作者:来自 Elastic Tomás Murúa

学习如何构建自定义 ChatGPT connector,并部署一个使用混合搜索来查询内部 GitHub issues 的 Elasticsearch MCP server。
Agent Builder 现在作为技术预览提供。你可以通过 Elastic Cloud Trial 开始使用,并在这里查看 Agent Builder 的文档。
最近,OpenAI 在 Pro/Business/Enterprise 和 Edu 方案中发布了 ChatGPT 的 custom connectors 功能。除了提供开箱即用的 Gmail、GitHub、Dropbox 等 connectors 外,你也可以通过 MCP servers 来创建自定义 connectors。
自定义 connectors 让你能够把现有的 ChatGPT connectors 与 Elasticsearch 等额外数据源结合,从而获得更完整的答案。
本文将构建一个 MCP server,把 ChatGPT 连接到一个包含内部 GitHub issues 和 pull requests 信息的 Elasticsearch index。这样就能用自然语言查询,并由你的 Elasticsearch 数据来回答。
我们会使用 FastMCP 在 Google Colab 上部署 MCP server,并通过 ngrok 获取一个 ChatGPT 可连接的公共 URL,而不需要复杂的基础设施。
如果你想了解 MCP 及其生态系统的完整介绍,请参考 The Current State of MCP。
前提条件
开始之前,你需要:
-
Elasticsearch cluster(8.X 或更高版本)
-
对你的 index 有读取权限的 Elasticsearch API key
-
Google 账号(用于 Google Colab)
-
Ngrok 账号(免费方案即可)- 类似国内的花生壳
-
具有 Pro/Enterprise/Business 或 Edu 方案的 ChatGPT 账号
理解 ChatGPT MCP connector 的要求
ChatGPT MCP connectors 需要实现两个工具:search 和 fetch 。更多细节可参考 OpenAI Docs。
Search tool
根据用户查询,从你的 Elasticsearch index 返回相关结果列表。
它接收:
- 一段用户的自然语言查询字符串。
- 示例: "Find issues related to Elasticsearch migration."
它返回:
一个包含 result 键的对象,result 是一个结果对象数组。每个结果包含:
- id ------ 文档的唯一标识符
- title ------ issue 或 PR 的标题
- url ------ issue/PR 的链接
在我们的实现中:
return {
"results": [
{
"id": "PR-612",
"title": "Fix memory leak in WebSocket notification service",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/pulls/612"
},
# ... more results
]
}Fetch tool
获取指定文档的完整内容。
它接收:
一段来自搜索结果的 Elasticsearch 文档 ID 字符串
示例: "Get me the details of PR-578."
它返回:
一个完整的文档对象,包含:
-
id ------ 文档的唯一标识符
-
title ------ issue 或 PR 的标题
-
text ------ 完整的 issue/PR 描述和细节
-
url ------ issue/PR 的链接
-
type ------ 文档类型( issue 、 pull_request )
-
status ------ 当前状态( open 、 in_progress 、 resolved )
-
priority ------ 优先级( low 、 medium 、 high 、 critical )
-
assignee ------ 负责此 issue/PR 的人
-
created_date ------ 创建时间
-
resolved_date ------ 解决时间(如果适用)
-
labels ------ 文档的标签
-
related_pr ------ 关联的 pull request ID
return {
"id": "PR-578",
"title": "Security hotfix: Patch SQL injection vulnerabilities",
"text": "Description: CRITICAL SECURITY FIX for ISSUE-1889. Patches SQL...",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/pulls/578",
"type": "pull_request",
"status": "closed",
"priority": "critical",
"assignee": "sarah_dev",
"created_date": "2025-09-19",
"resolved_date": "2025-09-19",
"labels": "security, hotfix, sql",
"related_pr": null
}
注意:这个示例使用的是扁平结构,所有字段都在根级。OpenAI 的要求是灵活的,也支持嵌套的 metadata 对象。
GitHub issues 和 PRs 数据集
在这个教程中,我们会使用一个内部 GitHub 数据集,包含 issues 和 pull requests。它代表了一个场景:你想通过 ChatGPT 查询私有的、内部的数据。
数据集在这里可以找到。我们会使用 bulk API 来更新这些数据的 index。
这个数据集包含:
-
带有描述、状态、优先级和负责人信息的 issues
-
带有代码变更、评审和部署信息的 pull requests
-
issues 和 PRs 之间的关联关系(例如:PR-578 修复 ISSUE-1889)
-
标签、日期以及其他 metadata
Index mappings
这个 index 使用下面的 mappings 来支持带 ELSER 的混合搜索。字段 text_semantic 用于语义搜索,而其他字段用于 keyword 搜索。
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"text": {
"type": "text"
},
"text_semantic": {
"type": "semantic_text",
"inference_id": ".elser-2-elasticsearch"
},
"url": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"type": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"status": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"priority": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"assignee": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"created_date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "iso8601"
},
"resolved_date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "iso8601"
},
"labels": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"related_pr": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}构建 MCP server
我们的 MCP server 实现了两个遵循 OpenAI 规范的工具,使用混合搜索将 semantic search 与 text matching 结合,以获得更好的结果。
Search tool
使用带有 RRF ( Reciprocal Rank Fusion ) 的混合搜索,结合 semantic search 和 text matching:
@mcp.tool()
async def search(query: str) -> Dict[str, List[Dict[str, Any]]]:
"""
Search for internal issues and PRs using hybrid search (semantic + text with RRF).
