目录
之前做项目过程中,需要通过PAL制接口实现图像显示。今天刚好有时间,将实现过程记录一下。
1.PAL制概述
场正程:是指场扫描周期中电子束由上到下的扫描。
场逆程:是指场扫描周期中电子束由下面返回到初始位置。且场正程时间远大于场逆程时间,两者相加为场周期,场周期的倒数是场频。
美国制定电视机标准如下:
1)每一划面525条水平扫描线;
2)每秒30张(Frame);
3)采用交错式扫描(Interlace,"交错式"),每秒60个图场(Field)。
由于制定该标准的是"美国电子工业协会",英文是"Electronics Industry Association"简写就是"EIA",因此黑白电视的美规就叫"EIA"。后来发明了彩色电视,这时候是由"国家电视系统委员会"来制定标准的,英文是"National Television System Committee"简称为"NTSC",因此NTSC是彩色系统中的美规。NTSC制式是1952年美国国家电视标准委员会定义的彩色电视广播标准,称为正交平衡调幅制。525/行帧,30帧/秒(29.97fps,33.37ms/frame);高宽比,电视画面的长宽比(电视为4:3;电影为3:2;高清晰度电视为16:9);隔行扫描,一帧分成2场(field),262.5线/场在每场的开始部分保留20扫描线作为控制信息,因此只有485条线的可视数据;每行63.5μs,水平回扫时间10μs(包含5μs的水平同步脉冲),所以显示时间是53.5μs;颜色模型:YIQ。