回归的流程与分类基本一致,只需要把评估指标改动一下就行。回归输出的是损失曲线、R^2曲线、训练集预测值与真实值折线图、测试集预测值散点图与真实值折线图。输出效果如下:
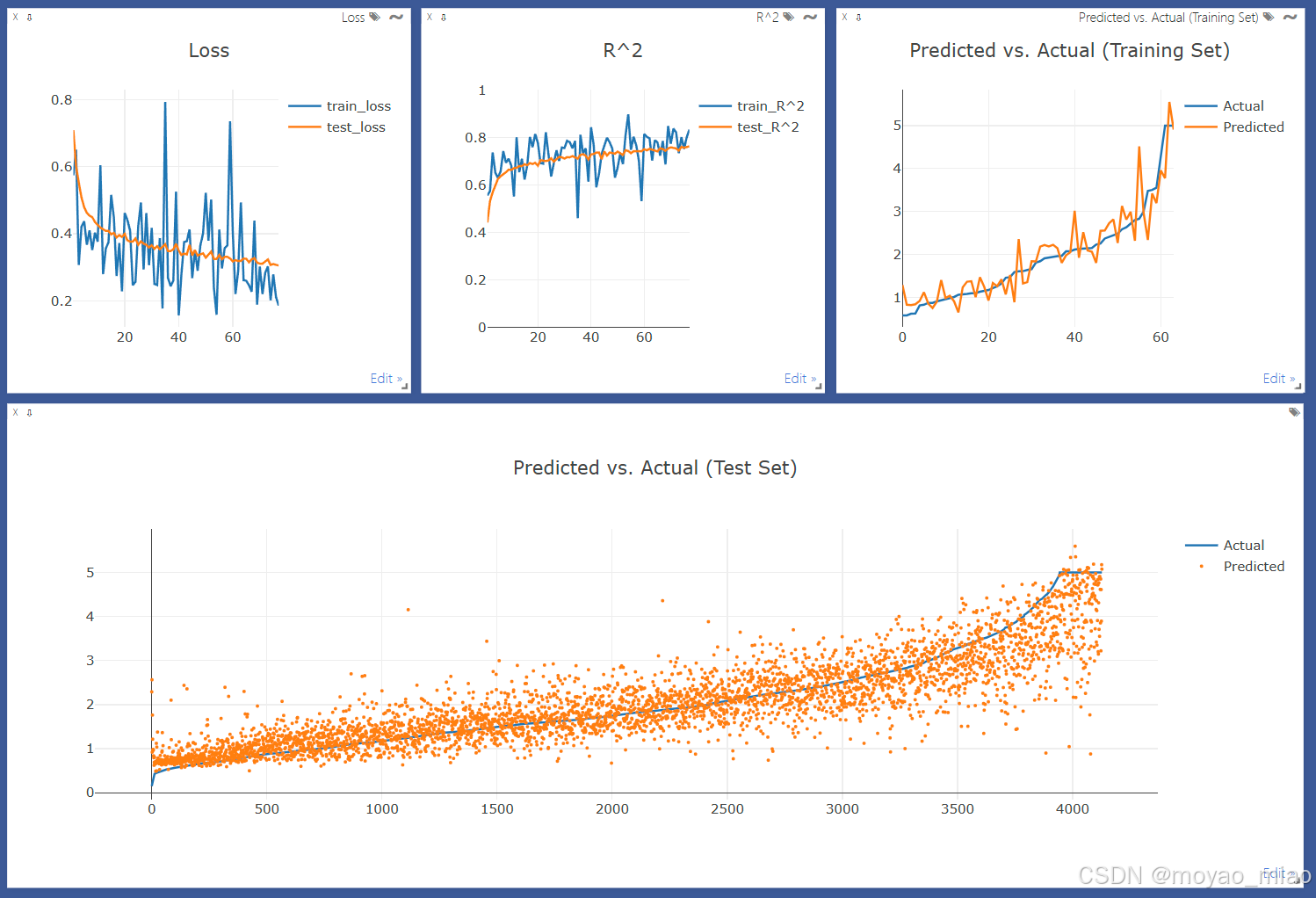
注意:预测值与真实值图像处理为按真实值排序,图中呈现的升序与数据集趋势无关。
代码如下:
python
from functools import partial
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import label_binarize
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, roc_curve, r2_score
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset, Dataset
from visdom import Visdom
from typing import Union, Optional
from sklearn.base import TransformerMixin
from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
def regress(
data: tuple[Union[np.ndarray, Dataset], Union[np.ndarray, Dataset]],
model: nn.Module,
optimizer: Optimizer,
criterion: nn.Module,
scaler: Optional[TransformerMixin] = None,
batch_size: int = 64,
epochs: int = 10,
device: Optional[torch.device] = None
) -> nn.Module:
"""
回归任务的训练函数。
:param data: 形如(X,y)的np.ndarray类型,及形如(train_data,test_data)的torch.utils.data.Dataset类型
:param model: 回归模型
:param optimizer: 优化器
:param criterion: 损失函数
:param scaler: 数据标准化器
:param batch_size: 批大小
:param epochs: 训练轮数
:param device: 训练设备
:return: 训练好的回归模型
"""
if isinstance(data[0], np.ndarray):
X, y = data
# 分离训练集和测试集,指定随机种子以便复现
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 数据标准化
if scaler is not None:
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 转换为tensor
X_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train.astype(np.float32))
X_test = torch.from_numpy(X_test.astype(np.float32))
y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train.astype(np.float32))
y_test = torch.from_numpy(y_test.astype(np.float32))
# 将X和y封装成TensorDataset
train_dataset = TensorDataset(X_train, y_train)
test_dataset = TensorDataset(X_test, y_test)
elif isinstance(data[0], Dataset):
train_dataset, test_dataset = data
else:
raise ValueError('Unsupported data type')
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=2,
)
test_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=2,
)
model.to(device)
vis = Visdom()
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(epochs):
for step, (batch_x_train, batch_y_train) in enumerate(train_loader):
batch_x_train = batch_x_train.to(device)
