AB包:
1.是什么?
是特定平台的资产压缩包,包括(模型,贴图,预制体,音效,材质球)
Resources:核心必需资源 + 常驻内存 + 不热更,主打 "随用随取、不用折腾";
AB 包:非必需资源 + 动态加载 / 卸载(省内存) + 支持热更,主打 "灵活可控、适配手游场景"。
2.有什么用?
打包层面,相较于resources的资源打包,可以指定,位置,压缩方式(减小包大小)还可以动态更新(热更新)
3.生成打包AB包
Asset Bundle Browser资源包,unity已经2020后取消了
然后就可以选择要打包的资源了。
然后在Windows工具栏里面就有了,完事呢(中间有一个打包页签):

4.使用解包AB包
同一个ab包不能重复加载包
加载ab包和里面的资源:
同步:
bash
//加载AB包
AssetBundle ab= AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.streamingAssetsPath+"/"+"f");//包名
//加载AB包里面的资源
GameObject obj=ab.LoadAsset<GameObject>("Cube");
GameObject obj2=ab.LoadAsset("Cube",typeof(GameObject)) as GameObject;
Instantiate(obj);异步:
bash
StartCoroutine(LoadABRes("f","Cube"));
}
//异步不知到什么时候成功,所有要携程,本质不依赖携程的分时执行,只是要携程的顺序执行
IEnumerator LoadABRes(string ABname,string RESname)
{
AssetBundleCreateRequest AB=AssetBundle.LoadFromFileAsync(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + ABname);
yield return AB;
AssetBundleRequest ab= AB.assetBundle.LoadAssetAsync(RESname,typeof(GameObject));
yield return ab;
GameObject jg= ab.asset as GameObject;
Instantiate(jg);
}卸载ab包以及是否影响已经使用的资源:
bash
//false不影响,true影响
ab.unLoad(true);//单个
AssetBundle.UnloadAllAssetBundles(false);//全部5.AB包依赖:
某个包里面的资源的组成部分都会也必须在ab包里面。
当需要的组成部分和资源不在一个包:1,放一个包,2,加载资源们所在包(解压缩到内存占据容器)3,使用主包找某个包的依赖包(主包名字在biudin里面可以看)
bash
//加载主包StandaloneWindows
AssetBundle zhu = AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + "StandaloneWindows");
//加载主包固定文件夹:
AssetBundleManifest abManifest = zhu.LoadAsset<AssetBundleManifest>("AssetBundleManifest");
//从固定文件夹得到依赖信息
string[] strs = abManifest.GetAllDependencies("one");
for (int i = 0; i < strs.Length; i++)
{
Debug.Log(strs[i]);
AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + strs[i]);
}
AssetBundle one= AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/" + "one");
GameObject obj=one.LoadAsset("Cube",typeof(GameObject)) as GameObject;
Instantiate(obj);右键我们的主包就是默认包可以看到里面每个自定义包的依赖包:

6.AB包资源加载管理器
用到了之前封装好的这个mono单例模块,毕竟是个管理器
bash
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Events;
public class ABMsg : SingletonAutoMono<ABMsg>
{
private Dictionary<string, AssetBundle> abDic = new Dictionary<string, AssetBundle>();
private AssetBundle mainAB = null;
private AssetBundleManifest mainfest = null;
/// <summary>
/// 获取AB包的路径
/// </summary>
private string PathUrl
{
get
{
return Application.streamingAssetsPath;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 主包名,随着平台改变
/// </summary>
private string MainABName
{
get
{
#if UNITY_IOS
return "IOS";
#elif UNITY_ANDROID
return "Android";
