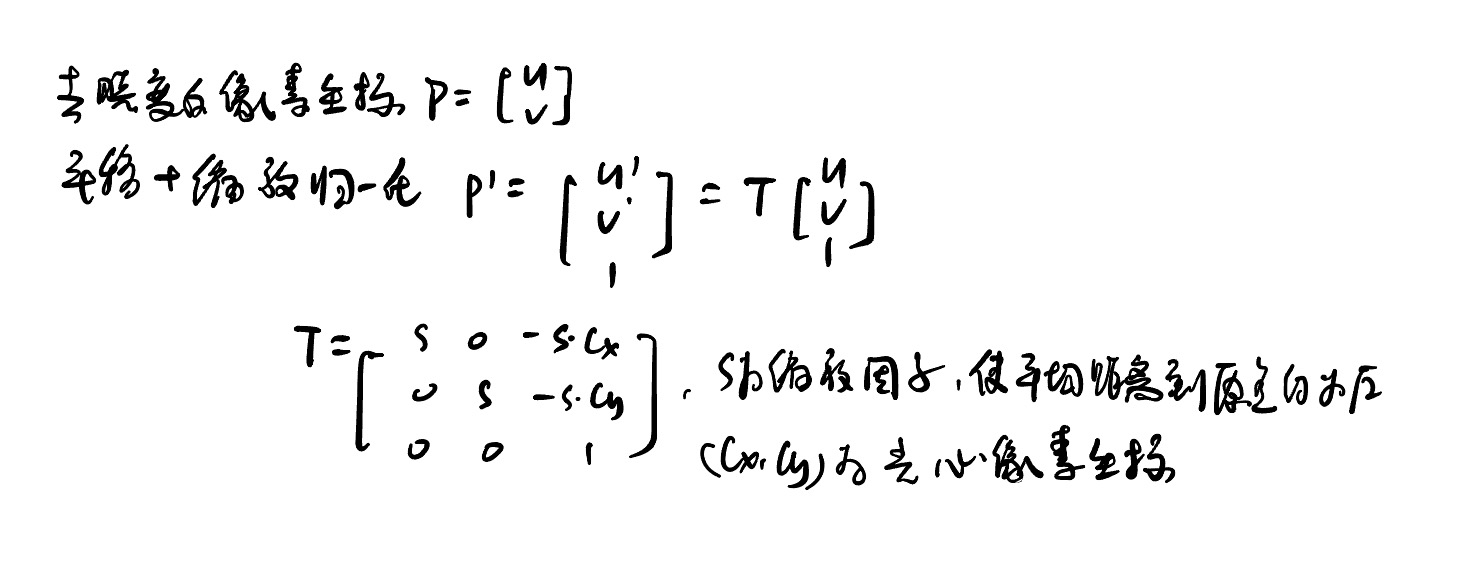目录
[1 单应矩阵](#1 单应矩阵)
[1.1 作用](#1.1 作用)
[1.2 参数及含义](#1.2 参数及含义)
[1.3 逻辑关系](#1.3 逻辑关系)
[1.4 代码](#1.4 代码)
[1.5 解析](#1.5 解析)
[1.5.1 准备阶段](#1.5.1 准备阶段)
[1.5.1.1 T矩阵说明](#1.5.1.1 T矩阵说明)
[1.5.1.2 Normalize() 函数说明,找到T矩阵](#1.5.1.2 Normalize() 函数说明,找到T矩阵)
[1.5.2 初始化变量](#1.5.2 初始化变量)
[1.5.3 RANSAC 主循环](#1.5.3 RANSAC 主循环)
[1.5.3.1 CheckHomography() 函数](#1.5.3.1 CheckHomography() 函数)
[2 基础矩阵](#2 基础矩阵)
[2.1 参数及含义](#2.1 参数及含义)
[2.2 代码](#2.2 代码)
[2.3 解析](#2.3 解析)
[2.3.1 初始化及归一化](#2.3.1 初始化及归一化)
[2.3.2 初始化结果和临时变量](#2.3.2 初始化结果和临时变量)
[2.3.3 RANSAC循环](#2.3.3 RANSAC循环)
为保证求解的可靠性,代码中求解与定义式有较大出入,详见如下。
1 单应矩阵
1.1 作用
计算单应矩阵H。
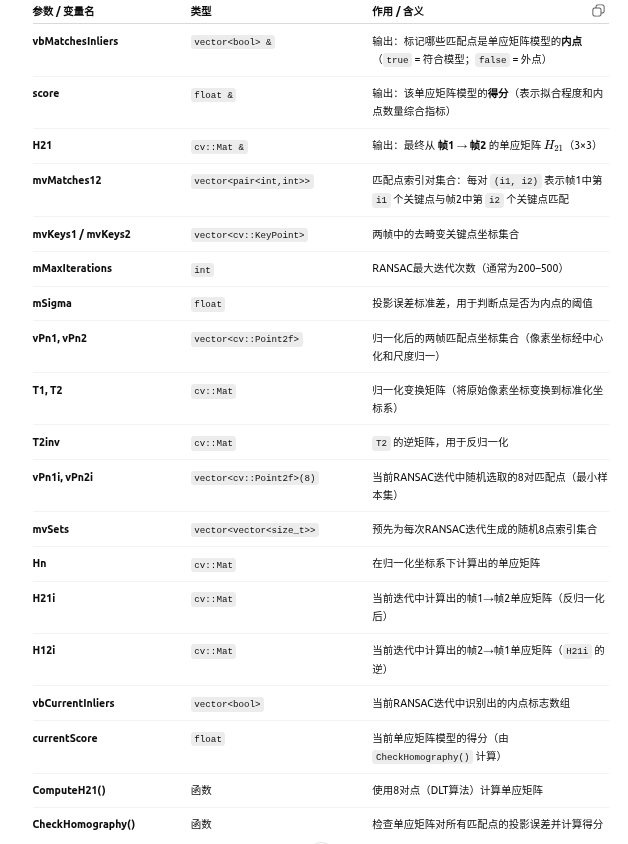
1.2 参数及含义
1.3 逻辑关系
mvKeys1, mvKeys2 (去畸变关键点)
↓
mvMatches12 (匹配点索引集合)
↓
vPn1, vPn2(归一化后匹配点集合) ← Normalize() → T1, T2
↓
RANSAC循环 (mMaxIterations次)
├─ 从 mvSets[it] 抽取 8 对匹配点
├─ ComputeH21(vPn1i, vPn2i) → Hn
├─ 反归一化: H21i = T2inv * Hn * T1
├─ H12i = H21i.inv()
├─ CheckHomography() → currentScore, vbCurrentInliers
└─ 若得分更高 → 更新 H21, vbMatchesInliers, score
1.4 代码
void Initializer::FindHomography(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float &score, cv::Mat &H21) { // Number of putative matches const int N = mvMatches12.size(); // Normalize coordinates vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; cv::Mat T1, T2; Normalize(mvKeys1,vPn1, T1); Normalize(mvKeys2,vPn2, T2); cv::Mat T2inv = T2.inv(); // Best Results variables score = 0.0; vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N,false); // Iteration variables vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); cv::Mat H21i, H12i; vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N,false); float currentScore; // Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score for(int it=0; it<mMaxIterations; it++) { // Select a minimum set for(size_t j=0; j<8; j++) { int idx = mvSets[it][j]; vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; } cv::Mat Hn = ComputeH21(vPn1i,vPn2i); H21i = T2inv*Hn*T1; H12i = H21i.inv(); currentScore = CheckHomography(H21i, H12i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); if(currentScore>score) { H21 = H21i.clone(); vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; score = currentScore; } } }
1.5 解析
1.5.1 准备阶段
