论文:DIN-SQL: Decomposed In-Context Learning of Text-to-SQL with Self-Correction
⭐⭐⭐⭐
NeurIPS 2023, arXiv:2304.11015
文章目录
-
- 一、论文速读
-
- [1.1 Schema Linking Module](#1.1 Schema Linking Module)
- [1.2 Classification & Decomposition Module](#1.2 Classification & Decomposition Module)
- [1.3 SQL Generation Module](#1.3 SQL Generation Module)
-
- [1.3.1 EASY 类型](#1.3.1 EASY 类型)
- [1.3.2 NON-NESTED 类型](#1.3.2 NON-NESTED 类型)
- [1.3.3 NESTED 类型](#1.3.3 NESTED 类型)
- [1.4 Self-correction Module](#1.4 Self-correction Module)
- [二、Error cases 分析](#二、Error cases 分析)
- 三、总结
一、论文速读
这篇论文通过对 LLM 做 prompt 来实现 Text2SQL,过程中通过 prompt 让 LLM 分解任务来降低难度,每个子任务通过 in-context learning 让 LLM 来完成,并在完成 SQL 生成后,通过 self-correction 来检查和纠正可能有错误的 SQL。最终,在执行精确度指标上超越了现有的 SOTA 模型。
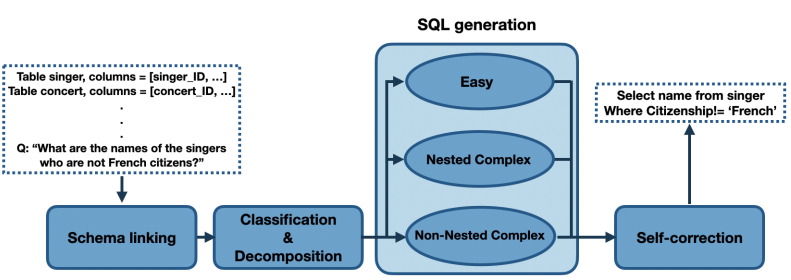
生成 SQL 被分成四个阶段:
- Schema Linking:输入 NL query 和 DB schema,找出与 query 相关的 tables、columns 以及不同表之间的外键关系
- Classification & Decomposition:将 query 分成了三种不同的难度:EASY、NON-NESTED、NESTED
- SQL Generation:根据不同类型的 query,按照不同的策略来生成对应的 SQL
- Self-correction:通过 prompt 来让 LLM 检查和纠正可能错误的 SQL
1.1 Schema Linking Module
这个 module 输入 NL query 和 DB 的 schema 信息,输出的是将 query 链接到 DB 中的一些信息,具体来说输出就是:
- table 和 columns 的名称:找到 query 中涉及到的 DB 的 table 和 columns 的名称
- 条件值:从查询中提取出用于条件过滤的值,比如在查询"Find the departments with a budget greater than 500"中,需要提取出条件值"500"。
- 外键关系的确定:如果查询涉及到多个表,需要确定它们之间的关系,如通过外键连接。
下面是使用 in-context learning + CoT 来让 LLM 做 schema-linking 的示例:
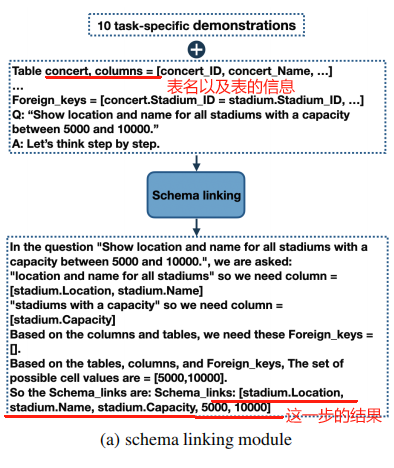
demostration 的一个示例如下:
plain
Table advisor, columns = [*,s_ID,i_ID]
Table classroom, columns = [*,building,room_number,capacity]
Table course, columns = [*,course_id,title,dept_name,credits]
Table department, columns = [*,dept_name,building,budget]
Table instructor, columns = [*,ID,name,dept_name,salary]
Table prereq, columns = [*,course_id,prereq_id]
Table section, columns = [*,course_id,sec_id,semester,year,building,room_number,time_slot_id]
Table student, columns = [*,ID,name,dept_name,tot_cred]
Table takes, columns = [*,ID,course_id,sec_id,semester,year,grade]
Table teaches, columns = [*,ID,course_id,sec_id,semester,year]
Table time_slot, columns = [*,time_slot_id,day,start_hr,start_min,end_hr,end_min]
Foreign_keys = [course.dept_name = department.dept_name,instructor.dept_name = department.dept_name,section.building = classroom.building,section.room_number = classroom.room_number,section.course_id = course.course_id,teaches.ID = instructor.ID,teaches.course_id = section.course_id,teaches.sec_id = section.sec_id,teaches.semester = section.semester,teaches.year = section.year,student.dept_name = department.dept_name,takes.ID = student.ID,takes.course_id = section.course_id,takes.sec_id = section.sec_id,takes.semester = section.semester,takes.year = section.year,advisor.s_ID = student.ID,advisor.i_ID = instructor.ID,prereq.prereq_id = course.course_id,prereq.course_id = course.course_id]
Q: "Find the buildings which have rooms with capacity more than 50."
