本文涉及知识点
P1354 房间最短路问题
题目描述
在一个长宽均为 10 10 10,入口、出口分别为 ( 0 , 5 ) (0,5) (0,5)、 ( 10 , 5 ) (10,5) (10,5) 的房间里,有几堵墙,每堵墙上有两个缺口,求入口到出口的最短路经。
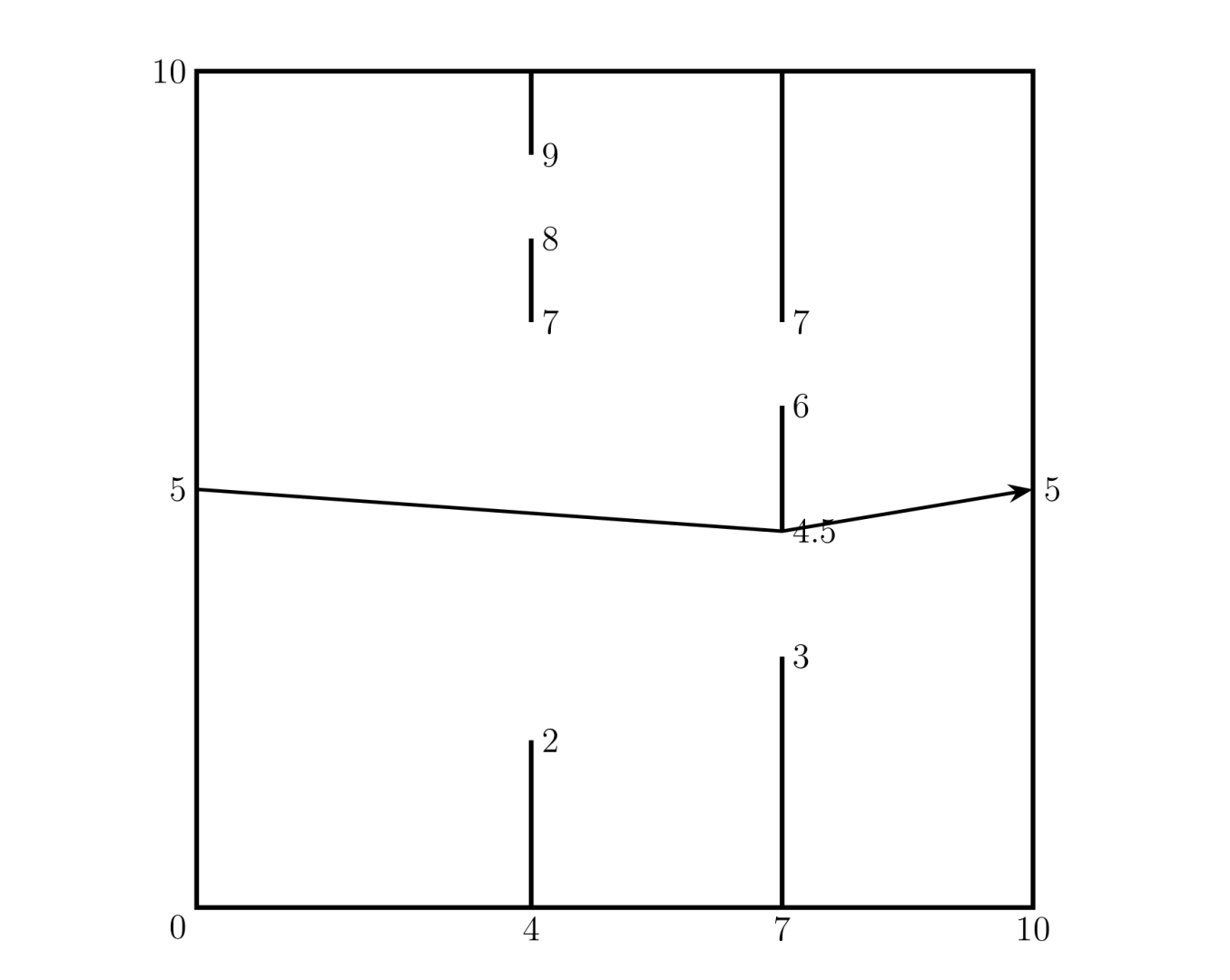
输入格式
第一排为 n n n( n ≤ 20 n \le 20 n≤20),墙的数目。
接下来 n n n 排,每排 5 5 5 个实数 x , a 1 , b 1 , a 2 , b 2 x,a_1,b_1,a_2,b_2 x,a1,b1,a2,b2。
x x x 表示墙的横坐标(所有墙都是竖直的), a 1 ∼ b 1 a_1 \sim b_1 a1∼b1 和 a 2 ∼ b 2 a_2 \sim b_2 a2∼b2 之间为空缺。
a 1 , b 1 , a 2 , b 2 a_1,b_1,a_2,b_2 a1,b1,a2,b2 保持递增, x 1 ∼ x n x_1 \sim x_n x1∼xn 也是递增的。
输出格式
输出最短距离,保留 2 2 2 位小数。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
2
4 2 7 8 9
7 3 4.5 6 7输出 #1
10.06动态规划
起点和终点也看成墙。将墙上各点映射成整数。即: ⌊ 200 × y ⌋ \lfloor 200 \times y \rfloor ⌊200×y⌋,重新映射后,y ∈ \in ∈[0,2000] 。M=2000
动态规划的状态表示
dp[x][y]表示,起点到达第x堵墙 y/200.0的最短路程。空间复杂度:O(NM)
动态规划的填表顺序
枚举前驱状态,x=0 to n y = 0 to 200
动态规划的转移方程
y1 = 0 to 200
如果y和y1都在缺口,则:MinSelf(dp[x+1][y1],dp[x][y]+(y和y1间的距离))
单个状态的时间复杂度:O(MM),总时间复杂度:O(NMM)。
动态规划的初始状态
dp[0][1000]=0,其它10万。
动态规划的返回值
dp[n+1][10000]
计算几何
只需要考虑各缺口的两个端点。
O是直线AB和线段DE的交点,如何|AO|+|BO|最短
如果AB和直线DE的交点在DE上,则最短是|AB|的长度,因为两点间直线距离最短。下面讨论交点不在线段DE上。以O为原点,以AB为x轴,改变x轴,y轴的方向使得DE在第一象限,不失一般性,令D距离原点比E近。
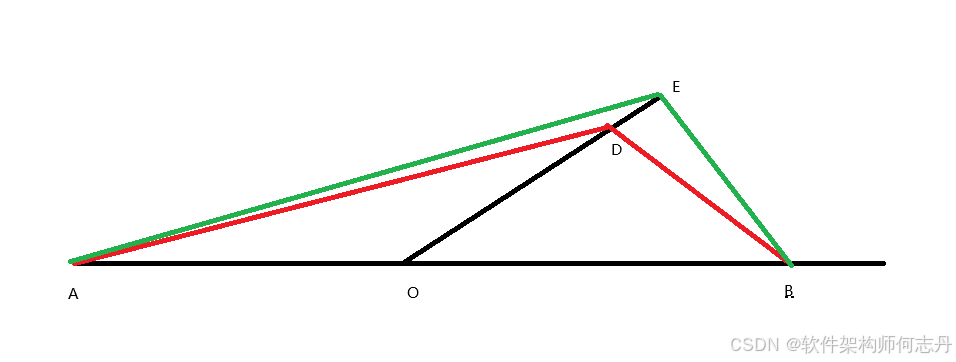
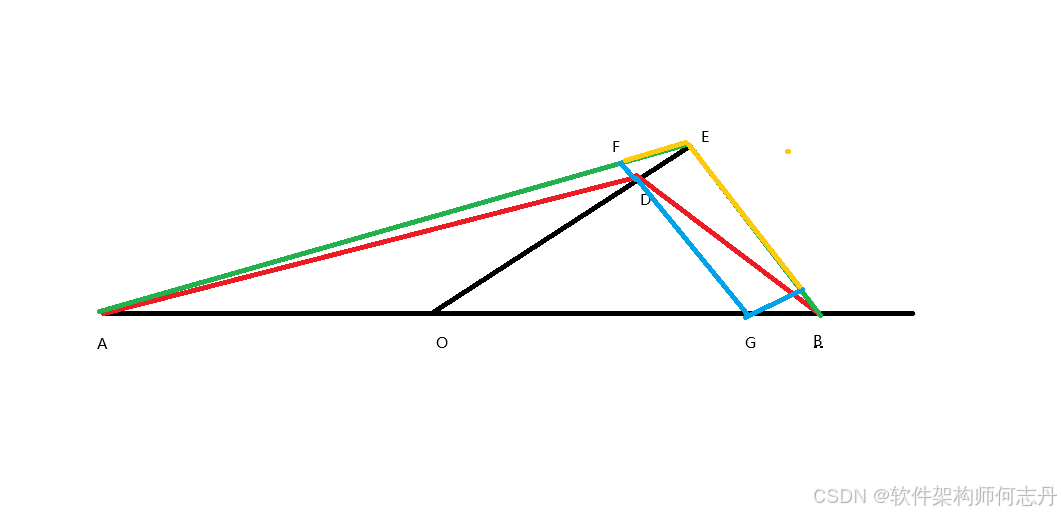
过D做平行于BE的平行线(蓝色),蓝金边组成的四边形是平行四边形,故蓝边等于金边。
故|AE|+|EB|=绿边+蓝边+绿边。
一,根据正弦定理,第一条绿边大于第一条红边。根据正弦定理:
∣ A G ∣ sin ∠ A G F = ∣ A F ∣ sin ∠ A F G |AG|\sin\angle AG F= |AF|\sin\angle AFG ∣AG∣sin∠AGF=∣AF∣sin∠AFG
∣ A G ∣ sin ∠ A G D = ∣ A D ∣ sin ∠ A D G |AG|\sin\angle AGD= |AD|\sin\angle ADG ∣AG∣sin∠AGD=∣AD∣sin∠ADG ,
由于 ∠ A G F 就是 ∠ A G D \angle AGF就是\angle AGD ∠AGF就是∠AGD,故 ∣ A F ∣ sin ∠ A F G = ∣ A D ∣ sin ∠ A D G |AF|\sin \angle AFG=|AD|\sin \angle ADG ∣AF∣sin∠AFG=∣AD∣sin∠ADG。 ∠ A F G < ∠ A D G < 90 ∘ \angle AFG < \angle ADG<90^\circ ∠AFG<∠ADG<90∘,故|AF|>|AD|。
根据三角形内角和定理。
∠ A G F + ∠ G F A + ∠ F A G = ∠ A G D + ∠ G D A + ∠ D A G \angle AGF + \angle GFA + \angle FAG=\angle AGD + \angle GDA + \angle DAG ∠AGF+∠GFA+∠FAG=∠AGD+∠GDA+∠DAG
∠ G F A + ∠ F A G = ∠ G D A + ∠ D A G \angle GFA + \angle FAG= \angle GDA + \angle DAG ∠GFA+∠FAG=∠GDA+∠DAG
