机器学习:线性回归
线性回归
线性回归的概念
线性回归是一种强大但有限制性的算法。当特征与整体的目标值呈现较强的线性关系时,可以使用线性回归进行拟合。但是需要说明,线性回归中,"线性"指的是参数是线性的,不是特征必须是线性的。例如:
y = w 1 x 1 + w 2 x 2 + b ( 1 ) y=w_1x_1+w_2x_2+b\quad \quad\quad\quad\quad\quad(1) y=w1x1+w2x2+b(1)
y = w 1 w 2 x 1 + w 3 x 2 + b ( 2 ) y=w_1w_2x_1+w_3x_2+b\quad \quad\quad\quad\quad(2) y=w1w2x1+w3x2+b(2)
y = w 1 x 2 + w 2 x 2 + b ( 3 ) y=w_1x^2+w_2x_2+b\quad\quad\quad\quad \quad\quad(3) y=w1x2+w2x2+b(3)
上述三个式子中,只有(2)是非线性的,而对于多项式拟合,也属于线性回归的一种。
损失函数的度量
损失函数指用来衡量预测值和真实值之间的偏差,在回归任务中,通常用均方误差(Mean Square Error,以下简称MSE)来衡量模型的预测能力。其计算方式如下:
M S E = ∑ i = 1 n ( y i − y i p ) 2 MSE=\sum_{i=1}^{n} (y_i-y^p_i)^2 MSE=i=1∑n(yi−yip)2
其中, y i y_i yi为实际值, y i p y^p_i yip为预测值。
优化函数
优化函数的目标是:找到让损失函数最小化的模型参数 。
主要有两种优化函数,即Adam和SGD
1.SGD随机梯度下降
SGD全称stochastic gradient descent,即随机梯度下降。其主要根据损失函数对各个参数的梯度来更新参数。随机梯度下降中的"随机",指的是在对损失函数优化时,主要是沿着梯度的反方向进行优化,如果对整个训练集上的数据求解梯度,代价太大,此时一般会随机选取b个样本,使用这b个样本的损失来求解梯度。简化运算量 。其主要学习以下两个内容:
1.梯度方向:参数应该向哪个方向能够减少损失
2.更新步长:学习率控制每次更新的幅度
2.Adam自适应学习率
Adam全称adaptive moment estimation,即自适应学习率。不仅学习梯度的方向,还学习每个参数的最佳学习率。主要学习以下三个内容:
1.梯度方向
2.梯度幅度(用于调整学习率)
3.每个参数独立的学习率
线性回归的实现
