🔥个人主页: Milestone-里程碑
❄️**个人专栏: <<力扣hot100>> <<C++>> <<Linux>>**
🌟心向往之行必能至
目录
u前言
本篇文章会拆解常用的6个基础指令----pwd/ls/cd/mkdir/touth/rm,会详细讲解如何使用,帮助初学者入门
pwd指令
语法:pwd
功能:显⽰⽤⼾当前所在的⽬录
我们面对Linux的终端一大堆代码,可能会疑惑,当前到底在哪里,此时pwd就可以帮助进行定于查找目录
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# pwd
/root定位原理
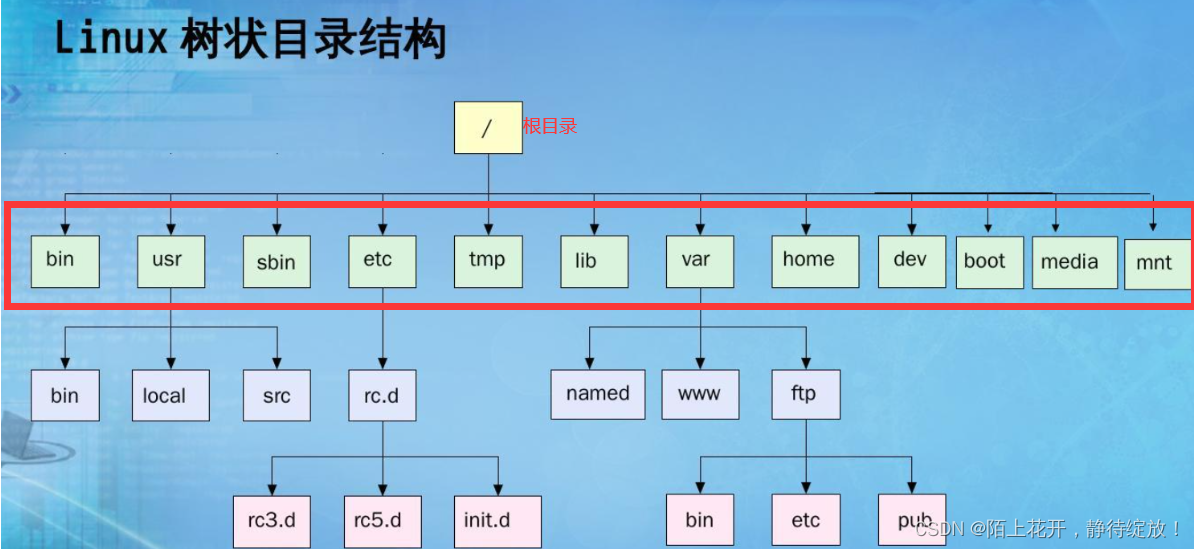
pwd定位,即在Linux的路径地图上定位
其中路径地图可以看成是一个多叉树,一个父节点有多个孩子,但一个孩子只有一个节点,公共的祖先节点,就是Linux默认的根目录(root)
绝对节点,就是从根节点开始到你当前处于的节点的完整路线
叶子节点一般是普通文件/空目录 其他节点都是目录
ls指令
语法:ls [选项] [⽬录或⽂件]
功能:对于⽬录,该命令列出该⽬录下的所有⼦⽬录与⽂件。对于⽂件,将列出⽂件名以及其他信息。
如果pwd是帮助我们进行定位,那么ls则是帮助我们获取当前位置的信息,显示当前目录下的所有文件/文件夹
搭配ls的命令行选项,可以合理地显示我们需要的信息
|-------|-----------------|-------------------------------------------|
| 指令 | 作用 | 示例输出(提前加了dir) |
| ls | 显示非隐藏的文件 / 文件夹名 | dir |
| ls -l | 显示详细属性(长格式) | drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 19:32 dir |
| ls -a | 显示所有文件(含隐藏文件) | . .. .hello |
此处的.是标识当前位置,..是标识上一级位置,后续仍会讲
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls
dir snap
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls -a
. .. .bash_history .bashrc .cache dir .history .profile snap .ssh .Xauthority
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls -l
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 9 19:36 dir
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 snap注意:ls 后续的指令 -a与-l可以任意搭配,不影响结果
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls -al
total 32
drwx------ 5 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:42 .
drwxr-xr-x 21 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3106 Oct 15 2021 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Apr 22 2025 .cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 9 19:36 dir
-rw------- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 161 Jul 9 2019 .profile
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 snap
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 .ssh
-rw------- 1 root root 177 Dec 9 19:42 .Xauthority
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls -l -a
total 32
drwx------ 5 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:42 .
drwxr-xr-x 21 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3106 Oct 15 2021 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Apr 22 2025 .cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 9 19:36 dir
-rw------- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 161 Jul 9 2019 .profile
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 snap
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 .ssh
-rw------- 1 root root 177 Dec 9 19:42 .Xauthority
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# ls -la
total 32
drwx------ 5 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:42 .