一帧图像的总行数为525行,分两场扫描。行扫描频率为15750Hz,周期为63.5μs;场扫描频率是60Hz,周期为16.67ms;帧频是30Hz,周期33.33ms。每一场的扫描行数为525/2=262.5行。除了两场的场回扫外,实际传送图像的行数为480行。
欧洲电视标准规格如下:
1)每一划面625条水平扫描线;
2)每秒25张(Frame);
3)采用交错式扫描(Interlace,"交错式"),每秒50个图场(Field)。
制定该标准的是"Committee Consultation International Radio Telecommunique"国际无线通讯咨询委员会,简称"CCIR"。因此CCIR就是欧规的黑白系统。进入彩色时代,由于彩电的原理是在原有黑白讯号上加上彩色系色波(Color Carrier),每条扫描线有一个系色波,用改变相位的方式得到每条线的颜色,在英文上的说法是"Phase Alternate(交替) Line"简写就是PAL,因此PAL就是欧规的彩色系统。由于NTSC制存在相位敏感造成彩色失真的缺点,因此德国于1962年制定了PAL(Phase-Alternative Line)制彩色电视广播标准,称为逐行倒相正交平衡调幅制。625行(扫描线)/帧,25帧/秒(40ms/帧);长宽比(aspectratio):4:3;隔行扫描,2场/帧,312.5行/场;颜色模型:YUV。PAL制式中根据不同的参数细节,又可以进一步划分为G、I、D等制式,其中PAL-D制是中国大陆采用的制式。
一般来讲,EIA代表美规黑白,NTSC代表美规彩色;CCIR代表欧规黑白,PAL代表欧规彩色。但现在大家都把NTSC当做"N制"或美规的意思,所以黑白说NTSC也没啥不对。同样的PAL是"P制"或欧规的意思,把黑白说成PAL也行。其实两种标准中的30、60、25、50都跟交流电有关,当时美国电源频率是60Hz,而欧洲是50Hz。
2.PAL和NTSC的区别
常见的电视信号制式是PAL和NTSC,另外还有SECAM等。NTSC即正交平衡调幅制,PAL为逐行倒像正交平衡调幅制。
(1)PAL电视标准
PAL电视标准,每秒25帧,电视扫描线为625线,奇场在前,偶场在后,标准的数字化PAL电视标准分辨率为720×576,24比特的色彩位深,画面的宽高比为4:3,PAL电视标准用于中国、欧洲等国家和地区。
(2)NTSC电视标准