// Number of putative matches const int N = mvMatches12.size(); // Normalize coordinates //存储参考帧(Frame 1)、当前帧F2的归一化关键点坐标 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; //T1,T2为后续平移+缩放归一化用(与相机内参归一化区分),详见下图 cv::Mat T1, T2; //将帧1、2特征点归一化 Normalize(mvKeys1,vPn1, T1); Normalize(mvKeys2,vPn2, T2); //求T2的逆 cv::Mat T2inv = T2.inv();
1.5.1.1 T矩阵说明
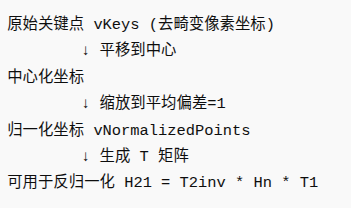
1.5.1.2 Normalize() 函数说明,找到T矩阵
void Initializer::Normalize(const vector<cv::KeyPoint> &vKeys, vector<cv::Point2f> &vNormalizedPoints, cv::Mat &T) { //计算关键点的质心 float meanX = 0; float meanY = 0; const int N = vKeys.size(); vNormalizedPoints.resize(N); for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { meanX += vKeys[i].pt.x; meanY += vKeys[i].pt.y; } meanX = meanX/N; meanY = meanY/N; //每个关键点减去质心,得到中心化后的坐标 float meanDevX = 0; float meanDevY = 0; for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { vNormalizedPoints[i].x = vKeys[i].pt.x - meanX; vNormalizedPoints[i].y = vKeys[i].pt.y - meanY; //计算每个方向的平均绝对偏差,确定缩放因子s meanDevX += fabs(vNormalizedPoints[i].x); meanDevY += fabs(vNormalizedPoints[i].y); } //缩放关键点,使平均偏差 = 1,平衡 x、y 方向尺度,数值稳定性更好 meanDevX = meanDevX/N; meanDevY = meanDevY/N; float sX = 1.0/meanDevX; float sY = 1.0/meanDevY; for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { vNormalizedPoints[i].x = vNormalizedPoints[i].x * sX; vNormalizedPoints[i].y = vNormalizedPoints[i].y * sY; } //构建归一化矩阵 T T = cv::Mat::eye(3,3,CV_32F); T.at<float>(0,0) = sX; T.at<float>(1,1) = sY; T.at<float>(0,2) = -meanX*sX; T.at<float>(1,2) = -meanY*sY; }思路:
1.5.2 初始化变量
// Best Results variables score = 0.0; //初始化内点标记数组,N个点现在都是外点 vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N,false); // Iteration variables //为 RANSAC 的最小点集准备存储空间 vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); //H21i:存储当前迭代下,从参考帧(Frame1)到当前帧(Frame2)的候选单应矩阵 //H12i:H21i的逆 cv::Mat H21i, H12i; vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N,false); float currentScore;
1.5.3 RANSAC 主循环
// Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score for(int it=0; it<mMaxIterations; it++) { // Select a minimum set for(size_t j=0; j<8; j++) { int idx = mvSets[it][j]; vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; } cv::Mat Hn = ComputeH21(vPn1i,vPn2i); H21i = T2inv*Hn*T1; H12i = H21i.inv(); currentScore = CheckHomography(H21i, H12i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); if(currentScore>score) { H21 = H21i.clone(); vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; score = currentScore; } }
