
文章目录
图片只是辅助理解,真正还是要看代码
这些图片只是网上找来的,如果只写代码,会被认为是垃圾文章
一、原理
1、图的存储
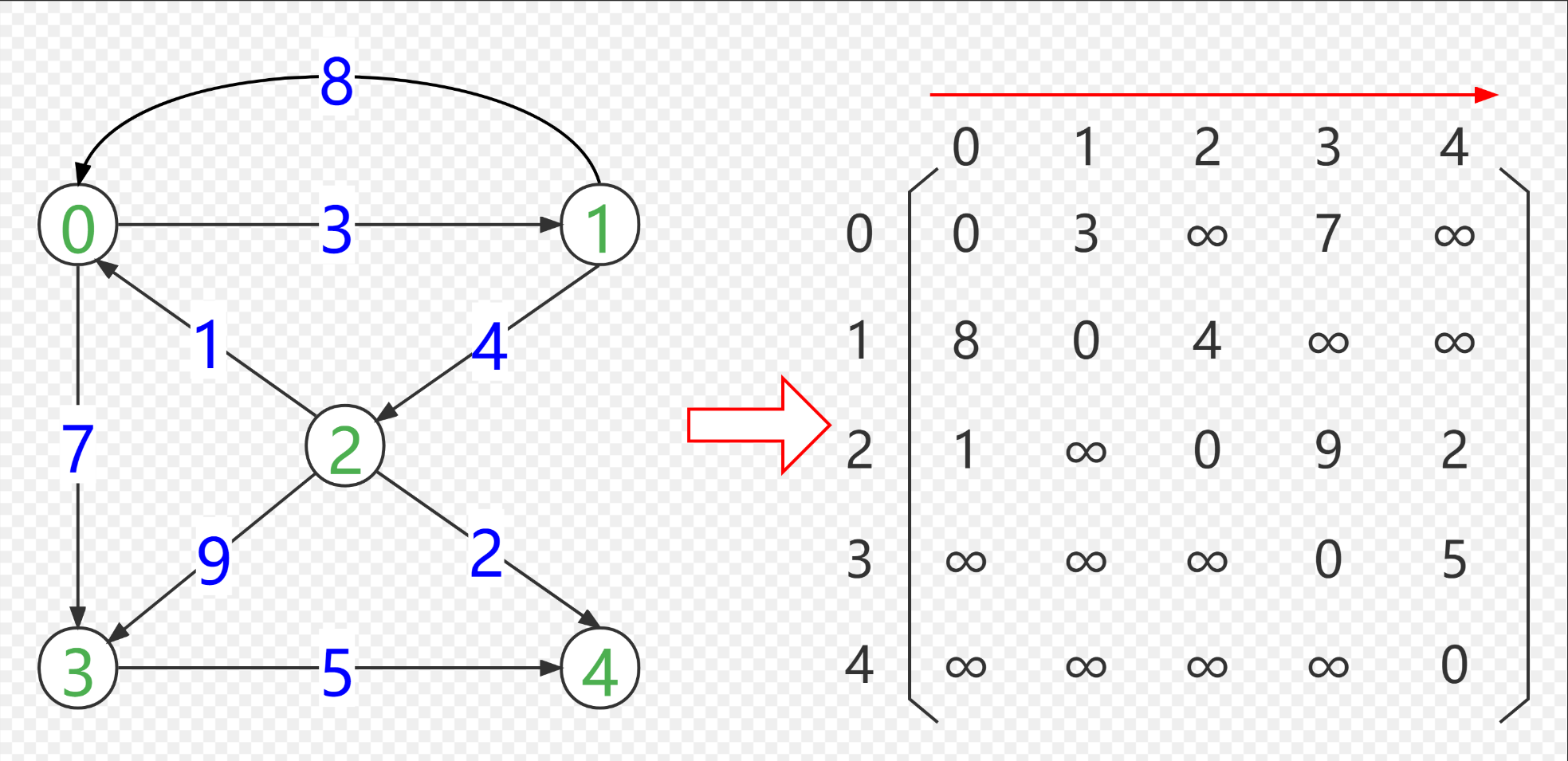
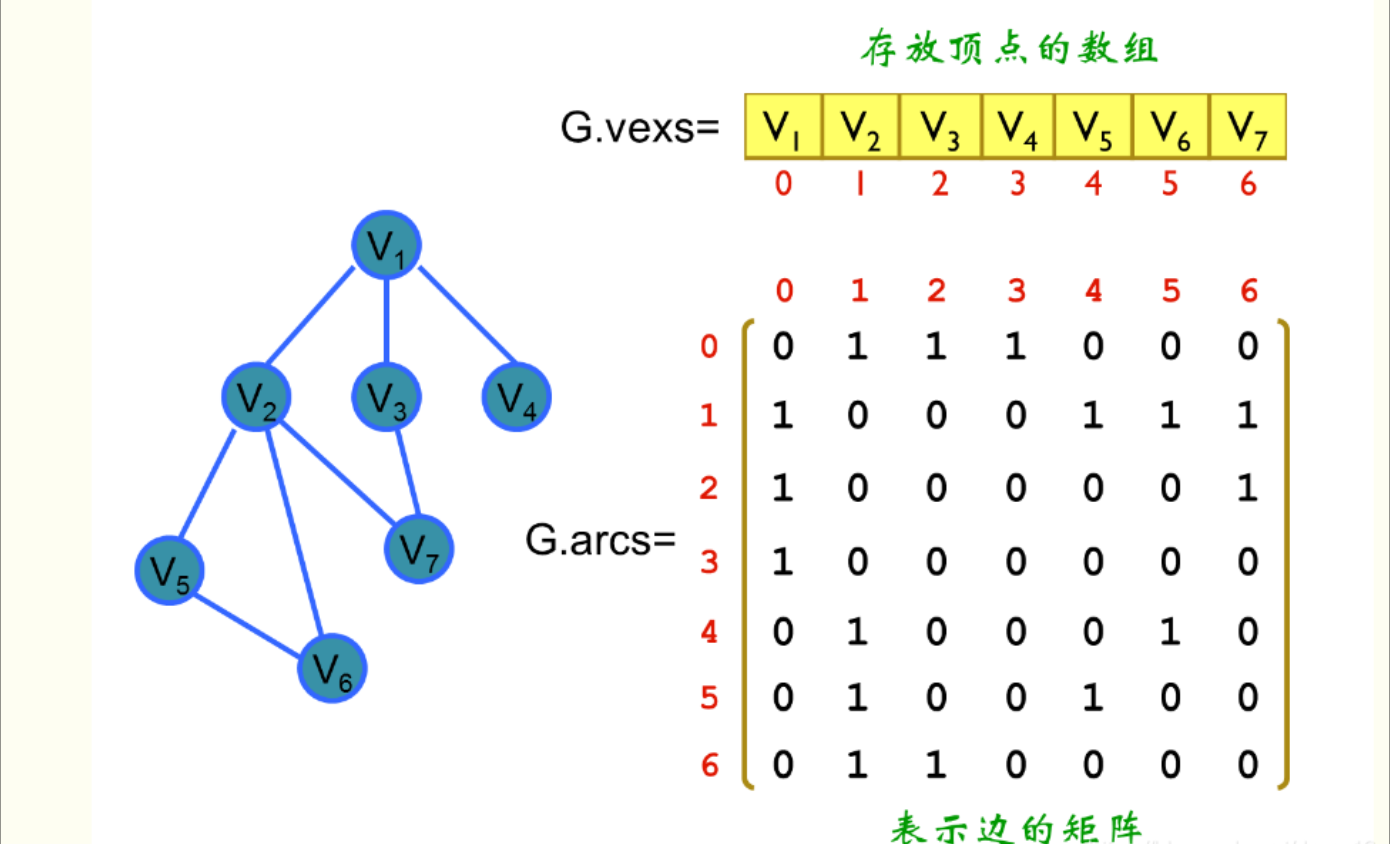
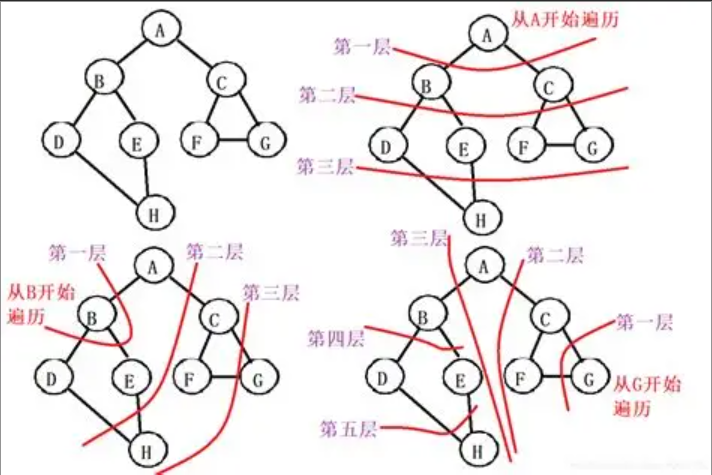
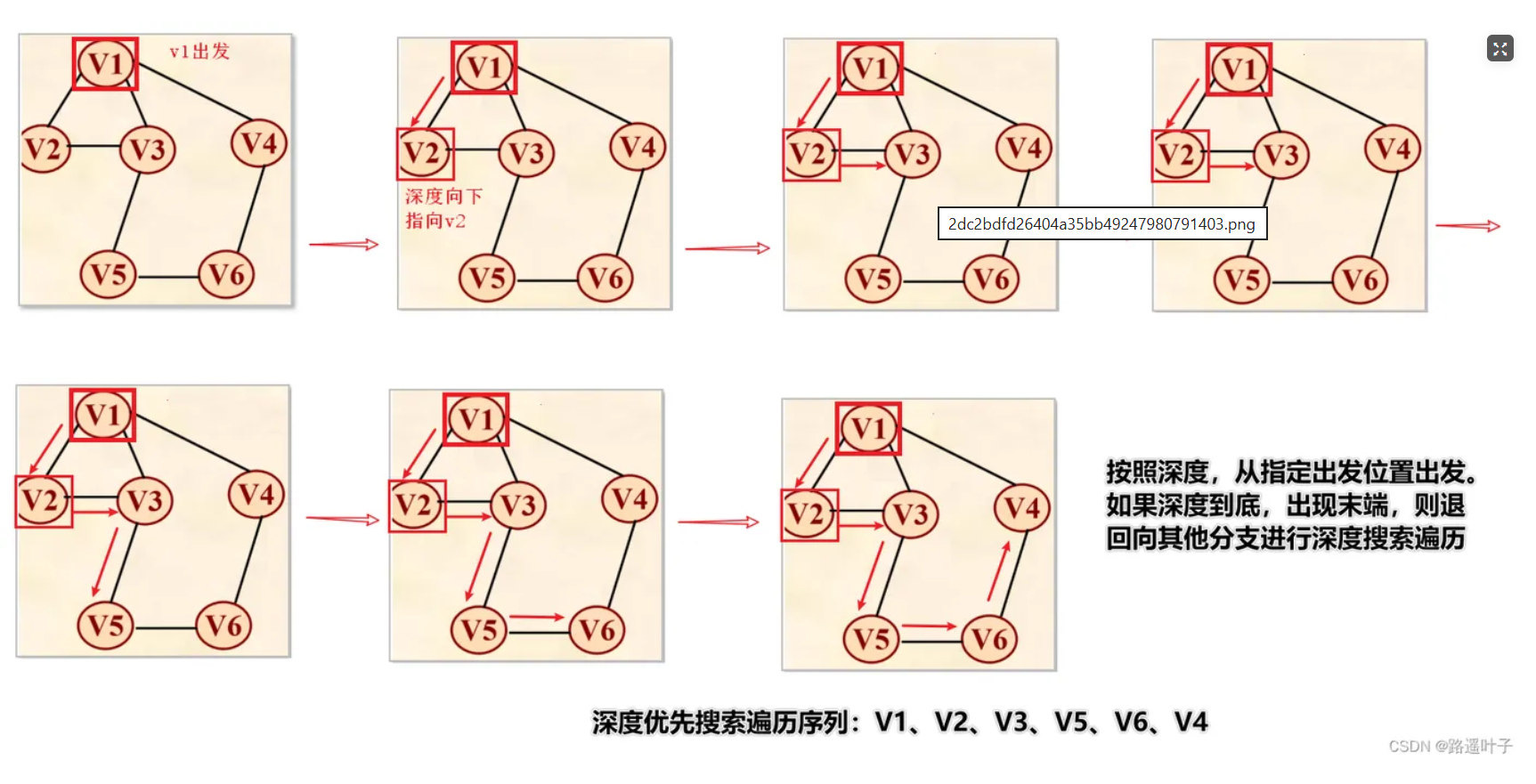
2. 图的搜索
3. 最小生成树
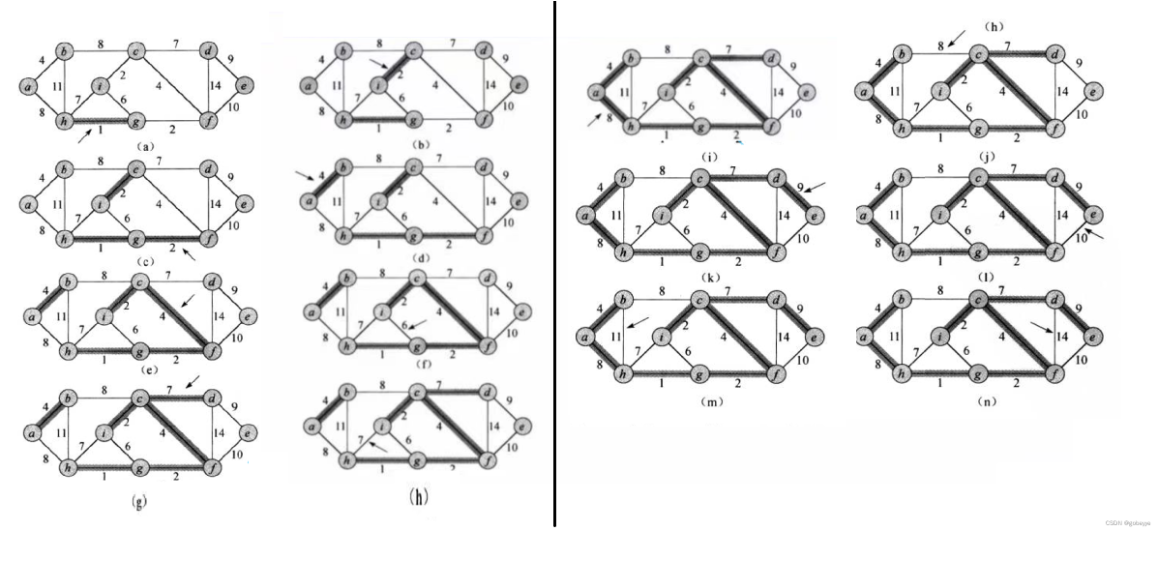
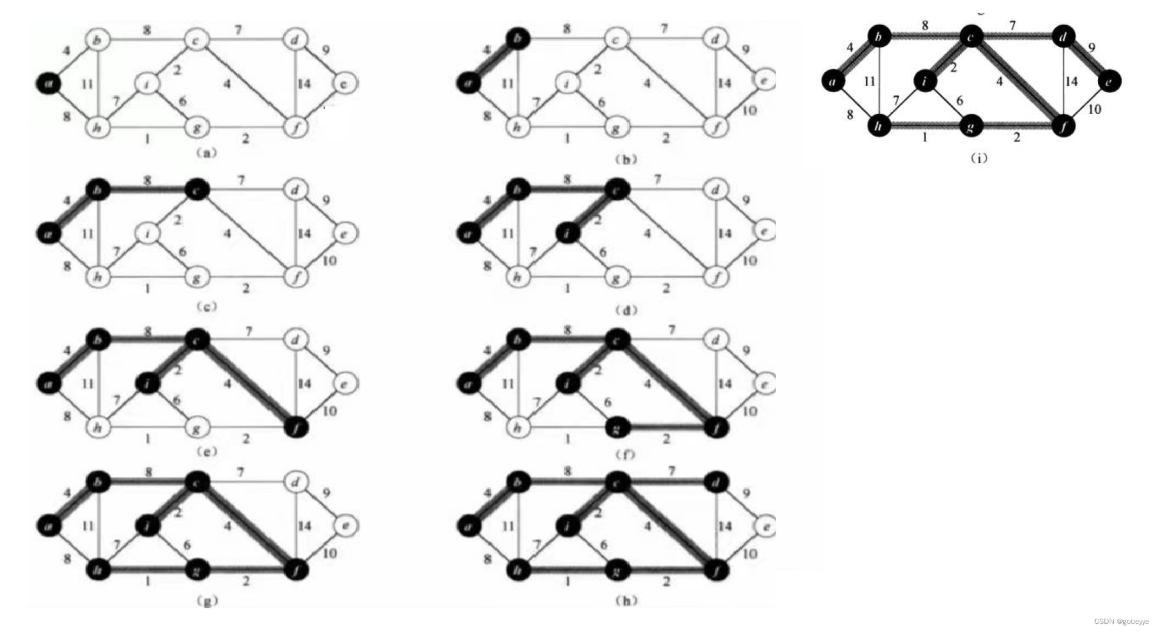
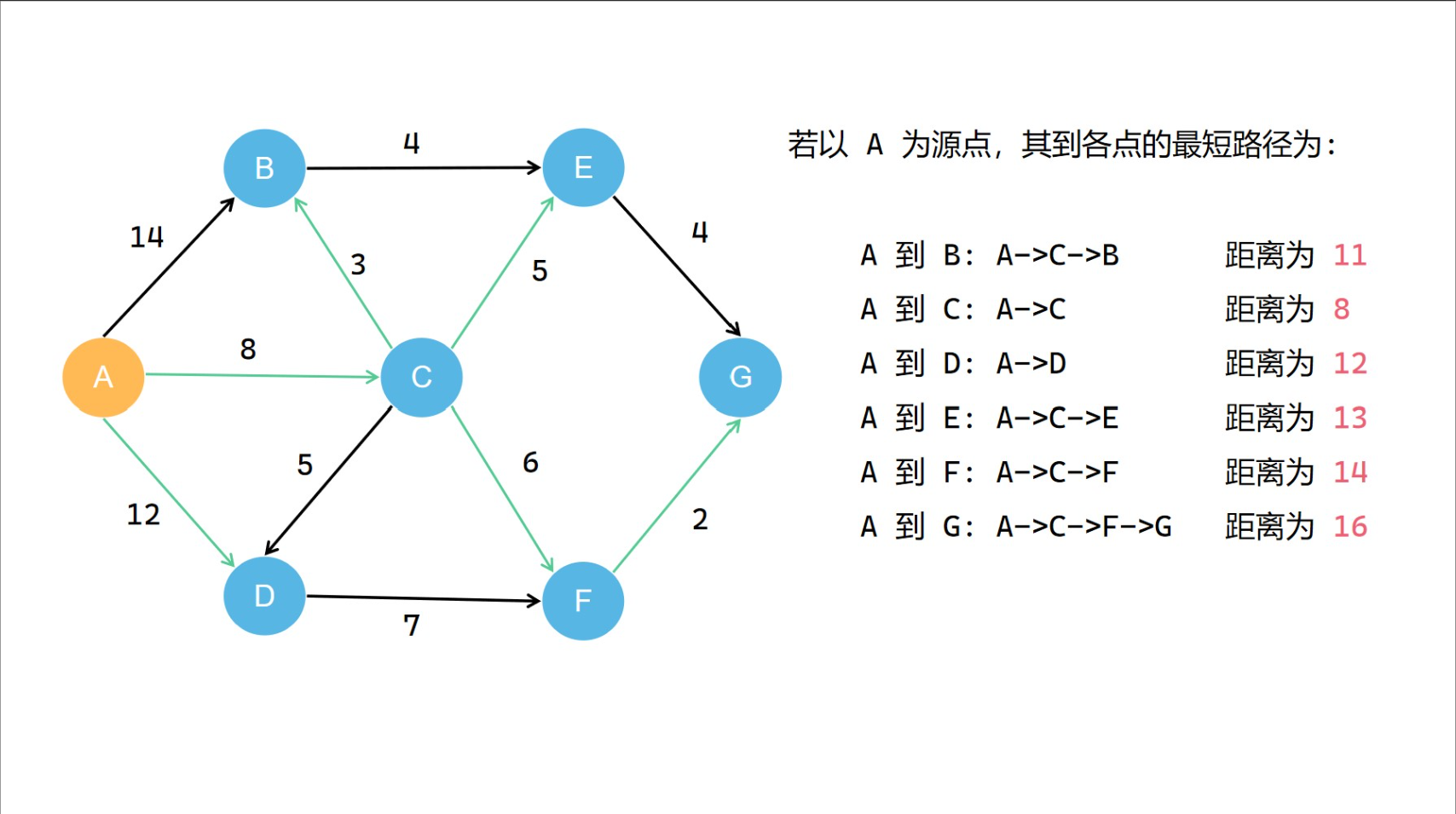
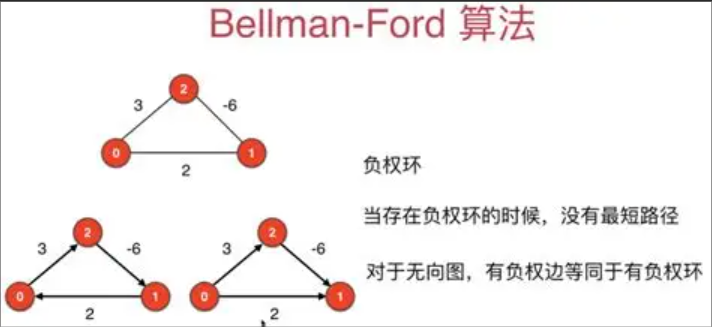
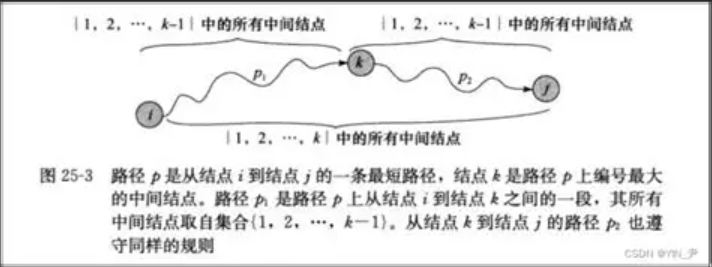
4. 最短路径
二、代码部分
1. 使用邻接矩阵存储
java
package Graph;
import UnionFindSet.UnionFindSet;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author pluchon
* @create 2026-02-13-14:21
* 作者代码水平一般,难免难看,请见谅
*/
//通过邻接矩阵实现图的存储,可能存在大面积空间浪费现象
public class GraphByMatrix {
private HashMap<Character,Integer> vertexs;//存放顶点的数组,内部表示字符和下标
private int [][] edges;//存放边的情况的邻接矩阵,横坐标表示起点,纵坐标表示终点
private boolean isDirection;//是否是有向图
//定义无穷大常量
private static final int INF = 0X3f3f3f3f;
//顶点个数,是否是有向图
public GraphByMatrix(int vertexsCount,boolean isDirection) {
this.vertexs = new HashMap<>(vertexsCount);
this.edges = new int[vertexsCount][vertexsCount];
this.isDirection = isDirection;
//记得全部初始化为+∞,方便表示有向图情况
for(int i = 0;i < vertexsCount;i++){
Arrays.fill(edges[i],INF);
//自己对自己要设为0
edges[i][i] = 0;
}
}
//初始化我们的顶点数组
public void initVertexs(char [] vertexsInit){
for(int i = 0;i < vertexsInit.length;i++){
vertexs.put(vertexsInit[i],i);
}
}
//给顶点边加上权值,如果是无向图,需要自己制定1这个值
public void addEdge(char start,char dest,int value){
//先寻找到下标
int indexStart = getVertex(start);
int indexDest = getVertex(dest);
//设置值,要判断
if(indexStart == -1 || indexDest == -1){
return;
}
edges[indexStart][indexDest] = value;
//如果是无向图,记得反方向也要设置
if(!isDirection){
edges[indexDest][indexStart] = value;
}
}
//获取对应字符下标
public int getVertex(char ch){
Integer index = vertexs.get(ch);
return index == null ? -1 : index;
}
//获取顶点的度
public int getValue(char ch){
//先获取下标
int index = getVertex(ch);
//判断
if(index == -1){
return -1;
}
//正式获取
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < edges[index].length;i++){
if(edges[index][i] != 0 && edges[index][i] != INF){
//说明有边相连
count++;
}
}
//如果是有向图,要检查反向,这里由于是要锁定到哪一列,因此只能一列列找
if(isDirection){
for (int i = 0;i < edges.length;i++) {
//入度指的是其他顶点到当前顶点,因此要跳过当前顶点列
if (i != index && edges[i][index] != 0 && edges[i][index] != INF) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
//打印矩阵和顶点数组
public void print() {
System.out.println("--- 顶点映射 ---");
vertexs.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + " -> index[" + value + "]"));
System.out.println("--- 邻接矩阵 ---");
for (int[] row : edges) {
for (int val : row) {
if (val == INF) {
System.out.printf("%4s", "∞");
}else {
System.out.printf("%4d", val);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//深度优先遍历
public void dfs(char start){
//一般来说都是搞一个visited数组用于标记,有多少个顶点就搞多大的空间
boolean [] isVisited = new boolean[vertexs.size()];
//获取下标
int index = vertexs.get(start);
//直接开始递归
dfsVertexs(index,isVisited);
}
private void dfsVertexs(int index,boolean [] isVisited){
//标记
isVisited[index] = true;
//打印
char ch = getVertexChar(index);
System.out.println("key->"+ch+"|||index->"+index);
//遍历邻接矩阵当前行
for(int i = 0;i < edges.length;i++){
//i不能是自己
if(i != index && edges[index][i] != 0 && edges[index][i] != INF && !isVisited[i]){
//发现新的与之相连的节点,递归
dfsVertexs(i,isVisited);
}
}
}
//从下标找字符
private char getVertexChar(int index){
return vertexs.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getValue() == index)
