在上一篇文章中,详细介绍了工具调用的基本流程,以及创建工具的几种方式,工具创建完成后,下一步就是让大语言模型(LLM)进行工具调用。
可能第一次听到工具调用的同学,会认为是LLM直接调用了工具本身,实际上并非如此,LLM只会根据用户提问,给出要调用的工具并生成调用工具的参数,实际是否调用工具,由应用本身决定。
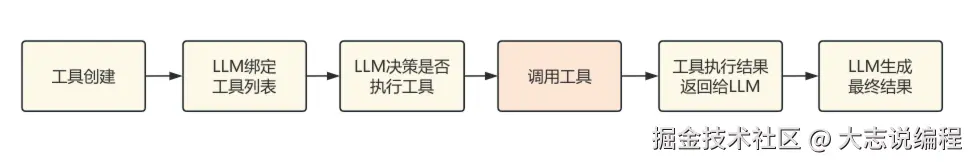
整个工具调用基本流程如下,本文将会对如何让LLM完成工具调用进行详细的介绍。
文中所有示例代码:github.com/wzycoding/l...
一、工具创建
首先,创建一个根据IP获取用户地理位置信息的工具,这个工具调用高德地图的IP定位API,该API文档地址如下:
高德地图IP定位:lbs.amap.com/api/webserv...
在.env文件中配置高德开放平台API KEY
properties
# 高德开放平台API KEY
GAODE_API_KEY=***************************之后,通过继承BaseTool类的方式创建工具,在_run方法中实现工具逻辑,实际上就是调用指定API,传递IP地址和API KEY即可,具体大家结合文档理解。
python
class GaoDeIPLocationInput(BaseModel):
"""IP定位入参"""
ip: str = Field(description="ip地址")
class GaoDeIPLocationTool(BaseTool):
"""根据IP定位位置工具"""
name = "ip_location_tool"
description = "当你需要根据IP,获取定位信息时,可以调用这个工具"
args_schema = GaoDeIPLocationInput
def _run(self, ip: str) -> str:
api_key = os.getenv("GAODE_API_KEY")
if api_key is None:
return "请配置GAODE_API_KEY"
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/ip?ip={ip}&key={key}".format(ip=ip, key=api_key)
session = requests.session()
response = session.request(
method="GET",
url=url,
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8"},
)
result = response.json()
return result.get("province") + result.get("city")
另一个工具是此前已经创建过的工具:加法计算器,具体实现代码如下:
python
class AddNumberInput(BaseModel):
"""加法工具入参"""
num1: int = Field(description="第一个数")
num2: int = Field(description="第二个数")
class AddNumberTool(BaseTool):
"""加法工具"""
name = "add_number_tool"
description = "两数相加工具"
args_schema = AddNumberInput
def _run(self, num1: int, num2: int) -> int:
return num1 + num2创建这两个工具的对象,并把它们放到一个字典当中,key是工具的名称,value是工具对象,这样做的原因是方便后面LLM返回工具调用信息,可以根据工具名称获取工具对象,从而进行工具调用,后面会详细解释。
python
# 创建工具对象
add_number_tool = AddNumberTool()
gaode_ip_location_tool = GaoDeIPLocationTool()
tools_dict = {
add_number_tool.name: add_number_tool,
gaode_ip_location_tool.name: gaode_ip_location_tool,
}二、工具绑定
在进行工具调用之前,需要先使用.bind_tools()方法将工具列表绑定到LLM对象上,只有绑定了工具列表的LLM,LLM在执行过程中才知道可以调用哪些工具、参数有哪些。
这里一定要注意使用新的变量llm_with_tool接收,并且后续调用中使用llm_with_tool,如果继续使用llm进行调用,是无法触发大模型返回工具调用参数的。
python
# 1.创建Prompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system",
"你是一个智能助手,可以帮助用户解决问题。当问题需要使用工具时,必须调用提供的工具,并一次性调用所有必要工具,避免分步调用。"),
("human", "{query}"),
])
# 2.创建LLM并绑定工具
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o")
llm_with_tool = llm.bind_tools(tools=[tool for tool in tools_dict.values()])三、调用工具
完成工具绑定之后,构建并调用chain,传递query查询,LLM会返回一个AIMessage,在消息内部如果需要调用工具会返回tool_calls列表,里面包含要tool_call_id(工具调用的唯一id标识)、调用工具的名字、生成的调用参数等信息。
python
# 3.创建链
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
# 4.调用链
query = "帮我查询一下IP为122.234.134.158用户的位置"
resp = chain.invoke({"query": query})
print("LLM生成内容:", resp.content)
print("LLM生成调用信息:", resp.tool_calls)接下来,构建一个消息列表messages,把之前渲染模板的消息列表保存messages,这个列表的作用是将这些历史消息以及调用工具生成的工具消息,一起发送给LLM生成回答。
保存好消息记录后,通过判断AIMessage中的tool_calls是否为None判断是否存在工具调用,如果存在工具调用,则遍历tools_calls,取出每一个tool_call,根据tool_call里面的name属性,获取对应的工具对象。
接下来,调用工具并传入tool_call中的args属性中生成的参数,接收工具调用结果,构建一个ToolMessage,即工具消息,ToolMessage包含tool_call_id、工具调用结果,最后,将工具消息添加到messages消息列表中。
python
# 5.构建消息列表,插入AI返回的AIMessage
messages = prompt.invoke({"query": query}).to_messages()
messages.append(resp)
# 6.判断是否需要工具调用
if resp.tool_calls is None:
print(resp.content)
else:
# 7.遍历工具调用信息
for tool_call in resp.tool_calls:
# 8.根据调用的工具名称获取工具对象
print("工具{tool_name}调用信息:{tool_call}".format(tool_name=tool_call.get("name"), tool_call=tool_call))
target_tool = tools_dict.get(tool_call.get("name"))
# 9.执行工具调用
result = target_tool.invoke(tool_call.get("args"))
print("工具{tool_name}调用结果:{result}".format(tool_name=target_tool.name, result=result))
tool_call_id = tool_call.get("id")