#else
return "StandaloneWindows";
#endif
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 代码复用,实现多形式同步加载资源
/// </summary>
/// <param name="abName"></param>
public void LoadAB(string abName)
{
//加载主包
if (mainAB == null)
{
string mainABPath = System.IO.Path.Combine(PathUrl, MainABName);
mainAB = AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(mainABPath);
mainfest = mainAB.LoadAsset<AssetBundleManifest>("AssetBundleManifest");
}
//获取并加载依赖包
string[] dependencies = mainfest.GetAllDependencies(abName);
for (int i = 0; i < dependencies.Length; i++)
{
if (!abDic.ContainsKey(dependencies[i]))
{
string depPath = System.IO.Path.Combine(PathUrl, dependencies[i]);
AssetBundle depAB = AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(depPath);
if (depAB != null)
{
abDic.Add(dependencies[i], depAB);
}
else
{
Debug.LogError("加载依赖AB包失败: " + depPath);
}
}
}
//加载目标包
if (!abDic.ContainsKey(abName))
{
string abPath = System.IO.Path.Combine(PathUrl, abName);
if (!System.IO.File.Exists(abPath))
{
Debug.LogError("目标AB包不存在: " + abPath);
return;
}
AssetBundle targetAB = AssetBundle.LoadFromFile(abPath);
if (targetAB != null)
{
abDic.Add(abName, targetAB);
}
else
{
Debug.LogError("加载目标AB包失败: " + abPath);
return;
}
}
}
//同步加载资源(普通)
public Object LoadRes(string abName, string resName)
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
Object res = abDic[abName].LoadAsset(resName);
if (res == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
return res;
}
//同步加载资源(泛型)
public Object LoadRes<T>(string abName, string resName) where T:Object
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
T res = abDic[abName].LoadAsset<T>(resName);
if (res == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
return res;
}
//同步加载资源(类型)
public Object LoadRes(string abName,string resName,System.Type type)
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
Object res = abDic[abName].LoadAsset(resName,type);
if (res == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
return res;
}
//异步加载(协程是为了管理异步阶段,比较后台不阻塞需要一个携程得到当异步准备好了后触发回调委托)
public void LoadResAsync(string abName,string resName,UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
StartCoroutine(ReallyLoadResAsync(abName,resName,callback));
}
private IEnumerator ReallyLoadResAsync(string abName, string resName, UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
AssetBundleRequest rab = abDic[abName].LoadAssetAsync(resName);
yield return rab;
if (rab.asset == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
else
{
callback(rab.asset);