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.findFirst().orElse('?');
}
//广度优先遍历
public void bfs(char start){
//一般来说都是搞一个visited数组用于标记,有多少个顶点就搞多大的空间
boolean [] isVisited = new boolean[vertexs.size()];
//借助队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//获取下标
int index = vertexs.get(start);
//首顶点入队
queue.offer(index);
//标记
isVisited[index] = true;
//层层扩展
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int top = queue.poll();
//打印
char ch = getVertexChar(top);
System.out.println("key->"+ch+"|||index->"+top);
//标记
isVisited[top] = true;
//遍历这一行其他与之相邻的顶点
for(int i = 0;i < edges.length;i++){
if(i != index && edges[top][i] != 0 && edges[top][i] != INF && !isVisited[i]){
//发现新的与之相连的节点,入队
queue.offer(i);
//标记
isVisited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
//求最小生成树,存储边
static class Edge{
private int start;//边的起点下标
private int dest;//边的终点下标
public int value;//边权值
public Edge(int start, int dest, int value) {
this.start = start;
this.dest = dest;
this.value = value;
}
}
//根据两个下标添加边
private void addEdgeByIndex(int start,int end,int value){
edges[start][end] = value;
//无向图,记得反方向也要设置
if(!isDirection){
edges[end][start] = value;
}
}
//kruskal算法,最后返回结果
public int kruskal(GraphByMatrix minGraphByMatrix) throws Exception {
//判断是不是无向图
if(isDirection){
throw new Exception("最小生成树必须是无向图");
}
//定义优先级队列,根据权值排序
PriorityQueue<Edge> edgePriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.value));
//顶点个数
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//添加矩阵值进队列
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < countVertexs;j++){
//因为本质上要求无向图,因此只需要添加矩阵下三角部分就好
if(i < j && edges[i][j] != 0 && edges[i][j] != INF){
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(i,j,edges[i][j]));
}
}
}
//引入并查集,并指定几个顶点
UnionFindSet unionFindSet = new UnionFindSet(countVertexs);
//开始统计
int sumValue = 0;
//统计边个数,为后续判断是不是本来就是不连通图打下基础
int countEdge = 0;
//N个顶点只需要N-1条边
while(countEdge < countVertexs-1 && !edgePriorityQueue.isEmpty()){
//弹出边
Edge edge = edgePriorityQueue.poll();
int start = edge.start;
int dest = edge.dest;
//判断是否属于同一个集合,只有不是同一个集合才统计
if(!unionFindSet.isSameSet(start,dest)){
System.out.println("起点:"+start+"->终点:"+dest+"||权值:"+edges[start][dest]);
//加入最小生成树
minGraphByMatrix.addEdgeByIndex(start,dest,edge.value);
//加入并查集,进行合并
unionFindSet.toUnion(start,dest);
//统计权值
sumValue += edge.value;
//边的条数加一
countEdge++;
}
}
//最后判断是否不是连通图
return countEdge == countVertexs-1 ? sumValue : -1;
}
//prim算法,最后返回结果,这里要给定一个起始顶点
public int prim(GraphByMatrix minGraphByMatrix,char startCh){
//获取起始顶点的下标
int startIndex = vertexs.get(startCh);
//定义两个集合,集合X表示已经确定的顶点,集合Y表示未确定的顶点
HashSet<Integer> setX = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Integer> setY = new HashSet<>();
//添加起点
setX.add(startIndex);
//统计顶点个数
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//把除了起点外的所有顶点添加到集合Y中
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
if(i != startIndex){
setY.add(i);
}
}
//定义优先级队列,确保每一次取得的都是最小边
PriorityQueue<Edge> edgePriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.value));
//初始化所有起点的临边
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
if(edges[startIndex][i] != 0 && edges[startIndex][i] != INF){
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(startIndex,i,edges[startIndex][i]));
}
}
//定义边计数器和权值统计
int countEdge = 0;
int sumValue = 0;
