目录
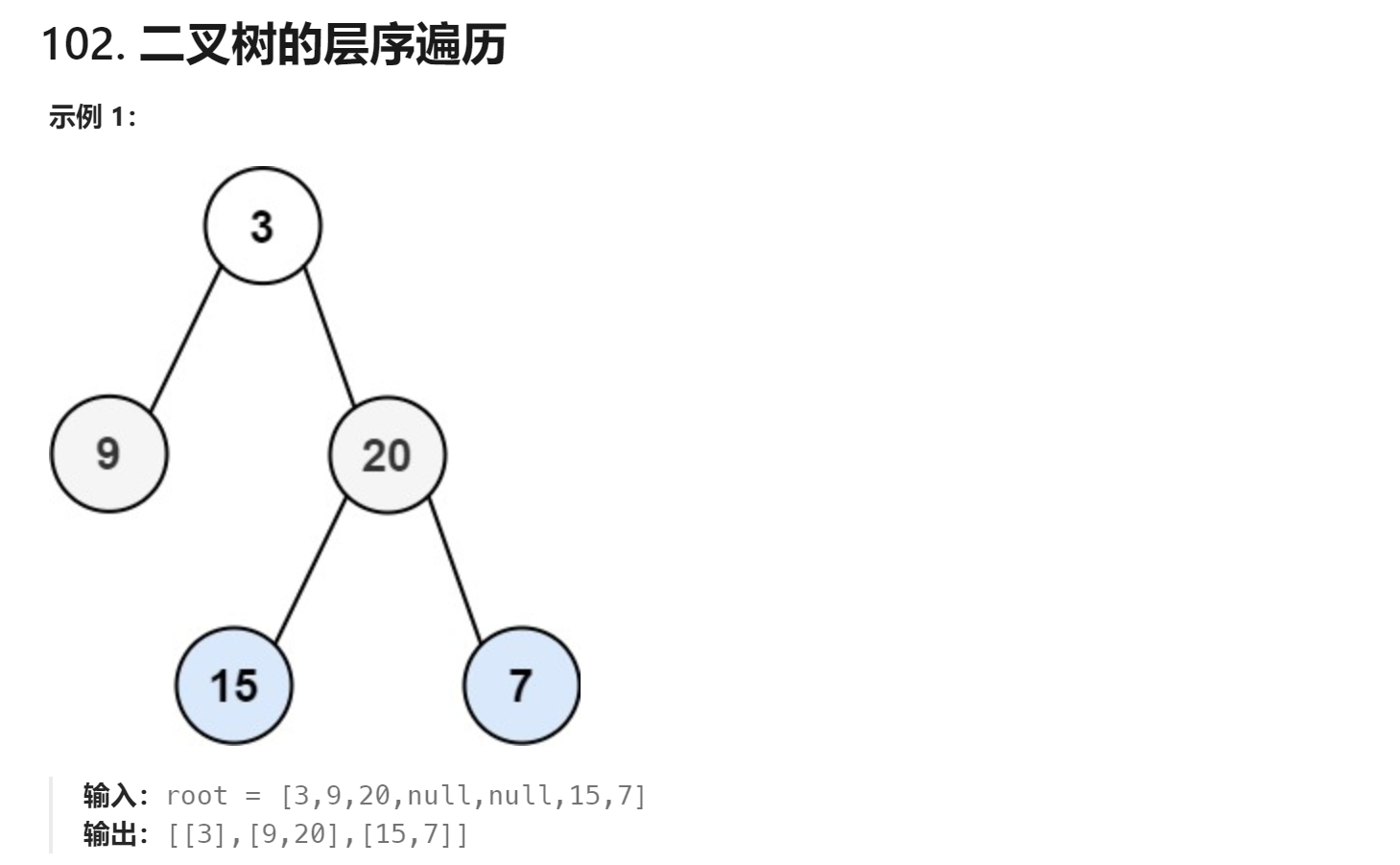
1、二叉树的层次遍历
oj:102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
java
// 标准层次遍历
void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
if(cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
java
// 符合力扣题目的层次遍历
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder2(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);//A
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();//1
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
while (size != 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
//System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
tmp.add(cur.val);
size--;//0
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
ret.add(tmp);
}
return ret;
}2、判断是不是完全二叉树
思路:
与层次遍历不同的是,结点的左右子树为null,null也有入队
出队时若遇到null,则跳出循环
再判断队列中是否还有不为空的元素,有则不是完全二叉树,全为空则是
注:队列中的元素全为空,队列不为空,有几个元素 大小就是几
java
// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else {
break;//结束这个循环
}
}
//需要判断队列当中 是否有非空的元素
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//一个元素 一个元素 出队来判断 是不是空
TreeNode tmp = queue.peek();
if(tmp == null) {
queue.poll();
}else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}3、两个结点的最近公共祖先
oj:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)

思路:
- 如果root是p或q中的一个,那么root就是最近公共祖先
- 如果p和q分布在root的左右两侧,那么root就是最近公共祖先
- p和q在root的同一侧,递归左右子树,遇到p或q就返回,左边为空右边不为空,最近公共祖先就是右边这个不为空的值,反之亦然
- p和q在root的同一侧,在下图的这种情况,返回的右边不为空的值是root
java
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
TreeNode leftTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightTree = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftTree != null && rightTree != null) {
return root;
}else if(leftTree != null) {
return leftTree;
}else {
return rightTree;
}
}思路2:
把根节点到p和q路径上的所有节点使用栈保存下来
比较两个栈的大小,大的出栈两个栈的差值次
然后依次对两个栈的栈顶元素比较,不相同则一起出栈,相同则是公共祖先
java
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stackP = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackQ = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stackP);
getPath(root,q,stackQ);
int sizeP = stackP.size();
int sizeQ = stackQ.size();
if(sizeP > sizeQ) {
int size = sizeP - sizeQ;