一元线性回归
使用sklearn实现
接下来,将从以下几个步骤进行实现:
①数据生成
②数据处理
③模型构建
④模型训练
⑤可视化
python
# 使用sklearn实现LineRegression
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error as MSE
# 1.数据生成
np.random.seed(42)
X = np.linspace(0,10,100).reshape(-1,1)
y = 1.5*X.ravel()+2+np.random.normal(0,1,100) # y=1.5x+2
# 2.数据处理
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,shuffle=True)
# 3.定义模型
model = LinearRegression()
# 4.模型训练
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
# 5.计算模型损失并可视化
X_train_pred = model.predict(X_train)
X_test_pred = model.predict(X_test)
train_mse = MSE(X_train_pred,y_train)
test_mse = MSE(X_test_pred,y_test)
print(f'目标函数为:y=1.5x+2,预测函数为:y={model.coef_[0]:.3f}x+{model.intercept_:.3f}')
print(f"测试集损失:{train_mse:.3f},训练集损失:{test_mse:.3f}")
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
pred_data = model.coef_[0]*X+model.intercept_
plt.scatter(X,y,label='Raw_Data')
plt.plot(X,pred_data,label='fit_line',color='red')
plt.legend()
plt.show()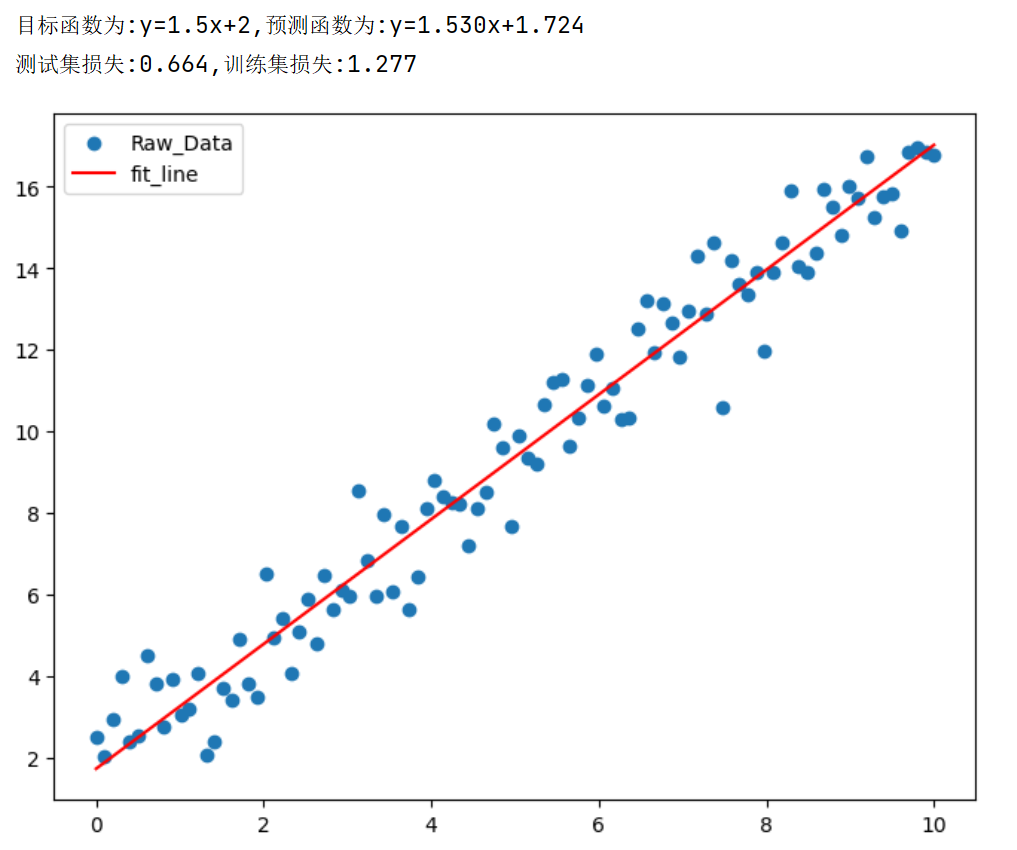
使用Pytorch实现
使用torch实现线性回归,从以下几个方面进行构建
①数据生成
②模型构建
③损失函数、优化器定义
④模型训练
⑥模型评估
⑦可视化
python