1.5.3.1 CheckHomography() 函数
(1)作用
用于评估给定单应矩阵 H21(Frame1 → Frame2)是否正确,通过检查匹配点的重投影误差,计算一个评分,并标记每个匹配点是否为内点。
(2)代码
float Initializer::CheckHomography(const cv::Mat &H21, const cv::Mat &H12, vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float sigma) { const int N = mvMatches12.size(); const float h11 = H21.at<float>(0,0); const float h12 = H21.at<float>(0,1); const float h13 = H21.at<float>(0,2); const float h21 = H21.at<float>(1,0); const float h22 = H21.at<float>(1,1); const float h23 = H21.at<float>(1,2); const float h31 = H21.at<float>(2,0); const float h32 = H21.at<float>(2,1); const float h33 = H21.at<float>(2,2); const float h11inv = H12.at<float>(0,0); const float h12inv = H12.at<float>(0,1); const float h13inv = H12.at<float>(0,2); const float h21inv = H12.at<float>(1,0); const float h22inv = H12.at<float>(1,1); const float h23inv = H12.at<float>(1,2); const float h31inv = H12.at<float>(2,0); const float h32inv = H12.at<float>(2,1); const float h33inv = H12.at<float>(2,2); vbMatchesInliers.resize(N); float score = 0; const float th = 5.991; const float invSigmaSquare = 1.0/(sigma*sigma); for(int i=0; i<N; i++) { bool bIn = true; const cv::KeyPoint &kp1 = mvKeys1[mvMatches12[i].first]; const cv::KeyPoint &kp2 = mvKeys2[mvMatches12[i].second]; const float u1 = kp1.pt.x; const float v1 = kp1.pt.y; const float u2 = kp2.pt.x; const float v2 = kp2.pt.y; // Reprojection error in first image // x2in1 = H12*x2 const float w2in1inv = 1.0/(h31inv*u2+h32inv*v2+h33inv); const float u2in1 = (h11inv*u2+h12inv*v2+h13inv)*w2in1inv; const float v2in1 = (h21inv*u2+h22inv*v2+h23inv)*w2in1inv; const float squareDist1 = (u1-u2in1)*(u1-u2in1)+(v1-v2in1)*(v1-v2in1); const float chiSquare1 = squareDist1*invSigmaSquare; if(chiSquare1>th) bIn = false; else score += th - chiSquare1; // Reprojection error in second image // x1in2 = H21*x1 const float w1in2inv = 1.0/(h31*u1+h32*v1+h33); const float u1in2 = (h11*u1+h12*v1+h13)*w1in2inv; const float v1in2 = (h21*u1+h22*v1+h23)*w1in2inv; const float squareDist2 = (u2-u1in2)*(u2-u1in2)+(v2-v1in2)*(v2-v1in2); const float chiSquare2 = squareDist2*invSigmaSquare; if(chiSquare2>th) bIn = false; else score += th - chiSquare2; if(bIn) vbMatchesInliers[i]=true; else vbMatchesInliers[i]=false; } return score; }