∠ D A G < ∠ F A G 故 ∠ A F G < ∠ A D G \angle DAG < \angle FAG故\angle AFG < \angle ADG ∠DAG<∠FAG故∠AFG<∠ADG
二,蓝边+第二条绿边 > |BD|。忽略FD,余下的边,也大于|BD|,两点之间直线最短。
实现
枚举起点、终点、各缺口端点。建立邻接表,求最短路。
坐标相同的点,无需联通。
由于线段不是垂直于x轴,故可以用斜截式,方便计算交点。
判断墙和线段关系:
x方向:墙是否在线段上,如果不是,不会交叉。如果是,求y,如果y不在缺口,忽略。
时间复杂度 :O ( N 3 ) (N^3) (N3),第一层第二层循环枚举线段端点,第三层循环枚举墙。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<iomanip>
#include<numeric>
#include <math.h>
#include <climits>
#include<assert.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<list>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
template<class T1, class T2>
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, pair<T1, T2>& pr) {
in >> pr.first >> pr.second;
return in;
}
template<class T1, class T2, class T3 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3>& t) {
in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t);
return in;
}
template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& t) {
in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t);
return in;
}
template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4,class T5 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4,T5>& t) {
in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t) >> get<4>(t);
return in;
}
template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read() {
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
vector<T> ret(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> ret[i];
}
return ret;
}
template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read(int n) {
vector<T> ret(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> ret[i];
}
return ret;
}
template<int N = 1'000'000>
class COutBuff
{
public:
COutBuff() {
m_p = puffer;
}
template<class T>
void write(T x) {
int num[28], sp = 0;
if (x < 0)
*m_p++ = '-', x = -x;
if (!x)
*m_p++ = 48;
while (x)
num[++sp] = x % 10, x /= 10;
while (sp)
*m_p++ = num[sp--] + 48;
AuotToFile();
}
inline void write(char ch)
{
*m_p++ = ch;
