作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo
探索使用 Elastic Agent Builder 、 MCP 和 semantic search 构建用于自动化威胁分析的安全 agent 的 agentic 参考架构
Agent Builder 现已以 tech preview 形式提供。你可以通过 Elastic Cloud Trial 开始使用,并在这里查看 Agent Builder 的文档。
在本文中,我们将介绍一个参考架构,用于通过 Elastic Agent Builder 使用具备 AI 能力的 Elasticsearch ,并暴露一个 MCP server 来访问 Agent Builder tools 和 Elasticsearch data 。
Model Context Protocol ( MCP ) 是一个开源标准,使应用和 LLM 可以通过 MCP tools(编程能力)与外部系统通信,而 LangGraph( LangChain 的扩展)提供了这些 agentic workflows 的编排框架。
我们将实现一个应用,它可以同时搜索内部知识(存储在 Elasticsearch 中的数据)和外部来源(互联网上的数据),以识别与特定工具相关的潜在和已知漏洞。该应用将收集这些信息,并生成一份详细的发现总结。
要求
- Elasticsearch 9.2
- Python 3.1x
- OpenAI API Key
- Elasticsearch API Key
- Serper API Key
Elastic Agent Builder
Elastic Agent Builder 是一组由 AI 驱动的能力,用于开发和集成可以与你的 Elasticsearch 数据交互的 agent 。它提供了一个内置 agent ,可用于与你的数据或实例进行自然语言对话,同时也支持 tool 创建、 Elastic APIs 、 A2A 和 MCP 。在本文中,我们将重点介绍使用 MCP server 从外部访问 Elastic Agent Builder tools 。
要了解更多 Agent Builder 的功能,你可以阅读这篇文章。
Agent Builder MCP 功能
MCP server 在 Agent Builder 中可用,并可以通过以下地址访问:
