目录
[全排列 II](#全排列 II)
[N 皇后](#N 皇后)
[不同路径 III](#不同路径 III)
全排列

思路:
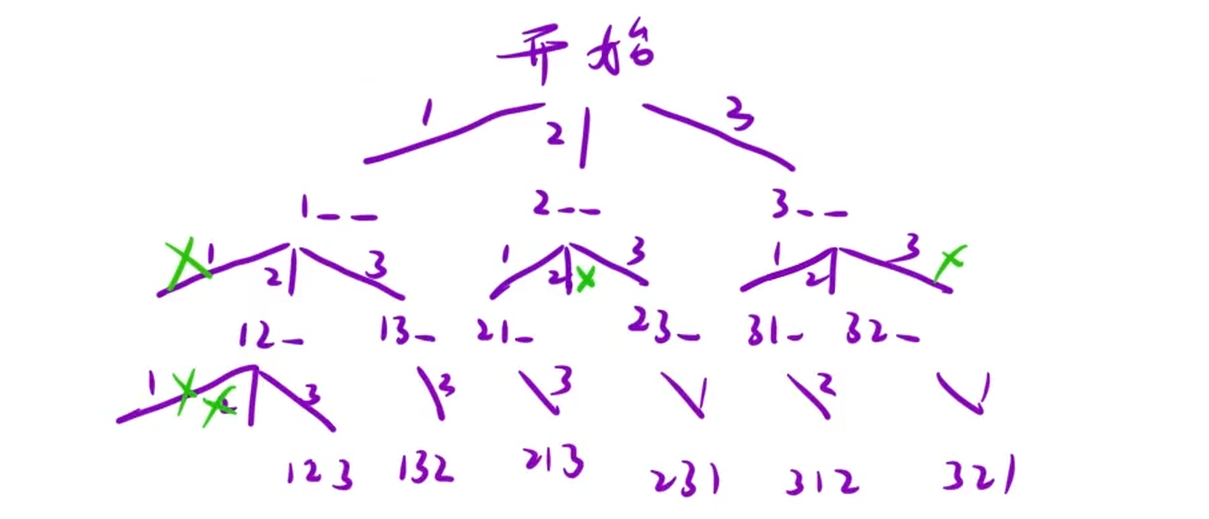
根据上图所画的决策树,我们只需要通过递归,前序遍历这颗决策树,然后把所有的路径都存起来,这些路径其实就是全排列。但是递归的过程中已经选过的数字就不能再选了,所以可以通过一个标记数组来解决这个问题,用它标记哪些数是被选过的,然后遍历数组选数字的时候,选过的数就不选了。另外还需要一个变量记录每条路径,当路径长度和数组元素个数相等,说明这条路径已经到底了(即这条路径结束了),将这个路径放入结果数组中即可。
**细节问题:**回溯的时候(即递归向上返回的时候)需要恢复现场,因为一旦回溯,说明当前这条路径遍历完成了,要开始遍历下一条路径了,那么当前存储路径的这个变量中,属于当前这条路径,但是不属于下一条路径的这些节点都要去除,并且随着这些节点从路径中去除,标记数组也要恢复,因为标记数组标记哪些节点被选了,但是现在这些节点因为回溯回到没有被选的状态,那么标记数组也要恢复。
**恢复有两种方式:**一种是返回上一层之前恢复,这种要找代码中哪里会返回,然后,返回前进行恢复现场;另一种是返回后恢复,这中要找当前代码中递归调用自己的地方,在这个地方下面进行恢复现场(下面代码是返回后恢复的现场)。
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
bool check[7];
public:
vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int>& nums)
{