while (countEdge < countVertexs-1 && !edgePriorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge edge = edgePriorityQueue.poll();
int start = edge.start;
int dest = edge.dest;
//首先看看取出的这个边的结尾顶点是否已经在X集合中了,起点不用看,因为我们添加到时候就已经添加进来了
if(!setX.contains(dest)){
//此时结尾顶点是新的顶点,我们添加到最小生成树
minGraphByMatrix.addEdgeByIndex(start,dest,edge.value);
//打印
System.out.println("起点:"+start+"->终点:"+dest+"||权值:"+edges[start][dest]);
//添加入X集合,并在Y集合中删除
setX.add(dest);
setY.remove(dest);
//计数器和权值统计
countEdge++;
sumValue += edges[start][dest];
//记住,要把我们新添加顶点连接出的其他顶点对应的边也添加了
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
//注意也不能构成环
if(edges[dest][i] != 0 && edges[dest][i] != INF && !setX.contains(i)){
//添加进队列
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(dest,i,edges[dest][i]));
}
}
}
}
//最后判断一下是不是连通图
return countEdge == countVertexs-1 ? sumValue : -1;
}
//求最短路径->dijkstra算法:起点字符,距离数组,路径数组
public void dijkstra(char startCh,int[] dist,int[] pPath) {
//获取起始下标
int startIndex = getVertex(startCh);
//初始化
//默认初始化为无穷大
Arrays.fill(dist,INF);
//默认初始化为-1
Arrays.fill(pPath,-1);
//初始化起点
pPath[startIndex] = startIndex;
dist[startIndex] = 0;
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//定义一个标记数组
boolean [] isDetermined = new boolean[countVertexs];
//遍历每一个节点
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
//假设最短路径是最大值
int minPath = INF;
//从起点开始找,但是我们初始化为-1
//用于判断是否还能找到可达点
int minStart = -1;
//遍历整个dist数组,寻找值最小的小下标
for(int j = 0;j < countVertexs;j++){
//不能是已经标记过的
if(!isDetermined[j] && dist[j] < minPath){
minPath = dist[j];
minStart = j;
}
}
//判断有没有找到
//如果找不到可达的最小点,说明剩下的点都不连通了
if (minStart == -1){
break;
}
//此时已经找到了,标记
isDetermined[minStart] = true;
//松弛边,也就是尽量把dist顶点的值变得更小
for(int j = 0;j < countVertexs;j++){
//前提是minStart到j之间有联系
//不能被标记,并且j顶点的原始值如果比从(minStart->j的值+dist[minStart])值更大,就要更新
if(!isDetermined[j] && edges[minStart][j] != INF && edges[minStart][j] != 0
&& dist[minStart]+edges[minStart][j] < dist[j]){
dist[j] = dist[minStart]+edges[minStart][j];
//更新父节点下标
pPath[j] = minStart;
}
}
}
}
//打印路径:起点字符,距离数组,路径数组
public void printShortPath(char startCh,int[] dist,int[] pPath) {
//获取起点下标
int startIndex = getVertex(startCh);
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//遍历pPath数组每个值,一直向上溯源
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
//不能自己打印自己
if(i != startIndex){
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int parent = i;
//一直向上溯源到头
//不能写成>=0,如果到了0会一直打印0,死循环
//而且不能溯源到未初始化的顶点
while(parent != startIndex && parent != -1){
path.add(parent);
parent = pPath[parent];
}
//注意0下标没有被打印到,要手动添加
path.add(0);
//翻转,转换成从0下标的起始路径
Collections.reverse(path);
//打印出来
for (int pos : path) {
System.out.print(getVertexChar(pos)+" -> ");
}
System.out.println("最短距离值:"+dist[i]);
}
}
}
//求最短路径->bellmanFord算法:起点字符,距离数组,路径数组,适合负权图
public boolean bellmanFord(char startCh,int[] dist,int[] pPath) {
//获取顶点下标
int srcIndex = getVertex(startCh);
//初始化父顶点数组下标为-1
Arrays.fill(pPath, -1);
//初始化dist数组
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
//对起点进行初始化,给一个最小值 方便第一次就能找到最小值
dist[srcIndex] = 0;
int count = vertexs.size();
//N个顶点遍历N次,就可以找到所有情况
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < count; k++) {
if(edges[j][k] != INF && edges[j][k] != 0 && dist[j]+edges[j][k] < dist[k]){
//更新
dist[k] = dist[j]+edges[j][k];
pPath[k] = j;
}
}
}
}
//为了避免负权图,因此要判断下
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
if(edges[i][j] != INF && edges[i][j] != 0 && dist[i]+edges[i][j] < dist[j]){
