本系列介绍增强现代智能体系统可靠性的设计模式,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。本系列一共 14 篇文章,这是第 14 篇。原文:Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI[1]
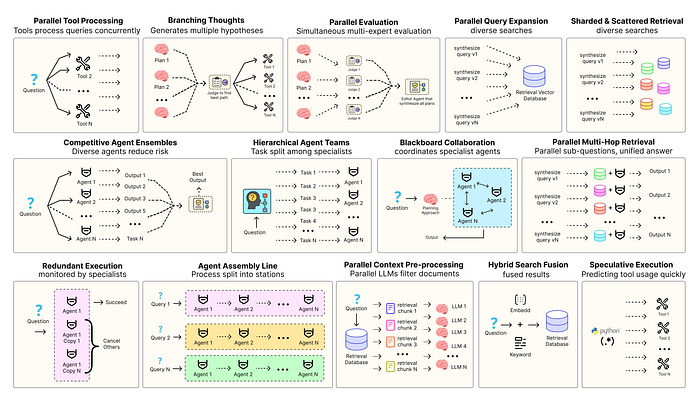
优化智能体解决方案需要软件工程确保组件协调、并行运行并与系统高效交互。例如预测执行[2],会尝试处理可预测查询以降低时延 ,或者进行冗余执行[3],即对同一智能体重复执行多次以防单点故障。其他增强现代智能体系统可靠性的模式包括:
- 并行工具:智能体同时执行独立 API 调用以隐藏 I/O 时延。
- 层级智能体:管理者将任务拆分为由执行智能体处理的小步骤。
- 竞争性智能体组合:多个智能体提出答案,系统选出最佳。
- 冗余执行:即两个或多个智能体解决同一任务以检测错误并提高可靠性。
- 并行检索和混合检索:多种检索策略协同运行以提升上下文质量。
- 多跳检索:智能体通过迭代检索步骤收集更深入、更相关的信息。
还有很多其他模式。
本系列将实现最常用智能体模式背后的基础概念,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。
所有理论和代码都在 GitHub 仓库里:🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀[4]
代码库组织如下:
agentic-parallelism/
├── 01_parallel_tool_use.ipynb
├── 02_parallel_hypothesis.ipynb
...
├── 06_competitive_agent_ensembles.ipynb
├── 07_agent_assembly_line.ipynb
├── 08_decentralized_blackboard.ipynb
...
├── 13_parallel_context_preprocessing.ipynb
└── 14_parallel_multi_hop_retrieval.ipynb深度推理的多跳检索
许多复杂的用户查询并非单一问题,而是比较性的、多步骤的调研任务,需要从多个不同来源的文档中综合信息。
 并行多跳
并行多跳
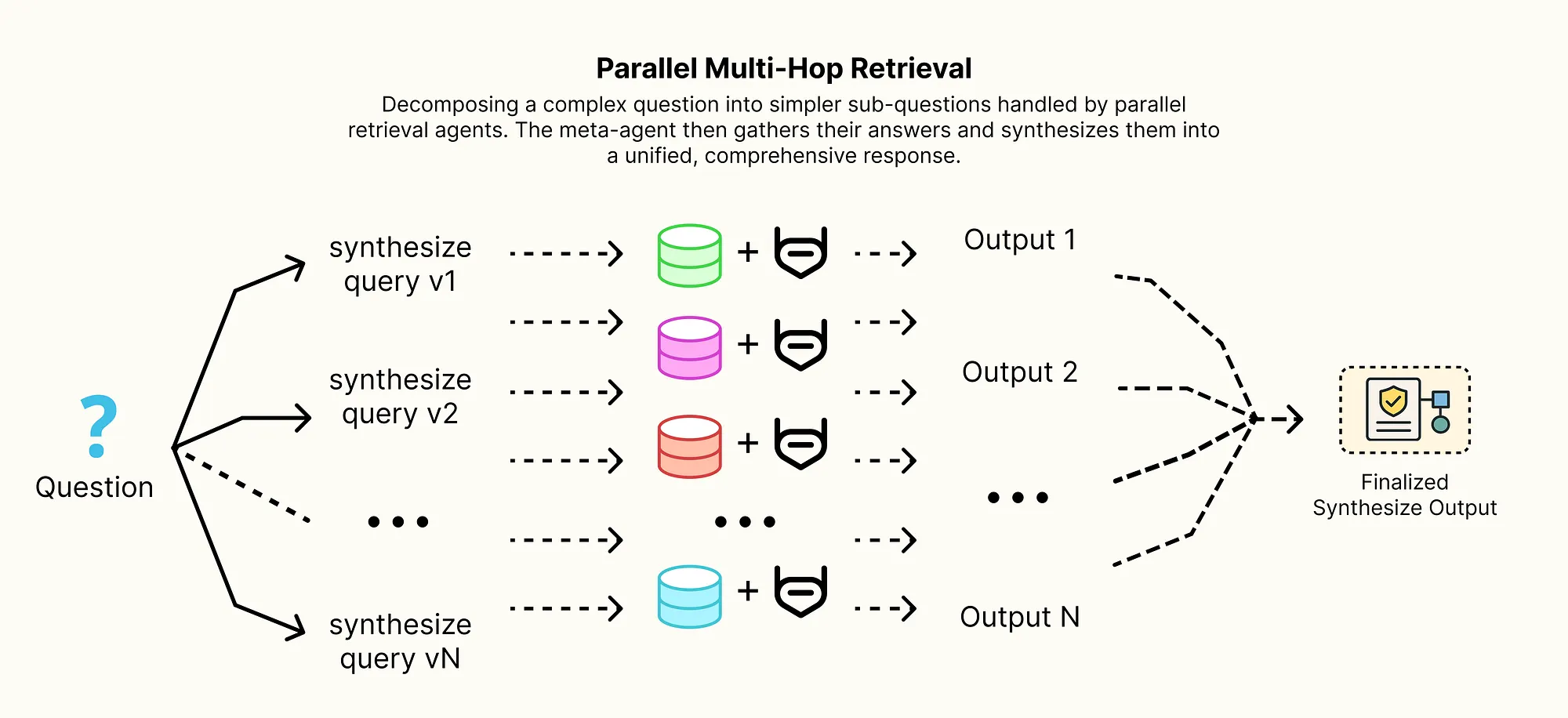
解决方案是 并行多跳检索(Parallel Multi-Hop Retrieval) 架构,这种模式将 RAG 系统提升为真正的调研代理,工作流模拟人类研究员如何处理复杂问题的过程:
- 分解(Decompose):高级元代理首先分析复杂的用户查询,将其分解为几个更简单、独立的子问题。
- 分散(并行检索):每个子问题都被派发给各自的专用检索代理。这些代理并行运行,每个代理执行标准 RAG 流程,为特定子问题寻找答案。
- 收集与综合:元代理收集所有子问题的答案,进行最终推理步骤,将它们综合为对原始复杂查询的单一、全面的答案。
我们将以一个无法通过单一检索回答的比较性问题为例,构建并比较简单 RAG 系统与多跳 RAG 系统,证明只有多跳系统才能成功收集必要的证据,以提供准确且富有洞察力的最终答案。
首先为初始分解步骤定义 Pydantic 模型,从而结构化元代理规划阶段输出的内容。
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List
class SubQuestions(BaseModel):
"""分解代理输出的Pydantic模型,包含一组独立的子问题"""
questions: List[str] = Field(description="A list of 2-3 simple, self-contained questions that, when answered together, will fully address the original complex query.")这个 SubQuestions 模型是元代理首次行动的合约,迫使 LLM 将复杂查询分解为一系列简单、可回答的问题,是并行"分而治之"策略的基础步骤。
然后构建高级多跳系统作为 LangGraph 图。第一个节点将是"分解器",即元代理的规划角色。
from typing import TypedDict, List, Dict, Annotated
import operator
class MultiHopRAGState(TypedDict):
original_question: str