dfs(nums);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums)
{
if(path.size() == nums.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if(check[i] == false)
{
path.push_back(nums[i]);
check[i] = true;
dfs(nums);
path.pop_back();
check[i] = false;
}
}
}
};子集
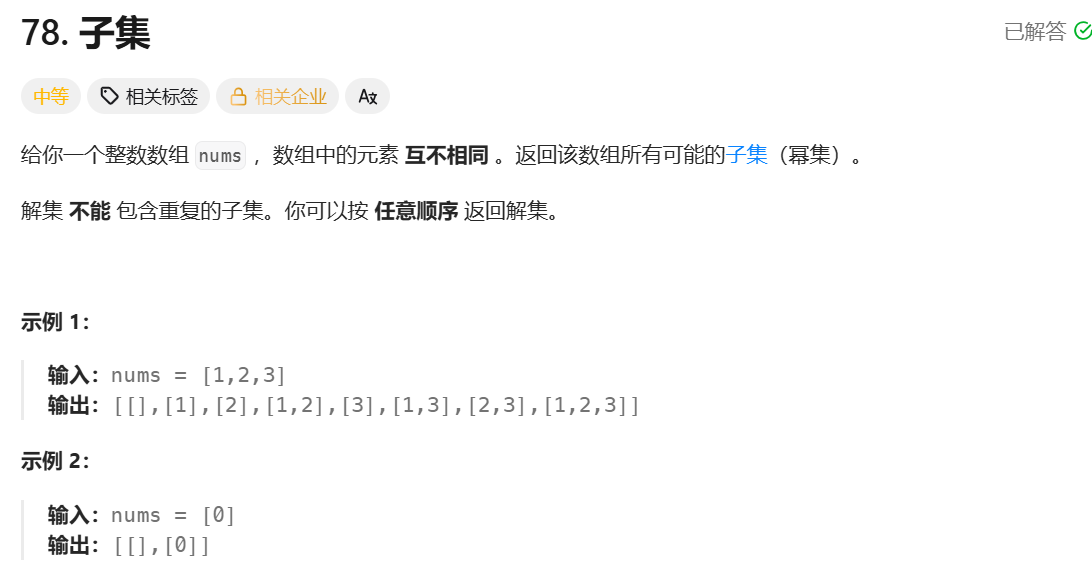
思路:
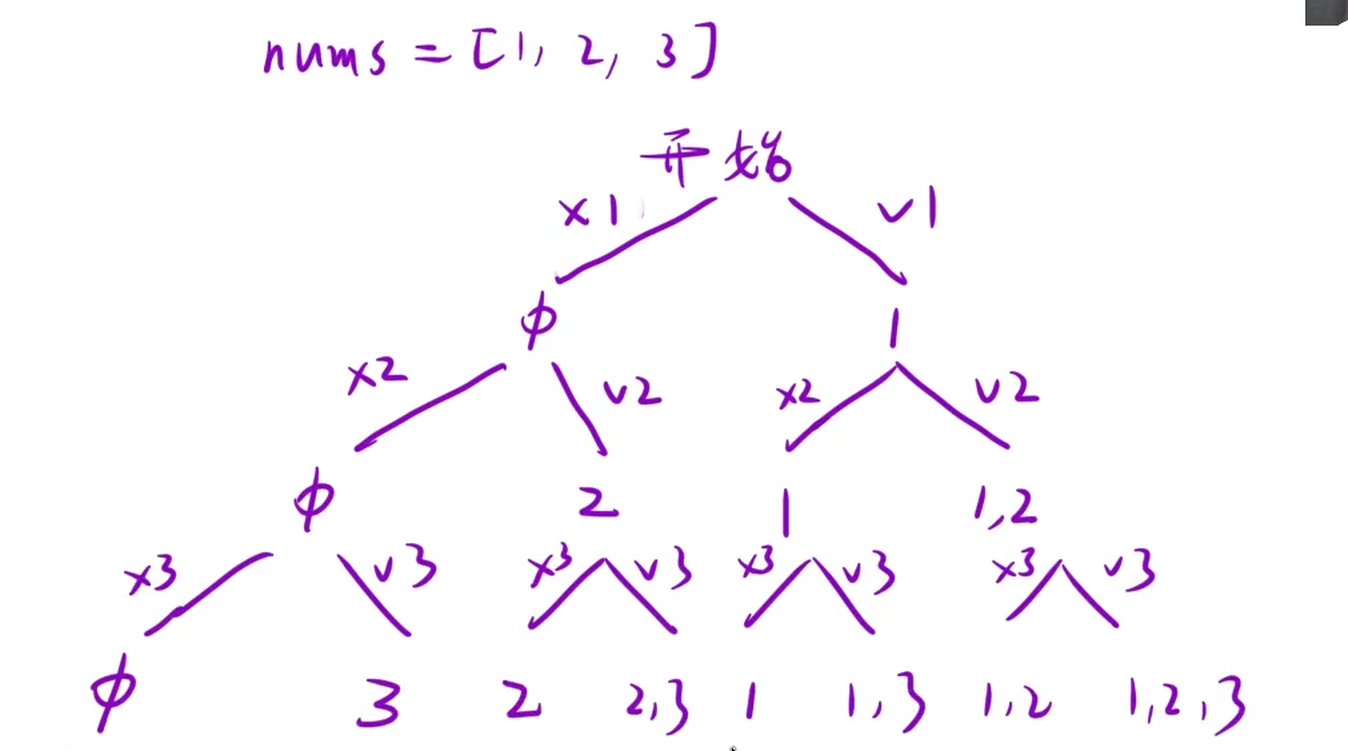
基于当前遍历到的值是选择还是不选择构建一颗决策树,前序遍历这颗数,每条路径就是一个子集,所以递归找到所有路径即可。
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums)
{
dfs(nums, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int pos)
{
if(pos == nums.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
//选择这个值
path.push_back(nums[pos]);
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
path.pop_back();
//不选这个值
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
}
};找出所有子集的异或总和再求和