}
}
//异步加载(泛型)
public void LoadResAsync<T>(string abName, string resName, UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
StartCoroutine(ReallyLoadResAsync<T>(abName, resName, callback));
}
private IEnumerator ReallyLoadResAsync<T>(string abName, string resName, UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
AssetBundleRequest rab = abDic[abName].LoadAssetAsync<T>(resName);
yield return rab;
if (rab.asset == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
else
{
callback(rab.asset);
}
}
//异步加载(类型)
public void LoadResAsync(string abName, string resName,System.Type type, UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
StartCoroutine(ReallyLoadResAsync(abName, resName,type, callback));
}
private IEnumerator ReallyLoadResAsync(string abName, string resName, System.Type type, UnityAction<Object> callback)
{
LoadAB(abName);
//加载并返回资源
AssetBundleRequest rab = abDic[abName].LoadAssetAsync(resName,type);
yield return rab;
if (rab.asset == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"在AB包 {abName} 中找不到资源: {resName}");
}
else
{
callback(rab.asset);
}
}
//卸载单个AB包
public void UnloadAB(string abName, bool unloadAllLoadedObjects = false)
{
if (abDic.ContainsKey(abName))
{
abDic[abName].Unload(unloadAllLoadedObjects);
abDic.Remove(abName);
}
}
//卸载全部AB包
public void UnloadAll()
{
AssetBundle.UnloadAllAssetBundles(false);
abDic.Clear();
mainAB = null;
mainfest = null;
}
}使用:
bash
private void Start()
{
Object x=ABMsg.GetInstance().LoadRes("one", "Cube");
Object y=ABMsg.GetInstance().LoadRes<GameObject>("one", "Cube");
ABMsg.GetInstance().LoadResAsync("one","Cube",typeof(GameObject),cc);
ABMsg.GetInstance().LoadResAsync<GameObject>("one","Cube",cc);
Instantiate(x);
Instantiate(y);
}
public void cc(object a)
{
Instantiate(a as GameObject);
print("你好");
}
private void Update()
{
}Lua热更新:
用vscode可以写,但是我们目前用这个sublime text超强文本编辑器
1.快捷键:
ctrl+B运行
选择open 文件夹=打开文件夹做这个目录吧
2.lua语法:
第一个程序
bash
print("*********第一个程序*********")
--单行注释
print("你好世界")--可以省略分好
print("你好世界")
--[[
第一种多行注释
]]
--[[
第二种多行注释
]]--
--[[
第三种多行注释
--]]
变量
bash
print("**********变量********")
--lua当中的简单变量类型
--nil number string boolean
--lua中的变量申明不需要变量类型,会自动判断
print("**********nil********")
print(b)--没有声明过的变量默认为nil空
a = nil
print(type(a))--可以使用这个函数得到类型,这个函数的返回值是string
print(type(type(a)))
print(a)
print("**********number********")
a=1
print(a)
a=1.99
print(a)
print("**********string********")
a="123"
print(a)
a='123'
print(a)
print("**********boolean********")
a=true
print(a)
a=false
print(a)
--lua当中的复杂变量类型