while(size != 0) {
stackP.pop();
size--;
}
}else {
int size = sizeQ - sizeP;
while(size != 0) {
stackQ.pop();
size--;
}
}
//两个栈当中的元素是一样多
while(!stackP.isEmpty() && !stackQ.isEmpty()) {
if(stackP.peek() == stackQ.peek()) {
return stackP.peek();
}else{
stackP.pop();
stackQ.pop();
}
}
return null;
}
private boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack) {
if(root == null || node == null) {
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if(root == node) {
return true;
}
boolean flg = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(flg) {
return true;
}
boolean flg2 = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(flg2) {
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}4、根据前序与中序构造二叉树
oj:105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
下方代码中成员变量 preIndex 之所以不用static修饰,是因为被static修饰的成员变量 只有一份,他是和很多对象共享的。如果题目只有一个测试用例可以用static修饰
java
class SolutionCreateTree {
static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public int preIndex ;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
private TreeNode buildTreeChilde(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;//没有 左树 或者 没有 右树
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
int rootIndex = findIndexRoot(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
preIndex++;
root.left = buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreeChilde(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
private int findIndexRoot(int[] inorder,int inbegin, int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin; i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}5、根据后序与中序构造二叉树
oj:106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
java
class SolutionCreateTree2 {
public int postIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
postIndex = postorder.length-1;
return buildTreeChilde(postorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
private TreeNode buildTreeChilde(int[] postorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;//没有 左树 或者 没有 右树
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
int rootIndex = findIndexRoot(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);