思路:

基于当前遍历到的值是选择还是不选择构建一颗决策树,前序遍历这颗数,每条路径就是一个子集,定义一个 path 变量记录路径中所有值的异或结果,然后当一条路径遍历结束后将这个 path 加到总的结果中。
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
int sum = 0;
int path = 0;
public:
int subsetXORSum(vector<int>& nums) {
dfs(nums, 0);
return sum;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int pos){
if(pos == nums.size()){
sum += path;
return;
}
path ^= nums[pos]; //选择当前这个数
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
path ^= nums[pos]; //递归返回到这一层的时候恢复现场
dfs(nums, pos + 1); //不选择当前这个数
}
};全排列 II

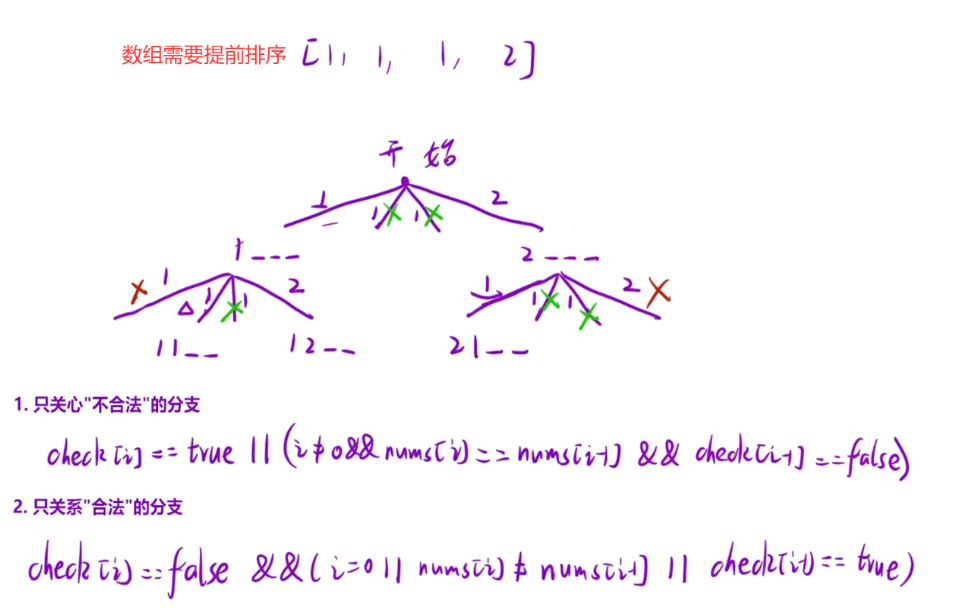
**思路:**剪枝思路如下图
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
bool check[8];
public:
vector<vector<int>> permuteUnique(vector<int>& nums)
{
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dfs(nums, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int pos)
{
if(pos == nums.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if(check[i] == false && (i == 0 || nums[i] != nums[i - 1] || check[i - 1] == true))
{
path.push_back(nums[i]);
check[i] = true;
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
check[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
}
};电话号码的字母组合
思路:
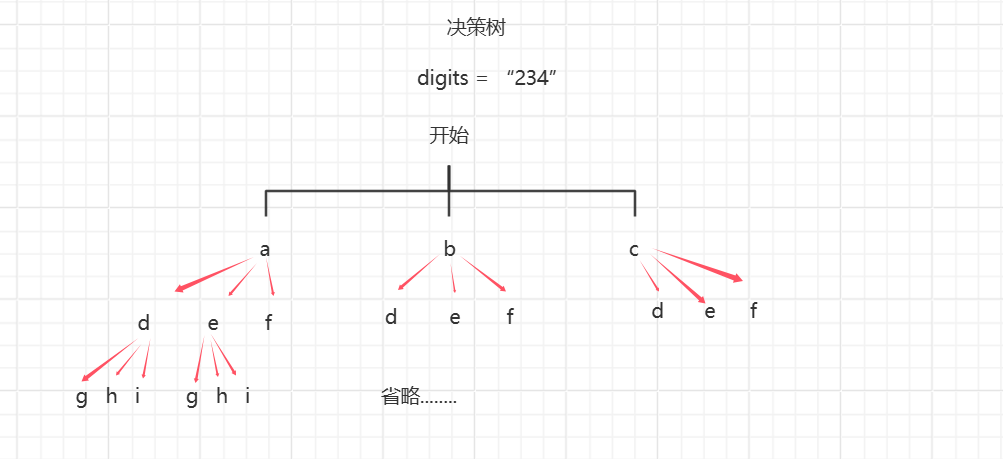
通过哈希将数字和字符串映射起来,然后结合上图决策树,递归遍历每条路径,所有路径合起来就是所有的字母组合。
**为什么不需要标记数组表示当前值有没有被选过:**全排列那道题需要标记数组表示当前值有没有被选过,选过就不能选了,那是因为那道题是针对一组元素进行排列,如下图:
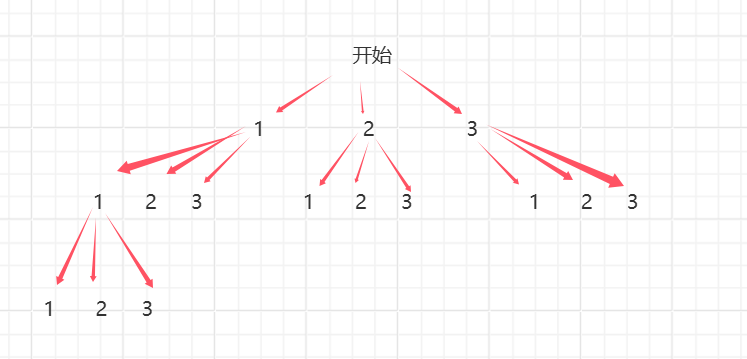
第二层的 1 和第一层是同一个数,第一轮已经选过了,所以不能选,需要标记数组标记一下,防止选重复。但是这道题每层的值和上一层的值都没有关系,都是一组新的元素,即使可能是重复的,比如 digits 是 "222" 的情况下,但是这是三组元素,它们各自独立,可以重复选,所以不需要这个标记数组。
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
vector<string> ret;
string path;
string hash[10] = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
if(digits.size() == 0)
return ret;
dfs(digits, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(string& digits, int n){
if(path.size() == digits.size()){
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(auto ch : hash[digits[n] - '0']){
path.push_back(ch);
dfs(digits, n + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};括号生成
思路:
有效的括号组合的条件:
- 左括号的数量 = 右括号的数量
- 从头开始的任意一个子串,左括号的数量 >= 右括号的数量
决策树:
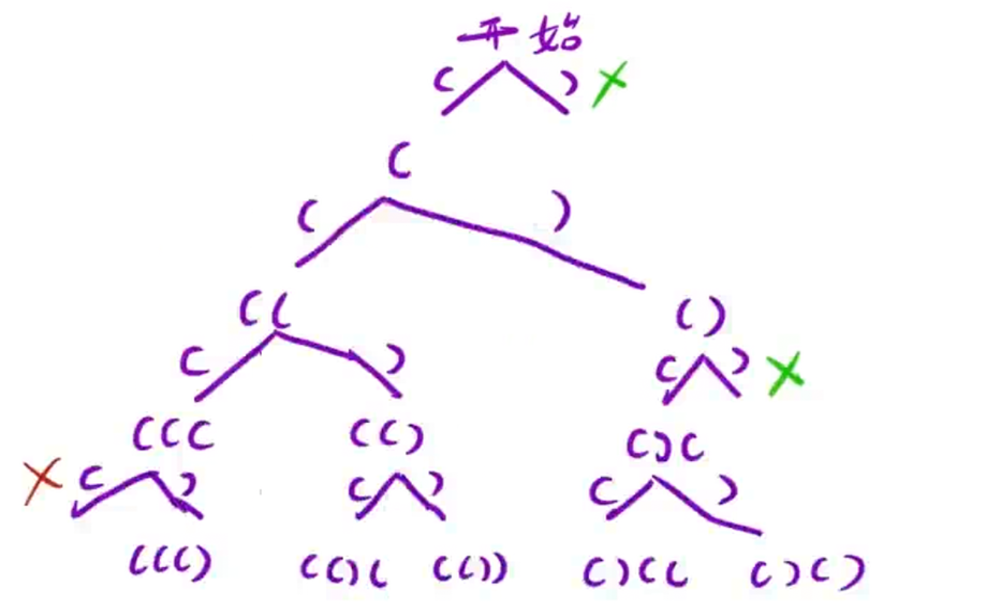
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
int left, right, _n;
string path;
vector<string> ret;
public:
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
left = right = 0;
_n = n;
dfs();
return ret;
}
void dfs(){
if(right == _n){
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
if(left < _n){
path.push_back('(');
left++;
dfs();
path.pop_back();
left--;
}
if(right < left){
path.push_back(')');
right++;
dfs();
path.pop_back();
right--;
}
}
};组合