Returns list with id, title, and url per OpenAI spec.
"""
if not query or not query.strip():
return {"results": []}
logger.info(f"Searching for: '{query}'")
try:
# Hybrid search with RRF (Reciprocal Rank Fusion)
response = es_client.search(
index=ELASTICSEARCH_INDEX,
size=10,
source=["id", "title", "url", "type", "priority"],
retriever={
"rrf": {
"retrievers": [
{
# Semantic search with ELSER
"standard": {
"query": {
"semantic": {
"field": "text_semantic",
"query": query
}
}
}
},
{
# Text search (BM25) for keyword matching
"standard": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": [
"title^3",
"text^2",
"assignee^2",
"type",
"labels",
"priority"
],
"type": "best_fields",
"fuzziness": "AUTO"
}
}
}
}
],
"rank_window_size": 50,
"rank_constant": 60
}
}
)
results = []
if response and 'hits' in response:
for hit in response['hits']['hits']:
source = hit['_source']
results.append({
"id": source.get('id', hit['_id']),
"title": source.get('title', 'Unknown'),
"url": source.get('url', '')
})
logger.info(f"Found {len(results)} results")
return {"results": results}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Search error: {e}")
raise ValueError(f"Search failed: {str(e)}")要点:
-
多字段匹配 ( multi-match ):在多个字段中搜索并加权(
title^3、text^2、assignee^2)。符号^会乘以相关性得分,使标题匹配优先于内容匹配。 -
模糊匹配 :fuzziness: AUTO 通过允许近似匹配来处理拼写错误和笔误。
-
RRF 参数调整:
-
rank_window_size: 50------ 指定在合并前,每个检索器(语义和文本)考虑的前 N 个结果。 -
rank_constant: 60------ 决定各个结果集中某文档对最终排名的影响量。
-
-
只返回必需字段 :按照
OpenAI规范只返回id、title、url,避免不必要地暴露额外字段。
Fetch tool
通过文档 ID 获取文档详情(如果存在):
@mcp.tool()
async def fetch(id: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Retrieve complete issue/PR details by ID.
Returns id, title, text, url.
