目录
(一)线性表
-
线性表(liner list)是具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
-
常见线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串。
-
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,在物理上不一定连续存储。
(二)顺序表
(1)概念与结构
-
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构。
-
一般用数组存储。
逻辑结构和物理结构如上图。
顺序表和数组有什么区别嘞?
-
顺序表的底层结构是数组。
-
顺序表是对数组的封装,实现了常用的增删查改等接口。
(2)分类
①静态顺序表
- 使用定长数组存储元素。
给一段定义静态顺序表的代码:
cpp
typedef int SLDataType;
#define N 7
typedef struct SeqentialList
{
SLDataType a[N]; //fixed-length array
int size; //number of valid elements
}SL;(英文注释是因为本人英语不好,但是还要过六级)
②动态顺序表
- 只定义顺序表头指针实现可增容
给一段定义动态顺序表的代码:
cpp
typedef int SLDataType; //type of sequential list element
typedef struct SeqentialList
{
SLDataType* a; //dynamically allocated array
int size; //number of valid elements
int capacity; //current available space
}SL;(3)动态顺序表的实现
dynamicSequentialList.h
cpp
#define INIT_CAPACITY 4
typedef int SLDataType; //type of sequential list element
typedef struct DynamicSeqentialList
{
SLDataType* a; //dynamically allocated array
int size; //number of valid elements
int capacity; //current available space
}DSL;
// 1.initialization and destruction
void DSLInit(DSL* ps);
void DSLDestroy(DSL* ps);
void DSLPrint(DSL* ps);
// 2.expand capacity
void DSLCheckCapacity(DSL* ps);
// 3.insert and delete at the head (tail)
void DSLPushFront(DSL* ps, SLDataType x);
void DSLPopFront(DSL* ps);
void DSLPushBack(DSL* ps, SLDataType x);
void DSLPopBack(DSL* ps);
// 3.insert and delete before the specified position
void DSLInsert(DSL* ps,int pos,SLDataType x);
void DSLErase(DSL* ps,int pos);
// 4.find data
int DSLFind(DSL* ps,SLDataType x);dynamicSequentialList.c
①初始化、销毁和打印
cpp
void DSLInit(DSL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void DSLDestroy(DSL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
free(ps);
}
void DSLPrint(DSL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0;i < ps->size;++i)
{
printf("%d, ",i,ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}②扩容
cpp
void DSLCheckCapacity(DSL* ps)
{
if (ps == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
if (ps->size < ps->capacity)
{
return;
}
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? sizeof(SLDataType) : 2 * ps->capacity;
//in-place expansion
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity);
if(tmp == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}-
安全性
- 检查ps和tmp是否为空。
-
是否有必要扩容
- 检查size是否小于capacity。
-
扩容多少空间
- 一般在原来基础上扩容两倍。
-
tmp临时指针
- 为避免realloc申请不到空间,创建临时指针指向扩容后的空间。
-
更新a,capacity
③头插
cpp
void DSLPushFront(DSL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
if (ps == NULL || x == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
DSLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size;i > 0;--i)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i - 1];
}
ps->a[0] = x;
++ps->size;
}-
安全性
-
检查参数ps和x是否为空。
-
检查是否需要扩容。
-
-
更新a,size
④头删
cpp
void DSLPopFront(DSL* ps)
{
if (ps == NULL || ps->size == 0)
{
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0;i < ps->size - 1;++i)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->a[--ps->size;] = NULL;
}-
安全性
-
检查ps是否为空。
-
检查size是否为0。
-
-
更新a,size
⑤尾插
cpp
void DSLPushBack(DSL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
if (ps == NULL || x == NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
DSLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size++] = x;