思路:
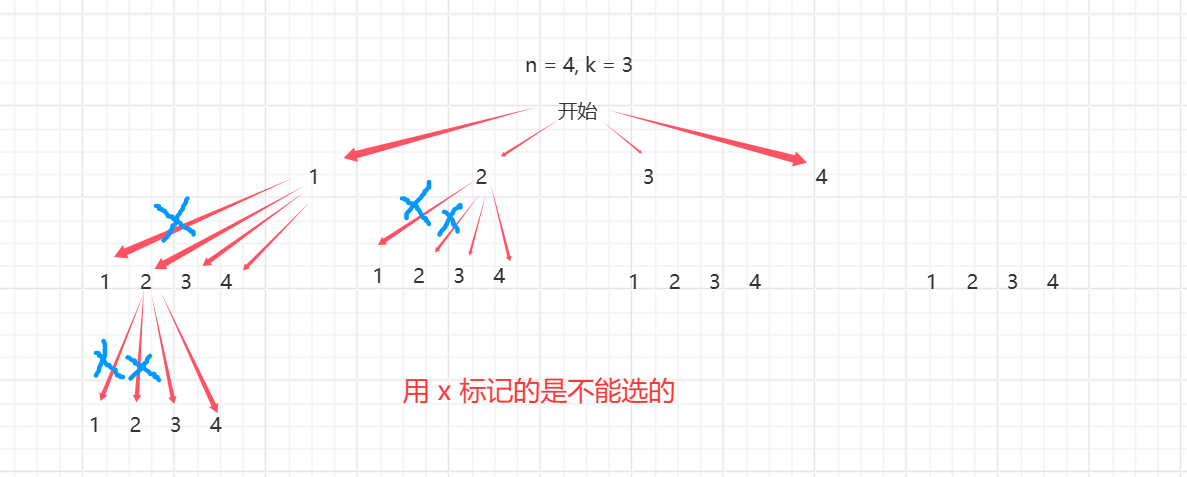
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
int _n, _k;
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
public:
vector<vector<int>> combine(int n, int k) {
_n = n;
_k = k;
dfs(1);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int num){
if(path.size() == _k){
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = num; i <= _n; i++){
path.push_back(i);
dfs(i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};目标和