--function函数 table表 userdata数据结构 thread协同程序
字符串操作
bash
print("*********字符串操作*********")
str="nihao你好"--英文占一个字符,中文占三个
print("*********字符串长度*********")
print(#str)
print("*********字符串换行*********")
print("123\n123")
s=[[第一行
第二行
第三行
]]
print(s)
print("*********字符串拼接*********")
print("123"..111.9)
print(string.format("我是%s,我今年%d","xzc",19))
print("*********转字符串*********")
print(tostring(true))
print("*********公共方法*********")
print(string.upper(str))--大写
print(string.lower(str))--小写
print(string.reverse(str))--翻转
print(string.find(str,"好"))--索引从一开始,并且返回的是字节第一个和最后一个
print(string.sub(str,3,4))--截取>=3<=4
print(string.rep(str,4))--重复
print(string.gsub(str,"你好","你坏"))--修改(修改了多少次)
a=string.byte("Lua",1,3)--转ascll妈>=1<=3区间
print(a)
print(string.char(a))--ascll码转字符串
运算符
bash
print("*********运算符*********")
print("*********算数运算符*********")
-- + - * / %
-- 没有自增自减++ --
--没有复合运算符 += -= /= *= %=
-- 字符串在运算符里面自动转换成number如果可以
print((1+2).."|"..(1-2).."|"..("12"*2).."|"..(9/3).."|"..(9%2))
print("幂运算"..2^3)
print("*********条件运算符*********")
--> < >= <= ~=
print(1~=9)
print("*********逻辑运算符*********")
-- && || ! and or not"遵循前面满足后面不执行,短路"
print(true and false)
print(true or false)
print(not (true and false))
print("*********位运算符*********")--不支持
print("*********三目运算符*********")--不支持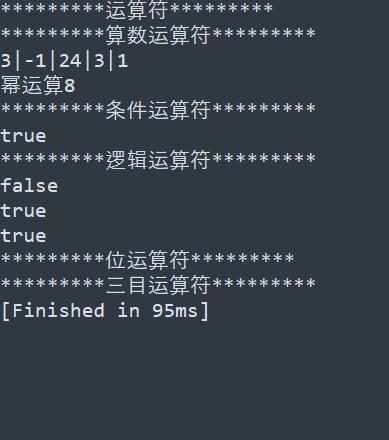
条件分支
bash
print("*********条件分支*********")
a=5
if a<5 then
print("1")
elseif a>5 then
print("2")
else
print("3")
end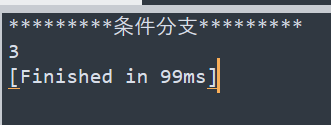
循环语句
bash
print("*********循环语句*********")
print("*********while语句*********")
num=0
while num<5 do
print(num)
num=num+1
end
print("*********do while语句*********")
num=0
repeat
print(num)
num=num+1
until num>5--结束条件
print("*********for语句*********")
for i=1,10,2 do--i默认从初+第三个参数(默认1)
print(i)
end
函数
bash
print("*********函数*********")
print("*********无参无返回值*********")
function F( )
print("s")
end
F( )
F1=function()
print("b")
end
F1()
print("*********有参数*********")
function F2(A)
print(A)
end
F2()
F2("1","2")
F2('1')
F2(12.9)
print("*********有返回值*********")
function F3(a)
print(a)
return a,"123",true--多返回值和接取
end
x,y,z,s=F3(11.3)
print(x,y,z,s)
print("*********函数类型*********")
F4=function ( )
-- body
end
print(type(F4))
print("*********函数重载*********")
--函数名相同,函数参数类型和个数不同,但是天然就是支持不同类型和不同参数
--不支持
print("*********变长参数*********")
function F5( ... )
--要先用一个表存起来
arg={...}
for i=1,#arg do
print(arg[i])
end
end
F5("1",2,true)
print("*********函数嵌套*********")
function F6()
F7=function()
print(123)
end
return F7
end
F8=F6()
F8()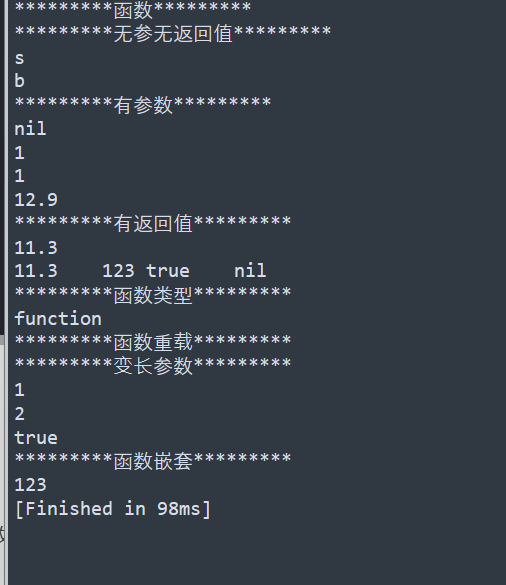
