pip install attention
pip install keras_tuner
import os
import re
import itertools
import numpy as np
import scipy.signal
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import scipy.io as scio
import tensorflow as tf
import keras_tuner as kt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer, OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay, classification_report, confusion_matrix, precision_score, recall_score, f1_score, accuracy_score, roc_curve, roc_auc_score, auc
from tensorflow import keras
from keras.layers import *
from keras import backend as k
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.models import Sequential,Model,load_model
from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau, ModelCheckpoint
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential,Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Input,Dense, Dropout, Flatten, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D
from attention import Attention
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')Data Visualization
working_cond = 40 #this corresponds to possible values under which the voltage source operates i.e., 40, 80 and 120
Path = r'/content/drive/MyDrive/ALL_DC_motor_Data/Ua_120V_Noise_2_perct'.format(working_cond) # Path of the folder containing CSV files from that working condition
file_name = os.listdir(path=Path) # List of all the files in the folder
fig, axs = plt.subplots(len(file_name), 2, figsize=(10, 2 * len(file_name)))
for i, file in enumerate(file_name):
csv_path = os.path.join(Path, file) # Obtains the exact path for that file
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path) # saves that Fault data in a dummy variable "df"
df = df.iloc[::50]
ax1 = axs[i][0]
ax2 = axs[i][1]
ax1.plot(df['time'], df['a1_lower'], '-r', label='')