**思路:**决策树如下
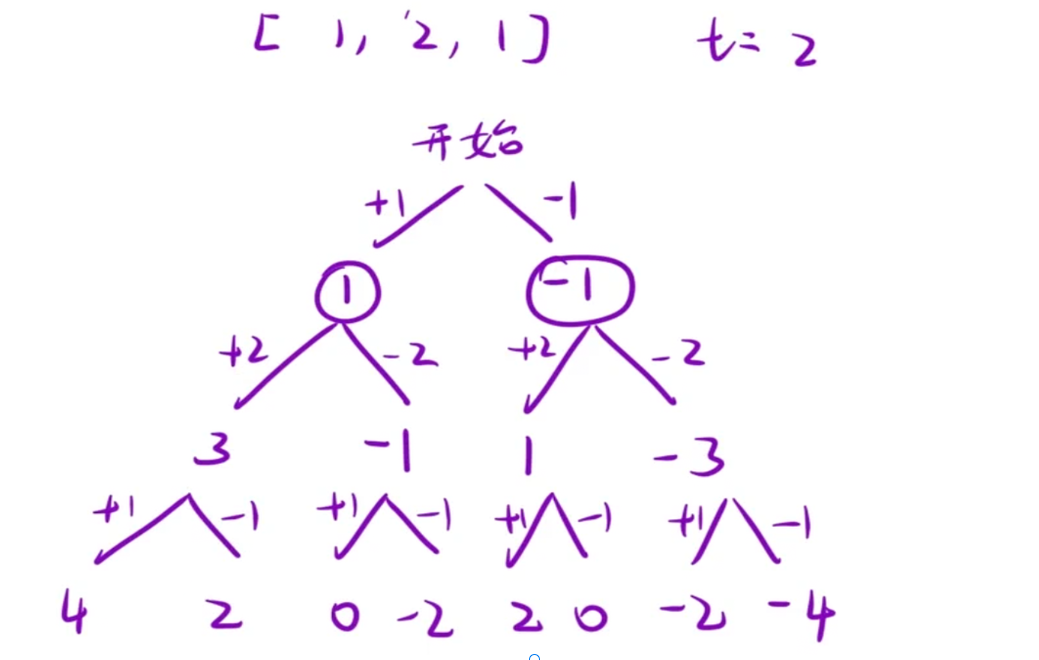
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
int ret, aim;
public:
int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target)
{
aim = target;
dfs(nums, 0, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& nums, int pos, int path)
{
if(pos == nums.size())
{
if(path == aim) ret++;
return;
}
dfs(nums, pos + 1, path + nums[pos]);
dfs(nums, pos + 1, path - nums[pos]);
}
};组合总和

**思路:**决策树如下
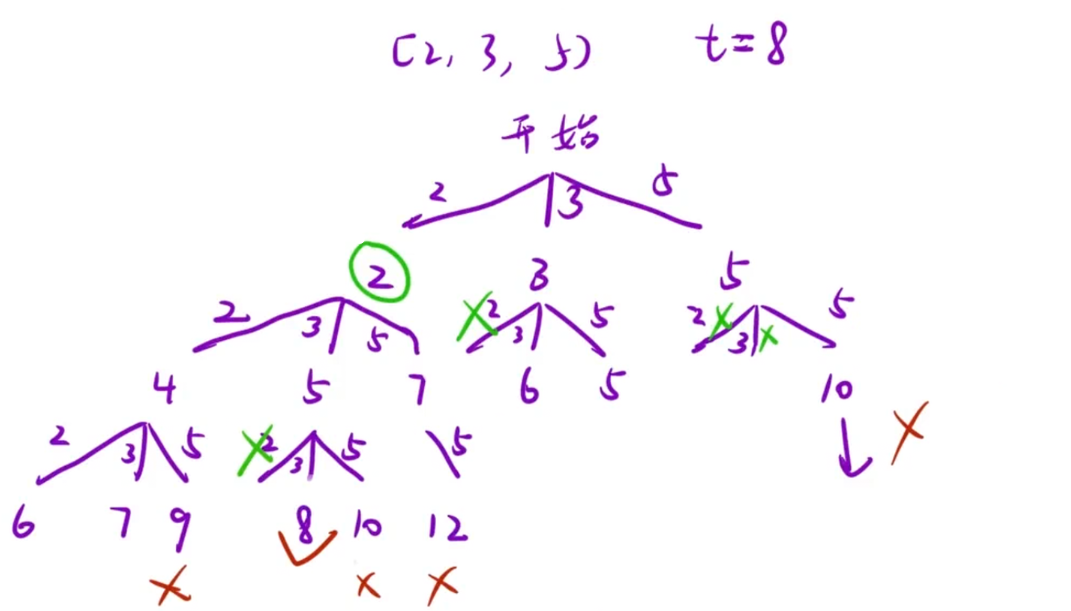
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
public:
vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int sum, int n){
if(sum >= target){
if(sum == target){
ret.push_back(path);
}
return;
}
for(int i = n; i < candidates.size(); i++){
path.push_back(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i);
path.pop_back();
}
}
};字母大小写全排列

思路:
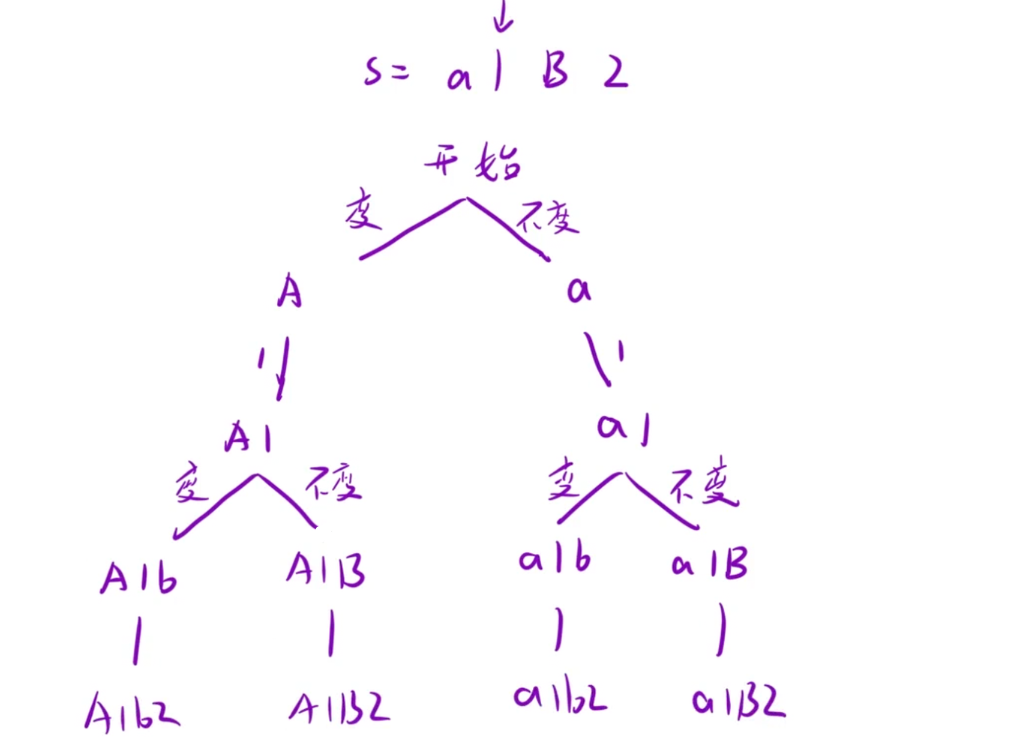
因为只有字母才涉及到变化,数字恒定不变,所以判断是否要变化的时候只需要判断字母即可。
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
vector<string> ret;
string path;
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string s)
{
dfs(s, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(string& s, int pos)
{
if(path.size() == s.size())
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
//大写变小写,小写变大写
if(s[pos] >= 'a' && s[pos] <= 'z')
{
path.push_back(s[pos] - 32);
dfs(s, pos + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
else if(s[pos] >= 'A' && s[pos] <= 'Z')
{
path.push_back(s[pos] + 32);
dfs(s, pos + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
//不变化
path.push_back(s[pos]);
dfs(s, pos + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
};优美的排列