"""
if not id:
raise ValueError("ID is required")
logger.info(f"Fetching: {id}")
try:
# Search by the 'id' field (not _id) since IDs are stored as a field
response = es_client.search(
index=ELASTICSEARCH_INDEX,
body={
"query": {
"term": {
"id": id # Search by your custom 'id' field
}
},
"size": 1
}
)
if not response or not response['hits']['hits']:
raise ValueError(f"Document with id '{id}' not found")
hit = response['hits']['hits'][0]
source = hit['_source']
result = {
"id": source.get('id', id),
"title": source.get('title', 'Unknown'),
"text": source.get('text', ''),
"url": source.get('url', ''),
"type": source.get('type', ''),
"status": source.get('status', ''),
"priority": source.get('priority', ''),
"assignee": source.get('assignee', ''),
"created_date": source.get('created_date', ''),
"resolved_date": source.get('resolved_date', ''),
"labels": source.get('labels', ''),
"related_pr": source.get('related_pr', '')
}
logger.info(f"Fetched: {result['title']}")
return result
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Fetch error: {e}")
raise ValueError(f"Failed to fetch '{id}': {str(e)}")要点:
- 按文档 ID 字段搜索:在自定义
id字段上使用 term query - 返回完整文档:包含带有所有内容的完整 text 字段
- 扁平结构:所有字段都在根级,符合 Elasticsearch 的文档结构
在 Google Colab 上部署
