
🔥小龙报:个人主页
🎬作者简介:C++研发,嵌入式,机器人等方向学习者
❄️个人专栏:《C语言》《【初阶】数据结构与算法》
✨ 永远相信美好的事情即将发生

文章目录
- 前言
- 一、通讯录框架Test.c
- 二、通讯录
-
- [2.1 Contacts.h](#2.1 Contacts.h)
- [2.2 Contacts.c](#2.2 Contacts.c)
- 三、底层逻辑
- [3.1 SeqList.h](#3.1 SeqList.h)
- [3.2 SeqList.c](#3.2 SeqList.c)
- 四、基于顺序表的通讯录实现效果
-
- [4.1 添加](#4.1 添加)
- [4.2 删除](#4.2 删除)
- [4.3 修改](#4.3 修改)
- [4.4 查找](#4.4 查找)
- [4.5 展示](#4.5 展示)
- 总结与每日励志
前言
本文聚焦C语言顺序表的实战应用,从零搭建功能完整的通讯录系统。通过封装顺序表的增删改查核心逻辑,实现联系人的添加、删除、修改、查找与展示功能,兼顾内存动态扩容与安全销毁机制。代码遵循模块化设计思想,清晰划分接口层与底层逻辑,既适合巩固数据结构基础,也为新手提供可直接复用的实战案例,助力快速掌握多文件编程与结构化开发思维(许多大学C语言期末大作业就是这个希望能给小伙伴们一些启发)。
一、通讯录框架Test.c
csharp
#include "seqlist.h"
#include "Contacts.h"
void menu()
{
printf("******************通讯录******************\n");
printf("*******1.增加联系人 2.删除联系人********\n");
printf("*******3.修改联系人 4.查找联系人********\n");
printf("*******5.展示联系人 0. 退出 *********\n");
printf("******************************************\n");
}
int main()
{
int op;
Contacts s;
SLInit(&s);
do
{
menu();
printf("请输入你的选择:");
scanf("%d", &op);
switch (op)
{
case 1:
ContactsAdd(&s);
break;
case 2:
ContactsDel(&s);
break;
case 3:
ContactsModify(&s);
break;
case 4:
ContactsFind(&s);
break;
case 5:
ContactsShow(&s);
break;
case 0:
printf("退出通讯录....\n");
break;
default:
printf("输入错误,请重新选择您的操作!\n");
break;
}
} while(op);
ContactsDestory(&s);
return 0;
}二、通讯录
2.1 Contacts.h
csharp
#define max_name 20
#define max_gender 20
#define max_tel 30
#define max_addr 50
//姓名 性别 年龄 电话 地址
typedef struct PersonalInfor
{
char name[max_name];
char gender[max_gender];
int age;
char tel[max_tel];
char addr[max_addr];
}peoInfo;
typedef struct SeqList Contacts;
//通讯录的初始化和销毁
void ContactsInit(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的销毁
void ContactsDestory(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的打印
void ContactsShow(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的插入
void ContactsAdd(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的删除
void ContactsDel(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的查找
void ContactsFind(Contacts* ps);
//通讯录的修改
void ContactsFind(Contacts* ps);注意
(1)为什么要typedef struct SeqList Contacts;这么写