思路:
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
int ret = 0;
bool check[15];
public:
int countArrangement(int n) {
dfs(n, 1);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int n, int k){
if(k == n + 1){
ret++;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(check[i] == false && (i % k == 0 || k % i == 0)){
check[i] = true;
dfs(n, k + 1);
check[i] = false;
}
}
}
};N 皇后

思路: 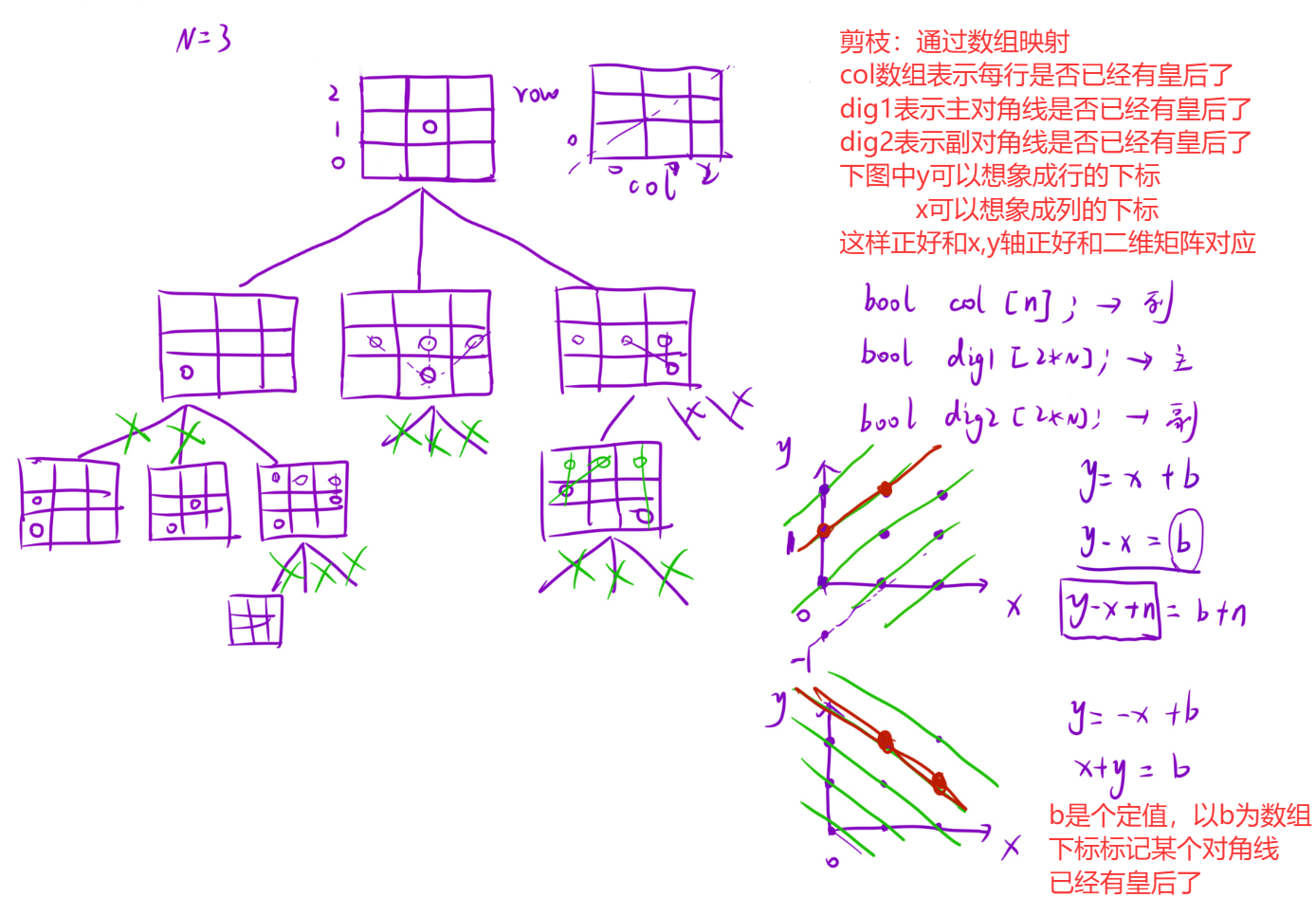
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
vector<vector<string>> ret;
vector<string> path;
bool checkCol[10];
bool checkDig1[20];
bool checkDig2[20];
int n;
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int _n)
{
n = _n;
path.resize(n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
path[i].append(n, '.');
}
dfs(0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int row)
{
if(row == n)
{
ret.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int col = 0; col < n; col++)
{
if(!checkCol[col] && !checkDig1[col - row + n] && !checkDig2[col + row])
{
path[row][col] = 'Q';
checkCol[col] = checkDig1[col - row + n] = checkDig2[col + row] = true;
dfs(row + 1);
path[row][col] = '.';
checkCol[col] = checkDig1[col - row + n] = checkDig2[col + row] = false;
}
}
}
};有效的数独