ax2.plot(df['time'], df['a2_lower'], '-r', label='')
ax1.plot(df['time'], df['a1_upper'], '-g', label='a1')
ax2.plot(df['time'], df['a2_upper'], '-g', label='a2')
ax1.plot(df['time'], df['ARR1'], '-b', label='')
ax2.plot(df['time'], df['ARR2'], '-b', label='')
ax1.set_title(file[:-13]) #to extract only the fault type from the name of fault file, _noise_02.csv contains 13 characters
ax1.set_ylim(-30, 30)
ax1.set_xlabel('Time')
ax1.set_ylabel('r1')
ax2.set_title(file[:-13])
ax2.set_ylim(-1, 1)
ax2.set_xlabel('Time')
ax2.set_ylabel('r2')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()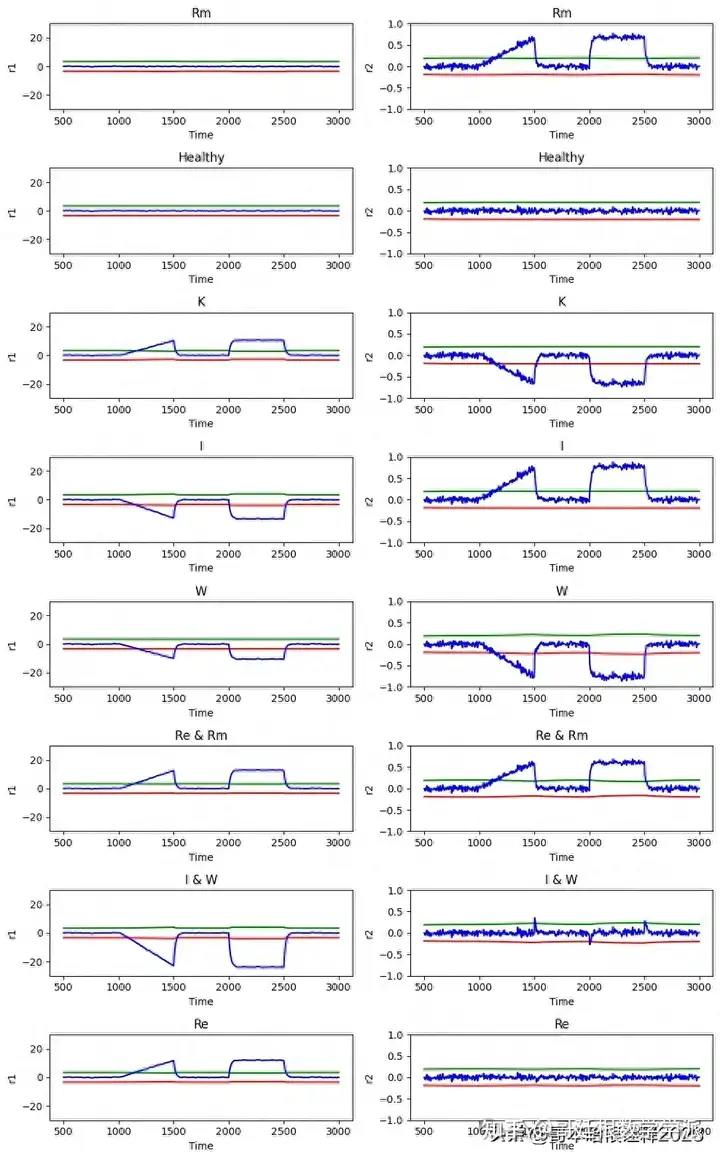
Path = r'/content/drive/MyDrive/ALL_DC_motor_Data/Ua_120V_Noise_2_perct'.format(40) # Path of the folder containing CSV files from that working condition
file_name = os.listdir(path=Path) # List of all the files in the folder
fig, axs = plt.subplots(len(file_name), 2, figsize=(10, 2 * len(file_name)))
for i, file in enumerate(file_name):
csv_path = os.path.join(Path, file)
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
df = df.iloc[::50]
ax1 = axs[i][0]
ax2 = axs[i][1]
ax1.plot(df['time'], df['Im'], '-r', label='')
ax2.plot(df['time'], df['Wm'], '-b', label='')
ax1.set_title(file[:-13])
ax1.set_ylim(20, 36)
ax1.set_xlabel('Time')
ax1.set_ylabel('$I_m$')
ax2.set_title(file[:-13])
ax2.set_ylim(250, 480)
ax2.set_xlabel('Time')
ax2.set_ylabel('$\omega_m$')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()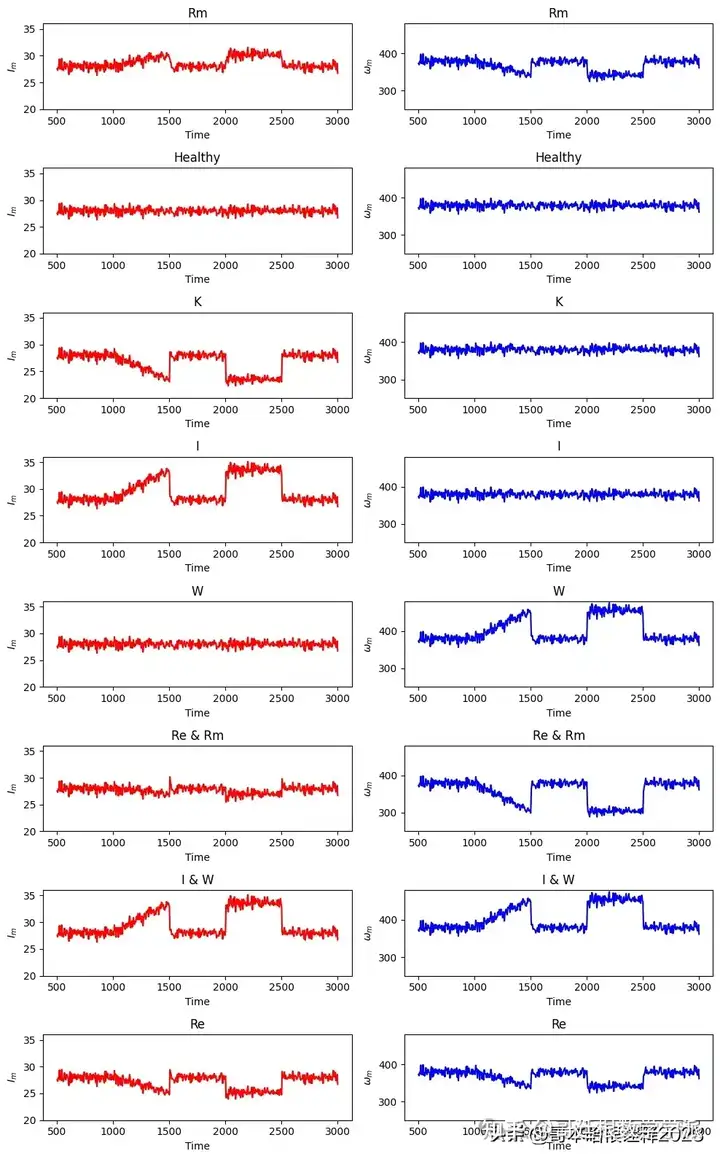
Dataframe Creation
def obtain_DataFrame_for_this_working_condition(working_cond):
# Input = "Working Condition" [40V, 80V, 120V]
# Output = "A dataFrame contaning all fault scnerio from that Working Condition"
# The DataFrame has following columns [time, I, W, ARR1, ARR2, a1_upper, a1_lower, a2_upper, a2_lower, activation_arr1, activation_arr2 FaultClass] for the given "working_cond"
Path = r'/content/drive/MyDrive/ALL_DC_motor_Data/Ua_{}V_Noise_2_perct'.format(working_cond) # Path of the folder containing CSV files from that working condition