我们将使用 Google Colab 运行 MCP server,并用 ngrok 将其公开,使 ChatGPT 可以连接。
步骤 1:打开 Google Colab notebook
访问我们的预配置 notebook Elasticsearch MCP for ChatGPT。
步骤 2:配置你的凭证
你需要三条信息:
- Elasticsearch URL :你的 Elasticsearch cluster URL
- Elasticsearch API Key :对你的 index 有读取权限的 API key
- Ngrok Auth Token :来自 ngrok 的免费 token。我们将使用 ngrok 将 MCP URL 暴露到互联网,以便 ChatGPT 可以连接
获取你的 ngrok token
- 在 ngrok 注册一个免费账号
- 打开 ngrok dashboard
- 复制你的 auth token
在 Google Colab 中添加 secrets
在 Google Colab notebook 中:
-
点击左侧栏的钥匙图 标以打开 Secrets
-
添加以下三个 secrets:
ELASTICSEARCH_URL=https://your-cluster.elastic.com:443 ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY=your-api-key NGROK_TOKEN=your-ngrok-token -
为每个 secret 启用 notebook 访问权限
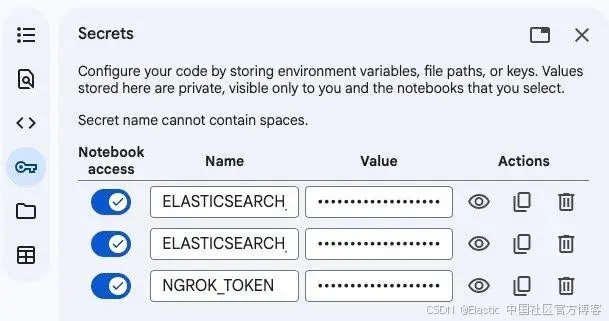
步骤 3:运行 notebook
-
点击 Runtime ,然后选择 Run all 来执行所有单元格
-
等待服务器启动(大约 30 秒)
-
查看输出,找到你的公共 ngrok URL

-
输出将显示类似如下内容:
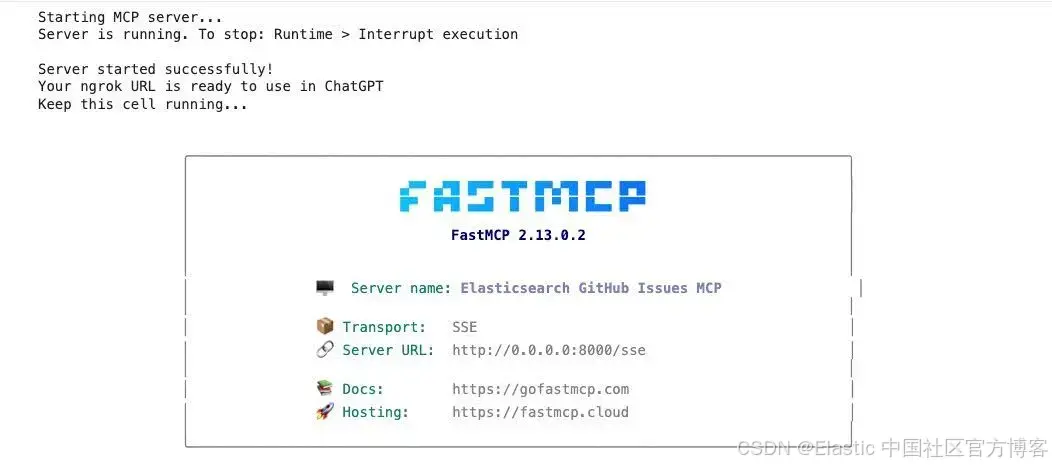
连接到 ChatGPT
现在我们将把 MCP server 连接到你的 ChatGPT 账号。
1)打开 ChatGPT 并进入 Settings
2)导航到 Connectors 。如果你使用的是 Pro 账号,需要在 connectors 中开启开发者模式(developer mode)
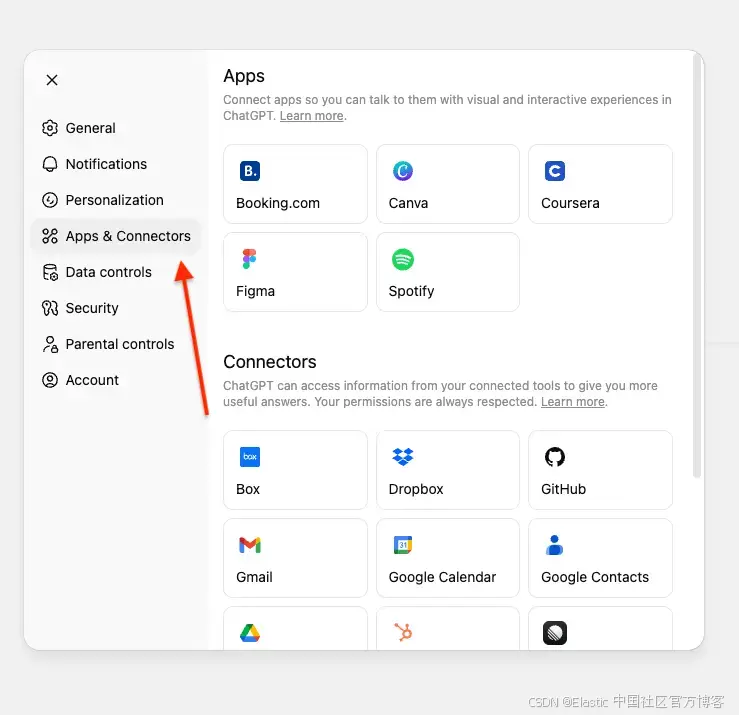
如果你使用的是 ChatGPT Enterprise 或 Business,需要将 connector 发布到你的工作区。
3)点击 Create。
注意:在 Business、Enterprise 和 Edu 工作区中,只有工作区所有者、管理员以及具有相应权限的用户(Enterprise/Edu)可以添加自定义 connectors。普通成员角色的用户无法自行添加自定义 connectors。