表table
bash
print("*********复杂数据类型表talbe*********")
--所有数据类型的根基
print("*********数组*********")
a={1,2,"s",true,nil}
print(a[0])--表的索引第一位是1
print(#a)--中间为空就会断
print("*********数组遍历*********")
for i=1,#a do
print(i)
end
print("*********二维数组*********")
a={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}
print(a[1][1])
print("*********二维数组遍历*********")
for i=1,#a do
b=a[i]
for j=1,#b do
print(b[j],a[i][j])
end
end
print("*********自定义索引*********")
aa={[0]=1,2,3,[-8]=4,5}--跳过的索引为nil
for i=-8,#aa do
print(aa[i])
end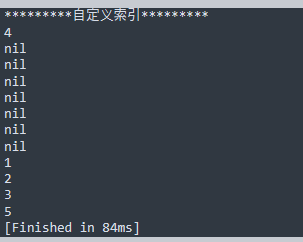
i.pairs迭代器遍历
bash
print("*********ipairs迭代器遍历(拉)*********")
--迭代器遍历 主要是用来遍历表的
--#得到的数组长度,受nil中断,自定义索引也会有坑
a={[0]=1,2,[-1]=3,4,5,[9]=100}
for i,k in ipairs(a) do
print(i..k)
--ipairs遍历是从1开始遍历,小于等于0的值得不到,
--中间断了也不成
end
print("*********pairs迭代器遍历(ok)*********")
for i,k in pairs(a) do--两个接着,table内容本质就是键值对
print("pairs"..i..k)
end
表table2
bash
print("*********复杂数据类型表talbe-2*********")
print("*********字典*********")
print("*********字典的申明*********")
a={["name"]="xzc",["age"]=14,["1"]=5}--声明(table可以自定义键)
a.name="dy"--修改
a["2"]=100--增加
a["2"]=nil--删除,因为不加默认是nilb
print(a["name"],a.age,a["1"],a["2"])--可以直接点,但是不能是数字
print("*********字典的遍历*********")
for k,v in pairs(a)do
print(k,v)
end
print("*********类和结构体*********")
--默认没有面向对象,需要自己实现
student={
age=1,
sex=true,
up=function(x)
--print(age)--成员之间不能直接调用
print(student.age)
print("成长函数",x)
end
}
student.name="t"
--lua的table中.和冒号区别
student.up()
student:up()--冒号调用会默认吧冒号者当第一个参数传入。self表示该函数的第一个参数
for i,j in pairs(student)do
print(i,j)
end
print("*********表的公共操作*********")
--表中table的公共操作
t1={{age=1,name="123"},{age=1,name="345"}}
t2={name="xzc",sex=true}
print("*********插入*********")
print(#t1)
table.insert(t1,t2)--插入
t2={name="xzc",sex=true}
print(#t1)
print("*********删除*********")
table.remove(t1,2)--删除指定,默认为1
print(t1[2].name)
print("*********排序*********")
t2={5,8,2,5}
table.sort( t2)
for i,j in pairs(t2) do
print(j)
end
table.sort( t2,function(a,b)
if a>b then
return true
end
end)
for i,j in pairs(t2) do
print(j)
end
print("*********拼接*********")
t2={20,1,"nihao"}--数字,字符串
str=table.concat( t2, ",",1,2 )
print(str)
多脚本执行
bash
print("*********多脚本执行*********")
print("*********全局本地变量*********")
for i=1,2 do
c="xzc"--全局变量
local d = 1--局部变量
end
print(c)
print(d)
print("*********多脚本执行*********")
--关键字require("脚本名")
print(aa)
require("first")--执行过了就可以使用另外一个脚本的访问权限满足的东西
require("first")--不能多次执行
print(require("first"),"返回值")--还可以得到另外脚本返回值
print(aa)
print(bb)
print("*********脚本卸载*********")
--关键字package.loaded["脚本名"]可以得到返回值判断是否被加载