drwxr-xr-x 21 root root 4096 Dec 9 19:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .bash_history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3106 Oct 15 2021 .bashrc
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Apr 22 2025 .cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 9 19:36 dir
-rw------- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 2025 .history
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 161 Jul 9 2019 .profile
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 snap
drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Dec 8 16:19 .ssh
-rw------- 1 root root 177 Dec 9 19:42 .Xauthority
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# cd指令
使用cd前,我们需要先认识linux的路径
• 绝对路径:⼀般从/开始,不依赖其他⽬录的定位⽂件的⽅式 (某某小区 某栋 某单元 某门牌号)
• 相对路径:相对于当前⽤⼾所处⽬录,定位⽂件的路径⽅式(如果你已经在某单元 那么前面的绝对定位前面的信息都可以不用,直接某门牌号)
• Linux系统中,磁盘上的⽂件和⽬录被组成⼀棵⽬录树,每个节点都是⽬录或⽂件
• 其中普通⽂件⼀定是⽬录树的叶⼦节点
• ⽬录可能是叶⼦(空⽬录), 也可能是路上节点
• 理解路径存在的意义: 树状组织⽅式,都是为了保证快速定位查找到指定的⽂件,⽽定位⽂件就 需要具有唯⼀性的⽅案来进⾏定位⽂件。其中任何⼀个节点,都只有⼀个⽗节点,所以,从根⽬录开始,定位指定⽂件,路径具有唯⼀性
• 绝对路径⼀般不会随着⽤⼾的路径变化⽽丧失唯⼀性,⼀般在特定服务的配置⽂件中经常被使⽤
• 相对路径因为它的便捷性,⼀般在命令⾏中使⽤较多
语法: cd ⽬录名
功能:改变⼯作⽬录。将当前⼯作⽬录改变到指定的⽬录下
上面提到的. ..
. 代表当前目录(cd. .基本不用到,但要理解)
.. 代表上一级目录(cd ..)
|-------------|-------------------------|------------------------------|
| 作用 | 指令 | 说明 |
| 跳转到绝对路径的目录 | cd /home/user/Documents | 不管当前在哪,都跳转到绝对路径的目录 |
| 跳转到当前目录的子目录 | cd ./Music | 当前在/home/user,跳转到Music的子目录 |
| 回到上一级目录 | cd .. | 跳转到当前位置的上一级位置 |
| 回到自己的"家目录" | cd ~(波浪号) | 不管当前在哪,一键回到/home/你的用户名 |
| 回到上一级目录 | cd -(减号) | eg:原来从A跳到B,-后就从B回到A |
cd /可以直接跳到根目录
cpp
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# pwd
/root
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# cd /root/dir
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# pwd
/root/dir
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# cd -
/root
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# cd ./dir
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# pwd
/root/dir
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# cd ..
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# pwd
/root
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# cd ./dir
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# cd ~
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# pwd
/root
[root@VM-4-4-centos dir]# cd /
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# pwd
/touch
语法: touch [ 选项 ]... ⽂件 ...
功能:touch命令参数可更改⽂档或⽬录的⽇期时间,包括存取时间和更改时间,或者新建⼀个不存在的⽂件。
此处先只讲创建空文件,修改时间这个之后还会再详细讲解的。
它的真实作用比这更实用 ------ 它的核心是修改文件的 "时间戳",如果目标文件不存在,才会自动新建一个空文件。
每个文件在Linux都有三个时间戳,我们可以通过stat来查看
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dirs# touch text.c 如果text.存在,就更新它的访问和修改时间
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dirs# ls
text.c
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dirs# pwd
/root/dirs
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dirs# 通过stat查看时间戳
-
atime(access time):最近访问内容的时间
-
mtime(modify time):最近修改内容的时间
-
ctime(change time):最近更改文件的时间,包括文件名、大小、内容、权限、属主、属组等。
-
后面会再讲解
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# touch text.c
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# stat text.c
File: text.c
Size: 0 Blocks: 0 IO Block: 4096 regular empty file
Device: fc01h/64513d Inode: 402490 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Access: 2025-12-10 07:54:42.658473265 +0800
Modify: 2025-12-10 07:54:42.658473265 +0800
Change: 2025-12-10 07:54:42.658473265 +0800
Birth: 2025-12-10 07:54:42.658473265 +0800
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# 文件类型区分特点
Linux不像Windows一样,依靠后缀来区分文件(系统不关心,但编译器关心),而是通过文件属性来识别;
常见文件类型标识
目录:以 d 开头,例如示例中的dir,用于存放其他文件或子目录。
普通文件:以 - 开头,涵盖可执行程序、文本文件、代码文件以及动静态库等多种类型。
文件 :是存储实际数据 的单元(如文本内容、程序代码、图片等),是 "内容的载体"。比如
text.txt是存储文本内容的文件,app.exe是存储可执行代码的文件。目录 :是一种特殊的 "容器型文件" ,本身不存储实际数据,而是存储其他文件 / 目录的名称和位置信息(相当于 "文件夹"),用于组织和管理文件
mkdir指令
新建文件夹,可以像Windows一样建立文件夹,进行分类
语法: mkdir [ 选项 ] dirname...