NTSC电视标准,每秒29.97帧(简化为30帧),电视扫描线为525线,偶场在前,奇场在后,标准的数字化NTSC电视标准分辨率为720×486,24比特的色彩位深,画面的宽高比为4:3。NTSC电视标准用于美、日等国家和地区。

3.ITU-RBT.601和ITU-RBT.656的区别
关于这两种信号的区别:
ITU-RBT.601:16位数据传输,21芯;Y、U、V信号并行传输,并有场频和行频传输线。最后更新的文档代号为:ITU-RBT.601-5。
ITU-RBT.656:8位数据传输,9芯;串行视频传输,不需要同步信号;传输速率是601的2倍。最后更新的文档代号为:ITU-RBT.656-4。
656输出的是串行数据,行场同步信号嵌入在数据流中,601是并行数据,行场同步有单独输出。
656只是数据传输接口而已,可以说是作为601的一个传输方式。简单的说ITU-RBT.601是"演播室数字电视编码参数"标准,而ITU-RBT.656则是ITU-RBT.601附件A中的数字接口标准,用于主要数字视频设备(包括芯片)之间采用27MHz/s并口或243Mb/s串行接口的数字传输接口标准。
4.PAL制与NTSC制的判定


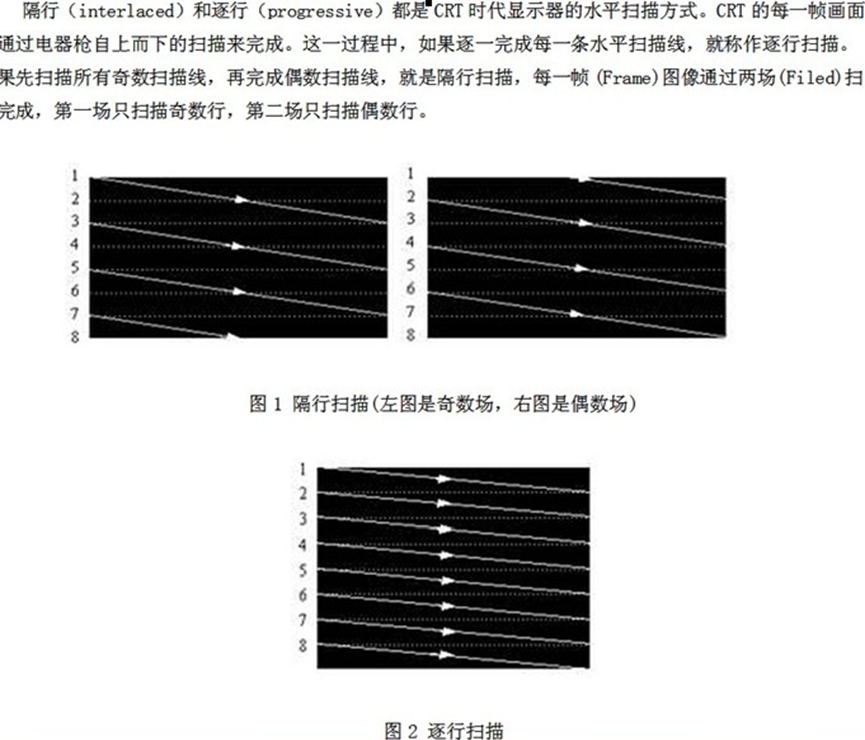
5.隔行扫描成像(场)
