文章目录
1.torch.cat()
torch.cat() 是 PyTorch 库中的一个函数,用于沿指定维度连接张量。它接受一系列张量作为输入,并沿指定的维度进行连接。
python
torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
"""
tensors:要连接的张量序列(例如,列表、元组)。
dim(可选):要沿其进行连接的维度。它指定了轴或维度编号。默认情况下,它设置为0,表示沿第一个维度进行连接。
out(可选):存储结果的输出张量。如果指定了 out,结果将存储在此张量中。如果未提供 out,则会创建一个新的张量来存储结果。
"""
python
import torch
# 创建两个张量
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# 沿着维度0连接两个张量
result = torch.cat((tensor1, tensor2), dim=0)
print(result)2.torch.column_stack()
torch.column_stack() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于按列堆叠张量来创建一个新的张量。它将输入张量沿着列的方向进行堆叠,并返回一个新的张量。
python
torch.column_stack(tensors)
"""
tensors:要堆叠的张量序列。它可以是一个包含多个张量的元组、列表或任意可迭代对象。
"""
python
import torch
tensor1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6])
result = torch.column_stack((tensor1, tensor2))
print(result)3.torch.gather()
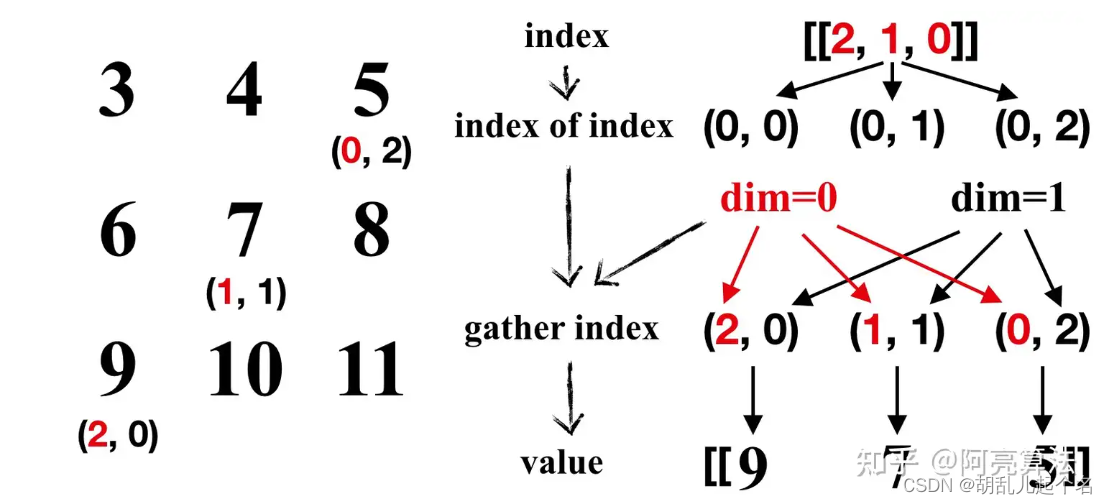
torch.gather() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于根据给定的索引从输入张量中收集元素。它允许你按照指定的索引从输入张量中选择元素,并将它们组合成一个新的张量。
python
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None, sparse_grad=False)
"""
input:输入张量,从中收集元素。
dim:指定索引的维度。
index:包含要收集元素的索引的张量。
out(可选):输出张量,用于存储结果。
sparse_grad(可选):指定是否启用稀疏梯度。默认为 False
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# 索引张量
index = torch.tensor([[0, 0], [1, 0]])
# 根据索引从输入张量中收集元素
result = torch.gather(input, 1, index)
print(result)
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# 索引张量
index = torch.tensor([[0, 0], [1, 0]])
# 根据索引从输入张量中收集元素
result = torch.gather(input, 0, index)
print(result)4.torch.hstack()
torch.hstack() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于沿着水平方向(列维度)堆叠张量来创建一个新的张量。它将输入张量沿着水平方向进行堆叠,并返回一个新的张量。
python
torch.hstack(tensors) -> Tensor
"""
tensors:要堆叠的张量序列。可以是一个包含多个张量的元组、列表或任意可迭代对象。
"""
python
import torch
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
result = torch.hstack((tensor1, tensor2))
print(result)
# tensor([[1, 2, 5, 6],
# [3, 4, 7, 8]])5.torch.vstack()
torch.vstack()是PyTorch中用于沿垂直方向(行维度)堆叠张量的函数。它将输入张量沿垂直方向进行堆叠,并返回一个新的张量。
python
torch.vstack(tensors) -> Tensor
python
import torch
tensor1 = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
result = torch.vstack((tensor1, tensor2))
print(result)
python
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6],
[7, 8]])6.torch.index_select()
torch.index_select() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于按索引从输入张量中选择元素并返回一个新的张量。
python
torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None) -> Tensor
