1. 项目概述
本项目旨在构建一个在本地计算机上运行的个人语音助手,以替代功能有限的商业产品。该助手能够处理比简单语音命令更复杂的任务。项目利用了大型语言模型(LLM)智能体和 MCP (Machine-to-Machine Communication Protocol)服务器的最新技术,实现了从语音识别、意图理解、工具调用到语音合成的完整流程。
2. 项目目标
- 本地化运行:所有组件均在本地计算机上运行,无需依赖付费的云服务或 API,从而避免了订阅费用和使用额度限制。
- 功能复现 :作为初期目标,首先复现现有智能音箱的核心功能,包括:
- 获取当前日期或时间。
- 获取今日天气信息
- 控制已连接的智能家居设备
- 快速响应:助手的响应时间应足够快,至少快于用户手动执行相同任务的时间,以确保良好的用户体验。项目后期将致力于将响应时间优化至毫秒级。
3. 系统架构
本项目采用模块化设计,主要由两大核心部分组成:语音助手应用和智能家居 MCP 服务器。
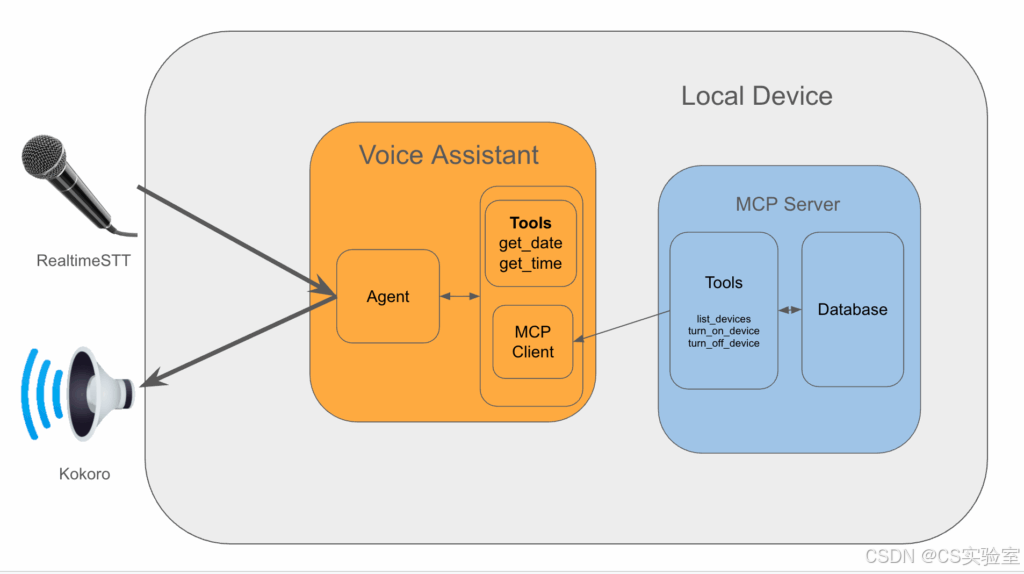
-
语音助手 (Voice Assistant)
- 语音转文本 (STT) 与文本转语音 (TTS) :
- 使用
RealtimeSTT库进行实时的唤醒词检测、语音活动检测和语音到文本的转录。 - 转录后的文本被发送给智能体进行处理。
- 智能体的响应文本通过流式传输方式,交由
KokoroTTS 模型进行语音合成,并最终通过扬声器播放。
- 使用
- 智能体 (Agent) :
- 使用
Ollama在本地运行大型语言模型(也可以使用 LLM 的 API,根据个人喜好确定)。 - 使用
LangGraph框架实现智能体的工作流。 - 智能体负责理解用户查询,并决定调用何种工具来生成回应。它集成了获取日期/时间的本地工具,并通过客户端与智能家居 MCP 服务器交互。
- 使用
- 语音转文本 (STT) 与文本转语音 (TTS) :
-
智能家居 MCP 服务器 (MCP Server for smart-home Connection)
- 这是一个独立的服务,专门用于封装发现、连接和管理智能家居设备的复杂逻辑。
- 使用 SQL 数据库(本项目中为
duckdb)来跟踪设备的连接信息和名称。 - 通过工具接口,允许智能体查询设备信息并控制其开关状态。
4. 技术实现
4.1 语音转文本 (STT) 实现
本项目的 STT 功能依赖 RealtimeSTT 库,它简化了实时语音处理的复杂性。
- 核心机制 :
- 创建一个线程持续监听用户的语音输入。
- 当检测到预设的唤醒词(例如 "hi,张三")后,开始录制用户的查询语音。
- 录制的音频被发送到 STT 模型进行转录,返回文本字符串。
- 集成方式 :
通过AudioToTextRecorder类的上下文管理器,在一个循环中不断监听和获取用户转录后的文本查询。
4.2 文本转语音 (TTS) 实现
为实现低延迟和高质量的语音输出,项目对多种 TTS 模型进行了评估(包括 Bark、Coqui TTS 等),最终推荐选择 Kokoro 作为实现方案。
- 设计模式 :
- 定义一个基础的
Voice类,封装通用的语音播放逻辑。 - 创建一个继承自
Voice的KokoroVoice子类,专门处理与Kokoro模型相关的实现细节。这种设计使得未来可以轻松切换到其他 TTS 模型。
- 定义一个基础的
- 核心功能 :
KokoroVoice类负责将智能体生成的文本转换为音频波形数据,并以流式方式将其写入音频输出设备,实现边生成边播放的效果,降低了用户的等待感。
4.3 智能家居 MCP 服务器实现
该服务器作为一个独立的进程运行,为语音助手提供控制智能家居的工具。
- 数据库 :
- 采用
duckdb作为后端数据库,轻量且易于集成。 - 设计了一张
device表,用于存储智能设备的唯一标识(device_id)、用户指定的名称(name)和用于控制的 IP 地址(ip_address)。
- 采用
- 设备管理 :
DeviceManager类负责与具体的智能设备(如 Tapo 智能插座)进行交互。- 它提供了三个核心的公共方法,这些方法将被注册为工具:
turn_on_device(打开设备)、turn_off_device(关闭设备)和list_devices(列出所有可用设备)。
- 工具暴露与服务启动 :
- 使用
FastMCP框架将DeviceManager中的公共方法注册为可供远程调用的工具。 - 服务器在每次启动时会自动发现网络中的设备并更新数据库,以确保设备信息的实时性。
- 通过
typer将服务器封装为命令行应用,便于启动和管理。
- 使用
- 客户端集成 :
在语音助手应用中,使用langchain_mcp_adapters库的MultiServerMCPClient作为客户端,连接到 MCP 服务器并自动获取其提供的所有工具。