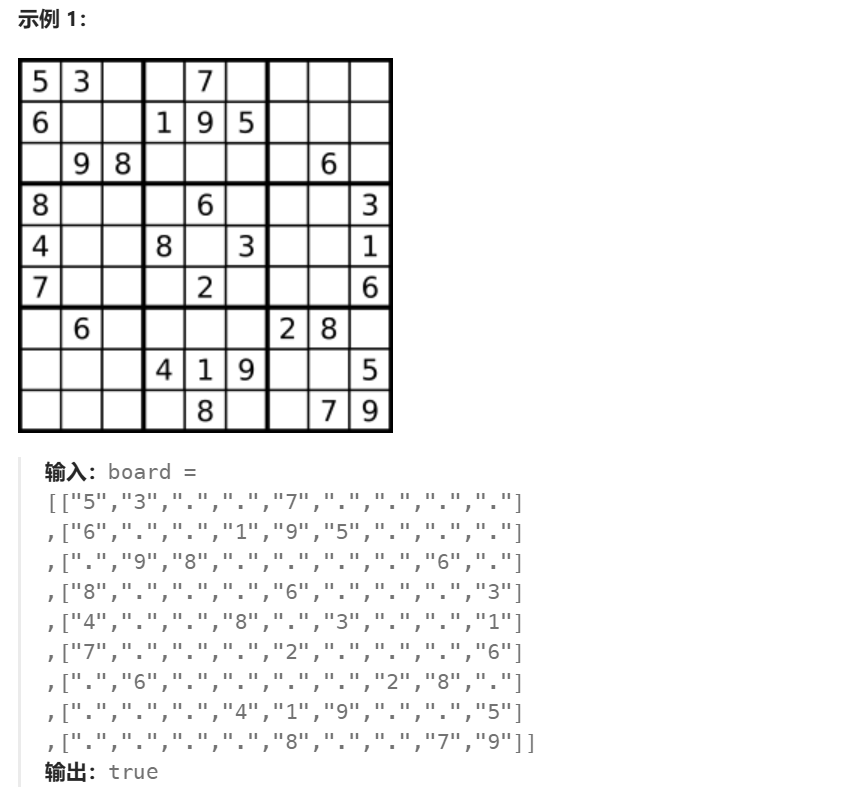
**思路:**创建三个布尔数组
- bool row[ 9 ][ 10 ]:row[i][j] 表示第 i 行,是否存在 j 这个数,如果存在就是 true。
- bool col[ 9 ][ 10 ]:col[i][j] 表示第 i 列,是否存在 j 这个数,如果存在就是 true。
- bool grid[ 3 ][ 3 ][ 10 ]:将原有的9x9的方格看做9个3x3的大格子,grid[i][j][k] 表示下标为 i,j 的格子是否存在 k 这个数,如果存在就是 true。
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
bool row[9][10];
bool col[9][10];
bool grid[3][3][10];
public:
bool isValidSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++){
if(board[i][j] != '.'){
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
if(row[i][num] || col[j][num] || grid[i / 3][j / 3][num])
return false;
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][num] = true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};解数独

思路:
创建三个布尔数组
- bool row[ 9 ][ 10 ]:row[i][j] 表示第 i 行,是否存在 j 这个数,如果存在就是 true。
- bool col[ 9 ][ 10 ]:col[i][j] 表示第 i 列,是否存在 j 这个数,如果存在就是 true。
- bool grid[ 3 ][ 3 ][ 10 ]:将原有的9x9的方格看做9个3x3的大格子,grid[i][j][k] 表示下标为 i,j 的格子是否存在 k 这个数,如果存在就是 true。