# 10.创建工具消息
tool_message = ToolMessage(
tool_call_id=tool_call_id,
content=result,
)
# 11.将工具消息添加到消息列表中
messages.append(tool_message)四、返回调用结果给大模型
最后,将包含工具消息的messages消息列表传递给LLM,大模型输出最终结果。
python
print("最终结果:" + llm.invoke(messages).content)执行结果如下,执行结果符合我们的预期
python
LLM生成内容:
LLM生成调用信息: [{'name': 'ip_location_tool', 'args': {'ip': '122.234.134.158'}, 'id': 'call_R36kxZo9S78PlOakiXk6Ib0M', 'type': 'tool_call'}]
工具ip_location_tool调用信息:{'name': 'ip_location_tool', 'args': {'ip': '122.234.134.158'}, 'id': 'call_R36kxZo9S78PlOakiXk6Ib0M', 'type': 'tool_call'}
工具ip_location_tool调用结果:浙江省杭州市
最终结果:IP地址为122.234.134.158的用户位于中国浙江省杭州市。完整案例代码如下:
python
import os
import dotenv
import requests
from langchain_core.messages import ToolMessage
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic.v1 import BaseModel, Field
# 读取env配置
dotenv.load_dotenv()
class GaoDeIPLocationInput(BaseModel):
"""IP定位入参"""
ip: str = Field(description="ip地址")
class GaoDeIPLocationTool(BaseTool):
"""根据IP定位位置工具"""
name = "ip_location_tool"
description = "当你需要根据IP,获取定位信息时,可以调用这个工具"
args_schema = GaoDeIPLocationInput
def _run(self, ip: str) -> str:
api_key = os.getenv("GAODE_API_KEY")
if api_key is None:
return "请配置GAODE_API_KEY"
url = "https://restapi.amap.com/v3/ip?ip={ip}&key={key}".format(ip=ip, key=api_key)
session = requests.session()
response = session.request(
method="GET",
url=url,
headers={"Content-Type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8"},
)
result = response.json()
return result.get("province") + result.get("city")
class AddNumberInput(BaseModel):
"""加法工具入参"""
num1: int = Field(description="第一个数")
num2: int = Field(description="第二个数")
class AddNumberTool(BaseTool):
"""加法工具"""
name = "add_number_tool"
description = "两数相加工具"
args_schema = AddNumberInput
def _run(self, num1: int, num2: int) -> int:
return num1 + num2
# 创建工具对象
add_number_tool = AddNumberTool()
gaode_ip_location_tool = GaoDeIPLocationTool()
tools_dict = {
add_number_tool.name: add_number_tool,
gaode_ip_location_tool.name: gaode_ip_location_tool,
}
# 1.创建Prompt
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system",
"你是一个智能助手,可以帮助用户解决问题。当问题需要使用工具时,必须调用提供的工具,并一次性调用所有必要工具,避免分步调用。"),
("human", "{query}"),
])
# 2.创建LLM并绑定工具
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o")
llm_with_tool = llm.bind_tools(tools=[tool for tool in tools_dict.values()])
# 3.创建链
chain = prompt | llm_with_tool
# 4.调用链
query = "帮我查询一下IP为122.234.134.158用户的位置"
resp = chain.invoke({"query": query})
print("LLM生成内容:", resp.content)
print("LLM生成调用信息:", resp.tool_calls)
# 5.构建消息列表,插入AI返回的AIMessage
messages = prompt.invoke({"query": query}).to_messages()
messages.append(resp)
# 6.判断是否需要工具调用
if resp.tool_calls is None:
print(resp.content)
else:
# 7.遍历工具调用信息
for tool_call in resp.tool_calls:
# 8.根据调用的工具名称获取工具对象
print("工具{tool_name}调用信息:{tool_call}".format(tool_name=tool_call.get("name"), tool_call=tool_call))
target_tool = tools_dict.get(tool_call.get("name"))
# 9.执行工具调用
result = target_tool.invoke(tool_call.get("args"))
print("工具{tool_name}调用结果:{result}".format(tool_name=target_tool.name, result=result))
tool_call_id = tool_call.get("id")
# 10.创建工具消息
tool_message = ToolMessage(
tool_call_id=tool_call_id,
content=result,
)
# 11.将工具消息添加到消息列表中
messages.append(tool_message)
print("最终结果:" + llm.invoke(messages).content)五、总结
本文从 工具创建 、LLM工具绑定 、调用工具 、 返回调用结果给LLM 、LLM生成最终结果,完整展示了LLM工具调用的全过程。
其中,需要特别注意以下几点:
- LLM 本身并不会直接执行工具,它的作用是决定是否调用工具、调用哪个工具和生成调用参数,实际的工具调用逻辑由应用本身控制。
- 即使绑定了工具,大模型也不一定会调用工具,是否调用工具、如何调用工具是由LLM本身决定的,
- 在调用工具完成之后,传递工具消息时,必须传递原始工具调用传入的
tool_call_id,这样LLM才能将工具调用结果与工具调用请求相匹配。
通过本文,相信你已经掌握了如何通过LLM进行工具调用,其实本文的案例代码就是一个Agent智能体的雏形,在下一篇文章中,将会对LangChain中的Agent智能体进行详细介绍,欢迎持续关注。