file_name = os.listdir(path=Path) # List of all the files in the folder
DF = pd.DataFrame() # Initialize an empty DataFrame
for f in file_name : #Iterate through each file, which coresponds to a Fault
csv_path = os.path.join(Path,f) #Obtains the exact path for that file
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path) #saves that Fault data in a dummy variable "df"
temp1=df[(df.time > 1050) & (df.time< 1500)] # Incipient Faults -----Taking samples after which the fault was introduced
temp2=df[(df.time > 2050) & (df.time< 2500)] # Step Faults-----------Taking samples after which the fault was introduced
df=pd.concat([temp1,temp2]) #Concatinate both Incipient and Step Fault
DF=pd.concat([DF,df]) # Append the "f"-Fault to the new dataframe DF
DF['Working_cond'] = np.repeat('U-{}V'.format(working_cond), len(DF))
return DF
df_120 = obtain_DataFrame_for_this_working_condition(working_cond=120)
df_40 = obtain_DataFrame_for_this_working_condition(working_cond=40)
df_80 = obtain_DataFrame_for_this_working_condition(working_cond=80)
DF = pd.concat([df_40,df_80,df_120]) # ALL 3 working conditions are saved in one DataFRame
sns.scatterplot(data=DF.iloc[::400,:],x='Im',y='Wm',hue='Fault_type',style='Fault_type',edgecolor='black')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
sns.scatterplot(data=DF.iloc[::200,:],x='ARR1',y='ARR2',style='Fault_type',hue='Fault_type', palette = 'deep', edgecolor = 'black')
plt.legend()
plt.show()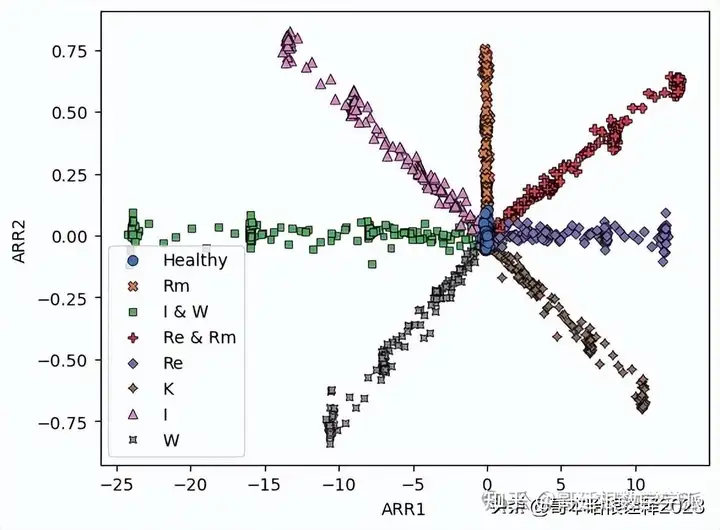
Data Augmentation
def Sliding_Window(df_temp, win_len, stride):
"""
Sliding window function for data segmentation and label extraction.
