目录
[2.3 插入数据](#2.3 插入数据)
[2.4 删除数据](#2.4 删除数据)
[2.5 查找数据](#2.5 查找数据)
[2.6 中序遍历](#2.6 中序遍历)
[2.6 析构函数](#2.6 析构函数)
[2.7 拷贝构造](#2.7 拷贝构造)
[2. 8 operator= 重载 (现代写法)](#2. 8 operator= 重载 (现代写法))
[4. 整体程序](#4. 整体程序)
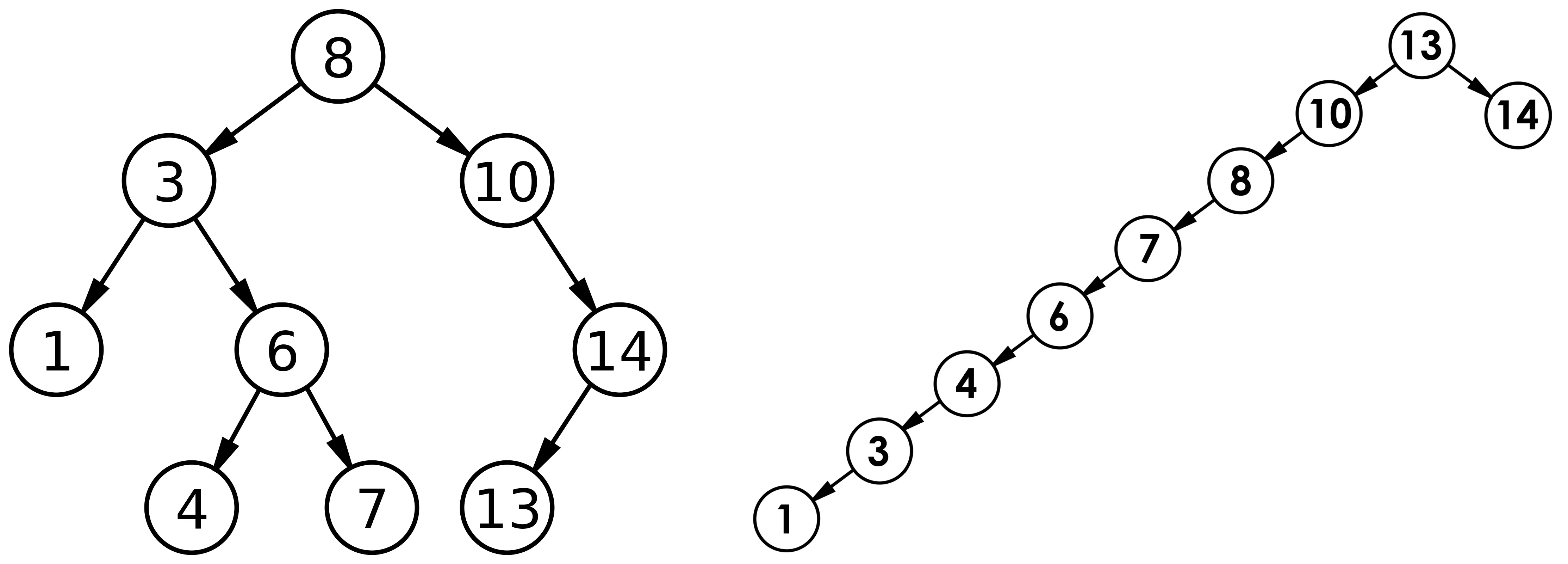
1.搜索二叉树的性质
搜索二叉树是在二叉树的上加入了一些特性,
- 左子树的节点小于根节点的值;
- 右子树的节点大于根节点的值。
- 左右子树均为搜索二叉树
2.模拟实现
2.1构建节点
首先构建节点,包含指向左右孩子的指针 ,以及存储的值。
cpp
template <class K>
class BSTreeNode
{
public:
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_right(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};由于是指针和K(后面的给的值有内置类型)需要显示构造 ,或者给缺省值,指针指向随机值,指向混乱。
2.2.树的结构
二叉树的采用链式结构 。根节点是整棵树的唯一入口,所有节点都通过根节点的左右指针串联,无需额外成员变量就能访问 / 操作整棵树。
cpp
template <class K>
class BSTree
{
public:
BSTree()
{
_root = nullptr;
}
private:
Node* _root;
};2.3 插入数据
- 树为空,直接插入
- 树不为空,根据插入值的大小,判断遍历的方向
- 等访问到空节点时候停止,插入新的节点。
1.遍历实现
cpp
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//寻找位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* newnode = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = newnode;
return true;
}
else
{
parent->_right = newnode;
return true;
}
return false;//插入失败的
}2.递归实现
cpp
bool InsertR (const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
// 这个引用是重中之重,因为引用相当于别名,所以树才可以连接上
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}形参列表中的引用,root为插入位置,如果删去引用,变为拷贝,即形参的修改不会影响实参,创建的节点无法挂在树上。
2.4 删除数据
先找到目标节点,再分三种情况删除(左空 / 右空 / 左右都有),
1.没有孩子的节点直接删除
2.有一个孩子的节点,左孩子和右孩子,直接交给父亲节点
3.有两个孩子的节点 ,找到左子树最大 (左子树最右边节点)的或者右子树最小(最左边节点)的节点,将最大或者最小节点和被删除的节点的值交换 ,然后删除最大或者最小节点。也就是将两个孩子转换成了一个孩子或者没有孩子。
最后删除节点,释放内存
注意: 第三种情况最后删除的时候可以遵守有一个孩子和没有孩子的情况,leftMax可能是父亲的左节点,也有可能是父亲的左节点(这种肯定有)
特例需要注意。
遍历方式
cpp
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//总体的目的就是寻找到cur,然后将删除,没有孩子和单个孩子看为一种 都是指向空
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//找到节点
{
//父母只有一个孩子或者没有孩子的情况
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左孩子为空 只有左节点或者没有节点的
{
if (cur == _root)//删除的节点是根节点
_root = cur->_right;
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr) // 没有右孩子
{
if (cur == _root)//删除的节点是根节点
_root = cur->_left;
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
// cur节点在parent的左边就放在左边,右边就连接右边
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
}
else//有两个孩子的
{
Node* parent = cur;
Node* leftMax = cur->_left; //找到可以替代的中间节点
while (leftMax->_right)
{
parent = leftMax;
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);
if (parent->_left == leftMax)
{
parent->_left = leftMax->_left;//这颗子树的左边就是最大值的情况,
}
else
{
parent->_right = leftMax->_left;
}
cur = leftMax;//
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}递归方式
cpp
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else//找到了
{
//三种情况,一种是 左子树有 右子树有,两个子树都有
Node* del = root;
if(root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else//存在问题
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(leftMax->_key, root->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);//在递归在字数中找到这个key然后删除
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}2.5 查找数据
查找数据最为简便,
查找值大于节点值,向右遍历,小于节点值,向左遍历啊。
遍历方式
cpp
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}递归方式
cpp
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
Node* _FindR(Node*root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else//相等返回的值
{
return root;
}
}2.6 中序遍历
采用先左,中根,后右顺序遍历二叉树
cpp
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
//中序遍历;左根右
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key<< " ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}2.6 析构函数
自定义类型的析构函数,由于类中使用了new动态内存,必须使用显示析构函数
递归的方式
cpp