print(package.loaded["first"])
package.loaded["first"]=nil
print(package.loaded["first"])
print("*********大G表*********")
--大G表(_G)是一个总表table,会把所有全局变量都存储
--for k,v in pairs(_G)do
-- print(k,v)
--end
bash
aa="123"
local bb = 1
print("first")
return 'ok'
Lua的特殊用法
bash
print("*********特殊用法*********")
print("*********多变量赋值*********")
a,b,c,d=1,true,"你好"--多变量为空,少变量取前
print(a,b,c,d)
print("*********多返回值*********")
function z()
return 1,2,3
end
a,b,c,d=z()
print(a,b,c,d)--多变量为空,少变量取前
print("*********and or*********")
--不止链接bool,只有nil,false是假,反正会程、返回代表真假的东西而不是true,false
print(nil and 1)
print(true and 1)
print(nil or 1)
print(nil or false)
print(false or nil)
--模拟三目运算符
xx=(1>3)and"ok"or"no"
print(xx)
xx=(1<3)and"ok"or"no"
print(xx)
协程
bash
print("*********协程*********")
print("*********协程创建*********")
function a()
print(123)
end
--coroutine.create(),返回线程类型
co = coroutine.create(a)
print(co,type(co))
--coroutine.wrap(),返回函数类型
co2 = coroutine.wrap(a)
print(co2,type(co2))
print("*********协程运行*********")
--coroutine.resume()
coroutine.resume(co)
--直接调用函数
co2()
print("*********协程挂起*********")
function b( )
local i=1
while true do
print(i)
i=i+1
print(coroutine.status(co3))
coroutine.yield(i)
end
end
--方式一:
co3=coroutine.create(b)
isok,re=coroutine.resume(co3)--第一个返回值是携程是否成功,第二个是返回值
print(isok,re)
isok,re=coroutine.resume(co3)
print(isok,re)
--方式二:
co4=coroutine.wrap(b)
co4()
re=co4()
print("返回值"..re)--第一个返回值就是写的返回值
print("*********协程状态*********")
--coroutine.status()
--dead结束
--suspended暂停
--running运行中
print(coroutine.status(co))
print(coroutine.status(co3))
--还有函数可以得到正在运行协程的线程号
print(coroutine.running())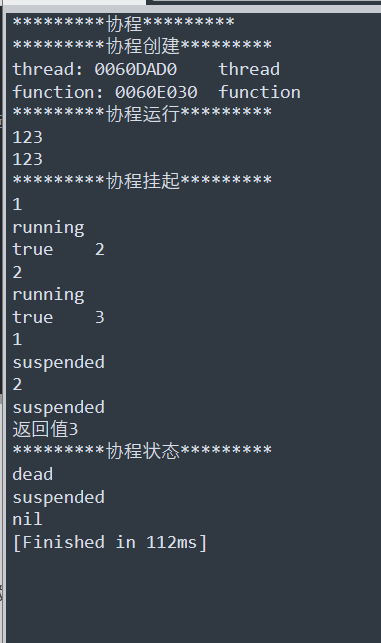
元表
bash
print("*********元表*********")
print("*********元表概念*********")
--任何表变量都可以作为另一个表变量的元表
--任何表变量都能拥有自己的元表(父)
--当我们子表中进行特定操作时,会执行元表内容
print("*********设置元表*********")
meta={}
myTable={}
--设置元表函数
--第一个参数(子表)。第二个参数(元表)(父)
setmetatable(myTable,meta)
print("*********特定操作*********")
print("*********特定操作__tostring*********")
mate2={
--当子表要被当string使用时,会默认调用原表的__tostring()方法
__tostring=function(t )--默认将自己作为第一个参数赋值
return t.name
end
}
myTable2={
name="xzc"
}
setmetatable(myTable2,mate2)
print(myTable2)
print("*********特定操作__call*********")
mate3={
--当子表要被当string使用时,会默认调用原表的__tostring()方法
__tostring=function(t)--默认将自己作为第一个参数赋值
return t.name
end,
--当子表要被当函数 使用时,会默认调用原表的__call()方法
__call=function(a,b)--默认将自己作为第一个参数赋值
print(a)
print("oi"..b)
end
}
myTable3={
name="xzc"
}
setmetatable(myTable3,mate3)
myTable3("你好")
print("*********特定操作__运算符重载*********")
