Description
You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array queries.
There are n cities numbered from 0 to n - 1. Initially, there is a unidirectional road from city i to city i + 1 for all 0 <= i < n - 1.
queries[i] = [ui, vi] represents the addition of a new unidirectional road from city ui to city vi. After each query, you need to find the length of the shortest path from city 0 to city n - 1.
There are no two queries such that queries[i][0] < queries[j][0] < queries[i][1] < queries[j][1].
Return an array answer where for each i in the range [0, queries.length - 1], answer[i] is the length of the shortest path from city 0 to city n - 1 after processing the first i + 1 queries.
Example 1:
Input: n = 5, queries = [[2,4],[0,2],[0,4]]
Output: [3,2,1]
Explanation: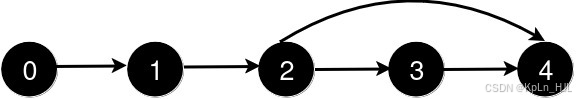
After the addition of the road from 2 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 3.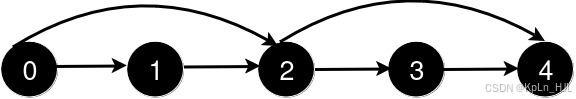
After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 2.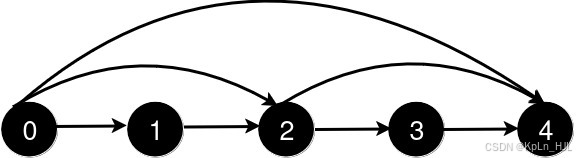
After the addition of the road from 0 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 1.Example 2:
Input: n = 4, queries = [[0,3],[0,2]]
Output: [1,1]
Explanation: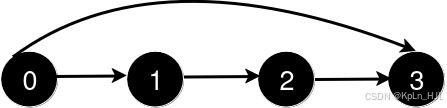
After the addition of the road from 0 to 3, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 3 is 1.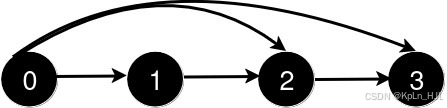
After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path remains 1.Solution
Similar to 3243. Shortest Distance After Road Addition Queries I, but this time with more data and an additional rule: no overlapped queries.
So we have a tricky way to solve this, because we don't have overlapped queries, so we could just drop the nodes between each query. And the length of the graph would be our answer.
Here we use a hash map to denote the graph.
Time complexity: o ( n + q ) o(n+q) o(n+q)
Space complexity: o ( n ) o(n) o(n)
Code
python3
class Solution:
def shortestDistanceAfterQueries(self, n: int, queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
neighbors = {i: i + 1 for i in range(n - 1)}
res = []
for each_query in queries:
start_city, end_city = each_query
# if start_city is in the graph and the new query gives us a shorter way
if start_city in neighbors and neighbors[start_city] < end_city:
cur_city = neighbors[start_city]
while cur_city < end_city:
cur_city = neighbors.pop(cur_city)
neighbors[start_city] = end_city
res.append(len(neighbors))
return res