~BSTree()
{
Destory(_root);
}
void Destory(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destory(root->_left);//限制条件在前,操作在后
Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}2.7 拷贝构造
cpp
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copynode = new Node(root->_key);
copynode->_left = Copy(root->_left);
copynode->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return copynode;
}2. 8 operator= 重载 (现代写法)
cpp
BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)//拷贝构造
{
swap(_root, t._root);//交换
return *this;//返回拷贝构造值,销毁局部对象
}3.总结
插入和删除操作都必须先查找 ,查找效率 代表了二叉搜索树 中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二
叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深 ,则 比较次数越多。
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树 ( 或者接近完全二叉树 ) ,其平均比较次数为:O(logN)
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树 ( 或者类似单支 ) ,其平均比较次数为: O(N)
为了保证二叉树的搜索效率,创建了平衡搜索二叉树(AVL树和红黑树)
4.使用方式
搜索二叉树的值本身为一种键值,key无法修改,需要一个value,key和value凑成键值对,这
样我们可以通过key寻找value,查找方便快捷,以及计数。pair形式的存储。
使用用例如下,均为KV模型(map),一个是计数,以及是英语字典。
一种为K模型,即K即使规律排序,便于查找。
cpp
namespace XLZ
{
template <class K, class V >
class BSTreeNode
{
public:
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
K _key;
V _value;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_right(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template <class K, class V>
class BSTree
{
public:
typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;
//构造函数
BSTree()
{
_root = nullptr;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destory(_root);
}
BSTree(const BSTree<K, V>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K, V>& operator=(BSTree<K, V> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
//二叉树使用递归是最为方便的,因此这里演示递归的使用方式
//查询函数
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copynode = new Node(root->_key);
copynode->_left = Copy(root->_left);
copynode->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return copynode;
}
void Destory(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destory(root->_left);//限制条件在前,操作在后
Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
Node* _FindR(Node*root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else//相等返回的值
{
return root;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)// 这个引用是重中之重,因为引用相当于别名,所以树才可以连接上
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key,value);
return true;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key,value);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key,value);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else//找到了
{
//三种情况,一种是 左子树有 右子树有,两个子树都有
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else//存在问题
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(leftMax->_key, root->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);//在递归在字数中找到这个key然后删除
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
//中序遍历;左根右
_Inorder(root->_left);
//printf("%s:%d", root->_key, root->_value);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root;
};
//创建一个词典
void TestBSTree1()
{
BSTree<string, string>dict;
dict.InsertR("insert", "插入");
dict.InsertR("erase", "删除");
dict.InsertR("data", "日期");
dict.InsertR("hello", "你好");
dict.InsertR("sorry", "对不起");
//输入单词
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
auto ret = dict.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
cout << "nothig" << endl;
else
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
}
void TestBSTree2()
{
// 11:44继续
// 统计水果出现的次数
string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
