给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。
示例 1:
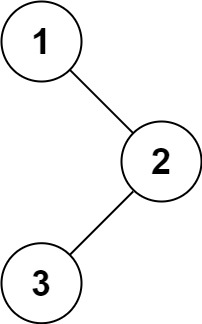
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]核心思路
二叉树遍历有三种方式:
- 前序:根 → 左 → 右
- 中序:左 → 根 → 右
- 后序:左 → 右 →根
中序遍历的结果对于二叉搜索树 来说是升序序列。
解法:递归(最简单)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, result);
return result;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode node, List<Integer> result) {
if (node == null) return;
inorder(node.left, result); // 左
result.add(node.val); // 根
inorder(node.right, result); // 右
}
}
```
### 详细演示
```
二叉树:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
递归调用栈:
inorder(1)
├─ inorder(2)
│ ├─ inorder(4)
│ │ ├─ inorder(null) 返回
│ │ ├─ add(4) → [4]
│ │ └─ inorder(null) 返回
│ │
│ ├─ add(2) → [4,2]
│ │
│ └─ inorder(5)
│ ├─ inorder(null) 返回
│ ├─ add(5) → [4,2,5]
│ └─ inorder(null) 返回
│
├─ add(1) → [4,2,5,1]
│
└─ inorder(3)
├─ inorder(null) 返回
├─ add(3) → [4,2,5,1,3]
└─ inorder(null) 返回
结果: [4,2,5,1,3]
```
## 解法2:迭代(使用栈)
### 思路
用栈模拟递归的过程:
1. 一路向左,将所有左子节点入栈
2. 弹出栈顶,访问节点
3. 转向右子树,重复步骤1
```
核心:先找到最左边的节点,然后回溯本质
中序遍历的核心:
- 递归思想 --- 左子树中序 + 根 + 右子树中序
- 模拟栈 --- 迭代用栈保存回溯路径
- Morris技巧 --- 利用空指针建立临时连接
应用场景:
- 二叉搜索树中序遍历得到升序序列
- 验证二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树中第K小元素