batch_y_train = batch_y_train.to(device)
# 前向传播
output = model(batch_x_train)
loss = criterion(output, batch_y_train)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
niter = epoch * len(train_loader) + step + 1 # 计算迭代次数
if niter % 100 == 0:
# 评估模型
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
eval_dict = {
'test_loss': [],
'test_r2': [],
'y_test': [],
'y_pred': [],
}
for batch_x_test, batch_y_test in test_loader:
batch_x_test = batch_x_test.to(device)
batch_y_test = batch_y_test.to(device)
test_output = model(batch_x_test)
test_predicted_tuple = (batch_y_test.numpy(), test_output.numpy())
# 计算并记录损失、R^2、真实值、预测值
eval_dict['test_loss'].append(criterion(test_output, batch_y_test))
eval_dict['test_r2'].append(r2_score(*test_predicted_tuple))
eval_dict['y_test'].append(batch_y_test)
eval_dict['y_pred'].append(test_output)
# 画出损失曲线
vis.line(
X=torch.ones((1, 2)) * (niter // 100),
Y=torch.stack((loss, torch.mean(torch.tensor(eval_dict['test_loss'])))).unsqueeze(0),
win='loss',
update='append',
opts=dict(title='Loss', legend=['train_loss', 'test_loss']),
)
# 画出R^2曲线
train_r2 = r2_score(batch_y_train.numpy(), output.numpy())
vis.line(
X=torch.ones((1, 2)) * (niter // 100),
Y=torch.tensor((train_r2, np.mean(eval_dict['test_r2']))).unsqueeze(0),
win='R^2',
update='append',
opts=dict(title='R^2', legend=['train_R^2', 'test_R^2'], ytickmin=0, ytickmax=1),
)
# 画出训练集预测值和真实值折线图
sorted_train_idx = torch.argsort(batch_y_train) # 按真实值排序
vis.line(
X=torch.arange(batch_size).repeat(2, 1).t(),
Y=torch.stack((batch_y_train[sorted_train_idx], output[sorted_train_idx]), dim=1),
win='batch_train_line',
opts=dict(title='Predicted vs. Actual (Train Set)', legend=['Actual', 'Predicted']),
)
# 画出测试集预测值散点图和真实值折线图
x = list(range(len(y_test)))
y_test = torch.cat(eval_dict['y_test'])
y_pred = torch.cat(eval_dict['y_pred'])
sorted_test_idx = torch.argsort(y_test)
vis._send({
'data': [
{'x': x, 'y': y_test[sorted_test_idx].tolist(), 'type': 'custom', 'mode': 'lines', 'name': 'Actual'},
{'x': x, 'y': y_pred[sorted_test_idx].tolist(), 'type': 'custom', 'mode': 'markers', 'name': 'Predicted', 'marker': {'size': 3}}
],
'win': 'test_line',
'layout': {'title': 'Predicted vs. Actual (Test Set)'},
})
return model