{KIBANA_URL}/api/agent_builder/mcp
# Or if you are using a custom Kibana space:
{KIBANA_URL}/s/{SPACE_NAME}/api/agent_builder/mcpAgent Builder 提供了 Built-in tools ,你也可以创建你自己的 custom tools 。
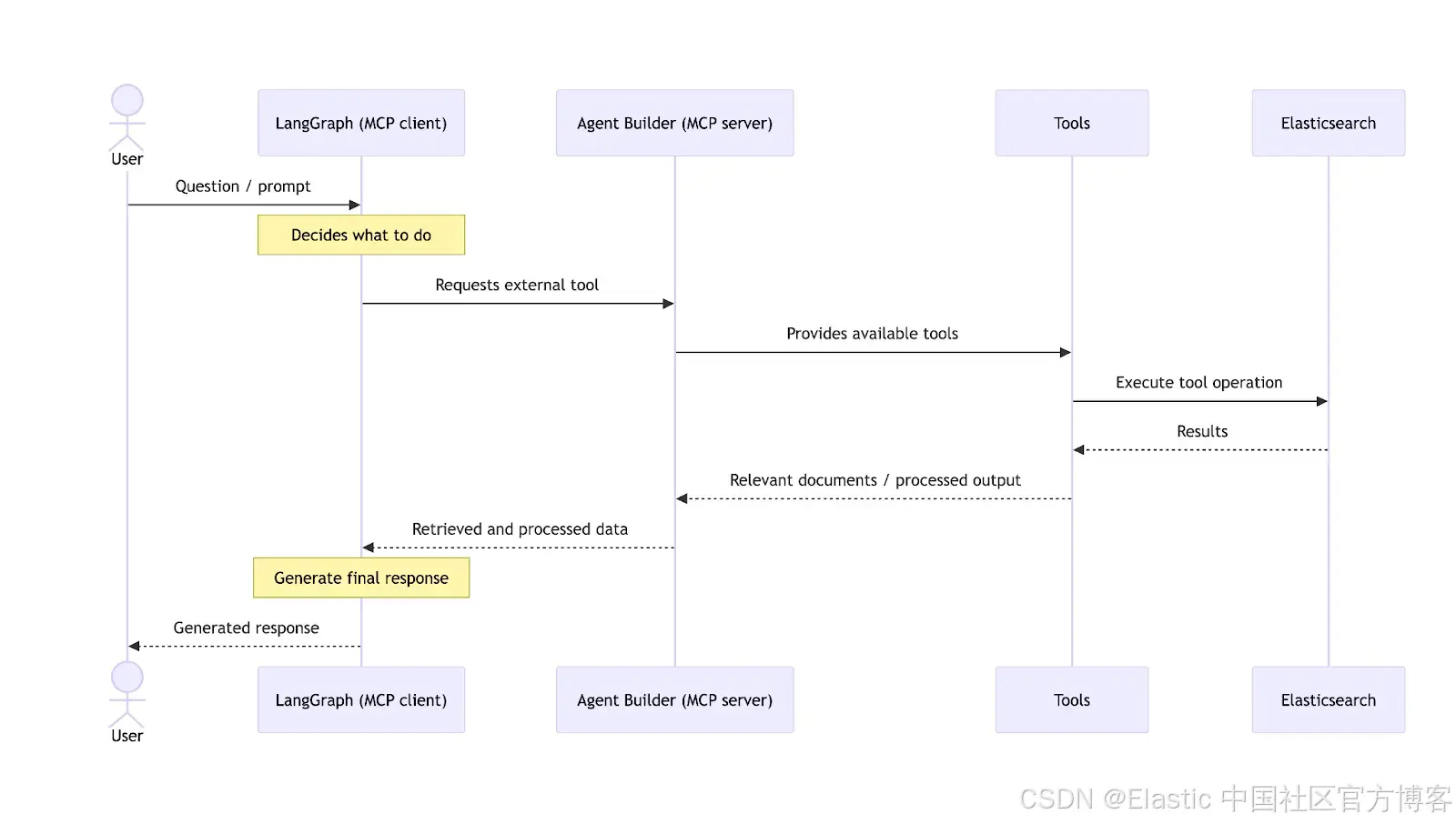
参考架构
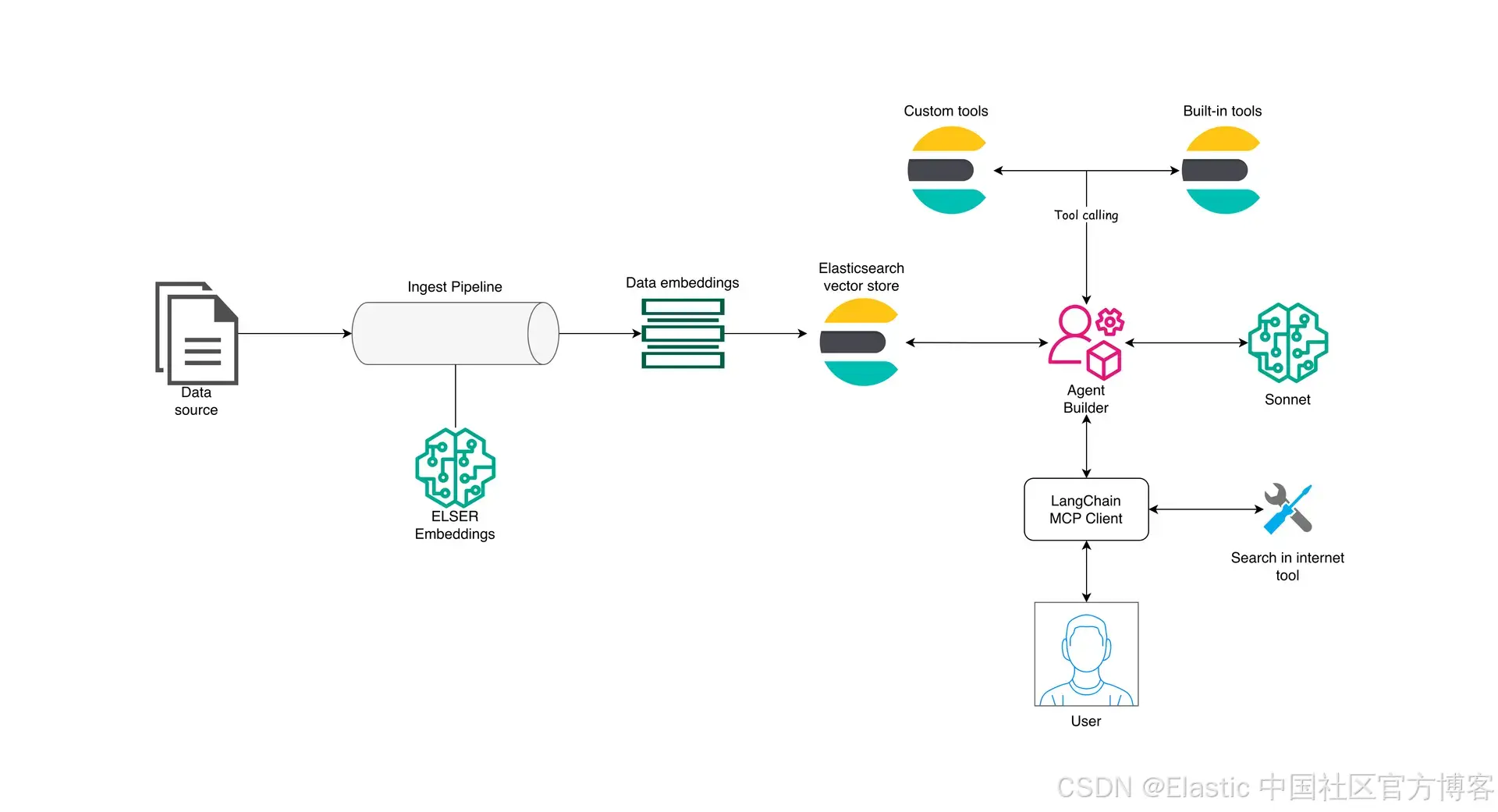
为了全面了解 agentic 应用在端到端工作流中使用的各个元素,我们来看下面这张示意图:
Elasticsearch 位于该架构的中心,作为 vector store ,提供 embeddings 生成模型,并同时提供 MCP server ,以便通过 tools 访问数据。为了更好地解释整个工作流,我们将分别来看 ingestion 层和 Agent Builder 层。
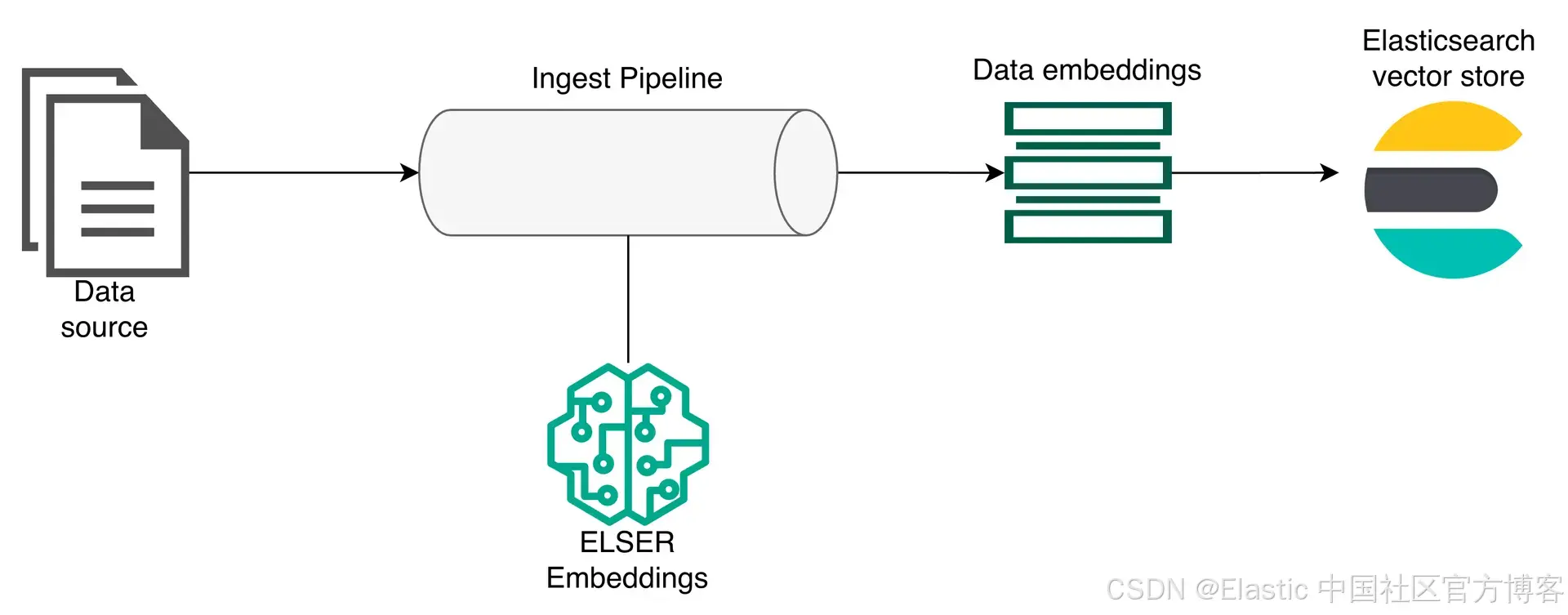
这里,第一个元素是将要存储在 Elasticsearch 中的数据。数据会经过一个 ingest pipeline ,在该过程中由 Elasticsearch ELSER 模型进行处理以生成 embeddings ,然后存储到 Elasticsearch 中。
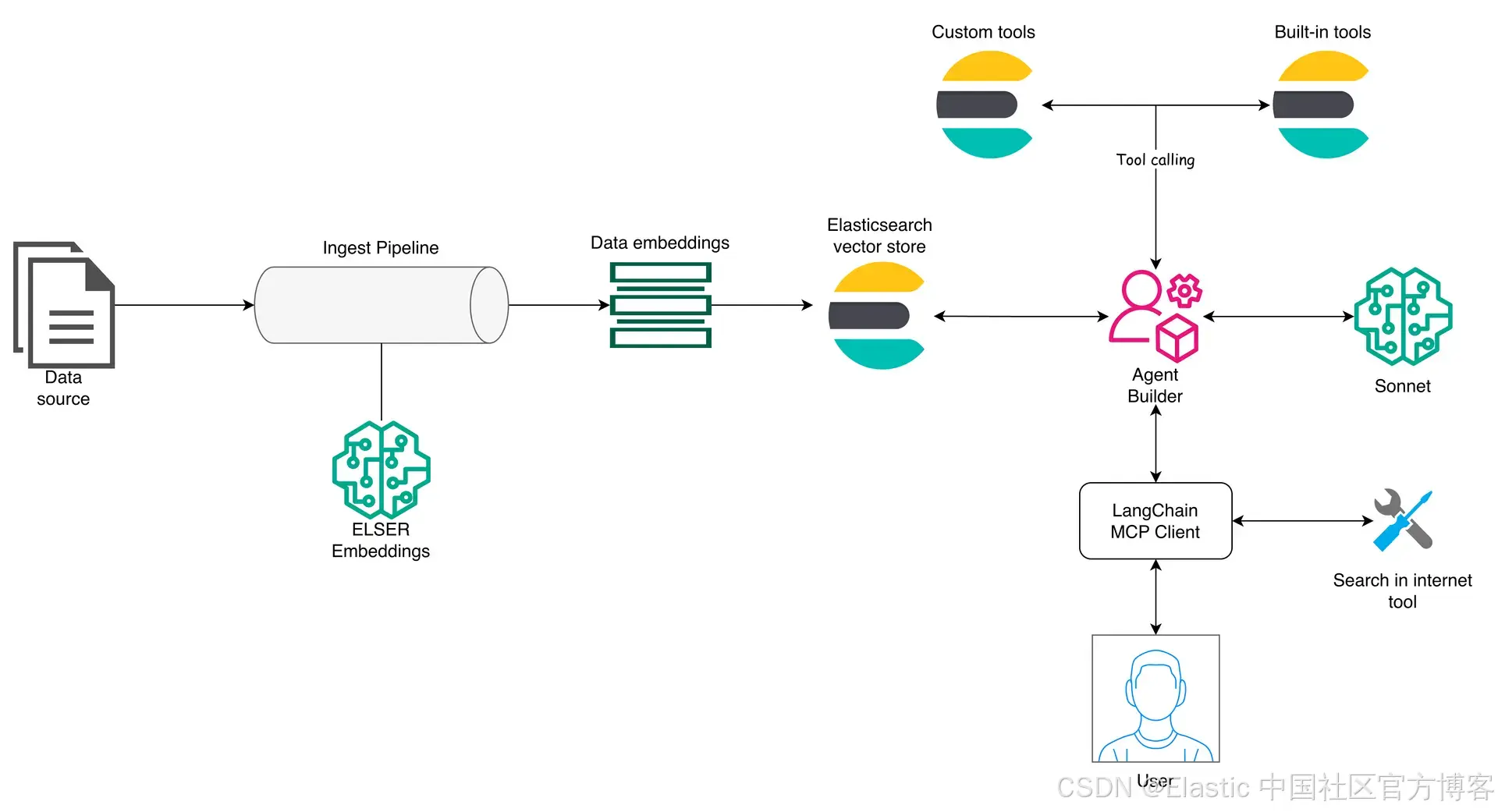
Elastic Agent Builder 层
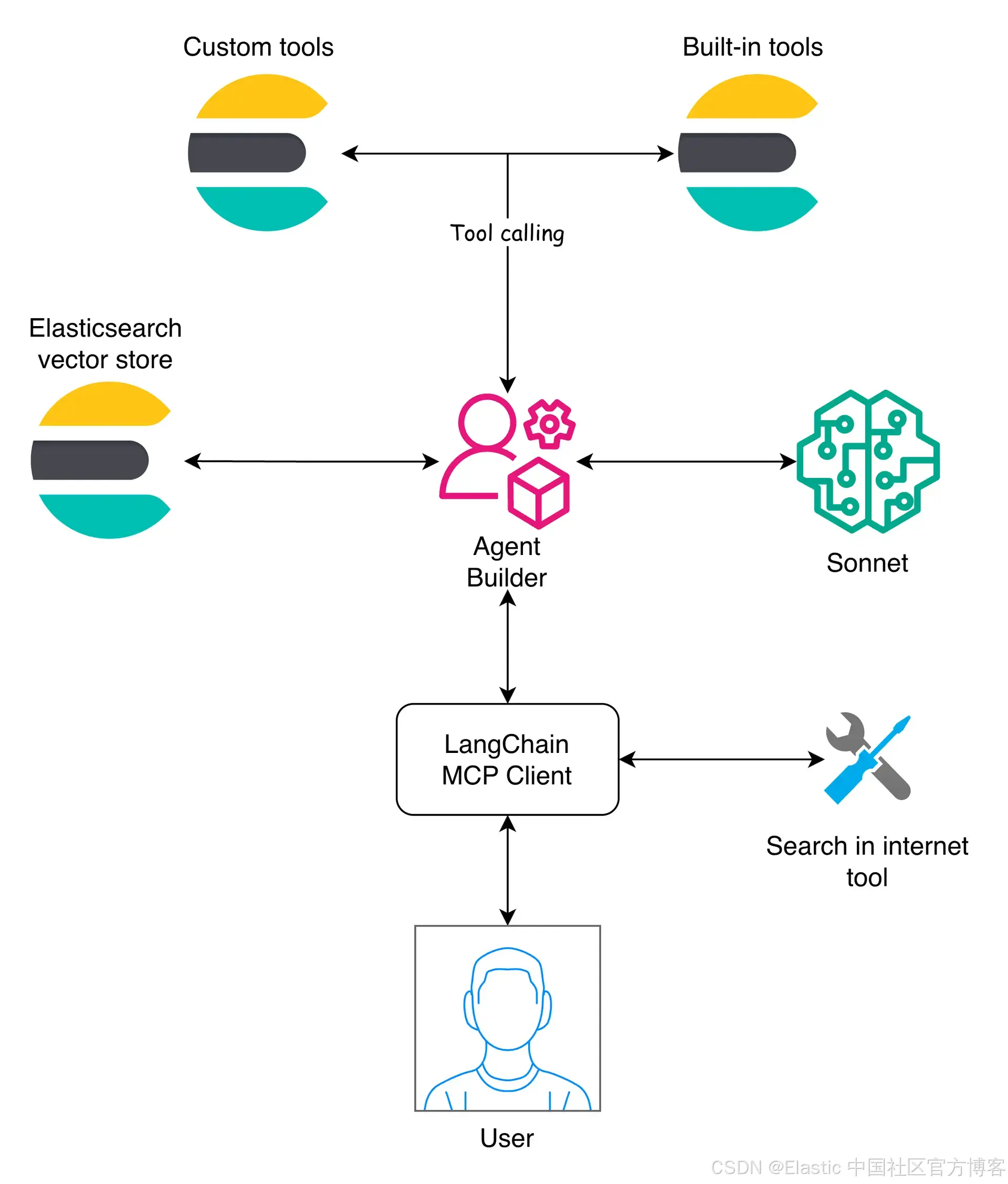
在这一层,Agent Builder 起核心作用,通过暴露与 Elasticsearch 数据交互所需的 tools 来管理在 Elasticsearch indices 上运行的工具,并将它们提供给使用者。然后 LangChain 通过 MCP client 处理编排。
该架构允许 Agent Builder 作为客户端可用的众多 MCP servers 之一,从而使 Elasticsearch agent builder 可以与其他 MCP 结合。这样,MCP client 可以提出跨来源的问题,然后合并答案。
用例:安全漏洞 agent
安全漏洞 agent 通过结合三个互补层,根据用户的问题识别潜在风险:
- 首先 ,它在内部知识库中使用 embeddings 执行 semantic search ,该知识库包含过去的事件、配置和已知漏洞,以检索相关的历史证据。
- 其次,它在互联网上搜索新发布的建议或威胁情报,这些信息可能尚未存在于内部。
- 最后,LLM 对内部和外部发现进行关联和优先排序,评估它们与用户特定环境的相关性,并生成清晰的解释以及潜在的缓解措施。
开发应用
应用的代码可以在附带的 notebook 中找到。
你可以在下面看到 Python 应用的设置:
# load environment variables
load_dotenv()
ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT = os.getenv("ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT")
ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY = os.getenv("ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY")
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
SERPER_API_KEY = os.getenv("SERPER_API_KEY")
KIBANA_URL = os.getenv("KIBANA_URL")
INDEX_NAME = "security-vulnerabilities"
KIBANA_HEADERS = {
"kbn-xsrf": "true",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"ApiKey {ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY}",
} # Useful for Agent Builder API calls
es_client = Elasticsearch(ELASTICSEARCH_ENDPOINT, api_key=ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY) # Elasticsearch client我们需要访问 Agent Builder 并创建一个专门处理安全查询的 agent,以及一个执行 semantic search 的 tool 。你需要先启用 Agent Builder才能进行下一步。一旦启用,我们将使用 tools API 创建一个用于执行 semantic search 的 tool 。