在了解中国电视的相关标准之前,先必需彻底的了解Field(场)概念。场是由电视接收图像信号成像的方式决定的。目前,世界各国的电视都是采用了隔行扫描成像的方式,这和我们使用的电脑显示器成像(逐行扫描)是不一样的。
逐行扫描:每一帧图像都是由一排排的像素构成的,电脑显示器就是从最左侧的第一个像素扫描并显示,扫描完成第一行之后,就会扫描第二行,直到扫描完整个屏幕。如果用电脑全屏播放视频的话,每秒钟显示器能扫描25帧。
隔行扫描:将一个完整的画面分割成两个场,分为上场和下场。先扫描完上场的内容,再扫描下场的内容。两个场都扫描完成后,合成一张完整的画面。这样做的好处是电视内容通过卫星、有线等进行传输的时候,每次发送的内容少了一半,这极大的提高了传输效率。由于每次发送的内容只有一半,因此25fps每秒的图像,需要不断的发送50次才能显示完整的1s内容。这就是我们熟知的电视刷新率为50Hz,说的就是每秒钟能扫描50场的意思。国外使用NTSC制的电视,刷新率为60Hz,代表每秒钟扫描60场。
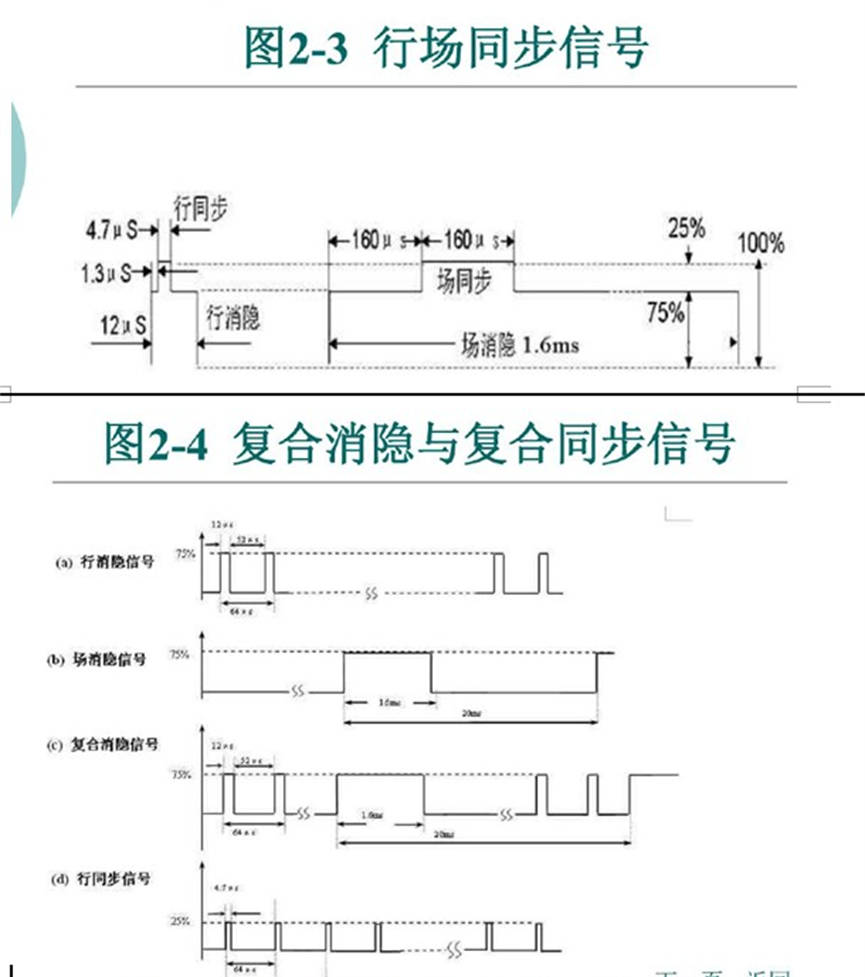
6.场同步和行同步
场同步(Vertical Sync):指定新图像从什么时候开始显示。
行同步(Horizontal Sync):指定新扫描线什么时候开始显示。
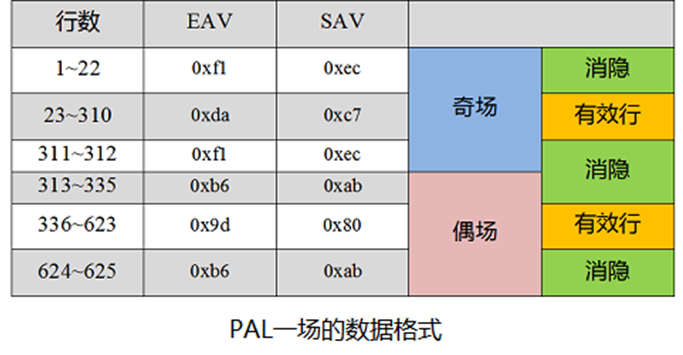