功能:在当前⽬录下创建⼀个名为 "dirname"的⽬录 ,也可创建多个
-p/--parents: 可以是⼀个路径名称。此时若路径中的某些⽬录尚不存在,加上此选项后,系统将⾃ 动建⽴好那些尚不存在的⽬录,即⼀次可以建⽴多个⽬录
|----------------------------------|-------------------------|-----------------------------------------------|
| 目的 | 指令 | 效果 |
| 在当前目录创建1个文件夹 | mkdir Test | 当前目录下多了一个叫Test的文件夹 |
| 在当前目录新建多个文件夹 | mkdir Test1 Test2 Test3 | 当前目录下多了Test1/Test2/Test3三个文件夹 |
| 新建多层嵌套文件夹(创建的文件夹是相对的父子关系,不是叔侄关系) | mkdir -p A/B/C | 一次性创建A文件夹,以及A里的B、B里的C(如果不加-p,会报错) |
第三个使用
命令作用
mkdir是 "make directory" 的缩写,用于创建目录。-p选项(或--parents)的作用是:如果父目录不存在,会自动创建所有缺失的父目录,而不会报错。
cpp
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# mkdir Test
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# ls -l
total 8
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 27 16:42 dir
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 27 18:09 Test
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# mkdir Test1 Test2 Test3
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# ls
dir Test Test1 Test2 Test3
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# mkdir -p A/B/C
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# ls
A dir Test Test1 Test2 Test3
[root@VM-4-4-centos ~]# cd ./A
[root@VM-4-4-centos A]# ls
B
[root@VM-4-4-centos A]# cd ./B
[root@VM-4-4-centos B]# ls
C任何一个目录下,即便是空的,系统也要默认给该目录生成. 和..
(根目录的. 和..都是它自己,其他的只有.是自己)
Windows同样,也只有一个根目录,即此电脑,像C D E盘,也只是Windows对这些文件夹进行了特殊的图形化(Windows的桌面也文件夹,是把文件以图标的形式可视化出现)
命令其实就是文件
命令的本质==可执行文件==我们写的C/C++
rmdir&&rm指令
在 Linux 中,删除文件可以通过多种方式完成,但要确保文件被永久删除且无法恢复,需要特别注意。以下是几种常用方法:
使用 rm 命令删除文件
-
删除单个文件:rm 文件名
-
删除多个文件:rm 文件1 文件2 文件3
-
递归删除文件夹及其内容:rm -r 文件夹名
-
强制删除(无提示):rm -f 文件名
注:可以直接强制删除根目录,不可随便删除
bash
# 删除普通⽂件
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 14:22 dir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 14:22 file.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 15:09 newFile.txt
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm file.txt
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 14:22 dir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 15:09 newFile.txt
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
# 删除⽬录⽂件
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 8
drwxrwxr-x 2 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 14:22 dir
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 15:09 newFile.txt
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm dir
rm: cannot remove 'dir': Is a directory
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm -r dir
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 15:09 newFile.txt
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
# 删除普通⽂件前询问
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 whb whb 0 Jan 11 15:09 newFile.txt
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm -i newFile.txt
rm: remove regular empty file 'newFile.txt'? y
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 4
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 4
drwxrwxr-x 3 whb whb 4096 Jan 11 15:26 path1
# 删除⽬录前询问
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ mkdir -p d/d/d/d
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ tree d
d
└── d
└── d
└── d
3 directories, 0 files
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm -ri d
rm: descend into directory 'd'? y
rm: descend into directory 'd/d'? y
rm: descend into directory 'd/d/d'? y
rm: remove directory 'd/d/d/d'? y
rm: remove directory 'd/d/d'? y
rm: remove directory 'd/d'? y
rm: remove directory 'd'? y
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 0
# 递归强制删除⾮空⽬录
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ tree path1/
path1/
├── myfile.txt
└── path2
└── myfile.txt
1 directory, 2 files
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm -f path1
rm: cannot remove 'path1': Is a directory
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ rm -rf path1
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ ll
total 0tree指令,帮助文件一览无余
在Linux开发中,只有一行一行的代码,我们似乎会忘记我们前面创建的文件之间的关系,此时就可以使用tree指令
有些电脑没预装,需要先安装

cpp
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# tree a
a
└── b
└── c
2 directories, 0 files
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# 总结
对于用习惯Windows的我们,Linux没有图形界面,刚开始上手困难,但在我们弄懂原理,敲个几十遍熟悉后,惊奇发现:这些指令就是电脑的快捷键,比图形界面还要简单方便