if(rootIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
postIndex--;
root.right = buildTreeChilde(postorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
root.left = buildTreeChilde(postorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
return root;
}
private int findIndexRoot(int[] inorder,int inbegin, int inend,int key) {
for(int i = inbegin; i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}6、根据二叉树创建字符串
oj:606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
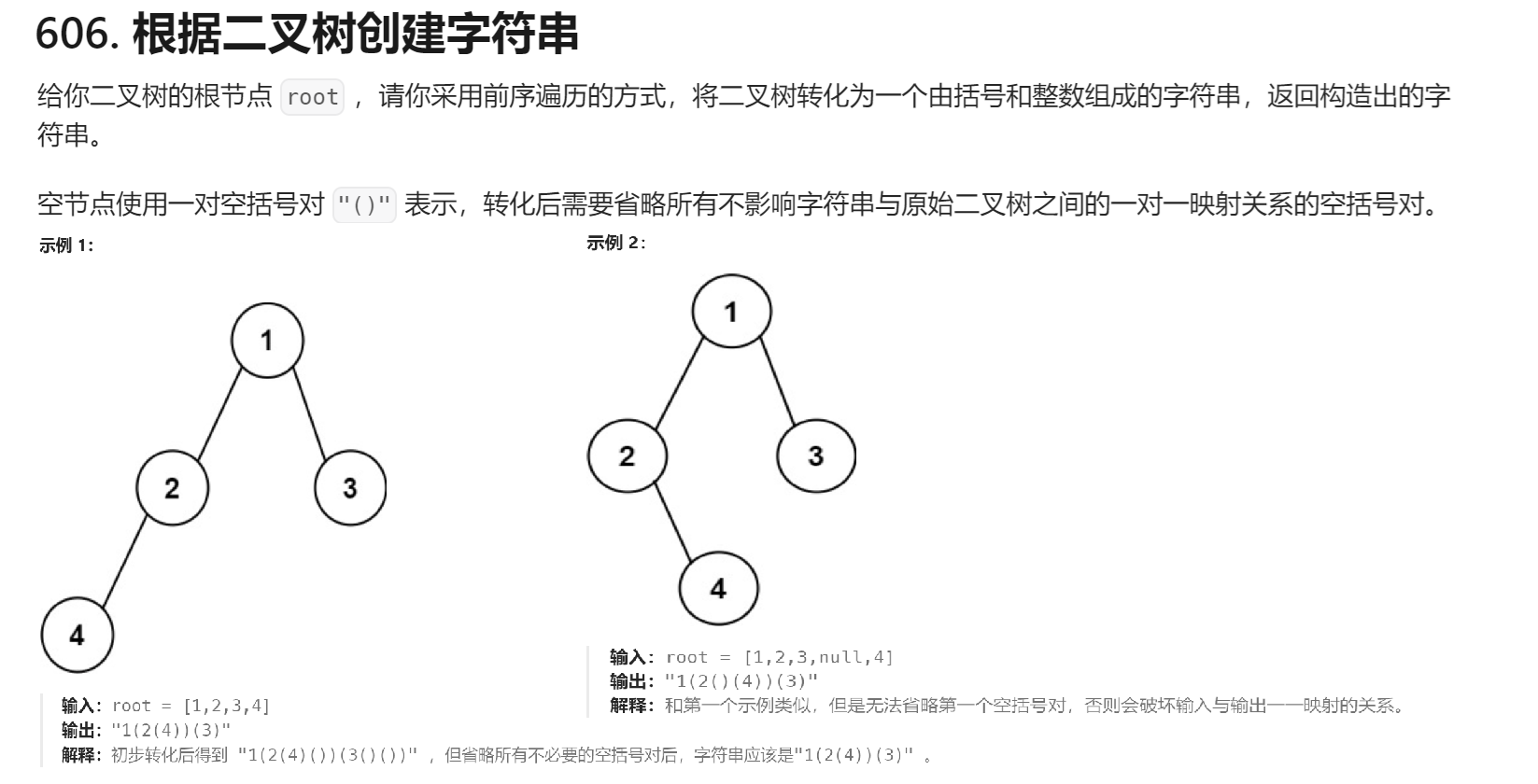
思路:
大方向:采用前序遍历的方式进行遍历
根节点直接拼接
左边为空&&右边为空的时候什么都不做
左边不为空 右边为空,对左边递归
左边为空 右边不为空,对左边加一对括号,对右边递归
java
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
tree2strChild(root,stringBuilder);
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
private void tree2strChild(TreeNode t,StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
if(t == null) {
return ;
}
stringBuilder.append(t.val);
if(t.left != null) {
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.left,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else {
if(t.right == null) {
return;
}else {
stringBuilder.append("()");
}
}
//判断右树
if(t.right != null) {
stringBuilder.append("(");
tree2strChild(t.right,stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.append(")");
}else {
return;
}
}7、二叉树前序非递归遍历实现
oj:144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
java
void preOrderNor(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
cur = top.right;
}
}8、二叉树中序非递归遍历实现
oj:94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
一直往左走遇到空停止,左树走完了弹出栈顶元素、并且打印
遍历弹出节点的右子树
java
void inOrderNor(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.pop();
System.out.print(top.val + " ");
cur = top.right;
}
}9、二叉树后序非递归遍历实现
oj:145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
java
void postOrderNor(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
// prev用于记录最新被打印的节点
TreeNode prev = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if(top.right == null || top.right == prev) {
System.out.print(top.val+" ");
stack.pop();
prev = top;
}else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
}