AuotToFile();
}
inline void ToFile() {
fwrite(puffer, 1, m_p - puffer, stdout);
m_p = puffer;
}
~COutBuff() {
ToFile();
}
private:
inline void AuotToFile() {
if (m_p - puffer > N - 100) {
ToFile();
}
}
char puffer[N], * m_p;
};
template<int N = 12 * 1'000'000>
class CInBuff
{
public:
inline CInBuff() {
fread(buffer, 1, N, stdin);
}
inline int Read() {
int x(0), f(0);
while (!isdigit(*S))
f |= (*S++ == '-');
while (isdigit(*S))
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (*S++ ^ 48);
return f ? -x : x;
}
private:
char buffer[N], * S = buffer;
};
template<class T>
class CVector2D;
template<class T>
class CPoint2D {
public:
T X, Y;
// 构造函数
CPoint2D() : X(0), Y(0) {}
CPoint2D(T x, T y) : X(x), Y(y) {}
// 两点距离
T Distance(const CPoint2D<T>& other) const {
T dx = X - other.X;
T dy = Y - other.Y;
return std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
// 向量运算
CVector2D<T> operator-(const CPoint2D<T>& other) const {
return CVector2D<T>(X - other.X, Y - other.Y);
}
CPoint2D<T> operator+(const CVector2D<T>& vec) const {
return CPoint2D<T>(X + vec.X, Y + vec.Y);
}
CPoint2D<T> operator-(const CVector2D<T>& vec) const {
return CPoint2D<T>(X - vec.X, Y - vec.Y);
}
bool operator<(const CPoint2D<T>& o) const {
if (X == o.X) { return Y < o.Y; }
return X < o.X;
};
};
template<class T>
class CVector2D {
public:
T X, Y;
// 构造函数
CVector2D() : X(0), Y(0) {}
CVector2D(T x, T y) : X(x), Y(y) {}
CVector2D(const CPoint2D<T>& from, const CPoint2D<T>& to)
: X(to.X - from.X), Y(to.Y - from.Y) {}
// 点积
T DotMul(const CVector2D<T>& other) const {
return X * other.X + Y * other.Y;
}
// 叉积(二维叉积返回标量)
T CrossMul(const CVector2D<T>& other) const {
return X * other.Y - Y * other.X;
}
// 与点的点积(常用于点到向量投影)
T DotMul(const CPoint2D<T>& point) const {
return X * point.X + Y * point.Y;
}
// 从两点创建向量(静态方法)
static CVector2D<T> From2Point(const CPoint2D<T>& ptFrom, const CPoint2D<T>& ptTo) {
return CVector2D<T>(ptTo.X - ptFrom.X, ptTo.Y - ptFrom.Y);
}
// 向量长度
T Len() const {
return std::sqrt(X * X + Y * Y);
}