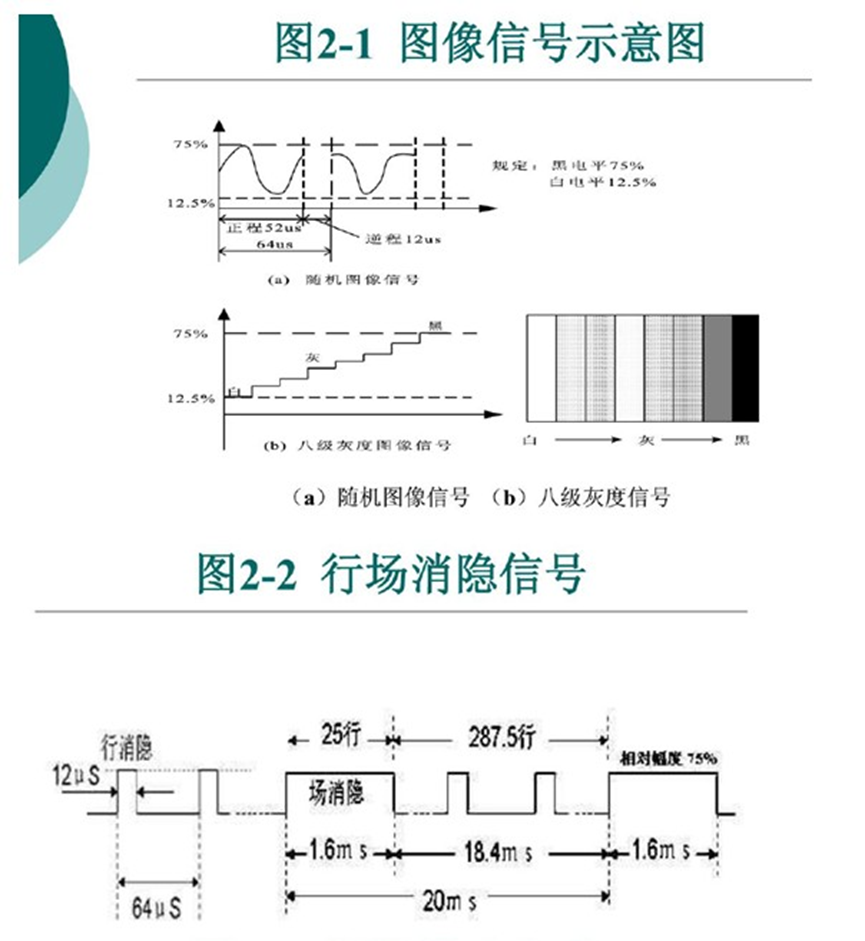
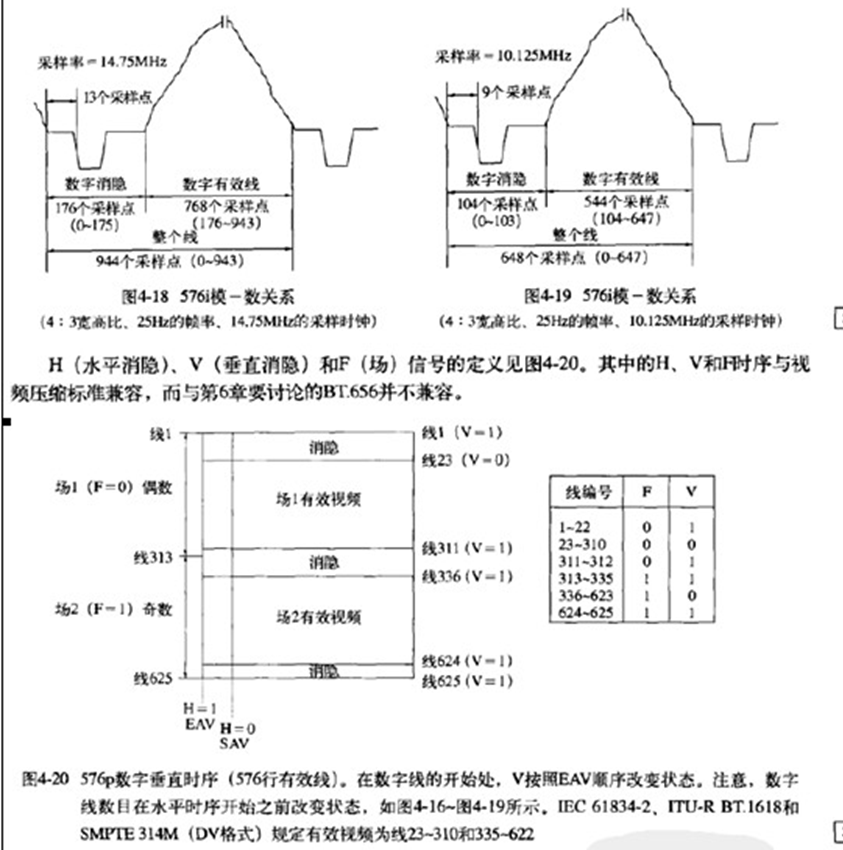
7.PAL制国标参数
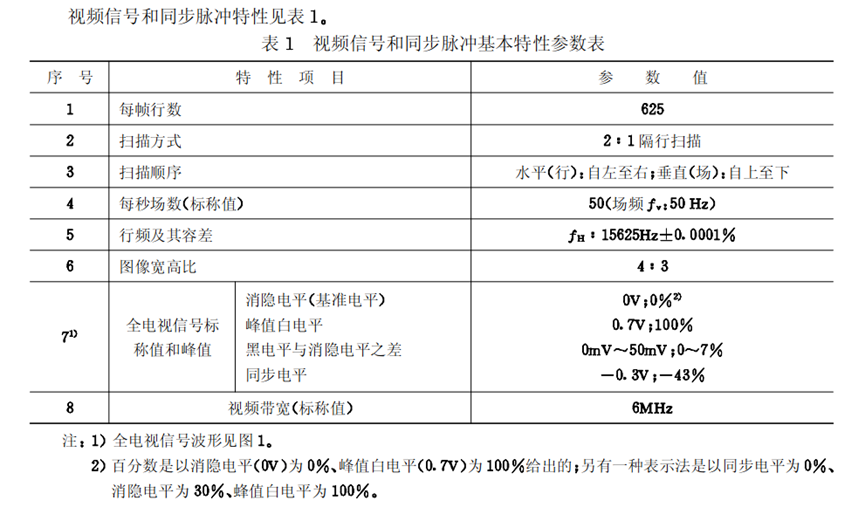
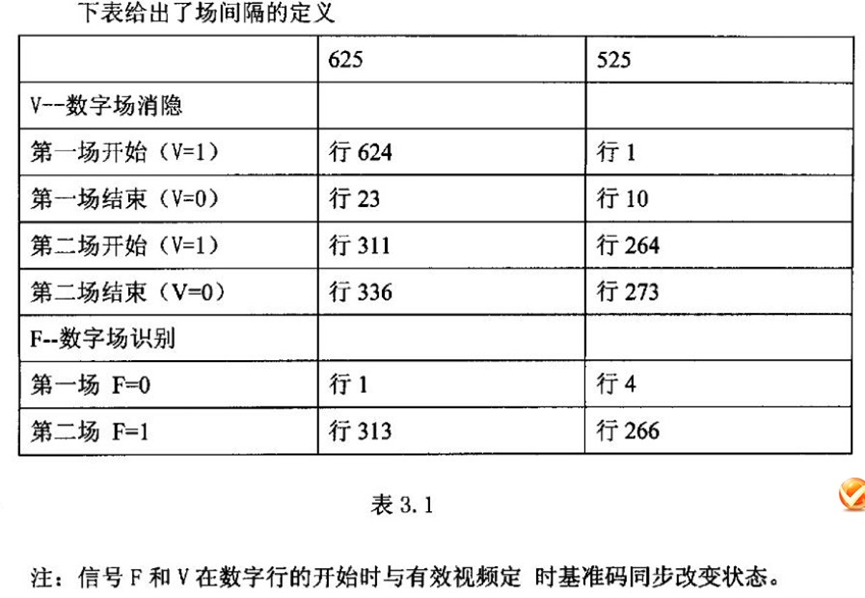
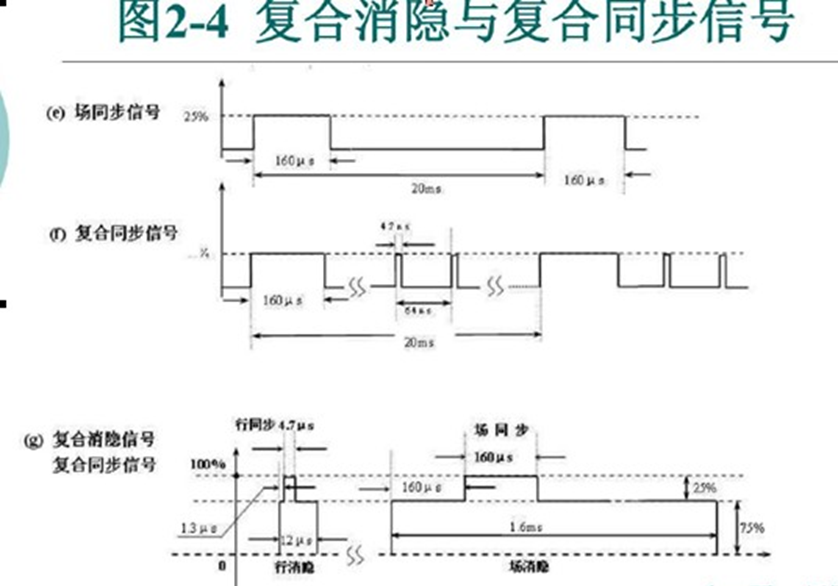
行场信号的具体长度时间参数:
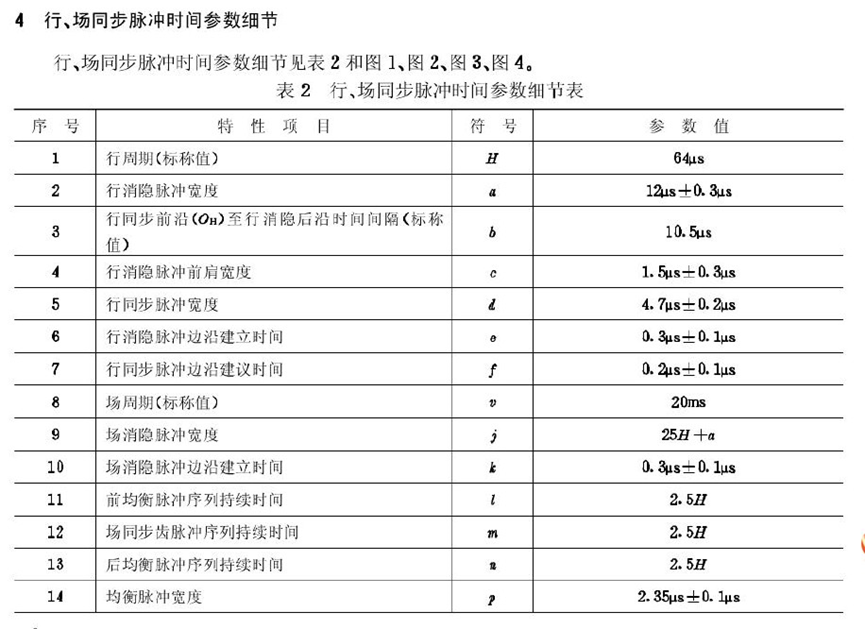
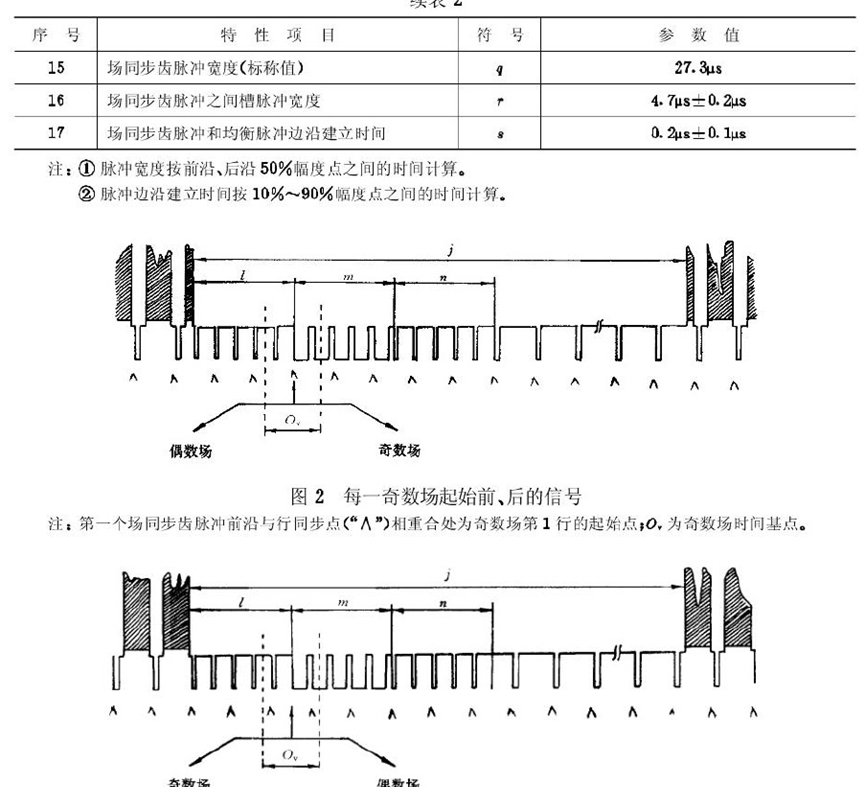
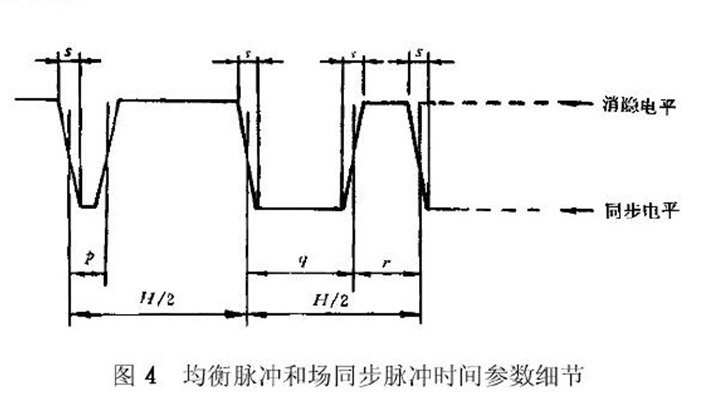
完整的PAL制视频信号波形:
8.PAL制行信号采样点计数


9.信号行场同步头以及消隐信号的具体时间参数
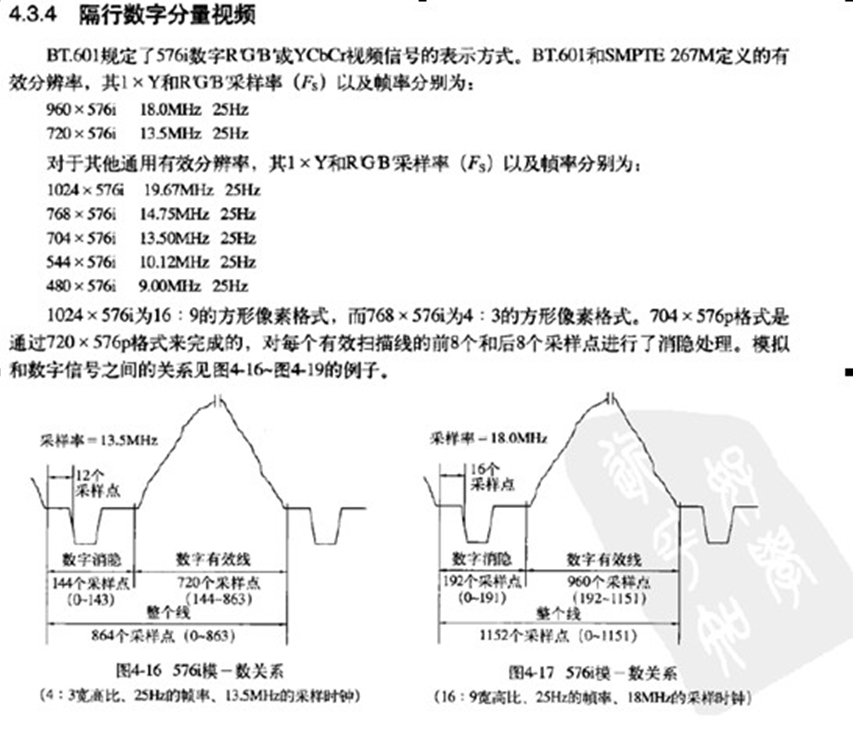
10.隔行数字分量视频
11.基于FPGA实现PAL制接口代码
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Company:
-- Engineer:
--
-- Create Date: 2021/10/08 19:57:38
-- Design Name:
-- Module Name: pal_sync_blank - Behavioral
-- Project Name:
-- Target Devices:
-- Tool Versions:
-- Description:
--
-- Dependencies:
--
-- Revision:
-- Revision 0.01 - File Created
-- Additional Comments:
--
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_ARITH.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if using
-- arithmetic functions with Signed or Unsigned values
--use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
-- Uncomment the following library declaration if instantiating
-- any Xilinx primitives in this code.