sub_questions: List[str]
# 字典以问题作为键,存储每个子问题的答案
sub_question_answers: Annotated[Dict[str, str], operator.update]
final_answer: str
# 节点 1:分解器(元代理的第一步)
decomposer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"You are a query decomposition expert. Your job is to break down a complex question into simple, independent sub-questions that can be answered by a retrieval system. "
"Do not try to answer the questions yourself.\n\n"
"Question: {question}"
)
decomposer_chain = decomposer_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(SubQuestions)
def decomposer_node(state: MultiHopRAGState):
"""获取原始复杂问题并将其分解为子问题列表"""
print("--- [Meta-Agent] Decomposing complex question... ---")
result = decomposer_chain.invoke({"question": state['original_question']})
print(f"--- [Meta-Agent] Generated {len(result.questions)} sub-questions. ---")
return {"sub_questions": result.questions}decomposer_node 是研究代理的战略大脑,它不会尝试回答查询,其唯一且关键的任务是分析用户意图并将其分解为一组独立、可并行化的研究任务。
下一个节点将并行为每个子问题协调执行标准的 RAG 流程。
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
# 标准、自包含的RAG链,是并行检索代理的"引擎"
sub_question_rag_chain = (
{"context": retriever | format_docs, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| generator_prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
def retrieval_agent_node(state: MultiHopRAGState):
"""节点 2:为每个子问题并行运行完整 RAG 进程"""
print(f"--- [Retrieval Agents] Answering {len(state['sub_questions'])} sub-questions in parallel... ---")
answers = {}
# 用 ThreadPoolExecutor 对每个子问题并发运行'sub_question_rag_chain'
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=len(state['sub_questions'])) as executor:
# 为每个待回答子问题构建一个 future
future_to_question = {executor.submit(sub_question_rag_chain.invoke, q): q for q in state['sub_questions']}
for future in as_completed(future_to_question):
question = future_to_question[future]
try:
answer = future.result()
answers[question] = answer
print(f" - Answer found for sub-question: '{question}'")
except Exception as e:
answers[question] = f"Error answering question: {e}"