XLZ::BSTree<string, int> countTree;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ret = countTree.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.InsertR(str, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
}
}4. 整体程序
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//二叉搜索树的底层实现
template <class K>
class BSTreeNode
{
public:
BSTreeNode<K>* _right;
BSTreeNode<K>* _left;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_right(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template <class K>
class BSTree
{
public:
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
//构造函数
BSTree()
{
_root = nullptr;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destory(_root);
}
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
BSTree<K>& operator=( BSTree<K> t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
//插入函数
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//寻找位置
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* newnode = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key > key)
{
parent->_left = newnode;
return true;
}
else
{
parent->_right = newnode;
return true;
}
return false;//插入失败的,基本没有吧
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//总体的目的就是寻找到cur,然后将删除,没有孩子和单个孩子看为一种 都是指向空
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = cur;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else//找到节点
{
//父母只有一个孩子或者没有孩子的情况
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左孩子为空 只有左节点或者没有节点的
{
if (cur == _root)//删除的节点是根节点
_root = cur->_right;
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr) // 没有右孩子
{
if (cur == _root)//删除的节点是根节点
_root = cur->_left;
else
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;// cur节点在parent的左边就放在左边 ,右边就连接右边
}
else
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
}
}
else//有两个孩子的
{
Node* parent = cur;
Node* leftMax = cur->_left; //找到可以替代的中间节点
while (leftMax->_right)
{
parent = leftMax;
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);
if (parent->_left == leftMax)
{
parent->_left = leftMax->_left;//这颗子树的左边就是最大值的情况,
}
else
{
parent->_right = leftMax->_left;
}
cur = leftMax;//
}
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//二叉树使用递归是最为方便的,因此这里演示递归的使用方式
//查询函数
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR (const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
private:
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
Node* copynode = new Node(root->_key);
copynode->_left = Copy(root->_left);
copynode->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return copynode;
}
void Destory(Node*& root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
Destory(root->_left);//限制条件在前,操作在后
Destory(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
Node* _FindR(Node*root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else//相等返回的值
{
return root;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)// 这个引用是重中之重,因为引用相当于别名,所以树才可以连接上
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//寻找位置
if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else//找到了
{
//三种情况,一种是 左子树有 右子树有,两个子树都有
Node* del = root;
if(root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else//存在问题
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(leftMax->_key, root->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);//在递归在字数中找到这个key然后删除
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
//中序遍历;左根右
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key<< " ";
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
Node* _root;
};