答:前置声明:因为在SeqList.h和Contacts.h里互相包含头文件会编译错误所以这么写。
前置声明:前向声明(前置声明)只是告诉编译器 "这个类型存在",但如果要实际使用这个类型(比如访问成员、创建非指针变量、调用相关函数),就必须要有完整的定义 。
(2)为什么不能typedef SL Contacts;这么写
答:因为在Contacts.h里面并没有包含SeqList.h这个头文件,所以无法识别SL是什么,它只认识 int、struct XXX 这类 "基础标识",不认识自定义的别名。
2.2 Contacts.c
本质:底层依赖顺序表的实现逻辑。
csharp
#include "SeqList.h"
#include "Contacts.h"
//初始化
void ContactsInit(Contacts* ps)
{
SLInit(ps);
}
//销毁
void ContactsDestory(Contacts* ps)
{
SLDestory(ps);
}
//打印
void ContactsShow(Contacts* ps)
{
SLPrint(ps);
}
//插入
void ContactsAdd(Contacts* ps)
{
peoInfo info;
printf("请输入要添加的联系人姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", info.name);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人性别:\n");
scanf("%s", info.gender);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &info.age);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人电话:\n");
scanf("%s", info.tel);
printf("请输入要添加的联系人住址:\n");
scanf("%s", info.addr);
SLPushBack(ps,info);
}
//删除
int FindName(Contacts* ps,char* str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (strcmp(ps->a[i].name, str) == 0)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void ContactsDel(Contacts* ps)
{
//要删除的数据必须要存在,才能执行删除操作
//查找
char name[30];
printf("请输入要删除的数据的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindName(ps,name);
if (find == -1)
{
printf("此数据已删除或未有此数据\n");
return;
}
SLErase(ps, find);
printf("删除成功!\n");
}
//通讯录的查找
void ContactsFind(Contacts* ps)
{
char name[max_name];
printf("请输入要查找的数据的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindName(ps, name);
if (find == -1)
{
printf("此数据已删除或未有此数据\n");
return;
}
printf("姓名: %s 性别 : %s 年龄 : %d 电话 : %s 地址 : %s\n", ps->a[find].name,ps->a[find].gender,ps->a[find].age,ps->a[find].tel,ps->a[find].addr);
}
//修改
void ContactsModify(Contacts* ps)
{
//通讯录不为空
if (ps->size == 0)
{
printf("当前通讯录为空\n");
return;
}
//要修改的联系人数据存在
char name[max_name];
printf("请输入要修改的用户姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", name);
int find = FindName(ps, name);
if (find < 0)
{
printf("要修改的联系人数据不存在!\n");
return;
}
else
{
//直接修改
printf("请输入新的姓名:\n");
scanf("%s", ps->a[find].name);
printf("请输入新的性别:\n");
scanf("%s", ps->a[find].gender);