4.4 智能体 (Agent) 实现
智能体是整个系统的"大脑",负责决策和任务执行。
- 框架 :使用
LangGraph构建状态化的、基于图的工作流。本项目采用了create_react_agent预构建图,其逻辑如下:- 接收用户查询。
- 智能体节点判断是否需要调用工具。
- 如果需要,则转移到工具节点执行工具,并将结果返回给智能体节点。此过程可重复。
- 如果不需要工具或已获取足够信息,则生成最终回复并结束流程。
- 构建流程 :
- 初始化 LLM :通过
Ollama加载本地语言模型(如llama3.2)。 - 集成工具集:整合所有可用的工具,包括本地实现的日期/时间工具和从 MCP 服务器获取的智能家居控制工具。
- 构建智能体执行器 :调用
create_react_agent方法,传入 LLM、工具集以及用于实现短期记忆(checkpointer)和长期记忆(store)的持久化存储对象(基于 SQLite)。
- 初始化 LLM :通过
- 响应处理与延迟优化 :
- 为减少延迟,不使用
invoke方法等待完整响应,而是使用stream方法以流式方式获取智能体的输出。 - 由于 TTS 模型无法处理单个词元(token),项目设计了
OutputChunkBuilder类。该类作为一个缓冲区,持续收集智能体输出的词元,直到累积成一个完整的句子(以句号、问号等标点符号为界),再将完整的句子块发送给 TTS 模型进行合成。
- 为减少延迟,不使用
4.5 本地工具实现
除了通过 MCP 服务器提供的工具外,项目还直接实现了一些基础工具。
- 实现方式 :使用
langchain_core.tools.structured中的StructuredTool类,将普通 Python 函数及其文档字符串(docstring)转换为智能体可用的工具。 - 日期和时间工具 :
get_current_time(): 获取格式化后的当前时间。get_current_date(): 获取格式化后的当前日期。- 文本归一化 :为了确保 TTS 模型能准确地读出日期(例如,将 "2025-01-01" 转换为 "January 1st, 2025"),在
get_current_date函数内部对日期字符串进行了预处理,将其转换为更自然的语言表达形式。
5. 系统整合与主流程
项目的主入口文件 (main.py) 负责整合所有组件并驱动整个应用。
- 初始化 :加载配置文件,实例化
KokoroVoice(TTS 模块)和OutputChunkBuilder(响应分块器)。 - 设置记忆 :使用
AsyncSqliteSaver和AsyncSqliteStore配置智能体的短期和长期记忆后端。 - 创建智能体 :调用
get_new_agent函数,传入配置、记忆后端和工具,创建智能体执行器。 - 启动主循环 :
- 启动
AudioToTextRecorder进行持续的语音监听。 - 当监听到用户查询后,将其传递给智能体执行器的
astream方法。 stream_voice异步函数接收智能体返回的响应流。- 在
stream_voice内部,OutputChunkBuilder将响应流聚合成句子。 - 一旦一个完整的句子准备好,就调用
voice.speak()方法进行语音播放。 - 该流程确保了从用户提问到语音回答的低延迟、流式体验。
- 启动
1. 文本转语音 (TTS) 实现
1.1 TTS 基础 Voice 类定义
python
class Voice():
def __init__(
self,
sample_rate: int = 24000,
chunk_size: int = 2048
):
self.sample_rate = sample_rate
self.chunk_size = chunk_size
self.initialise_model()
def initialise_model(self):
"""Initialise the model to use for TTS."""
pass
def convert_text_to_speech(self, text:str) -> list[np.ndarray]:
"""Convert text to sepeech and return the waveform as frames."""
pass
def speak(self, text:str):
"""Speak the provided text through device output."""
frames = self.convert_text_to_speech(self, text)
for frame in frames:
self.output_stream.write(frame.tobytes())1.2 TTS KokoroVoice 实现类