security_search_tool = {
"id": "security-semantic-search",
"type": "index_search",
"description": "Search internal security documents including incident reports, pentests, internal CVEs, security guidelines, and architecture decisions. Uses semantic search powered by ELSER to find relevant security information even without exact keyword matches. Returns documents with severity assessment and affected systems.",
"tags": ["security", "semantic", "vulnerabilities"],
"configuration": {
"pattern": INDEX_NAME,
},
}
try:
response = requests.post(
f"{KIBANA_URL}/api/agent_builder/tools",
headers=KIBANA_HEADERS,
json=security_search_tool,
)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("✅ Security semantic search tool created successfully")
else:
print(f"Response: {response.text}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error creating tool: {e}")按照 Elastic 为开发 Tools 定义的最佳实践配置你的 tools 。创建完成后,该 tool 就可以在 Kibana UI 中使用。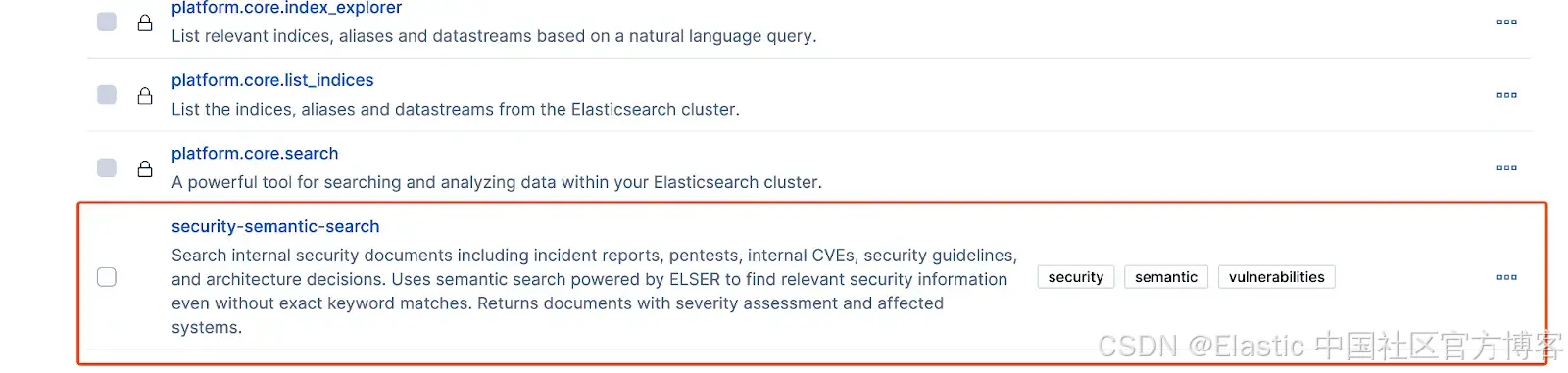