//存在负权图
return false;
}
}
}
//不存在负权图
return true;
}
//求多源最短路径->floydWarShall算法:距离数组,路径数组,适合负权图
//二维数组表示从i->j的最短距离
//核心原理
/*
如果想让i到j的距离变短,唯一的办法就是找个中转点k
如果dist[i->k]+dist[k->j] < dist[i->j],说明经过k绕路比直接走(或当前已知的路)更近
*/
//pPath[i][j]存储的是:从i走到j的最短路径上,j的前一个顶点的下标
public void floydWarShall(int[][] dist,int[][] pPath) {
//初始化dist数组和pPath数组
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
for (int i = 0; i < countVertexs; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], INF);//假设全图都不通
Arrays.fill(pPath[i], -1);//假设没有前驱
}
//遍历邻接矩阵数组,把直接每个顶点直接相连的权值更新到dist数组当中,相当于就是复制
for (int i = 0; i < countVertexs; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < countVertexs; j++) {
if (edges[i][j] != INF && edges[i][j] != 0) {
//存在权值则更新dist数组
//此时存在直接相连的路,先记录
dist[i][j] = edges[i][j];
//i->j直接相连的更新完了,此时i->j的父节点下标为i
//也就是说j的前驱是i
pPath[i][j] = i;
}
//i->j自己不存在距离,且没有父路径
if (i == j) {
dist[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
//每个顶点作为一次中转点,k表示
for (int k = 0; k < countVertexs; k++) {
//起点i
for (int i = 0; i < countVertexs; i++) {
//终点j
for (int j = 0; j < countVertexs; j++) {
//如果从i->k有路径 并且从k->j有路径
//并且 i->k + k->j 的距离小于从i直接到j 那么更新i->j的最短路径
if (dist[i][k] != INF && dist[k][j] != INF &&
dist[i][k] != 0 && dist[k][j] != 0 &&
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]){
//到了这里就说明绕路更近
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
//注意:我们要找的是"到达j之前的最后一个点"
//既然最后一段是从k走到j的(或者经过k中转后到达j的)
//那么到达j的前驱点,就应该等于从k走到j的路径中j的前驱点
//因为你想想,你从i->j的到达j前一个顶点下标,不就是k->j到达j的前一个顶点下标吗
//因为我们经过了k,假设i->a->b->k->c->d->j,此时从i->j的j前一个顶点是d
//同时从k->j的j前一个顶点也是d,一个意思
pPath[i][j] = pPath[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
//配合Floyd算法的打印辅助方法
public static void printFloydPath(GraphByMatrix g, char start, char dest, int[][] dist, int[][] pPath) {
int i = g.getVertex(start);
int j = g.getVertex(dest);
if (dist[i][j] == 0X3f3f3f3f) {
System.out.println(start + " 到 " + dest + " 不连通");
return;
}
List<Character> path = new ArrayList<>();
int curr = j;
while (curr != -1) {
// 这里调用的 getVertexChar 是你类里那个 stream 实现的方法
path.add(getVertexCharFromMap(g, curr));
if (curr == i) break;
curr = pPath[i][curr];
}
Collections.reverse(path);
System.out.print("路径: ");
for (int k = 0; k < path.size(); k++) {
System.out.print(path.get(k) + (k == path.size() - 1 ? "" : " -> "));
}
System.out.println(" | 总权值: " + dist[i][j]);
}
// 临时辅助:因为 main 是静态的,这里写个简单的转换
private static char getVertexCharFromMap(GraphByMatrix g, int index) {
// 假设你已经在类里把这个方法改成了 public 或者这里直接模拟
return (char)('A' + index); // 简单演示用
}
// ================= 测试用例 =================
public static void main1(String[] args) {
System.out.println("====== 场景 1: 无向图 (模拟朋友圈) ======");
GraphByMatrix friendGraph = new GraphByMatrix(4, false);
friendGraph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'});
// A和B是好友,B和C是好友,A和C是好友
friendGraph.addEdge('A', 'B', 1);
friendGraph.addEdge('B', 'C', 1);
friendGraph.addEdge('A', 'C', 1);
friendGraph.print();
System.out.println("顶点 B 的度: " + friendGraph.getValue('B')); // 应为 2
System.out.println("\n====== 场景 2: 有向图 (模拟单行道/权值) ======");
GraphByMatrix routeGraph = new GraphByMatrix(3, true);
routeGraph.initVertexs(new char[]{'S', 'M', 'E'}); // Start, Middle, End
// S -> M 耗时 10, M -> E 耗时 20
routeGraph.addEdge('S', 'M', 10);
routeGraph.addEdge('M', 'E', 20);
routeGraph.print();
System.out.println("顶点 M 的度: " + routeGraph.getValue('M')); // 出度1 + 入度1 = 2