python
from kokoro import KPipeline
class KokoroVoice(Voice):
def __init__(self, voice:str, sample_rate: int = 24000, chunk_size: int = 2048):
"""Initialise the model to use for TTS.
Args:
voice (str):
The voice to use.
See https://github.com/hexgrad/kokoro/blob/main/kokoro.js/voices/
for all voices.
sample_rate (int, optional):
The sample rate to use. Defaults to 24000.
chunk_size (int, optional):
The chunk size to use. Defaults to 2048.
"""
self.voice = voice
super().__init__(sample_rate, chunk_size)
def initialise_model(self):
"""Load the model to use for TTS."""
self.pipeline = KPipeline(lang_code="b")
def convert_text_to_speech(self, text:str) -> list[np.ndarray]:
"""Convert text to speech and return the waveform as frames."""
generator = self.pipeline(text, voice=self.voice)
frames = []
for i, (_, _, audio) in enumerate(generator):
for start in range(0, len(audio), self.chunk_size):
chunk = audio[start : start + self.chunk_size]
frames.append(chunk.numpy().astype(np.float32))
return frames2. 智能家居 MCP 服务器实现
2.1 数据库定义 (src/smarthome_mcp_server/database.py)
python
# src/smarthome_mcp_server/database.py
import os
import duckdb
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class TableSchema:
name:str
columns:dict[str, str]
primary_key:list[str]
def get_device_table_schema():
return TableSchema(
name="device",
columns={
"device_id" : "VARCHAR",
"name": "VARCHAR",
"ip_address": "VARCHAR",
},
primary_key=["device_id"],
)
def initialise_database(db_path:os.PathLike) -> duckdb.DuckDBPyConnection:
"""Get the database connection and create the tables if they don't exist."""
conn = duckdb.connect(db_path)
# initialise if not exists tables
conn.execute(
get_create_table_if_not_exists_query(get_device_table_schema())
)
return conn2.2 设备管理器 DeviceManager 类(部分实现)
python
import duckdb
from dotenv import
class DeviceManager:
def __init__(self, conn:duckdb.DuckDBPyConnection) -> None:
self._conn = conn
...
async def turn_on_device(self, device_name: str) -> str:
"""Turn on a device.
Args:
device_name (str):
The name of the device to turn on.