# 使用torch实现LineRegression
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
np.random.seed(42)
# 1.生成数据
X = np.linspace(-3,3,100).reshape(-1,1)
y = 3*X+2+np.random.normal(0,1,100).reshape(-1,1)
# 2.转换为tensor数据类型
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X,y,shuffle=True)
X_train_tensor = torch.from_numpy(X_train).float()
X_test_tensor = torch.from_numpy(X_test).float()
y_train_tensor = torch.from_numpy(y_train).float()
y_test_tensor = torch.from_numpy(y_test).float()
# 3.定义线性回归
class LineRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(1,1)
def forward(self,x):
output = self.linear(x)
return output
# 4.定义损失函数,优化器等
model = LineRegression()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.001) # 采用随机梯度下降
criterion = nn.MSELoss() # 使用均方误差
losses = [] # 记录训练误差
# 5.训练模型
epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(epochs):
outputs = model(X_train_tensor)
loss = criterion(outputs,y_train_tensor)
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.item())
if (epoch+1)%100==0:
print(f'{epoch+1}/{epochs},loss:{loss:.3f}')
# 可视化衡量
plt.figure(figsize=(12,5))
# 绘制损失函数
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(losses)
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.title('Loss of Epochs')
# 绘制拟合图形
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
weight = model.linear.weight.item()
bias = model.linear.bias.item()
pred_data = weight*X+bias
print(X.shape)
print(y.shape)
plt.scatter(X,y,label='Raw_Point')
plt.plot(X,pred_data,label='Fit_line',color='red')
plt.show()
# 查看模型预测的参数
print(f'线性回归结果为:y={model.linear.weight.item():.3f}x+{model.linear.bias.item():.3f}')
print(f'原直线为:y=3x+2')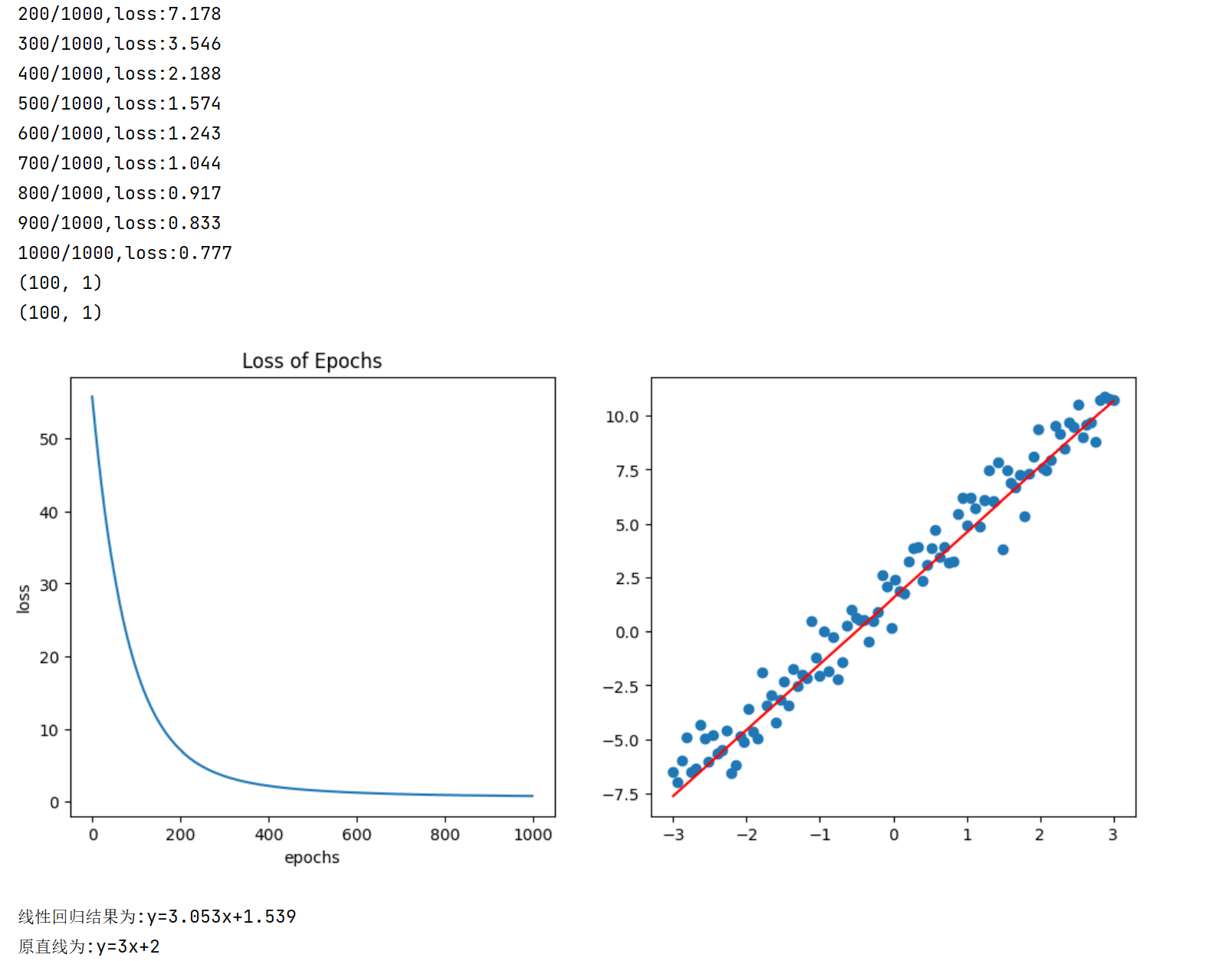
多项式回归
前面提过,多项式回归也属于线性回归。在这里,已三次函数为例,实现线性回归。
使用sklearn实现
python
# 使用sklearn实现多项式回归
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error as MSE
# np.random.seed(42)
# 1.生成数据
X = np.linspace(-3,3,100).reshape(-1,1)
y = 3*X.ravel()**3-2*X.ravel()**2+3*X.ravel()+1+np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=5,size=100) # y=3x^3-2x^2+3x+1
# 2.特征工程
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=3)
X_features = poly.fit_transform(X,y)
# 3.模型构建与拟合
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_features,y)