System.out.println("======广度和深度测试=====");
// 构造 4 个节点的图: A, B, C, D
GraphByMatrix graph = new GraphByMatrix(4, false);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'});
// 添加边,构成一个"菱形"
graph.addEdge('A', 'B', 1);
graph.addEdge('A', 'C', 1);
graph.addEdge('B', 'D', 1);
graph.addEdge('C', 'D', 1);
System.out.println("====== DFS 深度优先 (从 A 开始) ======");
// 预期顺序: A -> B -> D -> C (一条路钻到底)
graph.dfs('A');
System.out.println("\n====== BFS 广度优先 (从 A 开始) ======");
// 预期顺序: A -> B, C -> D (先扫邻居)
graph.bfs('A');
}
//最小生成树两种算法测试
public static void main2(String[] args) {
// 构造 5 个节点
char[] vs = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'};
GraphByMatrix graph = new GraphByMatrix(5, false);
graph.initVertexs(vs);
// 构建一个带权的无向图
graph.addEdge('A', 'B', 1);
graph.addEdge('A', 'C', 3);
graph.addEdge('B', 'C', 6);
graph.addEdge('B', 'D', 5);
graph.addEdge('C', 'D', 4);
graph.addEdge('D', 'E', 2);
System.out.println("--- 原图矩阵 ---");
graph.print();
try {
System.out.println("\n====== 挑战 Kruskal ======");
GraphByMatrix kMST = new GraphByMatrix(5, false);
kMST.initVertexs(vs);
int kRes = graph.kruskal(kMST);
System.out.println("Kruskal 总权值: " + kRes);
System.out.println("\n====== 挑战 Prim ======");
GraphByMatrix pMST = new GraphByMatrix(5, false);
pMST.initVertexs(vs);
int pRes = graph.prim(pMST, 'A');
System.out.println("Prim 总权值: " + pRes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//最短路径dijkstra测试
//这个算法不能用于负权值的图
public static void main3(String[] args) {
// 构造 5 个节点:A, B, C, D, E
GraphByMatrix graph = new GraphByMatrix(5, true); // 注意:Dijkstra 常用于有向图
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
graph.addEdge('A', 'B', 10);
graph.addEdge('A', 'C', 5);
graph.addEdge('B', 'D', 1);
graph.addEdge('C', 'B', 3);
graph.addEdge('C', 'D', 9);
graph.addEdge('C', 'E', 2);
graph.addEdge('D', 'E', 4);
graph.addEdge('E', 'D', 6);
int[] dist = new int[5];
int[] pPath = new int[5];
System.out.println("====== Dijkstra 最短路径测试 (起点 A) ======");
graph.dijkstra('A', dist, pPath);
graph.printShortPath('A', dist, pPath);
}
//最短路径bellmanFord算法测试
//这个算法能用于负权值的图,还可以判断负权回路
//负权回路会使你的路径值也就是dist值越来越小,无限循环
public static void main4(String[] args) {
// 构造一个简单的负权回路:A -> B -> C -> A (1 + 1 - 5 = -3)
GraphByMatrix graph = new GraphByMatrix(3, true);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C'});
graph.addEdge('A', 'B', 1);
graph.addEdge('B', 'C', 1);
graph.addEdge('C', 'A', -5); // 致命的负权边
int[] dist = new int[3];
int[] pPath = new int[3];
boolean hasNoCycle = graph.bellmanFord('A', dist, pPath);
System.out.println("是否存在负权回路? " + (hasNoCycle ? "否" : "是"));
// 这里应该输出:是
GraphByMatrix negativeGraph = new GraphByMatrix(5, true);
negativeGraph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
negativeGraph.addEdge('A', 'B', 10);
negativeGraph.addEdge('B', 'C', 1);
negativeGraph.addEdge('C', 'D', 1);
negativeGraph.addEdge('D', 'B', -5); // 制造负权回路
negativeGraph.addEdge('D', 'E', 2);
int[] dist2 = new int[5];
int[] pPath2 = new int[5];
boolean result = negativeGraph.bellmanFord('A', dist2, pPath2);
System.out.println("该图是否存在最短路径(无负权回路)? " + result);
// 预期结果:false
}
//多源最短路径测试代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个 4 个顶点的有向图
GraphByMatrix graph = new GraphByMatrix(4, true);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'});
/*
* 构造边的情况:
* A -> B (5), A -> C (2)
* B -> D (2)
* C -> B (-4) <-- 这是一个负权边!