一旦 connector 由所有者或管理员添加并启用,它就可以被工作区的所有成员使用。
4)输入所需信息以及以 /sse/ 结尾的 ngrok URL。注意 "sse" 后的斜杠 /,缺少它将无法工作:
- Name:Elasticsearch MCP
- Description:用于搜索和获取 GitHub 内部信息的自定义 MCP
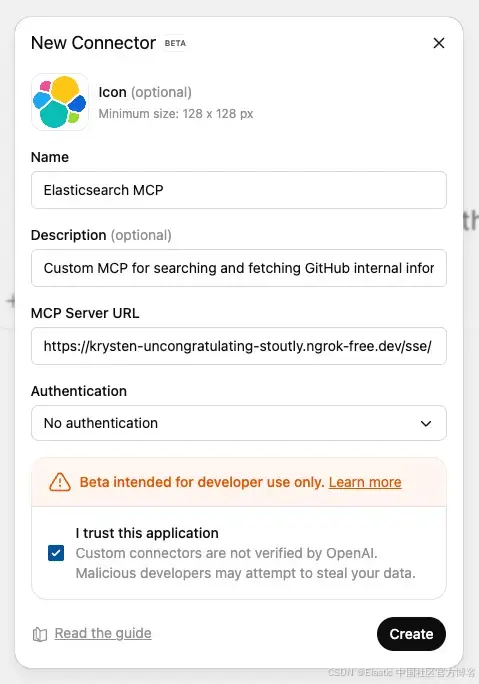
5)点击 Create 保存自定义 MCP。
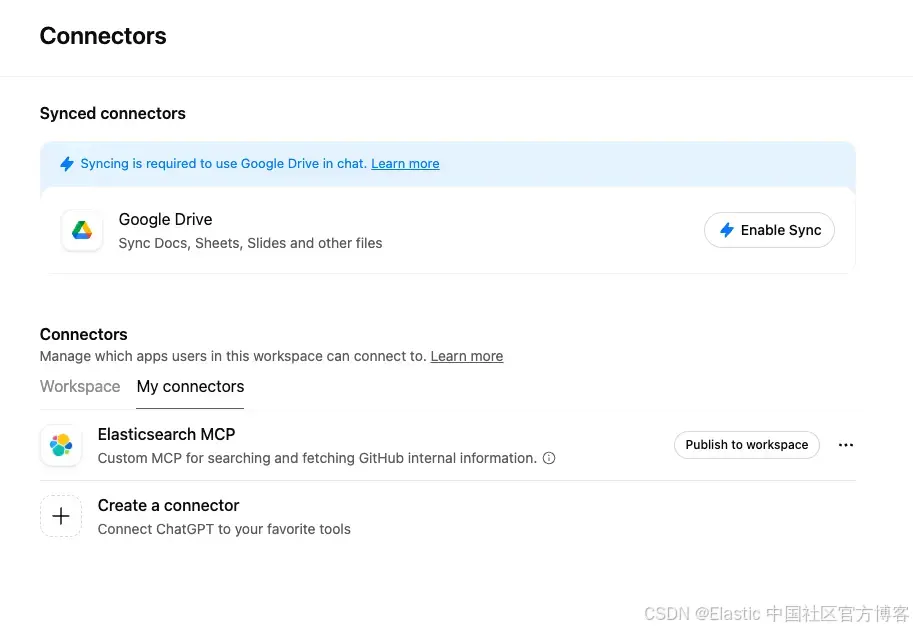
如果你的服务器正在运行,连接会立即生效。无需额外身份验证,因为 Elasticsearch API key 已在服务器中配置。
测试 MCP server
在提问之前,你需要选择 ChatGPT 应该使用哪个 connector。
Prompt 1:搜索 issues
提问: "Find issues related to Elasticsearch migration" 并确认调用了 actions tool。
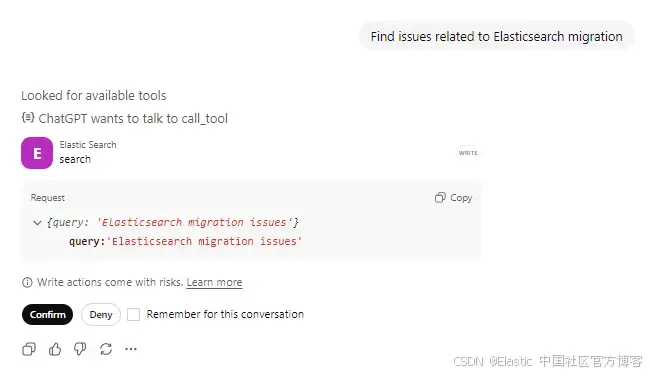
ChatGPT 会使用你的查询调用 search tool。你可以看到它正在查找可用工具,并准备调用 Elasticsearch tool,同时在对工具执行任何操作之前,会先向用户确认。
Tool 调用请求:
{
"query": "Elasticsearch migration issues"
}Tool response:
{
"results": [
{
"id": "PR-598",
"title": "Elasticsearch 8.x migration - Application code changes",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/pulls/598"
},
{
"id": "ISSUE-1712",
"title": "Migrate from Elasticsearch 7.x to 8.x",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/issues/1712"
},
{
"id": "RFC-045",
"title": "Design Proposal: Microservices Migration Architecture",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/rfcs/045"
}
// ... 7 more results
]
}ChatGPT 会处理结果,并以自然、对话式的格式展示给用户。
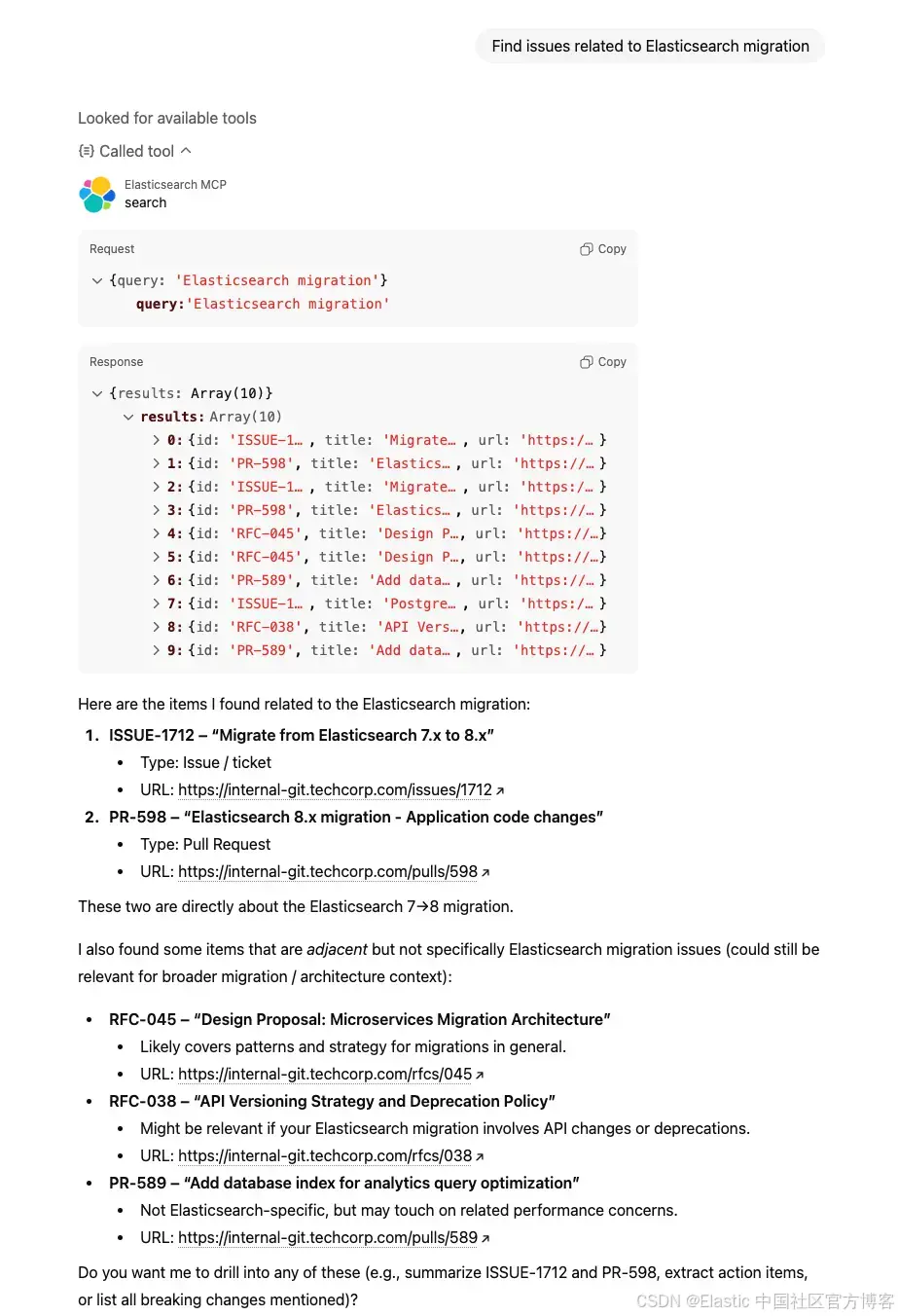
幕后流程
Prompt: "Find issues related to Elasticsearch migration"