# 4.模型评估
pred = model.predict(X_features)
loss = MSE(pred,y)
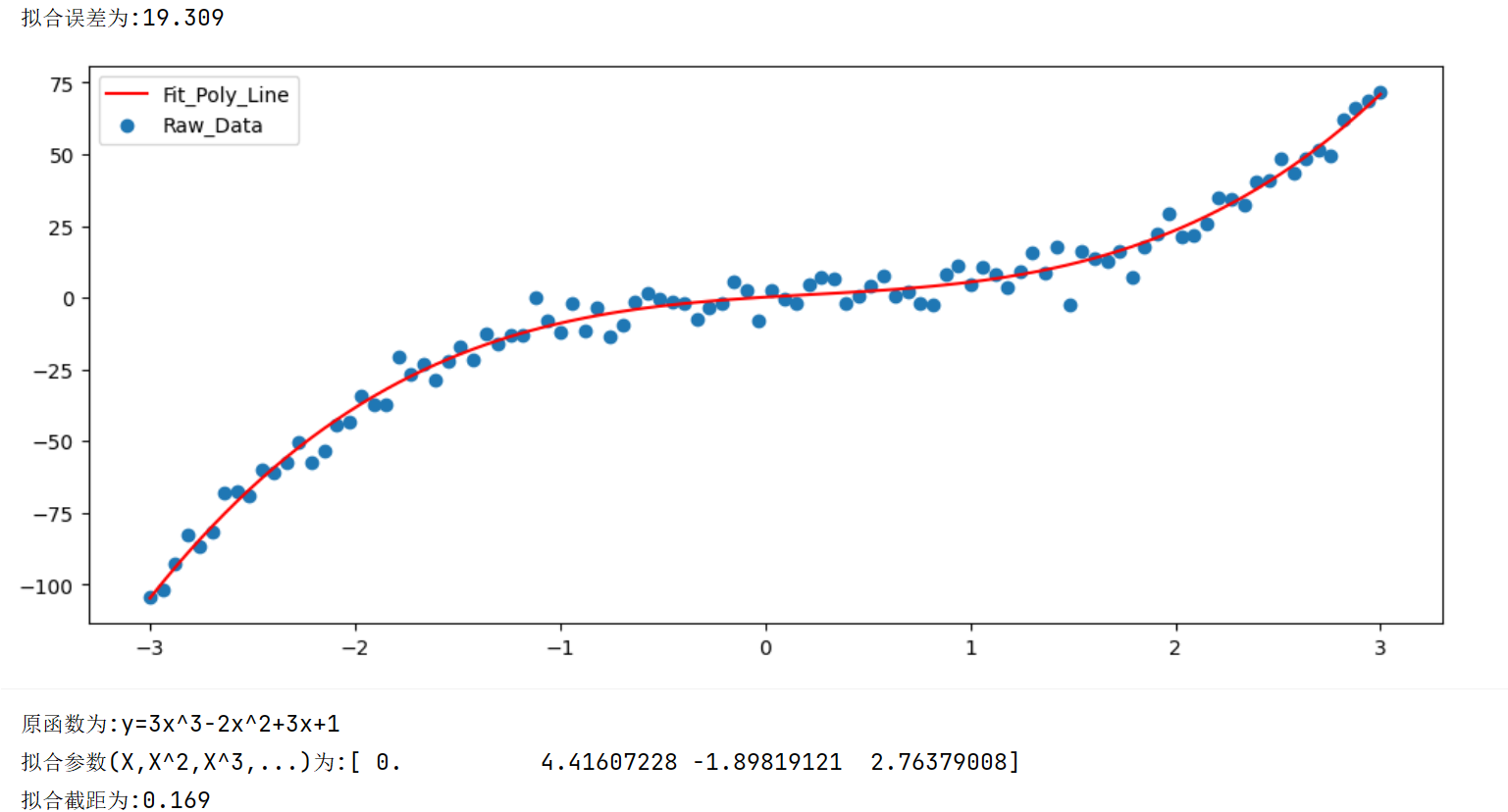
print(f"拟合误差为:{loss:.3f}")
# 5.可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(12,5))
plt.plot(X,pred,label='Fit_Poly_Line',color='red')
plt.scatter(X,y,label='Raw_Data')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 参数
print(f'原函数为:y=3x^3-2x^2+3x+1')
print(f'拟合参数(X,X^2,X^3,...)为:{model.coef_}')
print(f'拟合截距为:{model.intercept_:.3f}')输出结果如下:
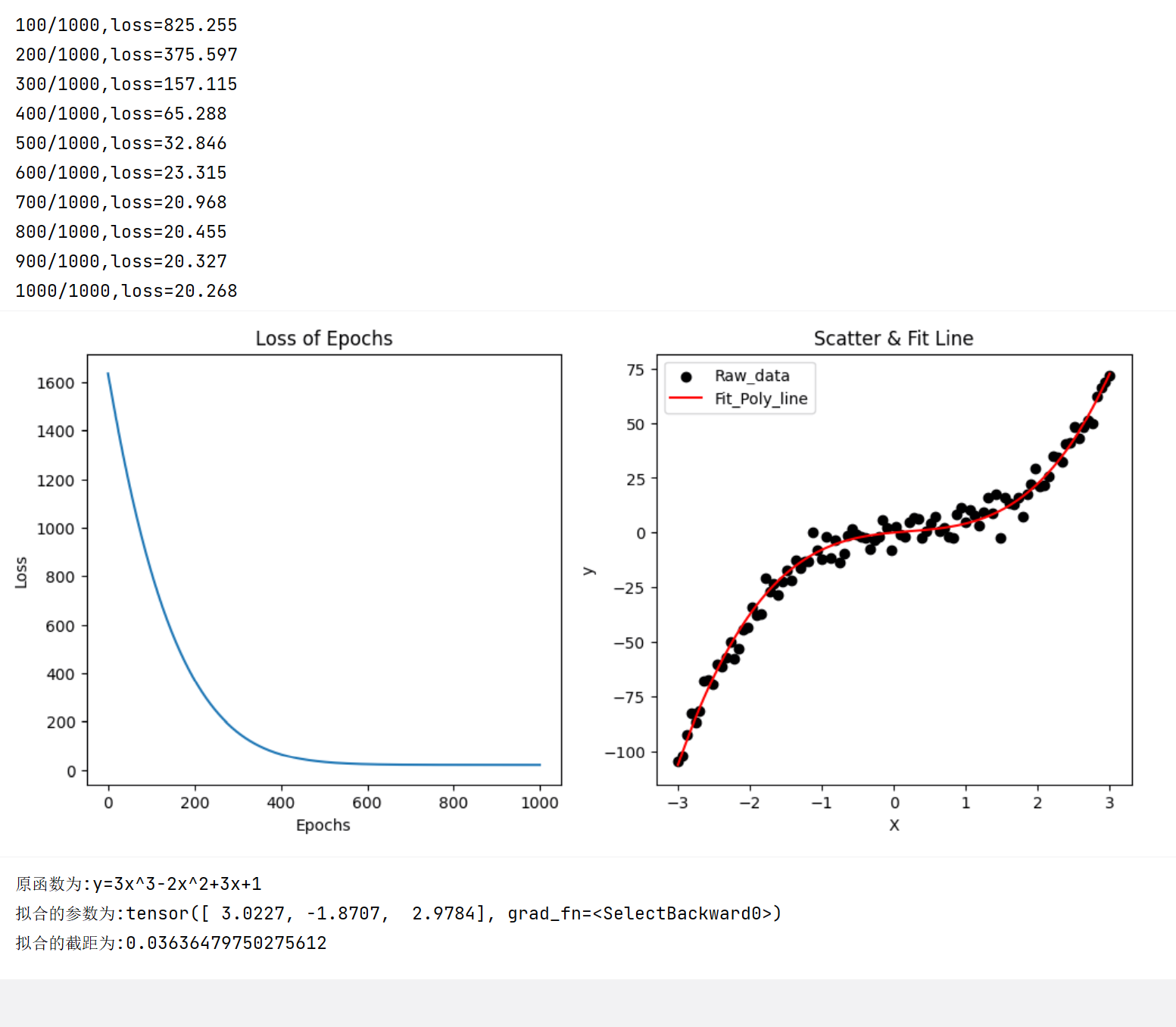
使用pytorch实现
使用pytorch更加灵活,能够调整参数以及训练轮次等信息。例如调整超参数degree可以拟合不同的次数
python
# 使用torch实现线性回归
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42)
# 1.生成数据
X = np.linspace(-3,3,100).reshape(-1,1)
y = 3*X.ravel()**3-2*X.ravel()**2+3*X.ravel()+1+np.random.normal(0,5,100) # y=3x^3-2x^2+3x+1
# 2.转换为tensor类型
X_tensor = torch.from_numpy(X).float().view(-1,1)
y_tensor = torch.from_numpy(y).float().view(-1,1)
# 3.定义模型
class PolyRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,degree):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(degree,1)
def forward(self,X):
poly_features = torch.cat([X**i for i in range(1,self.linear.in_features+1)],dim=1)
return self.linear(poly_features)
# 4.损失函数、优化器定义
degree = 3
model = PolyRegression(degree=degree)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.01)
losses = []
# 5.模型训练
epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 前向传播
outputs = model(X_tensor)
# 计算损失
loss = criterion(outputs,y_tensor)
# 反向传播优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
losses.append(loss.item())
if (epoch+1)%100==0:
print(f'{epoch+1}/{epochs},loss={loss:.3f}')
# 6.可视化
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = model(X_tensor)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.plot(losses)
plt.title('Loss of Epochs')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.scatter(X_tensor,y_tensor,label='Raw_data',color='black')
plt.plot(X_tensor,predictions,label='Fit_Poly_line',color='red')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Scatter & Fit Line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 7.参数输出
print(f'原函数为:y=3x^3-2x^2+3x+1')
print(f'拟合的参数为:{model.linear.weight[0]}')
print(f'拟合的截距为:{model.linear.bias.item()}')