* C -> D (6)
*/
graph.addEdge('A', 'B', 5);
graph.addEdge('A', 'C', 2);
graph.addEdge('B', 'D', 2);
graph.addEdge('C', 'B', -4);
graph.addEdge('C', 'D', 6);
System.out.println("--- 原始邻接矩阵 ---");
graph.print();
// 准备 Floyd 算法需要的矩阵
int n = 4;
int[][] dist = new int[n][n];
int[][] pPath = new int[n][n];
// 执行算法
graph.floydWarShall(dist, pPath);
System.out.println("\n--- Floyd 执行后的最短距离矩阵 ---");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (dist[i][j] == 0X3f3f3f3f) System.out.printf("%4s", "∞");
else System.out.printf("%4d", dist[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n--- 路径溯源验证 ---");
// 重点验证:A -> B 的最短路径
// 直接走是 5,但 A -> C -> B 是 2 + (-4) = -2
printFloydPath(graph, 'A', 'B', dist, pPath);
// 验证:A -> D 的最短路径
// A -> C -> B -> D 应该是 2 + (-4) + 2 = 0
printFloydPath(graph, 'A', 'D', dist, pPath);
}
}2. 使用邻接表存储
java
package Graph;
import UnionFindSet.UnionFindSet;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author pluchon
* @create 2026-02-13-15:10
* 作者代码水平一般,难免难看,请见谅
*/
//使用邻接表存储图,大大节省内存
public class GraphByNode {
//定义每一个节点
static class Node{
//起始下标,也就是说属于哪一个顶点的链表
private int start;
//终点下标,也就是当前顶点的编号
private int dest;
//下一个节点引用
private Node next;
//权值
private int value;
//构造方法
public Node(int start, int dest, int value) {
this.start = start;
this.dest = dest;
this.value = value;
}
}
private HashMap<Character,Integer> vertexs;//存放顶点的数组,内部表示字符和下标
private ArrayList<Node> edgeList;//每个顶点对应的链表
private boolean isDirect;//是否是有向图
//定义无穷大常量
private static final int INF = 0X3f3f3f3f;
//初始化,包含顶点个数,是否是有向图
public GraphByNode(int vertexsCount,boolean isDirect) {
this.vertexs = new HashMap<>(vertexsCount);
this.edgeList = new ArrayList<>(vertexsCount);
//初始化edgeList,避免后续get不到
for(int i = 0;i < vertexsCount;i++){
edgeList.add(null);
}
this.isDirect = isDirect;
}
//初始化我们的顶点数组
public void initVertexs(char [] vertexsInit){
for(int i = 0;i < vertexsInit.length;i++){
vertexs.put(vertexsInit[i],i);
}
}
//获取对应字符下标
public int getVertex(char ch){
Integer index = vertexs.get(ch);
return index == null ? -1 : index;
}
//添加权值
public void add(char start,char dest,int value){
//获取下标
int startIndex = getVertex(start);
int destIndex = getVertex(dest);
//判断
if(startIndex == -1 || destIndex == -1){
return;
}
addValue(startIndex,destIndex,value);
//如果是无向图,反方向也要添加
if(!isDirect){
addValue(destIndex,startIndex,value);
}
}
private void addValue(int startIndex,int destIndex,int value){
//先获取到startIndex所在链表
Node node = edgeList.get(startIndex);
//如果不为空,一直找,找到最后的一个位置,执行头插操作
while(node != null){
//如果这个destIndex已经存在了,就不用再重复添加
if(node.dest == destIndex){
return;
}
node = node.next;
}
//如果不存在,我们就执行添加操作,就是头插法
Node newNode = new Node(startIndex,destIndex,value);
//连接后续其他顶点
newNode.next = edgeList.get(startIndex);
//设置
edgeList.set(startIndex,newNode);
}
//获取顶点的度
public int getValue(char ch){
int index = getVertex(ch);
if(index == -1){
return -1;
}
//找到获取顶点的所在的链表
Node node = edgeList.get(index);
int count = 0;
while(node != null){
//计数
count++;
node = node.next;
}
//注意,如果是有向图,要统计其他定点到当前顶点的情况,只能整个全部遍历了
if(isDirect){
for(int i = 0;i < edgeList.size();i++){
//获取每一个顶点所在的链表,并且要跳过当前自己的顶点链表
if(i != index){
Node nodeInfo = edgeList.get(i);
while(nodeInfo != null){
if(nodeInfo.dest == index){
count++;
}
nodeInfo = nodeInfo.next;
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
//打印
public void print() {
System.out.println("--- 邻接表结构展示 ---");
// 创建一个反向映射,方便打印字符
char[] indexToChar = new char[vertexs.size()];
vertexs.forEach((ch, idx) -> indexToChar[idx] = ch);
for (int i = 0; i < edgeList.size(); i++) {
System.out.print("顶点 " + indexToChar[i] + " [" + i + "] : ");
Node current = edgeList.get(i);
if (current == null) {
System.out.println("NULL");
continue;
}
while (current != null) {
// 打印格式:-> [终点, 权值]
System.out.print("-> [" + indexToChar[current.dest] + ", w:" + current.value + "] ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//深度优先搜索
public void dfs(char ch){
boolean [] isVisited = new boolean[vertexs.size()];
int index = getVertex(ch);
//开始递归
dfsVertex(index,isVisited);
}
private void dfsVertex(int index,boolean [] isVisited){
//标记
isVisited[index] = true;
//打印
char ch = getVertexChar(index);
System.out.println("key->"+ch+"|||index->"+index);
//寻找符合条件的继续递归
Node node = edgeList.get(index);
while(node != null){
//和当前节点相连的都符合,而且要没有标记过的
if(!isVisited[node.dest]){
dfsVertex(node.dest,isVisited);
}
node = node.next;
}
}
//从下标找字符
private char getVertexChar(int index){
return vertexs.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getValue() == index)
.map(Map.Entry::getKey)
.findFirst().orElse('?');
}
//广度优先搜索
public void bfs(char ch){
//标记数组
boolean [] isVisited = new boolean[vertexs.size()];
//借助队列
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//获取下标
int index = getVertex(ch);
//标记
isVisited[index] = true;
//入队
queue.offer(index);
//层层扩展
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int top = queue.poll();
char key = getVertexChar(top);
System.out.println("key->"+key+"|||index->"+top);
//判断当前链表有没有其他符合条件的
Node node = edgeList.get(top);
while(node != null){
if(!isVisited[node.dest]){
queue.offer(node.dest);
//标记
isVisited[node.dest] = true;
}
node = node.next;
}
}
}
//求最小生成树,存储边
static class Edge{
private int start;//边的起点下标
private int dest;//边的终点下标
private int value;//边权值
public Edge(int start, int dest, int value) {
this.start = start;
this.dest = dest;
this.value = value;
}
}
//根据两个下标添加边
private void addEdgeByIndex(int start,int end,int value){
addValue(start,end,value);
//如果是无向图,反方向也要添加
if(!isDirect){
addValue(end,start,value);
}
}
//kruskal算法,最后返回结果
public int kruskal(GraphByNode minGraphByNode) throws Exception {
//判断是不是无向图
if (isDirect) {
throw new Exception("最小生成树必须是无向图");
}
//首先是定义优先级队列,根据权值进行排序
PriorityQueue<Edge> edgePriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.value));
//统计顶点个数
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//添加链表的值进入队列,但是不能重复添加
//我们利用下标关系大小去重
for(int i = 0;i < edgeList.size();i++){
//遍历每一个链表
Node node = edgeList.get(i);