"""
try:
device = await self._get_device(device_name)
except DeviceNotFoundError as e:
logger.exception(e)
return f"Device {device_name} not found."
await device.turn_on()
return f"Device {device_name} turned on."
async def turn_off_device(self, device_name: str) -> str:
"""Turn off a device.
Args:
device_name (str):
The name of the device to turn off.
"""
try:
device = await self._get_device(device_name)
except DeviceNotFoundError as e:
logger.exception(e)
return f"Device {device_name} not found."
await device.turn_off()
return f"Device {device_name} turned off."
async def list_devices(self) -> list[str]:
"""List the available device names.
Returns:
list[str]:
A list of device names.
"""
results = self._conn.query("SELECT name FROM device").fetchall()
return [result[0] for result in results]2.3 MCP 服务器初始化与工具注册
python
from fastmcp import FastMCP
def register_device_manager_tools(mcp_instance: FastMCP, device_manager: DeviceManager) -> FastMCP:
"""Register the methods defined in DeviceManager as tools for MCP server."""
mcp_instance.tool(name_or_fn=device_manager.list_devices)
mcp_instance.tool(name_or_fn=device_manager.turn_off_device)
mcp_instance.tool(name_or_fn=device_manager.turn_on_device)
return mcp_instance
async def populate_database(device_manager: DeviceManager):
"""Find all devices that are available and update the database."""
all_devices = await device_manager.discover_new_devices()
upsert_coroutines = [device_manager._upsert_device(device) for device in all_devices.values()]
await asyncio.gather(*upsert_coroutines)
def initialise_server(db_path: os.PathLike) -> FastMCP:
"""Initialise the server."""
conn = initialise_database(db_path)
device_manager = DeviceManager(conn)
# find all devices that are available and update the database
asyncio.run(populate_database(device_manager))
mcp = FastMCP(
name="smarthome-mcp-server",
instructions="This server is for finding and controlling smarthome devices.",
)
register_device_manager_tools(mcp, device_manager)
return mcp2.4 服务器主入口文件 (__main__.py)
python
# __main__.py
load_dotenv()
app = typer.Typer()
console = Console()
@app.command()
def main():
config = load_config()
# set up server data directory
root_dir = platformdirs.user_data_path(
appname="smarthome-mcp-server",
ensure_exists=True
)
db_path = Path(root_dir) / config.database.path
db_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
logger.info("Server data directory: %s", db_path)
# init and run
mcp_instance = initialise_server(db_path)
asyncio.run(mcp_instance.run_stdio_async())
if __name__ == "__main__":
app()3. 语音助手侧的 MCP 客户端与工具获取
python
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
def get_new_mcp_client() -> MultiServerMCPClient:
return MultiServerMCPClient(
{
"smarthome-mcp-server": {
"command": "smarthome_mcp_server",
"args": [],
"transport": "stdio",
}
}
)
def get_mcp_server_tools():
mcp_client = get_new_mcp_client()
tools = await mcp_client.get_tools()
return tools4. 语音转文本 (STT) 核心实现
python
from RealtimeSTT import AudioToTextRecorder
with AudioToTextRecorder(
model='tiny',
wakeword_backend='oww',
wake_words='hey jarvis',
device='cpu',
wake_word_activation_delay=3.0,
wake_word_buffer_duration=0.15,
post_speech_silence_duration=1.0
) as recorder:
while True:
# get the transcribed text from recorder
query = recorder.text()
if (query is not None) and (query != ""):
# get response from our langgraph agent
response_stream = await get_response_stream(
query, agent_executor, thread_config
)
# output the response to device audio
await stream_voice(response_stream, output_chunk_builder, voice)5. 智能体 (Agent) 实现
5.1 智能体构建函数 get_new_agent
python
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langgraph.graph.state import CompiledStateGraph
from voice_assistant.tools.datetime import get_tools as get_datetime_tools
def get_new_agent(
config, short_term_memory, long_term_memory
) -> CompiledStateGraph:
"""Build and return a new graph that defines the agent workflow."""