-
ChatGPT 调用
search("Elasticsearch migration") -
Elasticsearch 执行混合搜索
- Semantic search 理解 "upgrade" 和 "version compatibility" 等概念
- Text search 查找 "Elasticsearch" 和 "migration" 的精确匹配
- RRF 将两种方法的结果合并并排序
-
返回前 10 个匹配结果,包括
id、title、url -
ChatGPT 识别 "ISSUE-1712: migrate from Elasticsearch 7.x to 8.x" 为最相关结果
Prompt 2:获取完整详情
提问: "Get me details of ISSUE-1889"
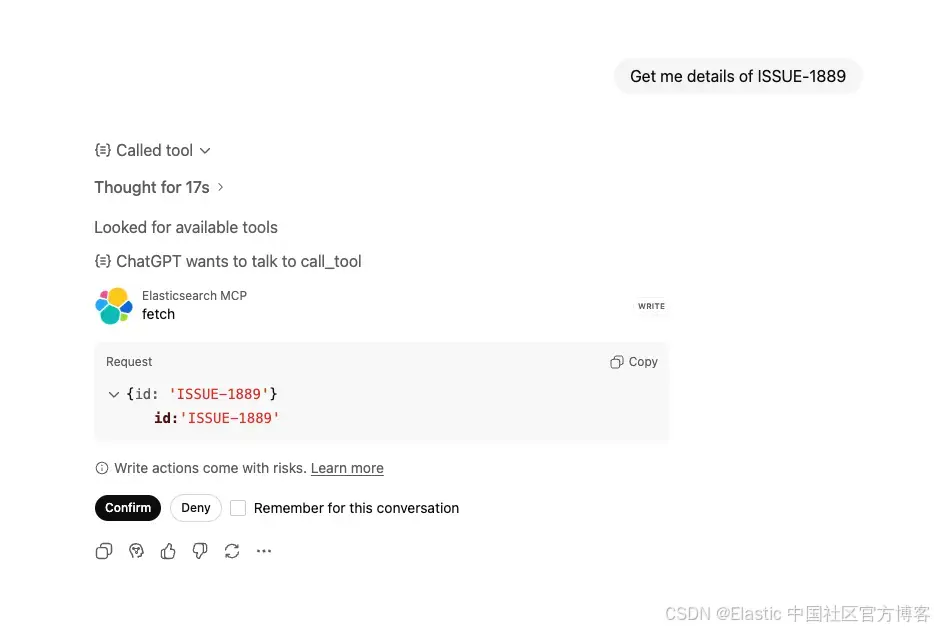
ChatGPT 识别到你想获取特定 issue 的详细信息,并调用 fetch tool,同时在对工具执行任何操作之前会先向用户确认。
Tool 调用请求:
{
"id": "ISSUE-1889"
}Tool 响应:
{
"id": "ISSUE-1889",
"title": "SQL injection vulnerability in search endpoint",
"text": "Description: Security audit identified SQL injection vulnerability in /api/v1/search endpoint. User input from query parameter is not properly sanitized before being used in raw SQL query. Severity: HIGH - Immediate action required Affected Code: - File: services/search/query_builder.py - Line: 145-152 - Issue: String concatenation used instead of parameterized queries Investigation: - @security_team_alice: Confirmed exploitable with UNION-based injection - @sarah_dev: Checking all other endpoints for similar patterns - @john_backend: Found 3 more instances in legacy codebase Remediation: - Rewrite using SQLAlchemy ORM or parameterized queries - Add input