while(node != null){
//要没有统计的才可以,并且只有起点下标小于终止下标才添加
if(i < node.dest){
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(i,node.dest,node.value));
}
node = node.next;
}
}
//引入并查集
UnionFindSet unionFindSet = new UnionFindSet(countVertexs);
//计数器以及权值
int countEdge = 0;
int sumValue = 0;
while(countEdge < countVertexs-1 && !edgePriorityQueue.isEmpty()){
//弹出边
Edge edge = edgePriorityQueue.poll();
int start = edge.start;
int dest = edge.dest;
//判断是否同属一个集合,必须要是不同的集合
if(!unionFindSet.isSameSet(start,dest)){
System.out.println("起点:"+start+"->终点:"+dest+"||权值:"+edge.value);
//加入到最小生成树
minGraphByNode.addEdgeByIndex(start,dest,edge.value);
//加入并查集,即合并集合
unionFindSet.toUnion(start,dest);
//统计
countEdge++;
sumValue += edge.value;
}
}
//最后判断是否不是连通图
return countEdge == countVertexs-1 ? sumValue : -1;
}
//prim算法,最后返回结果,这里要给定一个起始顶点
public int prim(GraphByNode minGraphByNode,char startCh) {
//获取起始顶点的下标
int startIndex = vertexs.get(startCh);
//定义两个集合,集合X表示已经确定的顶点,集合Y表示未确定的顶点
HashSet<Integer> setX = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Integer> setY = new HashSet<>();
//添加起点
setX.add(startIndex);
//统计顶点个数
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
//把和起点以外的所有顶点添加到集合Y中
for(int i = 0;i < countVertexs;i++){
if(i != startIndex){
setY.add(i);
}
}
//定义优先级队列,确保每一次取得的都是最小边
PriorityQueue<Edge> edgePriorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.value));
//初始化起点的所有临边
Node node = edgeList.get(startIndex);
while(node != null){
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(startIndex,node.dest,node.value));
node = node.next;
}
//定义计数器和权值统计
int countEdge = 0;
int sumValue = 0;
while(countEdge < countVertexs-1 && !edgePriorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge edge = edgePriorityQueue.poll();
int start = edge.start;
int dest = edge.dest;
//不能重复的加入集合
if(!setX.contains(dest)){
//加入到最小生成树
minGraphByNode.addEdgeByIndex(start,dest,edge.value);
//打印
System.out.println("起点:"+start+"->终点:"+dest+"||权值:"+edge.value);
//加入X集合,在集合Y中删除
setX.add(dest);
setY.remove(dest);
//计数器和权值统计
countEdge++;
sumValue += edge.value;
//要把新加入顶点的所有邻接顶点也加入,并且不能重复添加
Node insertNode = edgeList.get(dest);
while(insertNode != null){
if(!setX.contains(insertNode.dest)){
edgePriorityQueue.add(new Edge(dest,insertNode.dest,insertNode.value));
}
insertNode = insertNode.next;
}
}
}
//最后判断是否不是连通图
return countEdge == countVertexs-1 ? sumValue : -1;
}
//求最短路径->dijkstra算法:起点字符,距离数组,路径数组
public void dijkstra(char startCh, int[] dist, int[] pPath) {
//获取起始下标
int startIndex = getVertex(startCh);
//判断
if (startIndex == -1){
return;
}
int countVertexs = vertexs.size();
boolean[] isDetermined = new boolean[countVertexs];
//初始化
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
Arrays.fill(pPath, -1);
dist[startIndex] = 0;
pPath[startIndex] = startIndex;
//每次确定一个顶点的最短路径,共执行V次
for (int i = 0; i < countVertexs; i++) {
//手动寻找当前未确定的、距离起点最近的顶点
int minPath = INF;
int u = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < countVertexs; j++) {
if (!isDetermined[j] && dist[j] < minPath) {
minPath = dist[j];
u = j;
}
}
//如果找不到可达点,提前结束
if (u == -1){
break;
}
//标记该顶点已确定
isDetermined[u] = true;
//只遍历u的邻居
Node node = edgeList.get(u);
while (node != null) {
int v = node.dest;
int weight = node.value;
//如果经过u到达v的路径比当前记录的更短
if (!isDetermined[v] && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pPath[v] = u;
}
node = node.next;
}
}
}
//打印最短路径
public void printShortPath(char startCh, int[] dist, int[] pPath) {
//获取起点的下标
int startIndex = getVertex(startCh);
if (startIndex == -1){
return;
}
System.out.println("====== 从 " + startCh + " 出发的最短路径探测 ======");
//遍历所有顶点,打印到每一个顶点的路径
for (int i = 0; i < vertexs.size(); i++) {
//自己到自己不需要打印
if (i == startIndex){
continue;
}
//如果距离还是无穷大,说明根本走不通
if (dist[i] == INF) {
System.out.println("目标 [" + getVertexChar(i) + "] : 无法到达");
continue;
}
//利用 pPath 数组往回找
//我们用一个 List 来暂时存放这个"倒序"的路径
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int current = i;
//只要没回到起点,就一直往上找
//pPath[startIndex] 是自己,所以到起点就会停止
while (current != startIndex && current != -1) {
path.add(current);
current = pPath[current];
}
// 最后把起点加进去
path.add(startIndex);
Collections.reverse(path);
System.out.print("路径: ");
for (int j = 0; j < path.size(); j++) {
char vertexName = getVertexChar(path.get(j));
//优化打印
System.out.print(vertexName + (j == path.size() - 1 ? "" : " -> "));
}
System.out.println(" | 总权值: " + dist[i]);
}
}
//求最短路径->bellmanFord算法:起点字符,距离数组,路径数组,适合负权图
public boolean bellmanFord(char startCh, int[] dist, int[] pPath) {
int srcIndex = getVertex(startCh);
if (srcIndex == -1){
return false;
}
int count = vertexs.size();
//初始化
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
Arrays.fill(pPath, -1);
dist[srcIndex] = 0;
//核心逻辑:进行count轮松弛
//虽然理论上coun -1轮就能找到最短路,但第count轮可以用来检测负权回路
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
boolean hasChange = false;//本轮是否有更新
//遍历全图所有的边
for (int u = 0; u < count; u++) {
Node node = edgeList.get(u);
while (node != null) {
int v = node.dest;
int weight = node.value;
//如果起点到u的距离不是无限大,且经过u到v更近
if (dist[u] != INF && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
//如果是第count轮还能更新,说明存在负权回路
if (i == count - 1) {
return false;
}
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
pPath[v] = u;
hasChange = true;
}
node = node.next;//摸向u的下一条边
}
}
//如果某一轮没有任何边被松弛,说明已经提前达到最优态,可以直接跳出
if (!hasChange){
break;
}
}
return true;
}
//求多源最短路->Floyd-Warshall
public void floydWarShall(int[][] dist, int[][] pPath) {
int n = vertexs.size();
//初始化矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], INF);
Arrays.fill(pPath[i], -1);
dist[i][i] = 0;//自己到自己距离为 0
}
//数据迁移:从邻接表精准提取存在的边
//这一步比邻接矩阵版快,因为不需要去判断那些INF的格子
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Node node = edgeList.get(i);
while (node != null) {
int j = node.dest;
dist[i][j] = node.value;
pPath[i][j] = i;//i->j的前驱是i
node = node.next;
}
}
//状态转移方程:dist[i][j] = min(dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j])
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//如果经过中转点k能够缩短距离
