children;
bool _isEnd;
};
class Trie {
public:
using TrieNode = struct TrieNode;
Trie() {
_root = new TrieNode();
}
~Trie()
{
delete _root;
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c : word)
{
int idx = c - 'a';//获取到本次字母的下标
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
{
pcur->_children[idx] = new TrieNode();
}
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
pcur->_isEnd = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c:word)
{
int idx = c - 'a';
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
return false;
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
return pcur->_isEnd == true;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* pcur = _root;
for(auto& c:prefix)
{
int idx = c - 'a';
if(!pcur->_children[idx])
return false;
pcur = pcur->_children[idx];
}
return true;
}
private:
TrieNode* _root;
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie* obj = new Trie();
* obj->insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj->search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj->startsWith(prefix);
*/