通过上述三个数组标记哪些数字在当前位置不能使用,然后递归遍历二维矩阵中每个没有数字的位置,依次尝试 1 ~ 9,递归函数设计一个返回值,这样我们就可以根据返回值知道这个位置放置的这个数可不可以,如果返回的是 true,表明当前放置的数有最终结果,直接返回true(并且在递归过程中已经完成了每个位置的数字的填充);如果返回的是 false,直接恢复现场,然后尝试下一个数即可。如果一个位置所有数都不能放,就返回 false。
代码:
cpp
class Solution
{
bool row[9][10];
bool col[9][10];
bool grid[3][3][10];
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] != '.')
{
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][num] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board);
}
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board)
{
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] == '.')
{
for(int num = 1; num <= 9; num++)
{
if(!row[i][num] && !col[j][num] && !grid[i / 3][j / 3][num])
{
board[i][j] = '0' + num;
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][num] = true;
if(dfs(board)) return true;
board[i][j] = '.';
row[i][num] = col[j][num] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][num] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};单词搜索
思路: 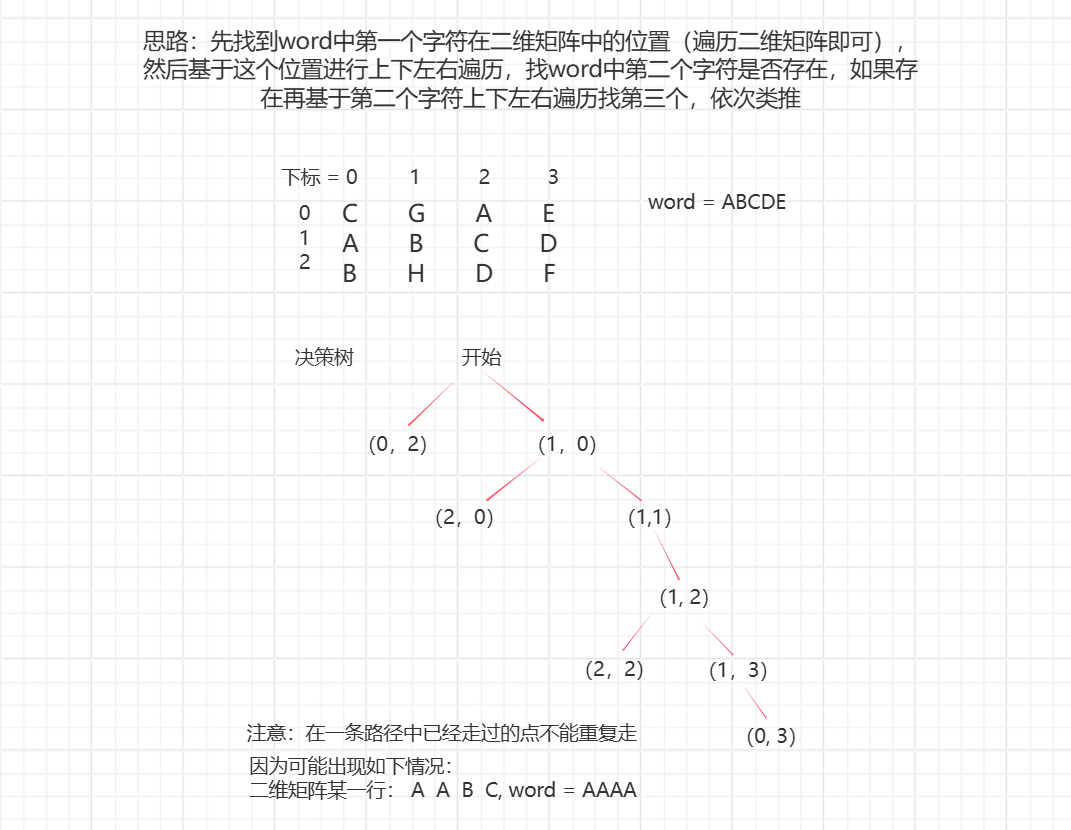
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
bool vis[7][7];
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int m;
int n;
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
m = board.size();
n = board[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(board[i][j] == word[0])
{
vis[i][j] = true;
if(dfs(board, i, j, word, 1)) return true;
vis[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return false;
}
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int i, int j, string& word, int pos)
{
if(pos == word.size())
return true;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && board[x][y] == word[pos])
{
vis[x][y] = true;
if(dfs(board, x, y, word, pos + 1))
return true;
vis[x][y] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
};黄金矿工

**思路:**遍历二维数组,找到不为 0 的数,然后遍历这个数上下左右四个位置,找到不为 0 且当前这条路径中没有走过的数,然后基于这个数继续上下左右遍历,当遍历到某个位置,它的上下左右四个位置都不合法(值为 0,下标越界,已经访问过了都是非法情况),此时说明这条路径走到底了,更新结果。这里 dfs 方法中 temp 参数是上一轮路径中所有值的总和,不包含 grid[i][j],所以更新结果的时候要把 grid[i][j] 加上。
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int m;
int n;
bool vis[15][15];
int ret = 0;
public:
int getMaximumGold(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
m = grid.size();
n = grid[0].size();
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(grid[i][j] != 0)
{
vis[i][j] = true;
dfs(grid, i, j, 0);
vis[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j, int temp)
{
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && grid[x][y] != 0)
{
vis[x][y] = true;
dfs(grid, x, y, temp + grid[i][j]);
vis[x][y] = false;
}
}
ret = max(ret, temp + grid[i][j]);
}
};不同路径 III

**思路:**直接把这道题当做一个迷宫问题,从起点开始深搜,找能走到终点的路径,然后记录这条路径中遇到的 0 的个数,如果这条路径中 0 的个数和二维矩阵中 0 的个数相等,那么这条路径就是符合题目要求的。
代码:
cpp
class Solution {
bool vis[21][21];
int dx[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int ret = 0;
int step = 0;
int m;
int n;
public:
int uniquePathsIII(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
m = grid.size();
n = grid[0].size();
int bx = 0, by = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if(grid[i][j] == 0)
{
step++;
}
else if(grid[i][j] == 1)
{
bx = i;
by = j;
vis[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(grid, bx, by, 0);
return ret;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int i, int j, int count)
{
if(grid[i][j] == 0)
count++;
if(grid[i][j] == 2)
{
if(count == step)
ret++;
}
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && grid[x][y] != -1)
{
vis[x][y] = true;
dfs(grid, x, y, count);
vis[x][y] = false;
}
}
}
};