2 基础矩阵
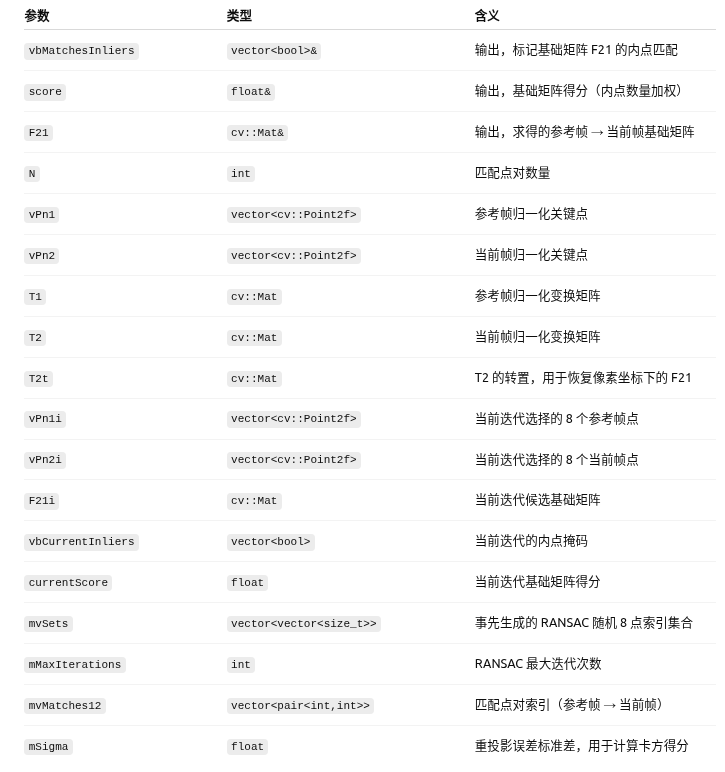
2.1 参数及含义
2.2 代码
void Initializer::FindFundamental(vector<bool> &vbMatchesInliers, float &score, cv::Mat &F21) { // Number of putative matches const int N = vbMatchesInliers.size(); // Normalize coordinates vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; cv::Mat T1, T2; Normalize(mvKeys1,vPn1, T1); Normalize(mvKeys2,vPn2, T2); cv::Mat T2t = T2.t(); // Best Results variables score = 0.0; vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N,false); // Iteration variables vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); cv::Mat F21i; vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N,false); float currentScore; // Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score for(int it=0; it<mMaxIterations; it++) { // Select a minimum set for(int j=0; j<8; j++) { int idx = mvSets[it][j]; vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; } cv::Mat Fn = ComputeF21(vPn1i,vPn2i); F21i = T2t*Fn*T1; currentScore = CheckFundamental(F21i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); if(currentScore>score) { F21 = F21i.clone(); vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; score = currentScore; } } }
2.3 解析
2.3.1 初始化及归一化
// Number of putative matches const int N = vbMatchesInliers.size(); // Normalize coordinates vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1, vPn2; cv::Mat T1, T2; Normalize(mvKeys1,vPn1, T1); Normalize(mvKeys2,vPn2, T2); cv::Mat T2t = T2.t();
2.3.2 初始化结果和临时变量
// Best Results variables score = 0.0; vbMatchesInliers = vector<bool>(N,false); // Iteration variables vector<cv::Point2f> vPn1i(8); vector<cv::Point2f> vPn2i(8); cv::Mat F21i; vector<bool> vbCurrentInliers(N,false); float currentScore;
2.3.3 RANSAC循环
// Perform all RANSAC iterations and save the solution with highest score for(int it=0; it<mMaxIterations; it++) { // Select a minimum set for(int j=0; j<8; j++) { int idx = mvSets[it][j]; vPn1i[j] = vPn1[mvMatches12[idx].first]; vPn2i[j] = vPn2[mvMatches12[idx].second]; } cv::Mat Fn = ComputeF21(vPn1i,vPn2i); F21i = T2t*Fn*T1; currentScore = CheckFundamental(F21i, vbCurrentInliers, mSigma); if(currentScore>score) { F21 = F21i.clone(); vbMatchesInliers = vbCurrentInliers; score = currentScore; } }