// 单位向量
CVector2D<T> Normalized() const {
T length = Len();
if (length == 0) return CVector2D<T>(0, 0);
return CVector2D<T>(X / length, Y / length);
}
/// <summary>
/// 以 ptOrigin 为原点,xAxis 为 X 轴正方向建立新坐标系,
/// 返回点 pt 在新坐标系中的坐标
/// </summary>
static CPoint2D<T> PositionInNewCoord(const CPoint2D<T>& pt,
const CPoint2D<T>& ptOrigin,
const CVector2D<T>& xAxis) {
T len = xAxis.Len();
if (len == 0) {
// 处理零向量情况
return CPoint2D<T>(0, 0);
}
CVector2D<T> v = From2Point(ptOrigin, pt);
T dDot = v.DotMul(xAxis);
T dCross = v.CrossMul(xAxis);
return CPoint2D<T>(dDot / len, dCross / len);
}
// 向量运算
CVector2D<T> operator+(const CVector2D<T>& other) const {
return CVector2D<T>(X + other.X, Y + other.Y);
}
CVector2D<T> operator-(const CVector2D<T>& other) const {
return CVector2D<T>(X - other.X, Y - other.Y);
}
CVector2D<T> operator*(T scalar) const {
return CVector2D<T>(X * scalar, Y * scalar);
}
CVector2D<T> operator/(T scalar) const {
return CVector2D<T>(X / scalar, Y / scalar);
}
};
//多源码路径
template<class T = int >
class CFloyd
{
public:
CFloyd(int n, const T INF = 1000 * 1000 * 1000) :m_INF(INF)
{
m_vMat.assign(n, vector<T>(n, m_INF));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
m_vMat[i][i] = 0;
}
}
void SetEdge(int i1, int i2, const T& dis, bool bDirect = false)
{
m_vMat[i1][i2] = min(m_vMat[i1][i2], dis);
if (!bDirect) {
m_vMat[i2][i1] = m_vMat[i1][i2];
}
}
vector<vector<T>> Dis()const
{
auto vResMat = m_vMat;
const int n = m_vMat.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{//通过i中转
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < n; i1++)
{
if (m_INF == vResMat[i1][i])
{
continue;
}
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < n; i2++)
{
//此时:m_vMat[i1][i2] 表示通过[0,i)中转的最短距离
vResMat[i1][i2] = min(vResMat[i1][i2], vResMat[i1][i] + vResMat[i][i2]);
//m_vMat[i1][i2] 表示通过[0,i]中转的最短距离
}
}
}
return vResMat;
};
vector<vector<T>> m_vMat;//结果串
const T m_INF;
};
class Solution {
public:
double Ans(vector<tuple<double, double, double, double, double>>& walls) {