validation and sanitization - Implement WAF rules as additional layer - Security regression tests Comments: - @tech_lead_mike: Stop all other work, this is P0 - @sarah_dev: PR-578 ready with fixes for all 4 vulnerable endpoints - @alex_devops: Deployed hotfix to production 2025-09-19 at 14:30 UTC - @security_team_alice: Verified fix, conducting full pentest next week Resolution: All vulnerable endpoints patched. Added pre-commit hooks to catch raw SQL queries. Security training scheduled for team.",
"url": "https://internal-git.techcorp.com/issues/1889",
"type": "issue",
"status": "closed",
"priority": "critical",
"assignee": "sarah_dev",
"created_date": "2025-09-18",
"resolved_date": "2025-09-19",
"labels": "security, vulnerability, bug, sql",
"related_pr": "PR-578"
}ChatGPT 会整合信息,并以清晰的方式呈现。
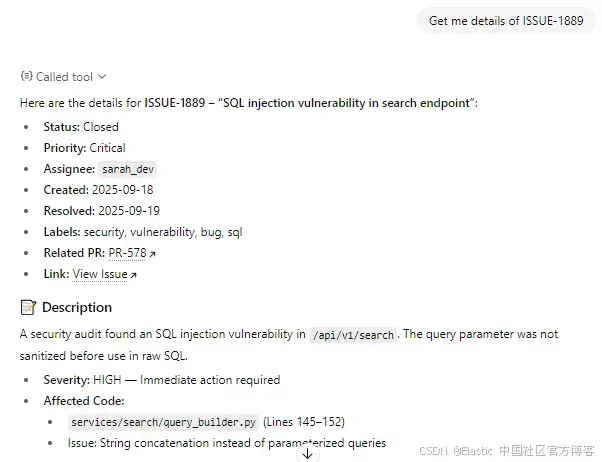
幕后流程
Prompt: "Get me the details of ISSUE-1889"
- ChatGPT 调用
fetch("ISSUE-1889") - Elasticsearch 检索完整文档
- 返回一个所有字段都在根级的完整文档
- ChatGPT 整合信息,并带上适当引用进行回答
结论
本文中,我们构建了一个自定义 MCP server,将 ChatGPT 连接到 Elasticsearch,使用专门的 search 和 fetch MCP 工具,使得可以通过自然语言查询私有数据。
这种 MCP 模式适用于任何 Elasticsearch index、文档、产品、日志或其他希望通过自然语言查询的数据。
原文:https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/chatgpt-connector-mcp-server-github-elasticsearch