在创建好 tool 后,我们可以开始编写 ingestion 工作流的代码:
Ingest pipeline
要定义数据结构,我们需要准备一个用于 ingestion 的 dataset。下面是本示例的一个 sample document:
{
"title": "Incident Report: Node.js Express 4.17 Prototype Pollution RCE",
"content": "In March 2024, our production Node.js Express 4.17 API gateway experienced a critical prototype pollution vulnerability leading to remote code execution. The attack vector involved manipulating object prototypes through JSON payloads in POST requests. This affected all Express middleware processing user input. Immediate mitigation: upgrade to Express 4.18.2+, implement input validation, use Object.freeze() for critical objects. Related to CVE-2022-24999.",
"doc_type": "incident_report",
"severity": "critical",
"affected_systems": [
"api-gateway-prod",
"api-gateway-staging"
],
"date": "2024-03-15"
}对于这种类型的 document,我们将使用以下 index mappings:
index_mapping = {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {"type": "text", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"content": {"type": "text", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"doc_type": {"type": "keyword", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"severity": {"type": "keyword", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"affected_systems": {"type": "keyword", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"date": {"type": "date"},
"semantic_field": {"type": "semantic_text"},
}
}
}
if es_client.indices.exists(index=INDEX_NAME) is False:
es_client.indices.create(index=INDEX_NAME, body=index_mapping)
print(f"✅ Index '{INDEX_NAME}' created with semantic_text field for ELSER")
else:
print(f"ℹ️ Index '{INDEX_NAME}' already exists, skipping creation")我们正在创建一个 semantic_text 字段,以使用标记了 copy_to 属性的字段中的信息执行 semantic search。
有了该 mapping 定义后,我们可以使用 bulk API 进行数据写入。
def build_bulk_actions(documents, index_name):
for doc in documents:
yield {"_index": index_name, "_source": doc}
try:
with open("dataset.json", "r") as f:
security_documents = json.load(f)
success, failed = helpers.bulk(
es_client,
build_bulk_actions(security_documents, INDEX_NAME),
refresh=True,
)
print(f"📥 {success} documents indexed successfully")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error during bulk indexing: {str(e)}")LangChain MCP client
在这里,我们将使用 LangChain 创建一个 MCP client 来使用 Agent Builder tools,并使用 LangGraph 构建工作流以编排 client 执行。第一步是连接到 MCP server:
client = MultiServerMCPClient(
{
"agent-builder": {
"transport": "streamable_http",
"url": MCP_ENDPOINT,
"headers": {"Authorization": f"ApiKey {ELASTICSEARCH_API_KEY}"},
}
}
)
tools = await client.get_tools()
print(f"📋 MCP Tools available: {[t.name for t in tools]}") # ['platform_core_search', ... 'security-semantic-search']接下来,我们创建一个 agent,根据用户输入选择合适的 tool:
reasoning = {"effort": "low"}
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model="gpt-5.2-2025-12-11", reasoning=reasoning, openai_api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY
) # LLM client
agent = create_agent(
llm,
tools=tools,
system_prompt="""You are a cybersecurity expert specializing in infrastructure security.