A: Let's think step by step. In the question "Find the buildings which have rooms with capacity more than 50.", we are asked:
"the buildings which have rooms" so we need column = [classroom.capacity]
"rooms with capacity" so we need column = [classroom.building]
Based on the columns and tables, we need these Foreign_keys = [].
Based on the tables, columns, and Foreign_keys, The set of possible cell values are = [50]. So the Schema_links are:
Schema_links: [classroom.building,classroom.capacity,50]如下面代码所示,schema linking 的结果就是从 GPT 的响应中解析出 Schema_links: 这个字符串后面的内容:
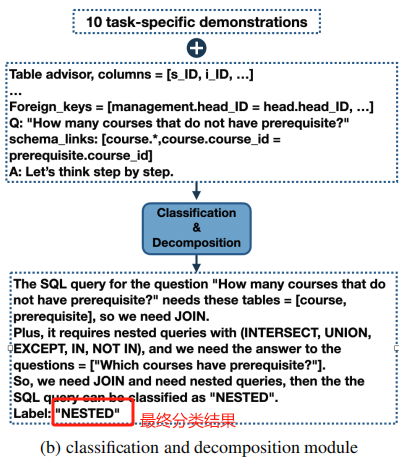
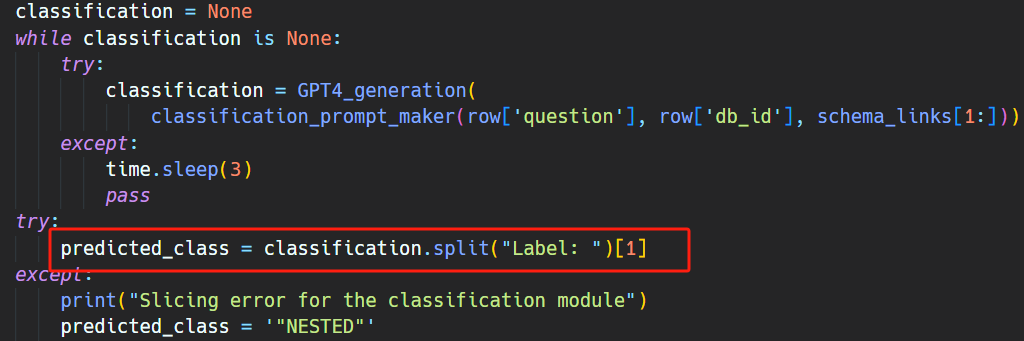
1.2 Classification & Decomposition Module
这一步将 query 分成三种不同的复杂度的类:
- EASY:没有 JOIN 和 NESTING 的单表查询
- NON-NESTED:需要 JOIN 但不需要子查询的查询
- NESTED:可以包含 JOIN、sub-query 和 set opr
下面是一个该 module 的示例:
这部分代码如下:
1.3 SQL Generation Module
这一个 module 根据 query 的复杂度类型,使用不同的策略来生成 SQL。
1.3.1 EASY 类型
对于 EASY 类型的 question,不需要中间步骤,只需要少量提示就足够了,下面是一个 exemplar:
plain
Q: "Find the buildings which have rooms with capacity more than 50."
Schema_links: [classroom.building,classroom.capacity,50]
SQL: SELECT DISTINCT building FROM classroom WHERE capacity > 50即要求 LLM 根据 question 和 schema links 输出 SQL。
1.3.2 NON-NESTED 类型
对于 NON-NESTED 类型的 question,启发 LLM 去思考从而生成 SQL,下面是一个 exemplar:
plain
Q: "Find the total budgets of the Marketing or Finance department."
Schema_links: [department.budget,department.dept_name,Marketing,Finance]
A: Let's think step by step. For creating the SQL for the given question, we need to join these tables = []. First, create an intermediate representation, then use it to construct the SQL query.
Intermediate_representation: select sum(department.budget) from department where department.dept_name = \"Marketing\" or department.dept_name = \"Finance\"
SQL: SELECT sum(budget) FROM department WHERE dept_name = 'Marketing' OR dept_name = 'Finance'也就是输入 question 和 schema links,然后加一句 Let's think step by step 启发 LLM 思考,从而得到 SQL。
1.3.3 NESTED 类型
在 "Classification & Decomposition Module" 模块中,除了为其复杂度分类,还会为 NESTED 类型的 user question 生成 sub-question,如下图:
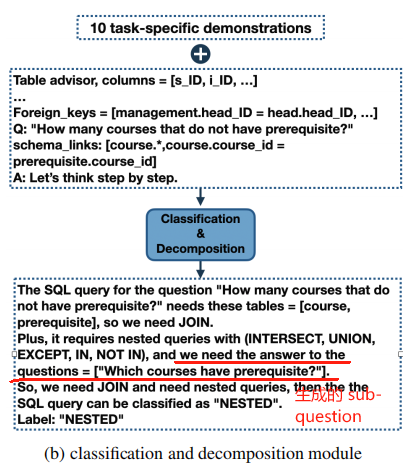
然后,这里的 sub-questions 会被传入 SQL Generation Module 的 prompt 中用于解决 NESTED 类型的 SQL 生成。下面是一个 exemplar:
plain
Q: "Find the title of courses that have two prerequisites?"