}-
安全性
-
检查参数ps和x是否为空。
-
检查是否需要扩容。
-
-
更新a,size
⑥尾删
cpp
void DSLPopBack(DSL* ps)
{
if (ps == NULL || ps->size == 0)
{
exit(1);
}
ps->a[--ps->size] = NULL;
}-
安全性
-
检查ps是否为空。
-
检查size是否为0。
-
-
更新a,size。
⑦指定位置插入
cpp
void DSLInsert(DSL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
if (ps == NULL || x == NULL || pos < 0 || pos > ps->size)
{
exit(1);
}
DSLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos;--i)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i-1];
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
++ps->size;
}-
安全性
-
检查参数ps,x是否为空。
-
检查参数pos是否合法。
-
检查是否需要扩容。
-
-
更新a,size
⑧指定位置删除
cpp
void DSLErase(DSL* ps, int pos)
{
if (ps == NULL || ps->size == 0 || pos < 0 || pos > ps->size)
{
exit(1);
}
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1;++i)
{
ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
}
ps->a[ps->size - 1] = NULL;
--ps->size;
}-
安全性
-
检查参数ps是否为空。
-
检查a是否是空数组。
-
检查参数pos合法性。
-
-
更新a,size
⑨查找元素
cpp
int DSLFind(DSL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
int result = 0;
int i = 0;
assert(ps);
assert(x);
if (ps->size == 0)
{
perror("the list is empty");
exit(1);
}
for (i = 0;i < ps->size; ++i)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
result = i;
break;
}
}
if (i == ps->size)
{
return -1;
}
return result;
}-
安全性
-
检查参数ps和x是否为空。
-
检查a是否是空数组。
-
-
循环查找x。
-
判断循环是找到了退出,还是遍历完了没有找到退出。
(4)顺序表算法题
①移除元素
解法一
cpp
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int k = numsSize;
for(int i = 0;i < k;++i)
{
if(nums[i] == val)
{
nums[i--] = nums[--k];
}
}
return k;
}-
遍历数组。
-
判断是否与val值相等。
-
如果与val值相等,则被数组最后一个元素覆盖。
-
被覆盖后,k值-1。
-
被覆盖后,还需要判断覆盖后的元素值是否与val值相等。
解法二:双指针法
cpp
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int src = 0;
int dst = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < numsSize;++i)
{
if(nums[src] != val)
{
nums[dst++] = nums[src];
}
++src;
}
return dst;
}-
两个指针 dst 和 src 遍历数组。
-
src找值不等于val的元素。
-
找到后把src指向的值赋值给dst指向的位置。
-
dst向前,src向前找下一个值不等于val的元素。
-
dst的值即为最后值不等于val的元素的个数。
②删除有序数组中的重复项
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解法一
cpp
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize) {
if(!numsSize)
{
return 0;
}
int k = 1;
for(int i = 1 ; i < numsSize;++i)
{
if(nums[i] != nums[i - 1])
{
nums[k++] = nums[i];
}
}
return k;
}-
数组第一个元素一定是第一个不重复的元素,k初始化为1。
-
遍历数组。
-
如果元素不等于前一个元素的值,就把这个元素放到下标为k的位置上,k值加1。
-
k值即为最后不重复元素的个数。
解法二:双指针法
cpp
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int dst = 0;
int src = 1;
while(src < numsSize)
{
if(nums[src] != nums[dst] && ++dst != src)
{
nums[dst] = nums[src];
}
++src;
}
return ++dst;
}-
src遍历数组。
-
如果找到和dst指向元素的值不相等的元素,则把src指向的元素赋值给dst后一个位置。
③合并两个有序数组
解法一:先合并再冒泡排序
cpp
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
int i = m;
int j = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int flag = 0;
while(i < nums1Size)
{
nums1[i++] = nums2[j++];
}
for(i = 0;i < nums1Size;++i)
{
flag = 0;
for(j = 0;j < nums1Size - i - 1;++j)
{
if(nums1[j] > nums1[j + 1])
{
tmp = nums1[j];
nums1[j] = nums1[j + 1];
nums1[j + 1] = tmp;
flag++;
}
}
if(!flag)
{
break;
}
}
}解法二:找最大排最后
cpp
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n) {
int i = m - 1;
int j = n - 1;
int tail = nums1Size - 1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0)
{
if(nums1[i] > nums2[j])
{
nums1[tail--] = nums1[i--];
}
else
{
nums1[tail--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