Your role is to:
1. Analyze security queries from users
2. Search internal security documents (incidents, pentests, CVEs, guidelines)
3. Provide actionable security recommendations
4. Assess vulnerability severity and impact
When responding:
- Always search internal documents first using the agent builder tools
- Provide specific, technical, and actionable advice
- Cite relevant internal incidents and documentation
- Assess severity (critical, high, medium, low)
- Recommend immediate mitigation steps
Be concise but comprehensive. Focus on practical security guidance.""",
)我们将使用 GPT-5.2 模型,它代表了 OpenAI 在 agent 管理任务方面的最先进水平。我们将其配置为低 reasoning effort,以实现比中等或高设置更快的响应,同时通过利用 GPT-5 系列的全部能力,仍能提供高质量的结果。你可以在这里阅读有关 GPT 5.2 的更多信息。
现在初始设置完成,下一步是定义一个能够做出决策、运行 tool 调用并总结结果的工作流。
为此,我们使用 LangGraph 。本文不会深入介绍 LangGraph;这篇文章提供了其功能的详细概述。
下图展示了 LangGraph 应用的高层视图。
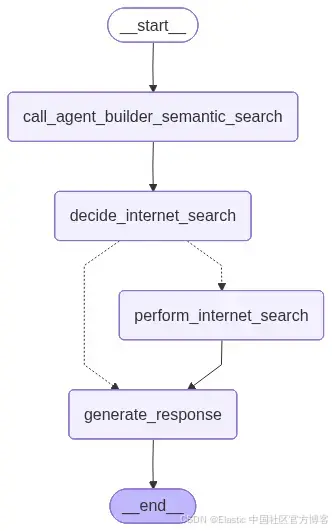
我们需要定义应用的 state:
class AgentState(TypedDict):
query: str
agent_builder_response: dict
internet_results: list
final_response: str
needs_internet_search: bool为了更好地理解工作流的运行方式,这里对每个函数做一个简要说明。有关完整实现细节,请参阅随附的 notebook。
- call_agent_builder_semantic_search:使用 Agent Builder MCP server 查询内部文档,并将检索到的消息存储在 state 中。
- decide_internet_search:分析内部结果,并确定是否需要进行外部搜索。
- perform_internet_search:在需要时使用 Serper API 执行外部搜索。
- generate_response:关联内部和外部发现,为用户生成最终的可操作的网络安全分析。
定义好工作流后,我们现在可以发送查询:
query = "We are using Node.js with Express 4.17 for our API gateway. Are there known prototype pollution or remote code execution vulnerabilities?"在此示例中,我们想评估该特定版本的 Express 是否受已知漏洞影响。
研究结果

请参见此文件中的完整响应。
该响应清晰地关联了内部和互联网的发现,并提供了可操作的缓解步骤。它成功地突出了漏洞的严重性,并提供了结构化的、安全为导向的总结。
扩展与未来增强
该架构是模块化的,允许通过替换、改进或添加组件来扩展其功能。我们可以添加另一个 agent,由相同的 MCP client 使用。我们还可以使用自动化的 ingestion 工作流,例如 Logstash、Kafka 或 Elastic 自管理连接器。你可以根据需要更换 LLM、MCP client 框架或 embeddings 模型,或添加更多 tools 。
结论
该参考架构展示了将 Elasticsearch、Agent Builder 和 MCP 结合构建 AI 驱动应用的实用方法。其结构保持各部分独立,使系统易于实现、维护和扩展。
你可以从一个简单的设置开始(如本文中的安全用例),随着需求增长,通过添加新的 tools、数据源或 agents 来进行扩展。总体来说,它为在 Elasticsearch 上构建灵活且可靠的 agentic workflows 提供了直接的路径。
原文:https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/agent-builder-mcp-reference-architecture-elasticsearch