# 将结果收集到"sub_question_answers"字典中
return {"sub_question_answers": answers}retrieval_agent_node 是系统中的分散-聚合核心,接收 sub_questions 列表,并用 ThreadPoolExecutor 将每个条目分配到各自独立的 RAG 链。这是一种强大的并行形式,同时运行多个完整 RAG 流程。在所有并行代理找到答案后,该节点将所有发现汇总到 sub_question_answers 字典中。
最后,"合成器"节点作为元代理的最终步骤,将并行发现整合为一个连贯的答案。
# 节点 3:合成器(元代理的最后一步)
synthesizer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"You are a synthesis expert. Your job is to combine the answers to several sub-questions into a single, cohesive, and comprehensive answer to the user's original complex question.\n\n"
"Original Question: {original_question}\n\n"
"Sub-Question Answers:\n{sub_question_answers}"
)
synthesizer_chain = synthesizer_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
def synthesizer_node(state: MultiHopRAGState):
"""获取子问题的答案,并合成最终的全面答案"""
print("--- [Meta-Agent] Synthesizing final answer... ---")
# 将收集的子问题答案格式化为最终提示
sub_answers_str = "\n".join([f"- Q: {q}\n- A: {a}" for q, a in state['sub_question_answers'].items()])
final_answer = synthesizer_chain.invoke({
"original_question": state['original_question'],
"sub_question_answers": sub_answers_str
})
return {"final_answer": final_answer}synthesizer_node 是至关重要的最终推理步骤,它本身不执行任何检索,任务是接收 sub_question_answers 中的预处理事实,并将其构造为能直接回应用户原始复杂查询的连贯叙述。
最后按线性顺序组装图:分解 -> 并行检索 -> 综合。
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
workflow = StateGraph(MultiHopRAGState)
workflow.add_node("decompose", decomposer_node)
workflow.add_node("retrieve_in_parallel", retrieval_agent_node)
workflow.add_node("synthesize", synthesizer_node)
workflow.set_entry_point("decompose")
workflow.add_edge("decompose", "retrieve_in_parallel")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve_in_parallel", "synthesize")
workflow.add_edge("synthesize", END)
multi_hop_rag_app = workflow.compile()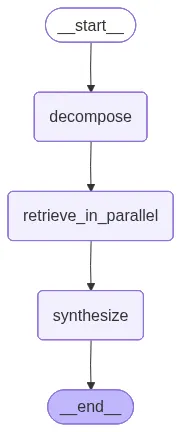 并行多跳检索
并行多跳检索
给两个系统一个复杂且需要比较的问题,这个问题无法通过单次检索调用正确回答,从而对比分析两种查询方式。
# 查询需要比较两个产品,信息在独立、不重叠的文档中
user_query = "Compare the QLeap-V4 and the Eco-AI-M2, focusing on their target use case and power consumption."