Args:
df_temp (DataFrame): Input dataframe containing the data.
win_len (int): Length of the sliding window.
stride (int): Stride or step size for sliding the window.
Returns:
X (ndarray): Segmented input sequences.
Y (ndarray): Extracted output labels.
T (ndarray): Corresponding timestamps.
"""
X = [] # List to store segmented input sequences.
Y = [] # List to store extracted output labels.
T = [] # List to store corresponding timestamps.
# Loop through the dataframe with the specified stride.
for i in np.arange(0, len(df_temp) - win_len, stride):
# Extract a subset of the dataframe based on the window length.
temp = df_temp.iloc[i:i + win_len, [3, 4]].values
# Append the segmented input sequence to the X list.
X.append(temp)
# Append the output label at the end of the window to the Y list.
Y.append(df_temp.iloc[i + win_len, -1])
# Append the timestamp at the end of the window to the T list.
T.append(df_temp.iloc[i + win_len, 0])
return np.array(X), np.array(Y), np.array(T)Data Preprocessing
def PreprocessData(working_cond, win_len, stride):
"""
Preprocessing function to extract input sequences and output labels from CSV files of a specific working condition.
Args:
working_cond (str): Working condition identifier used to locate the folder containing CSV files.
win_len (int): Length of the sliding window.
stride (int): Stride or step size for sliding the window.
Returns:
X_full (ndarray): Concatenated segmented input sequences.
Y_full (ndarray): Concatenated output labels.
"""
Path = r'/content/drive/MyDrive/ALL_DC_motor_Data/Ua_{}V_Noise_2_perct'.format(working_cond)
file_name = os.listdir(path=Path)
X_full, Y_full = [], [] # Lists to store concatenated segmented input sequences and output labels
for f in file_name: # Iterate through each file, which corresponds to a fault
csv_path = os.path.join(Path, f)
df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
temp_df_1 = df[(df.time > 1050) & (df.time < 1500)] # Incipient - Taking samples after which the parameter fault was introduced
x1, y1, _ = Sliding_Window(temp_df_1, win_len, stride)
temp_df_2 = df[(df.time > 2050) & (df.time < 2500)] # Step - Taking samples after which the parameter fault was introduced
x2, y2, _ = Sliding_Window(temp_df_2, win_len, stride)
x_temp, y_temp = np.concatenate((x1, x2), axis=0), np.concatenate((y1, y2), axis=0)
X_full.append(x_temp)
Y_full.append(y_temp)
X_full = np.array(X_full)
X_full = np.reshape(X_full, (-1, X_full.shape[2], X_full.shape[3]))
Y_full = np.array(Y_full)
Y_full = np.reshape(Y_full, (-1))
return X_full, Y_full
WL=20 # can be used for adjusting window length
S=40 # can be used for adjusting stride
# Preprocess data for working condition 120
X_120, Y_120 = PreprocessData(working_cond=120, win_len=WL, stride=S)
# Preprocess data for working condition 80
X_80, Y_80 = PreprocessData(working_cond=80, win_len=WL, stride=S)
# Preprocess data for working condition 40
X_40, Y_40 = PreprocessData(working_cond=40, win_len=WL, stride=S)
# Concatenate the preprocessed data from different working conditions
X_full = np.concatenate((X_40, X_80, X_120))
Y_full = np.concatenate((Y_40, Y_80, Y_120))
# Train Test split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_full, Y_full, train_size=256, random_state=42)
# Standardising the data
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_sc = scaler.fit_transform(X_train.reshape(-1,X_train.shape[-1])).reshape(X_train.shape)