"""
input:输入张量,从中选择元素。
dim:指定索引的维度。即要在 input 张量的哪个维度上进行索引。
index:指定要选择的索引的张量。它的形状可以与 input 张量的形状不同,但必须满足广播规则。
out(可选):输出张量,用于存储结果。如果提供了 out,则结果将存储在此张量中。
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# 索引张量
index = torch.tensor([0, 2])
# 根据索引从输入张量中选择元素
result = torch.index_select(input, 0, index)
print(result)
python
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[7, 8, 9]])7.torch.masked_select()
torch.masked_select() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于根据给定的掩码从输入张量中选择元素并返回一个新的张量。
python
torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None) -> Tensor
"""
input:输入张量,从中选择元素。
mask:掩码张量,用于指定要选择的元素。mask 张量的形状必须与 input 张量的形状相同,或者满足广播规则。
out(可选):输出张量,用于存储结果。如果提供了 out,则结果将存储在此张量中。
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# 掩码张量
mask = torch.tensor([[True, False, True], [False, True, False], [True, False, True]])
# 根据掩码从输入张量中选择元素
result = torch.masked_select(input, mask)
print(result)
python
tensor([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])8.torch.reshape
torch.reshape() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于改变张量的形状而不改变元素的数量。它返回一个具有新形状的新张量,其中的元素与原始张量相同。
python
torch.reshape(input, shape) -> Tensor
"""
input:输入张量,要改变形状的张量。
shape:指定的新形状。可以是一个整数元组或传递一个张量,其中包含新的形状。
torch.reshape() 函数将输入张量重新排列为指定的新形状。新的形状应该满足以下条件:
1. 新形状的元素数量与原始张量的元素数量相同。
2. 新形状中各维度的乘积与原始张量的元素数量相同。
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
# 改变形状为 (3, 2)
result1 = torch.reshape(input, (3, 2))
# 改变形状为 (1, 6)
result2 = torch.reshape(input, (1, 6))
# 改变形状为 (6,)
result3 = torch.reshape(input, (6,))
print(result1)
print(result2)
print(result3)9.torch.stack()
torch.stack() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于沿着新的维度对给定的张量序列进行堆叠操作。
python
torch.stack(tensors, dim=0, *, out=None) -> Tensor
"""
tensors:张量的序列,要进行堆叠操作的张量。
dim(可选):指定新的维度的位置。默认值为 0。
out(可选):输出张量。如果提供了输出张量,则将结果存储在该张量中。
"""
python
import torch
# 张量序列
tensor1 = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
tensor2 = torch.tensor([4, 5, 6])
tensor3 = torch.tensor([7, 8, 9])
# 在维度 0 上进行堆叠操作
result = torch.stack([tensor1, tensor2, tensor3], dim=0)
print(result)
python
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])10.torch.where()
torch.where() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于根据给定的条件从两个张量中选择元素。
python
torch.where(condition, x, y) -> Tensor
"""
condition:条件张量,一个布尔张量,用于指定元素选择的条件。
x:张量,与 condition 形状相同的张量,当对应位置的 condition 元素为 True 时,选择 x 中的对应元素。