mate4={
__add=function(a,b)
return a.age+b.age
end,
__sub=function(a,b)
return a.age-b.age
end,
__mul=function(a,b)
return a.age*b.age
end,
__div=function(a,b)
return a.age/b.age
end,
__mod=function(a,b)
return a.age%b.age
end,
__pow=function(a,b)
return a.age^b.age
end,
__eq=function(a,b)--比较
return a.age==b.age
end,
__lt=function(a,b)
return a.age<b.age
end,
__le=function(a,b)
return a.age<=b.age
end,
__concat=function(a,b)--..
return "a.age..b.age"
end,
}
MyTable4={
age=10
}
setmetatable(MyTable4,mate4)
print(MyTable4+MyTable4)
--条件运算符的重载要求两个表的元表一致
print("*********特定操作------index和newIndex*********")
---当表找不到属性会去找元表中__index指定的表的属性(得)
mate6 ={
age = 1
--__index={age = 1}
}
--下面这个代码要是写内部,会有坑,因为声明的同时不能立马用
mate6.__index=mate6
myTable6={
}
setmetatable(myTable6,mate6)
print(mate6.age)
--当赋值时,如果赋值一个不存在的索引,那么会把责怪值赋值到newubdex所指表中,不改自己(改)
mate7={}
mate7.__newindex={age=1}
MyTable7={
}
setmetatable(MyTable7,mate7)
MyTable7.age=11
print(mate7.__newindex.age)
print("*********其他操作*********")
--获取元表
print(getmetatable(MyTable7))--对标settmetatable
--忽视__index设置,只能自己表内找
print(rawget(MyTable7,"age"))
--忽视__newindex设置,如果表没有直接给表加上没有的
rawset(MyTable7,"age",99)
print(MyTable7.age)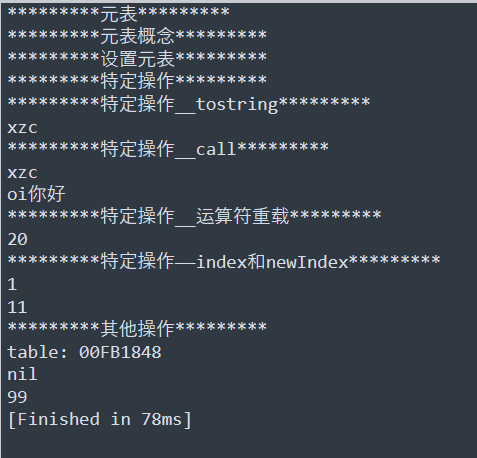
面向对象
bash
print("*********面向对象*********")
print("*********封装*********")
--调用时候用":",self赋值。声明时候":"提供默认self防止没人:调用,但是要用self.
Object={}
Object.id=1--添加成员变量
--实现封装一个类,可以被new
function Object:new()--添加成员函数
local obj = {}
--元表
self.__index=self
--self.__newindex=self//只允许得父类,不允许改父类,改的话就自己私有的了
setmetatable(obj,self)
return obj
end
function Object:hs()
print(self.id)
end
local myObj=Object:new()
myObj.id=10
myObj:hs()
print(Object.id)
print("*********继承*********")
--写一个继承方法.创建一个表并且继承:调用者
function Object:subClass(className)
_G[className]={}--声明一张全局表
local obj=_G[className]
self.__index=self
obj.base=self--自己定义base保留父类
setmetatable(obj,self)
end
Object:subClass("Person")--我们对于冒号声明的函数都要注意预留第一个参数,除非也是冒号调用
x=Person:new()
print(x.id)
print("*********多态*********")
--相同方法不同执行逻辑
Object:subClass("GameObject")
GameObject.posX=0;
GameObject.posY=0;
GameObject.posZ=0;
function GameObject:Speak()
print(self.posX,self.posY,self.posZ)
end
GameObject:subClass("Player")
function Player:Speak()
--self.base:Speak()--相当于传递的Gameobject的,改同一个父类
self.base.Speak(self)
print("重写")
end
yy=Player:new()
yy:Speak()
yx=Player:new()
yx:Speak()
封装面向对象
bash
--面向对象实现
--基类Object
Object={}
--new()方法->体现封装
function Object:new( )
--声明空表
local obj={}
--关联self表为元表,设置元表的__index属性
self.__index=self
setmetatable(obj,self)
--返回链接好元表的空表
return obj
end
--继承方法->体现继承
function Object:subClass( className )
--使用大G表声明一个全局的表,创建一个继承某类的类
_G[className]={}
local obj=_G[className]
--关联self表为元表,设置元表的__index属性
self.__index=self
setmetatable(obj,self)