X_test_sc = scaler.transform(X_test.reshape(-1,X_test.shape[-1])).reshape(X_test.shape)
# One Hot encoding
encoder = OneHotEncoder(sparse_output=False) # in case of error, add the argument handle_unknown = 'ignore'
y_train_ohe = encoder.fit_transform(y_train.reshape(-1,1))
y_test_ohe = encoder.transform(y_test.reshape(-1,1))Model Architecture
def build_model(hp):
num_classes=len(encoder.categories_[0])
# create model object
model = Sequential([
Conv1D(filters=hp.Int('conv_1_filter', min_value=16, max_value=128, step=32), kernel_size=hp.Choice('conv_1_kernel', values = [3,5]), activation='relu', input_shape=(X_train.shape[1],X_train.shape[2]), padding='same'),
MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2,padding='same'),
LSTM(units=hp.Int('lstm_1', min_value=16, max_value=128, step=32), return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.2),
LSTM(units=hp.Int('lstm_2', min_value=16, max_value=128, step=32), return_sequences=True),
LSTM(units=hp.Int('lstm_3', min_value=16, max_value=128, step=32), return_sequences=True),
Dropout(0.5),
Attention(),
Dense(units=hp.Int('dense_1_units', min_value=32, max_value=128, step=16), activation='relu'),
Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(hp.Choice('learning_rate', values=[1e-2, 1e-3])), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
tuner = kt.RandomSearch(build_model, objective='val_accuracy', max_trials = 10) #creating randomsearch object
tuner.search(X_train_sc,y_train_ohe,epochs=20,validation_data=(X_test_sc,y_test_ohe)) # search best parameter values
HyDeLA_model_tuned=tuner.get_best_models(num_models=1)[0]
HyDeLA_model_tuned.summary()
def HYDELA_model(encoder,X_train_transformed):
num_classes=len(encoder.categories_[0])
HyDeLA_model = Sequential()
HyDeLA_model.add(Conv1D(16, kernel_size=(5),activation='relu',input_shape=(X_train_transformed.shape[1],X_train_transformed.shape[2]),padding='same'))
HyDeLA_model.add(MaxPooling1D((2),padding='same'))
HyDeLA_model.add(LSTM(112, return_sequences=True))
HyDeLA_model.add(Dropout(0.2))
HyDeLA_model.add(LSTM(16,return_sequences=True))
HyDeLA_model.add(LSTM(48,return_sequences=True))
HyDeLA_model.add(Dropout(0.5))
HyDeLA_model.add(Attention())
HyDeLA_model.add(Flatten())
HyDeLA_model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
HyDeLA_model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
HyDeLA_model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.001),metrics=['accuracy'])
return HyDeLA_modelModel Training
# Define an EarlyStopping callback to monitor validation accuracy and restore best weights
callback = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=10, restore_best_weights=True)
# Create a model using the specified encoder and X_train_sc
hydela_model = HYDELA_model(encoder, X_train_sc)
# Train the model
history = hydela_model.fit(X_train_sc, y_train_ohe, epochs=200, batch_size=16, validation_data=(X_test_sc, y_test_ohe), callbacks=[callback], shuffle=False, verbose=1)
# Access the loss values
training_loss = history.history['loss']
validation_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(training_loss) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, training_loss, label='Training loss', marker = 'o', lw = 1)