y:张量,与 condition 形状相同的张量,当对应位置的 condition 元素为 False 时,选择 y 中的对应元素。
"""
python
import torch
# 条件张量
condition = torch.tensor([[True, False], [False, True]])
# 选择的张量 x
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# 选择的张量 y
y = torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
# 根据条件选择元素
result = torch.where(condition, x, y)
print(result)
#tensor([[1, 6],
# [7, 4]])
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([1.5, 0.8, -1.2, 2.7, -3.5])
# 阈值
threshold = 0
# 根据阈值选择元素
result = torch.where(input > threshold, torch.tensor(1), torch.tensor(0))
print(result)#tensor([1, 1, 0, 1, 0])11.torch.tile()
torch.tile() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于在指定维度上重复张量的元素。
python
torch.tile(input, reps) -> Tensor
"""
input:输入张量,要重复的张量。
reps:重复的次数,可以是一个整数或一个元组。
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
# 在维度 0 上重复 2 次
result = torch.tile(input, 2)
print(result)#tensor([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3])
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# 在维度 0 和维度 1 上重复
result = torch.tile(input, (2, 3))
print(result)
tensor([[1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4],
[1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 3, 4, 3, 4]])12.torch.take()
torch.take() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于在给定索引处提取张量的元素。
python
torch.take(input, indices) -> Tensor
"""
input:输入张量,要从中提取元素的张量。
indices:索引张量,包含要提取的元素的索引。它可以是一个一维整数张量或一个具有相同形状的张量。
"""
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# 索引张量
indices = torch.tensor([1, 4, 7])
# 提取元素
result = torch.take(input, indices)
print(result)# tensor([2, 5, 8])
python
import torch
# 输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
# 索引张量
indices = torch.tensor([[0, 2], [1, 2]])
# 提取部分元素
result = torch.take(input, indices)
print(result)
tensor([[1, 3],
[2, 3]])13.torch.scatter()
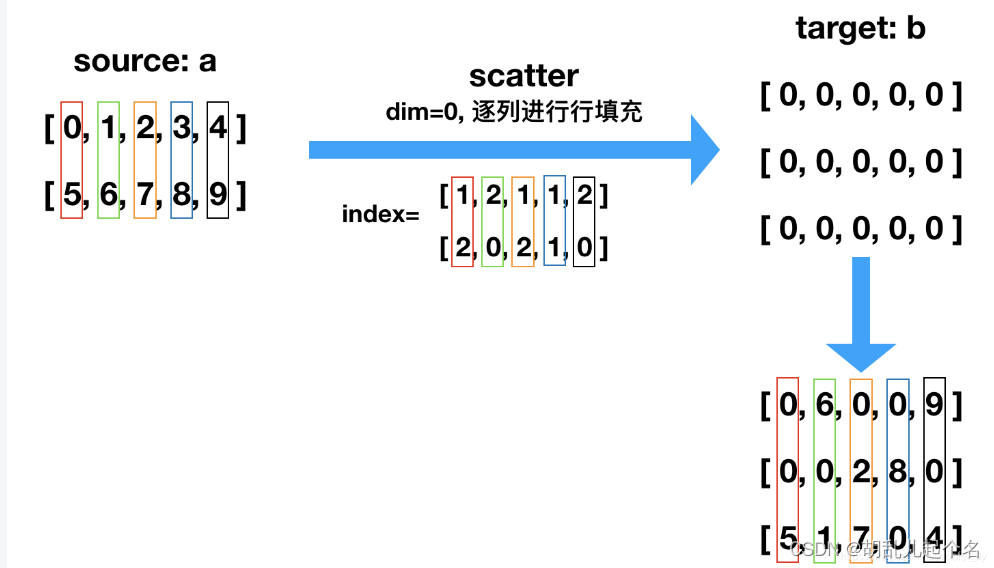
torch.scatter() 是 PyTorch 中的一个函数,用于根据索引在张量中进行散射操作。散射操作是指根据给定的索引,将源张量的值散布(写入)到目标张量的指定位置。
python
torch.scatter(input, dim, index, src)
"""
input:输入张量,表示目标张量,散射操作将在此张量上进行。
dim:整数值,表示散射操作沿着的维度。
index:索引张量,指定散射操作的目标位置。
src:源张量,包含要散射到目标张量中的值。
"""
python
import torch
# 创建目标张量
target = torch.zeros(3, 4)
# 创建索引张量和源张量
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1, 2, 0], [2, 1, 0, 2]])
source = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
# 执行散射操作
torch.scatter(target, dim=1, index=index, src=source)
print(target)
# 输出:
# tensor([[1., 4., 3., 1.],
# [0., 3., 2., 0.],
# [3., 2., 1., 3.]])