vector<CPoint2D<double>> pts = { {0,5},{10,5} };
for (const auto& [x, y1, y2, y3, y4] : walls) {
pts.emplace_back(CPoint2D<double>(x, y1));
pts.emplace_back(CPoint2D<double>(x, y2));
pts.emplace_back(CPoint2D<double>(x, y3));
pts.emplace_back(CPoint2D<double>(x, y4));
}
sort(pts.begin(), pts.end());
CFloyd<double> floyd(pts.size());
for (int i = 0; i < pts.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (pts[i].X == pts[j].X) { continue; }
const double k = (pts[i].Y - pts[j].Y) / (pts[i].X - pts[j].X);
const double b = pts[i].Y - k * pts[i].X;
bool bCross = false;
for (const auto& [x, y1, y2, y3, y4] : walls) {
if ((x <= pts[j].X) || (x >= pts[i].X)) { continue; }
const double y = k * x + b;
if ((y >= y1) && (y <= y2)) { continue; }
if ((y >= y3) && (y <= y4)) { continue; }
bCross = true;
}
if (!bCross) {
floyd.SetEdge(i, j, pts[i].Distance(pts[j]), false);
}
}
}
auto ans = floyd.Dis();
return ans[0].back();
}
};
int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUG
freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
#endif // DEBUG
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(nullptr);
auto walls = Read<tuple<double, double, double, double, double>>();
#ifdef _DEBUG
//printf("k=%d", k);
//Out(que, "que=");
Out(walls, ",walls=");
//Out(P, ",P=");
#endif // DEBUG
auto res = Solution().Ans(walls);
//cout << res << "\n";
printf("%.2lf\n", res);
return 0;
};
扩展阅读
| 我想对大家说的话 |
|---|
| 工作中遇到的问题,可以按类别查阅鄙人的算法文章,请点击《算法与数据汇总》。 |
| 学习算法:按章节学习《喜缺全书算法册》,大量的题目和测试用例,打包下载。重视操作 |
| 有效学习:明确的目标 及时的反馈 拉伸区(难度合适) 专注 |
| 员工说:技术至上,老板不信;投资人的代表说:技术至上,老板会信。 |
| 闻缺陷则喜(喜缺)是一个美好的愿望,早发现问题,早修改问题,给老板节约钱。 |
| 子墨子言之:事无终始,无务多业。也就是我们常说的专业的人做专业的事。 |
| 如果程序是一条龙,那算法就是他的是睛 |
| 失败+反思=成功 成功+反思=成功 |
视频课程
先学简单的课程,请移步CSDN学院,听白银讲师(也就是鄙人)的讲解。
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/38771
如何你想快速形成战斗了,为老板分忧,请学习C#入职培训、C++入职培训等课程
https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/6176
测试环境
操作系统:win7 开发环境: VS2019 C++17
或者 操作系统:win10 开发环境: VS2022 C++17
如无特殊说明,本算法 用**C++**实现。