if (dist[i][k] != INF && dist[k][j] != INF &&
dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] < dist[i][j]) {
//到了这里就说明绕路更近
dist[i][j] = dist[i][k] + dist[k][j];
//注意:我们要找的是"到达j之前的最后一个点"
//既然最后一段是从k走到j的(或者经过k中转后到达j的)
//那么到达j的前驱点,就应该等于从k走到j的路径中j的前驱点
//因为你想想,你从i->j的到达j前一个顶点下标,不就是k->j到达j的前一个顶点下标吗
//因为我们经过了k,假设i->a->b->k->c->d->j,此时从i->j的j前一个顶点是d
//同时从k->j的j前一个顶点也是d,一个意思
pPath[i][j] = pPath[k][j];
}
}
}
}
}
//配合Floyd算法的打印辅助方法
public static void testPrintPath(GraphByNode g, char start, char dest, int[][] dist, int[][] pPath) {
int i = g.getVertex(start);
int j = g.getVertex(dest);
if (i == -1 || j == -1 || dist[i][j] == 0X3f3f3f3f) {
System.out.println(start + " 到 " + dest + " : 不通或不存在");
return;
}
List<Character> path = new ArrayList<>();
int curr = j;
// 使用 pPath 矩阵进行回溯
while (curr != -1) {
// 调用你类里定义的通过下标取字符的方法
path.add(g.getVertexChar(curr));
if (curr == i) break;
curr = pPath[i][curr]; // 核心:跳向路径中的前一个点
}
Collections.reverse(path); // 翻转,得到 A -> C -> B 的顺序
System.out.print("从 " + start + " 到 " + dest + " 的最短路径: ");
for (int k = 0; k < path.size(); k++) {
System.out.print(path.get(k) + (k == path.size() - 1 ? "" : " -> "));
}
System.out.println(" | 总权值: " + dist[i][j]);
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
// 场景 1:无向图 - 宿舍社交圈
System.out.println("====== 场景 1: 无向图 (宿舍好友) ======");
GraphByNode dormGraph = new GraphByNode(4, false);
dormGraph.initVertexs(new char[]{'张', '王', '李', '赵'});
dormGraph.add('张', '王', 1);
dormGraph.add('张', '李', 1);
dormGraph.add('王', '赵', 1);
dormGraph.print();
System.out.println("张的度数: " + dormGraph.getValue('张')); // 应为 2
System.out.println("赵的度数: " + dormGraph.getValue('赵')); // 应为 1
System.out.println("\n====== 场景 2: 有向图 (城市单行道) ======");
GraphByNode cityGraph = new GraphByNode(3, true);
cityGraph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C'});
// A -> B (5km), B -> C (10km), A -> C (15km)
cityGraph.add('A', 'B', 5);
cityGraph.add('B', 'C', 10);
cityGraph.add('A', 'C', 15);
System.out.println("======广度和深度测试=====");
// B 的度数 = 出度(B->C) + 入度(A->B) = 2
System.out.println("B 的总度数: " + cityGraph.getValue('B'));
System.out.println();
// 构造一个稍微复杂的图测试搜索
System.out.println("====== 场景 3: 复杂图搜索测试 ======");
GraphByNode graph = new GraphByNode(5, false);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
// 构建:A-B, A-C, B-D, C-D, D-E
graph.add('A', 'B', 1);
graph.add('A', 'C', 1);
graph.add('B', 'D', 1);
graph.add('C', 'D', 1);
graph.add('D', 'E', 1);
graph.print();
System.out.println("\n--- DFS 深度优先 (从 A 开始) ---");
// 预期路径:钻到底 A -> C -> D -> E -> B (顺序取决于链表头插结果)
graph.dfs('A');
System.out.println("\n--- BFS 广度优先 (从 A 开始) ---");
// 预期路径:层层扩散 A -> [C, B] -> D -> E
graph.bfs('A');
}
//测试最小生成树的两个算法
public static void main2(String[] args) throws Exception {
GraphByNode graph = new GraphByNode(5, false);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
// 构建一个带权图
graph.add('A', 'B', 2);
graph.add('A', 'C', 4);
graph.add('B', 'C', 1);
graph.add('B', 'D', 7);
graph.add('C', 'D', 3);
graph.add('C', 'E', 5);
graph.add('D', 'E', 1);
System.out.println("====== Kruskal 挑战 ======");
GraphByNode kMST = new GraphByNode(5, false);
kMST.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
System.out.println("总权值: " + graph.kruskal(kMST));
System.out.println("\n====== Prim 挑战 ======");
GraphByNode pMST = new GraphByNode(5, false);
pMST.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
System.out.println("总权值: " + graph.prim(pMST, 'A'));
}
//最短路径dijkstra测试
//这个算法不能用于负权值的图
public static void main3(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 5 个顶点的有向图
GraphByNode graph = new GraphByNode(5, true);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'});
// A -> B(10), A -> C(5)
graph.add('A', 'B', 10);
graph.add('A', 'C', 5);
// B -> D(1)
graph.add('B', 'D', 1);
// C -> B(3), C -> D(9), C -> E(2)
graph.add('C', 'B', 3);
graph.add('C', 'D', 9);
graph.add('C', 'E', 2);
// D -> E(4)
graph.add('D', 'E', 4);
// E -> D(6)
graph.add('E', 'D', 6);
int n = 5;
int[] dist = new int[n];
int[] pPath = new int[n];
graph.dijkstra('A', dist, pPath);
graph.printShortPath('A', dist, pPath);
}
//最短路径bellmanFord算法测试
//这个算法能用于负权值的图,还可以判断负权回路
//负权回路会使你的路径值也就是dist值越来越小,无限循环
public static void main4(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 构造 3 个点:A, B, C
GraphByNode graph = new GraphByNode(3, true);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C'});
// A -> B (1), B -> C (1), C -> A (-5) ==> 形成总权值为 -3 的回路
graph.add('A', 'B', 1);
graph.add('B', 'C', 1);
graph.add('C', 'A', -5);
int[] dist = new int[3];
int[] pPath = new int[3];
boolean result = graph.bellmanFord('A', dist, pPath);
if (!result) {
System.out.println("警告:检测到负权回路,最短路径无意义!");
} else {
graph.printShortPath('A', dist, pPath);
}
}
//测试多源最短路径
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 构造一个 4 个顶点的有向图 (邻接表版)
GraphByNode graph = new GraphByNode(4, true);
graph.initVertexs(new char[]{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D'});
/*
* 测试数据:包含负权边 C -> B (-4)
* A -> B (5), A -> C (2)
* B -> D (2)
* C -> B (-4)
* C -> D (6)
*/
graph.add('A', 'B', 5);
graph.add('A', 'C', 2);
graph.add('B', 'D', 2);
graph.add('C', 'B', -4);
graph.add('C', 'D', 6);
System.out.println("====== 邻接表结构展示 ======");
graph.print();
// 2. 准备计算结果的容器
int n = 4;
int[][] dist = new int[n][n];
int[][] pPath = new int[n][n];
// 3. 执行 Floyd 算法
graph.floydWarShall(dist, pPath);
// 4. 打印计算出的距离矩阵
System.out.println("\n--- Floyd 执行后的最短距离矩阵 ---");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int value = dist[i][j];
if (value == 0X3f3f3f3f) {
System.out.printf("%4s", "∞");
} else {
System.out.printf("%4d", value);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 5. 路径溯源验证
System.out.println("\n--- 关键路径深度验证 ---");
// 验证 A -> B: 预期 A -> C -> B (权值 -2)
testPrintPath(graph, 'A', 'B', dist, pPath);
// 验证 A -> D: 预期 A -> C -> B -> D (权值 0)
testPrintPath(graph, 'A', 'D', dist, pPath);
// 验证 C -> D: 预期 C -> B -> D (权值 -2)
testPrintPath(graph, 'C', 'D', dist, pPath);
}
}END