# initialise the LLM
model = init_chat_model(
model=config.Agent.model,
model_provider=config.Agent.model_provider,
temperature=0,
reasoning=config.Agent.reasoning
)
# initialise the tools that the agent will use
server_tools = await get_mcp_server_tools()
tools = (
get_datetime_tools()
+ server_tools
)
# build the agent workflow given the LLM, its tools and memory.
agent_executor = create_react_agent(
model,
tools,
checkpointer=short_term_memory,
store=long_term_memory
)
return agent_executor5.2 响应流分块处理器 OutputChunkBuilder
python
class OutputChunkBuilder:
def __init__(self):
self._msg = ""
self.end_of_sentence = (".", "?", ";", "!", "\n")
def add_chunk(self, message_chunk:str):
self._msg += message_chunk
def output_chunk_ready(self) -> bool:
return self._msg.endswith(self.end_of_sentence)
def _reset_message(self):
self._msg = ""
def get_output_chunk(self):
msg = self._msg # Get the current message chunk
self._reset_message()
return msg6. 日期时间工具实现 (tools/datetime.py)
python
# tools/datetime.py
from datetime import datetime
from langchain_core.tools.structured import StructuredTool
def get_now_datetime() -> datetime:
"""Wrapper for easier mocking in unit test."""
return datetime.now()
def get_current_time() -> str:
"""Get the current time in format HH:MM AM/PM"""
return get_now_datetime().strftime("%I:%M%p")
def _convert_date_to_words(dt: datetime):
"""Change date values represented in YYYY-mm-dd format to word values as they would be pronounced."""
day = dt.day
if day == 1 or day == 21 or day == 31:
day_word = f"{day}st"
elif day == 2 or day == 22:
day_word = f"{day}nd"
elif day == 3 or day == 23:
day_word = f"{day}rd"
else:
day_word = f"{day}th"
date_obj = dt.strftime(f"%B {day_word}, %Y")
return date_obj
def get_current_date() -> str:
"""Get the current date in format YYYY-MM-DD"""
dt = get_now_datetime()
dt_str = _convert_date_to_words(dt)
return dt_str
def get_tools():
"""Get a list of tools for the agent.
Returns:
A list of tool functions available to the agent.
"""
return [
StructuredTool.from_function(get_current_time),
StructuredTool.from_function(get_current_date),
]7. 系统整合与主程序
7.1 配置文件加载模块 (settings.py)
python
# settings.py
import logging
from pathlib import Path
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
CONFIG_PATH = Path(__file__).parents[1] / "conf" / "config.yaml"
def load_config():
logger.debug(f"Loading config from: {CONFIG_PATH}")
return OmegaConf.load(CONFIG_PATH)7.2 异步语音流处理函数 stream_voice
python
async def stream_voice(
msg_stream: AsyncGenerator,
output_chunk_builder: OutputChunkBuilder,
voice: Voice
):
"""Stream messages from the agent to the voice output."""
async for chunk, metadata in msg_stream:
if metadata["langgraph_node"] == "agent":
# build up message chunks until a full sentence is received.
if chunk.content != "":
output_chunk_builder.add_chunk(chunk.content)
if output_chunk_builder.output_chunk_ready():
voice.speak(output_chunk_builder.get_output_chunk())
# if we have anything left in the buffer, speak it.
if output_chunk_builder.current_message_length() > 0:
voice.speak(output_chunk_builder.get_output_chunk())7.3 项目主程序入口 (main.py)
python
# main.py
from RealtimeSTT import AudioToTextRecorder
from langgraph.checkpoint.sqlite.aio import AsyncSqliteSaver
from langgraph.store.sqlite.aio import AsyncSqliteStore
from voice_assistant.agent import get_new_agent, get_response_stream
from voice_assistant.voice import KokoroVoice
from settings import load_config
async def main():
conf = load_config()
voice = KokoroVoice(**conf.KokoroVoice)
output_chunk_builder = OutputChunkBuilder()
thread_config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "abc123"}}
# short term memory
async with AsyncSqliteSaver.from_conn_string(conf.Agent.memory.checkpointer) as saver:
# long term memory
async with AsyncSqliteStore.from_conn_string(conf.Agent.memory.store) as store:
agent_executor = await get_new_agent(conf, saver, store)
with AudioToTextRecorder(**conf.AudioToTextRecorder) as recorder:
while True:
query = recorder.text()
if (query is not None) and (query != ""):
response_stream = await get_response_stream(
query, agent_executor, thread_config
)
await stream_voice(response_stream, output_chunk_builder, voice)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())