--为新诞生类添加一个成员属性,存储父类,以便实现多态
obj.base=self
end
Object:subClass("GameObject")
GameObject.x=0
GameObject.y=0
function GameObject:SP( )
self.x=1
self.y=9
end
go=GameObject:new()
print(go.x,go.y)
go:SP()
print(go.x,go.y)
GameObject:subClass("Player")
function Player:SP()
print("重载SP:")
self.base.SP(self)--得吧self传第一个参数,而不是base,子类使用父类方法,而不是直接拿父类方法
self.x=self.x+1
self.y=self.y+1
end
p=Player:new()
print(p.x,p.y)
p:SP()
print(p.x,p.y)
自带库
bash
print("*********自带库*********")
print("*********时间*********")
-- 1. 时间戳
print("当前时间戳:", os.time())
print("指定时间戳(2024-08-14):", os.time({year=2024, month=8, day=14}))
-- 2. 格式化获取当前时间
local currentDate = os.date("%Y-%m-%d") -- 年-月-日
local currentTime = os.date("%H:%M:%S") -- 时:分:秒
local fullTime = os.date("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") -- 完整时间(年-月-日 时:分:秒)
print("\n当前日期:", currentDate)
print("当前时间:", currentTime)
print("完整时间:", fullTime)
-- 3. 单独获取每个时间字段(按需提取)
local year = os.date("%Y")
local month = os.date("%m")
local day = os.date("%d")
local hour = os.date("%H")
local min = os.date("%M")
local sec = os.date("%S")
local week = os.date("%w") -- 星期(0=周日,1=周一,...,6=周六)
print("\n单独字段:")
print("年:", year)
print("月:", month)
print("日:", day)
print("时:", hour)
print("分:", min)
print("秒:", sec)
print("星期(0=周日):", week)
print("\n*********数学*********")
-- 数学库常用示例
--先设置随机数种子
math.randomseed(os.time())
print("随机数(0-1):", math.random())
print("随机数(1-100):", math.random(1, 100))
print("绝对值:", math.abs(-456))
print("平方根:", math.sqrt(25))
print("最大值(3,7,2):", math.max(3, 7, 2))
print("最小值(3,7,2):", math.min(3, 7, 2))
print("圆周率:", math.pi)
print("正弦值(π/2):", math.sin(math.pi/2)) -- 结果接近 1
print("弧度转角度",math.deg(math.pi))
print("向上取整",math.floor(2.6))
print("向下取整",math.ceil(2.6))
print("小数分离",math.modf(1.2))
print("\n*********路径*********")
--lua脚本加载路径
print(package.path)
package.path=package.path.."C:\\"
print(package.path)
垃圾回收
bash
print("*********垃圾回收*********")
--关键字collectgarbage
--获取当前lua占用内存数kb,返回值*1024=字节
print(collectgarbage("count"))
test={id=20,name="你好"}
print(collectgarbage("count"))
--垃圾回收(对标GC)
test=nil--解除羁绊就是变垃圾
collectgarbage("collect")
print(collectgarbage("count"))
--lua有自动计时进行GC方法
3.简单闭包:定义+意义
1. 定义
闭包 = 内部函数 + 捕获的外部函数局部变量
核心特点:内部函数被返回后,依然能访问/修改外部函数的局部变量(这些变量不会随外部函数执行结束而消失)。
lua
function 外部函数()
local 局部变量 = 0 -- 外部函数的局部变量
return function() -- 返回内部函数(闭包)
局部变量 = 局部变量 + 1
print(局部变量)
end
end
local 闭包实例 = 外部函数()
闭包实例() -- 输出1(记住了局部变量)
闭包实例() -- 输出2(继续修改局部变量)2. 意义
核心意义:让函数带"记忆",同时不污染全局变量
用大白话讲2个关键作用:
- 不用全局变量,也能让函数记住之前的状态(比如计数器、累加器);
- 保护变量不被随意修改(外部只能通过闭包接口操作,不能直接改)。
3.对比:不用闭包的麻烦
如果不用闭包,想实现计数器只能用全局变量:
lua
local 全局变量 = 0 -- 容易被其他代码误改
function 计数()
全局变量 = 全局变量 + 1
print(全局变量)
end而闭包能让"状态"(局部变量)和"操作"(内部函数)绑在一起,既安全又干净。