plt.plot(epochs, validation_loss, label='Validation loss', marker = 'x', lw = 1)
plt.xlabel('Number of Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss vs Number of Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()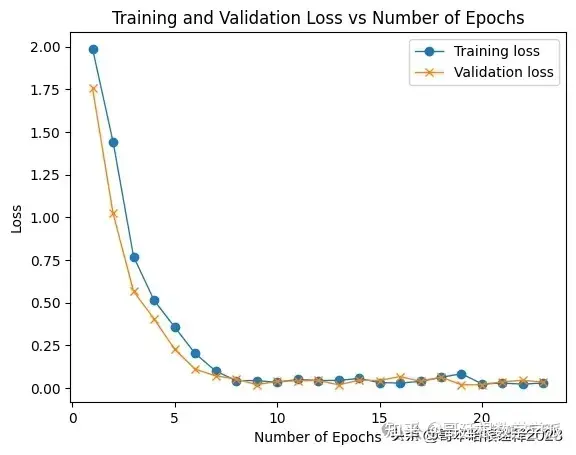
Model Evaluation
# Perform prediction using the CNN model on the scaled test data
y_pred = hydela_model.predict(X_test_sc)
# Inverse transform the predicted labels using the encoder
y_pred = encoder.inverse_transform(y_pred)
# Calculate and print precision, recall, F1-score and accuracy
precision = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"Training Sample Size = {len(X_train)}, F1 score is - {f1}")
print(f"Training Sample Size = {len(X_train)}, Accuracy is - {accuracy}")
print(f"Training Sample Size = {len(X_train)}, Precision is - {precision}")
print(f"Training Sample Size = {len(X_train)}, Recall is - {recall}")
160/160 [==============================] - 3s 8ms/step
Training Sample Size = 256, F1 score is - 0.9947349330945912
Training Sample Size = 256, Accuracy is - 0.9947265625
Training Sample Size = 256, Precision is - 0.9947711101749215
Training Sample Size = 256, Recall is - 0.9947265625
# Define the class labels
class_labels = ['Healthy', 'Re', 'Rm', 'I', 'W', 'K', 'Re & Rm', 'I & W']
# Create the confusion matrix
conf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred)
# Create a heatmap
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(conf_matrix, annot=True, cmap='Reds', fmt='d', xticklabels=class_labels, yticklabels=class_labels)
plt.xlabel("Predicted Labels")
plt.ylabel("Actual Labels")
plt.title("Confusion Matrix")
plt.show()
def lab_to_num(value):
"""
lab_to_num converts the literal labels to numeric labels as per the mapping function label_mapping = {'Re': 1, 'Rm': 2, 'I': 3, 'W': 4, 'K': 5, 'I & W': 7, 'Re & Rm': 6}
parameter : value is assumed to be numpy.ndarray()
"""
for i in range(len(value)):
if value[i]=='Re':
value[i]=1
elif value[i]=='Rm':
value[i]=2
elif value[i]=='I':
value[i]=3
elif value[i]=='W':
value[i]=4
elif value[i]=='K':
value[i]=5
elif value[i]=='I & W':
value[i]=7
elif value[i]=='Re & Rm':
value[i]=6
else:
value[i]=0
return value
num_label = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7']
test_roc = []
pred_roc = []
test_roc = [1 if label in num_label else 0 for label in lab_to_num(y_test)]
pred_roc = [1 if label in num_label else 0 for label in lab_to_num(y_pred)]
# Compute ROC curve
fpr, tpr, threshold = roc_curve(test_roc, pred_roc)
# Compute AUC (Area Under the Curve)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
# Plot ROC curve
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='b', lw=2, label=f"AUC = {roc_auc:.2f}")
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='gray', linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.ylim([-0.05, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate (FPR)')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate (TPR)')
plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve')
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.show()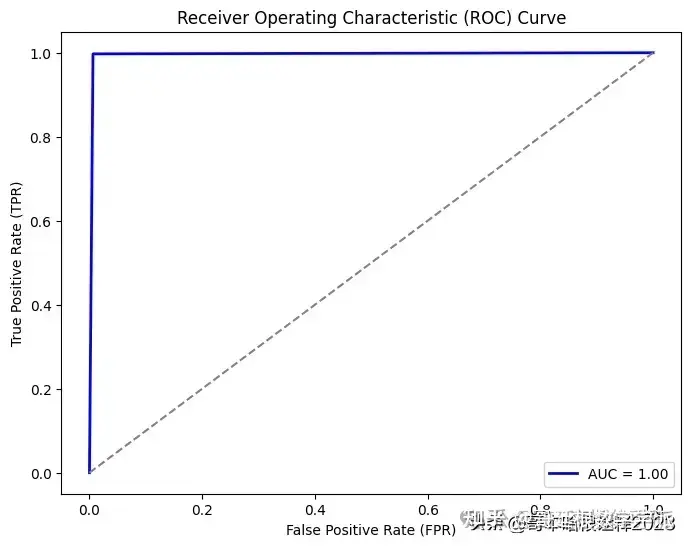
擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。
知乎学术咨询:https://www.zhihu.com/consult/people/792359672131756032?isMe=1
擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。