# --- 执行简单 RAG ---
print("="*60)
print(" SIMPLE RAG SYSTEM OUTPUT")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print(f"Final Answer:\n{simple_answer}")
# --- 执行多跳 RAG ---
print("\n" + "="*60)
print(" MULTI-HOP RAG SYSTEM OUTPUT")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("--- Sub-Question Answers ---")
for i, (q, a) in enumerate(multi_hop_result['sub_question_answers'].items()):
print(f"{i+1}. Q: {q}\n A: {a}")
print("\n--- Final Synthesized Answer ---")
print(multi_hop_result['final_answer'])
# --- 最终分析 ---
print("\n" + "="*60)
print(" ACCURACY & QUALITY ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("**Simple RAG Performance:**")
print("- Result: COMPLETE FAILURE.")
print("- Reason: The user's query contained terms for both products. Vector search found the documents that were, on average, most semantically similar to the entire query, retrieving only documents about the Eco-AI-M2. It completely failed to retrieve any information about the QLeap-V4. Without the necessary context for both products, a comparison was impossible.\n")
print("**Multi-Hop RAG Performance:**")
print("- Result: COMPLETE SUCCESS.")
print("- Reason: The system's intelligence was in the initial decomposition step. The Meta-Agent broke the complex comparative query into two simple, focused sub-questions: 1. Get info on Product A. and 2. Get info on Product B. The parallel Retrieval Agents had no trouble answering these simple questions, each retrieving the correct, focused context. The final Synthesizer agent then received a perfect, complete set of facts about both products, making the final comparison trivial.")输出为......
#### 输出 ####
============================================================
SIMPLE RAG SYSTEM OUTPUT
============================================================
Final Answer:
Based on the provided context, the Eco-AI-M2 chip is designed for edge computing and mobile devices, with a primary feature of low power consumption at only 15W under full load. The context does not contain information about the QLeap-V4, so I cannot provide a comparison.
============================================================
MULTI-HOP RAG SYSTEM OUTPUT
============================================================
--- Sub-Question Answers ---
1. Q: What is the target use case and power consumption of the QLeap-V4?
A: The QLeap-V4 processor is designed for maximum performance in data centers, with a primary use case of large-scale AI model training. It consumes 1200W of power under full load.
2. Q: What is the target use case and power consumption of the Eco-AI-M2?
A: The Eco-AI-M2 chip is designed for edge computing and mobile devices like drones and smart cameras. Its key feature is low power consumption, drawing only 15W under full load.
--- Final Synthesized Answer ---
The QLeap-V4 and the Eco-AI-M2 are designed for very different purposes, primarily distinguished by their target use case and power consumption.
- **QLeap-V4**: This is a high-performance processor intended for data centers. Its main use case is large-scale AI model training, and it has a high power consumption of 1200W.
- **Eco-AI-M2**: This is a low-power chip designed for edge computing and mobile devices. Its focus is on energy efficiency, consuming only 15W, making it suitable for applications like drones and smart cameras.最终分析得出明确结论,性能差异并非渐进式,而是一次能力上的飞跃。
- 单次检索步骤无法解决比较查询歧义,仅检索了两个产品中的一个上下文,从根本上无法收集必要的证据。
- 多跳系统之所以成功,是因为没有试图一次性回答复杂问题,而是识别了查询的比较性质,并将问题分解。
- 通过并行、专注的 RAG 代理来解决每个简单的子问题,确保收集了所有必要证据,最后的综合步骤只是简单的将预先处理的事实结合起来。
Hi,我是俞凡,一名兼具技术深度与管理视野的技术管理者。曾就职于 Motorola,现任职于 Mavenir,多年带领技术团队,聚焦后端架构与云原生,持续关注 AI 等前沿方向,也关注人的成长,笃信持续学习的力量。在这里,我会分享技术实践与思考。欢迎关注公众号「DeepNoMind」,星标不迷路。也欢迎访问独立站 www.DeepNoMind.com[5],一起交流成长。
参考资料 [1]
Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI: https://levelup.gitconnected.com/building-the-14-key-pillars-of-agentic-ai-229e50f65986
2
预测执行: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speculative_execution
3
4
🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀: https://github.com/FareedKhan-dev/agentic-parallelism
5
www.DeepNoMind.com: https://www.deepnomind.com
本文由mdnice多平台发布