--library UNISIM;
--use UNISIM.VComponents.all;
entity pal_sync_blank is
generic(
LINE_NUM : integer := 944 --944
);
port(
clk : in std_logic; --14.75MHz
rst : in std_logic;
sync : out std_logic;
blank : out std_logic;
odd_even : out std_logic;
rd_rom_en : buffer std_logic
);
end pal_sync_blank;
architecture Behavioral of pal_sync_blank is
constant LINE_NUM_HALF : integer := 433; --432
constant Time_1p5us : integer := 20;
constant Time_2p35us : integer := 32;
constant Time_4p7us : integer := 63;
constant Time_5p8us : integer := 78;
signal cnt_h : std_logic_vector(9 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal cnt_v : std_logic_vector(9 downto 0) := (others => '0');
signal blank_nx_1 : std_logic := '0';
signal blank_nx_2 : std_logic := '0';
signal vsync_nx : std_logic := '0';
signal drow_en : std_logic := '0';
begin
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
cnt_h <= (others => '0');
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if cnt_h = LINE_NUM - 1 then --行周期64us
cnt_h <= (others => '0');
else
cnt_h <= cnt_h + 1;
end if;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
cnt_v <= (others => '0');
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if cnt_h = LINE_NUM - 1 then
if cnt_v = 624 then
cnt_v <= (others => '0');
else
cnt_v <= cnt_v + 1;
end if;
end if;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
blank_nx_1 <= '0'; --同步
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
case conv_integer(cnt_v) is
when 0 | 1 | 313 | 314 => --垂直同步脉冲
if cnt_h < (LINE_NUM_HALF - Time_4p7us) or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM - Time_4p7us)) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when 2 => --垂直同步脉冲到后均衡脉冲切换
if cnt_h < (LINE_NUM_HALF - Time_4p7us) or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM_HALF + Time_2p35us)) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when 312 => --预均衡脉冲到垂直同步脉冲切换
if cnt_h < Time_2p35us or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM - Time_4p7us)) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when 317 => --后均衡脉冲到行同步切换
if cnt_h < Time_2p35us then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when 622 => --行同步到预均衡脉冲切换
-- if cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM - 768 - Time_1p5us) or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM_HALF + Time_2p35us)) then
if cnt_h < Time_4p7us or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM_HALF + Time_2p35us)) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when 3 | 4 | 310 | 311 | 315 | 316 | 623 | 624 => --预均衡和后均衡脉冲
if cnt_h < Time_2p35us or (cnt_h > LINE_NUM_HALF and cnt_h <= (LINE_NUM_HALF + Time_2p35us)) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
when others => --行同步
if cnt_h < Time_4p7us then --(LINE_NUM - 768 - Time_1p5us - Time_5p8us) then
blank_nx_1 <= '0';
else
blank_nx_1 <= '1';
end if;
end case;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
blank_nx_2 <= '0'; --消隐
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
case conv_integer(cnt_v) is
when 22 =>
if cnt_h >= (LINE_NUM - 384 - Time_1p5us) and cnt_h < (LINE_NUM - Time_1p5us) then
blank_nx_2 <= '1';
else
blank_nx_2 <= '0';
end if;
when 622 =>
if cnt_h >= (LINE_NUM - 768 - Time_1p5us) and cnt_h < (LINE_NUM_HALF - Time_1p5us) then
blank_nx_2 <= '1';
else
blank_nx_2 <= '0';
end if;
when others =>
if cnt_h >= (LINE_NUM - 768 - Time_1p5us) and cnt_h < (LINE_NUM - Time_1p5us) then
-- if cnt_h >= (Time_4p7us + Time_1p5us) and cnt_h < (Time_4p7us + Time_1p5us + 768) then
blank_nx_2 <= '1';
else
blank_nx_2 <= '0';
end if;
end case;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
vsync_nx <= '0';
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if (cnt_v > 21 and cnt_v < 310) or (cnt_v > 334 and cnt_v < 623) then
vsync_nx <= '1';
else
vsync_nx <= '0';
end if;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
sync <= '1';
blank <= '1';
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
sync <= blank_nx_1;
blank <= blank_nx_2 and vsync_nx;
end if;
end process;
-- process(rst,clk)
-- begin
-- if rst = '1' then
-- drow_en <= '0';
-- elsif rising_edge (clk) then
-- case conv_integer(cnt_v) is
-- when 40 =>
-- drow_en <= '1';
-- when 296 =>
-- drow_en <= '0';
-- when 353 =>
-- drow_en <= '1';
-- when 609 =>
-- drow_en <= '0';
-- when others =>
-- drow_en <= drow_en;
-- end case;
-- end if;
-- end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
drow_en <= '0';
elsif rising_edge (clk) then
case conv_integer(cnt_v) is
when 41 =>
drow_en <= '1';
when 297 =>
drow_en <= '0';
when 353 =>
drow_en <= '1';
when 609 =>
drow_en <= '0';
when others =>
drow_en <= drow_en;
end case;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
rd_rom_en <= '0';
elsif rising_edge (clk) then
if drow_en = '1' then
case conv_integer(cnt_h) is
when 168 =>
rd_rom_en <= '1';
when 808 =>
rd_rom_en <= '0';
when others =>
rd_rom_en <= rd_rom_en;
end case;
else
rd_rom_en <= '0';
end if;
end if;
end process;
process(rst,clk)
begin
if rst = '1' then
odd_even <= '0';
elsif rising_edge(clk) then
if cnt_v < 312 then
odd_even <= '1';
elsif cnt_v = 312 then
if cnt_h <= LINE_NUM_HALF then
odd_even <= '1';
else
odd_even <= '0';
end if;
else
odd_even <= '0';
end if;
end if;
end process;
end Behavioral;