printf("请输入新的年龄:\n");
scanf("%d", &ps->a[find].age);
printf("请输入新的电话:\n");
scanf("%s", ps->a[find].tel);
printf("请输入新的住址:\n");
scanf("%s", ps->a[find].addr);
printf("修改成功!\n");
}
}三、底层逻辑
3.1 SeqList.h
csharp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Contacts.h"
typedef peoInfo SLDateType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDateType* a; //存储数据
int size; //有效数据个数
int capacity; //空间容量
}SL;
void SLInit(SL* ps); //初始化
void SLDestory(SL* ps); //销毁
void SLPrint(SL* ps); //打印
//插入部分
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x); //尾插
//删除部分
void SLPopback(SL* ps); //尾删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps); //头删
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos); //任意位置删除3.2 SeqList.c
csharp
#include "seqlist.h"
#include "Contacts.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁
void SLDestory(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->a)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
}
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
printf("姓名:%s 性别:%s 年龄:%d 电话:%s 地址:%s\n", ps->a[i].name,ps->a[i].gender,ps->a[i].age,ps->a[i].tel,ps->a[i].addr);
}
//检查是否需要扩容
void CheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDateType* temp = realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDateType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
printf("开辟失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = temp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
CheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}
//任意位置删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
for (int i = pos + 1; i < ps->size; i++)
ps->a[i - 1] = ps->a[i];
ps->size--;
}四、基于顺序表的通讯录实现效果
4.1 添加
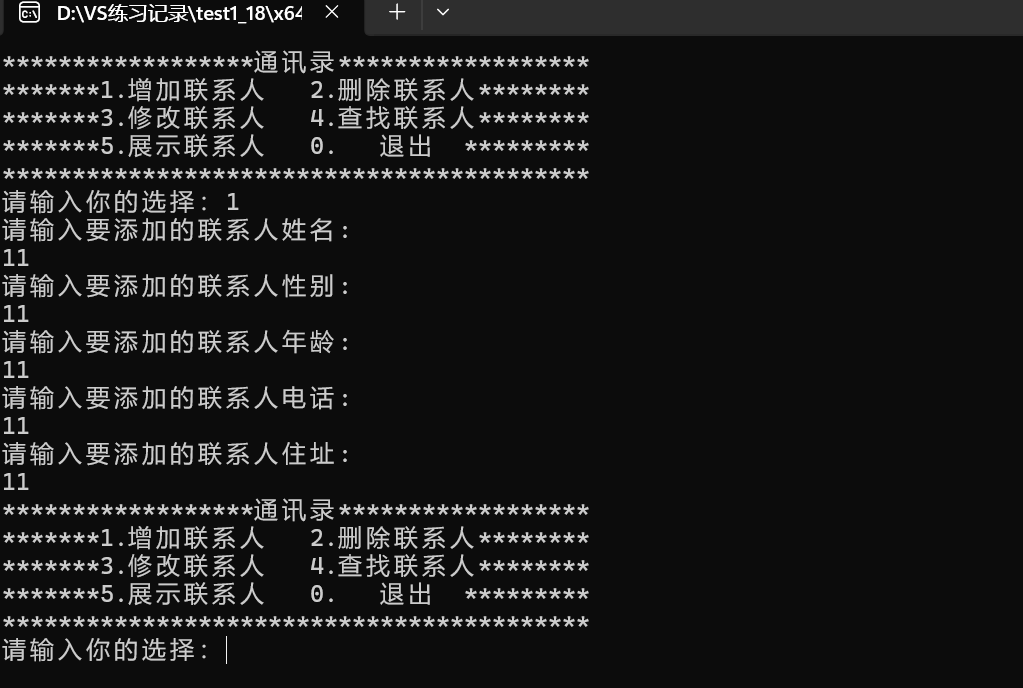
4.2 删除

4.3 修改
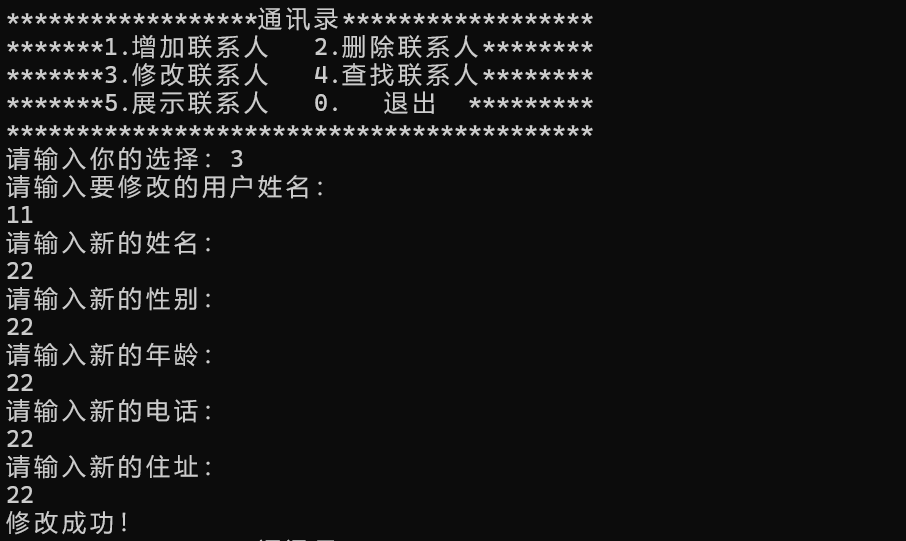
4.4 查找
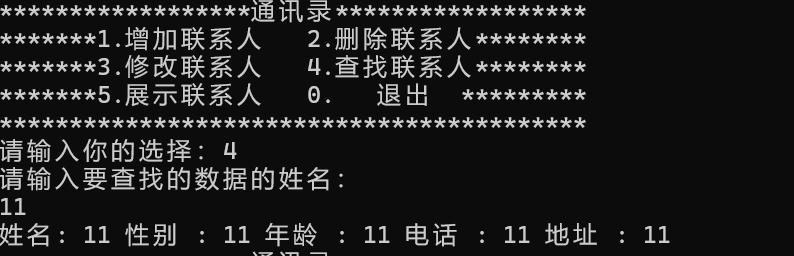
4.5 展示
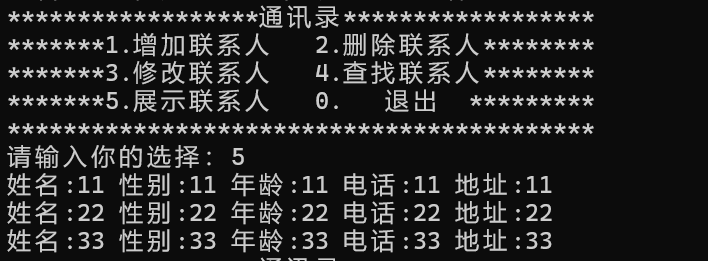
总结与每日励志
✨本文基于C语言顺序表实现通讯录管理系统,包含添加、删除、修改、查找和展示联系人功能。通过模块化设计将底层顺序表操作与通讯录业务逻辑分离,使用动态内存管理实现扩容机制。代码采用多文件结构,包含测试框架、通讯录接口和顺序表实现三部分,完整展示了数据结构的实际应用。系统具有以下特点:1)支持联系人信息的完整CRUD操作;2)采用类型封装解决头文件循环引用问题;3)提供内存安全保证;4)交互式菜单界面。该实现既可作为数据结构学习案例,也适用于C语言课程实践项目。