Schema_links: [course.title,course.course_id = prereq.course_id]
A: Let's think step by step. "Find the title of courses that have two prerequisites?" can be solved by knowing the answer to the following sub-question "What are the titles for courses with two prerequisites?".
The SQL query for the sub-question "What are the titles for courses with two prerequisites?" is SELECT T1.title FROM course AS T1 JOIN prereq AS T2 ON T1.course_id = T2.course_id GROUP BY T2.course_id HAVING count(*) = 2
So, the answer to the question "Find the title of courses that have two prerequisites?" is =
Intermediate_representation: select course.title from course where count ( prereq.* ) = 2 group by prereq.course_id
SQL: SELECT T1.title FROM course AS T1 JOIN prereq AS T2 ON T1.course_id = T2.course_id GROUP BY T2.course_id HAVING count(*) = 2exemplar 的 prompt 的组成如下:

可以看到,这就是输入 question、sub-questions、schema links 来生成 SQL。
1.4 Self-correction Module
这一模块的目的是通过 prompt 让 LLM 来检查和纠正生成的 SQL 中可能的错误。这里的 prompt 如下:
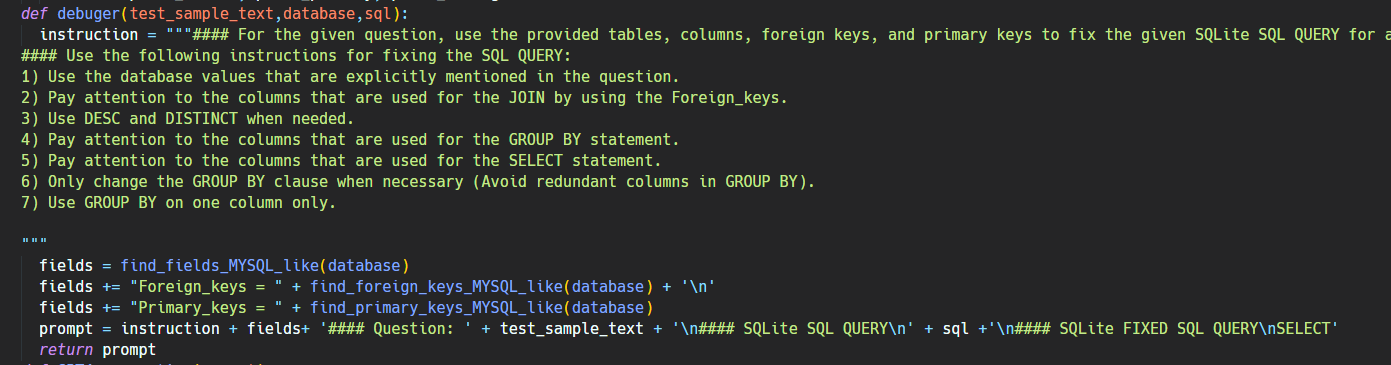
这里的 prompt 让 LLM 多关注自己在生成 SQL 时容易犯的错。
二、Error cases 分析
论文对 error cases 做了分析,总结了如下 LLM 容易出的错:
- Schema linking:这类是犯错最多的情况,指的是 model 错误地识别出 question 中提到的 column names、table names 或者 entities。
- JOIN:第二大类情况,指的是 model 不能识别出所有需要的 tables 以及正确地将这些 tables 连接起来的外键。
- GROUP BY:在生成 GROUP BY 子句时,可能会遗漏或者选错列
- Queries with nesting and set operations:模型不能识别出 nested structure 或者不能检测出正确的 nesting 或 set 操作
- Invalid SQL:一部分 SQL 有语法错误且不能执行
- Miscellaneous:还有其他乱七八糟的原因,比如缺少 predicate、缺少或冗余 DISTINCT、DESC 等关键字
这些容易犯的错,都会在 self-correction module 被多关注来检查和纠正。
三、总结
本论文设计的 prompt 以及思路让 LLM 在解决 Text2SQL 任务上有了不错的表现,产生了与最先进的微调方法相当甚至更优的结果。
但是,本文的思路需要多轮与 LLM 交互,从而产生了巨大的花费和延迟,论文给出,在使用 GPT4 响应 Spider 数据集中 question 时表现出大约 60s 的延迟。