while(j >= 0)
{
nums1[tail--] = nums2[j--];
}
}-
i,j 分别从后往前遍历两个数组。
-
判断下标 i 和下标 j 的值,大的放到下标 tail 的位置。
-
更新值大的下标和tail。
-
如果 i 遍历结束,此时 j 还没有遍历结束,则把nums2剩余元素放到nums1中。
(5)顺序表问题与思考
-
中间、头部插入数据,时间复杂度为O(N)。
-
增容(申请新空间,拷贝数据)带来的开销。
-
增容后空间的浪费。
(三)单链表
(1)概念与结构
-
单链表物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序。
-
逻辑顺序通过指针链接次序实现。
链表的性质
-
结点一般从堆上申请空间。
-
申请空间可能不连续。
(2)实现单链表
①头插/头删
cpp
void SLLPushFront(SLLNode** pphead, SLLDataType x)
{
SLLNode* newNode = SLLBuyNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
}-
申请新节点。
-
链表为空特殊处理,return。
cpp
void SLLPopFront(SLLNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead && *pphead);
SLLNode* phead = *pphead;
*pphead = phead->next;
free(phead);
}-
确保链表不为NULL。
-
释放原来表头节点空间。
-
表头节点更新。
②尾插/尾删
cpp
void SLLPushBack(SLLNode** pphead, SLLDataType x)
{
SLLNode* newNode = SLLBuyNode(x);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
SLLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur->next != NULL)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
}-
申请新节点。
-
链表为空特殊处理,return。
-
遍历到表尾节点,在其后插入新节点。
cpp
void SLLPopBack(SLLNode** pphead)
{
assert(pphead && *pphead);
SLLNode* tail = *pphead;
SLLNode* prev = tail;
if (tail->next == NULL)
{
free(tail);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
prev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
free(tail);
}-
确保链表不为NULL。
-
链表只有一个节点特殊处理,return。
-
遍历到表尾节点,更新prev->next指针。
-
释放原表尾节点空间。
③查找
cpp
SLLNode* SLLFind(SLLNode* phead, SLLDataType x)
{
assert(phead);
SLLNode* cur = phead;
while (cur != NULL && cur->data != x)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL)
{
printf("not query data found!\n");
}
return cur;
}-
确保链表不为NULL。
-
遍历链表,直到找到指定节点的值=给定值。
-
如果遍历完链表,都没找到,则返回NULL。
④在指定位置之前插入数据
cpp
void SLLInsert(SLLNode** pphead, SLLNode* pos, SLLDataType x)
{
assert(pphead && pos && x);
SLLNode* newNode = SLLBuyNode(x);
if (*pphead == pos)
{
newNode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newNode;
return;
}
SLLNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur != NULL && cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
if (cur == NULL)
{
perror("invalid input");
exit(1);
}
newNode->next = pos;
cur->next = newNode;
}-
确保链表和指定位置地址不为NULL。
-
创建指定值的新节点。
-
指定位置为表头节点特殊处理,return。
-
遍历链表,直到指定位置之前的节点。
-
修改该节点和新节点的next。
-
如果遍历完链表,都未找到指定位置,则报错后exit。
⑤删除指定节点
cpp
void SLLErase(SLLNode** pphead, SLLNode* pos)
{
if (pphead == NULL || *pphead == NULL || pos==NULL)
{
perror("invalid input");
exit(1);
}
if (*pphead == pos)
{
*pphead = pos->next;
free(pos);
return;
}
SLLNode* cur = *pphead;
assert(cur);
while (cur->next != pos)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
}-
确保链表和指定位置不为NULL。
-
指定位置为表头结点特殊处理,return。
-
遍历链表,直到指定位置之前节点。
-
更改该节点的next。
-
释放指定位置空间。
⑥在指定位置之后插入数据
cpp
void SLLInsertAfter(SLLNode* pos, SLLDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLLNode* newNode = SLLBuyNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newNode;
}-
确保指定位置不为NULL。
-
创建新节点。
-
更改新节点和指定位置节点的next。
⑦删除在指定位置之后的节点
cpp
void SLLEraseAfter(SLLNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
SLLNode* cur = pos->next;
if (cur == NULL)
{
return;
}
SLLNode* next = NULL;
pos->next = NULL;
while (cur!=NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}-
确保指定位置不为NULL。
-
指定位置节点的next为NULL特殊处理,return。
-
遍历链表,直到指定位置之后。
-
next保存cur->next的数据。
-
依次释放cur的空间,直到cur为NULL。
⑧销毁链表
cpp
void SLLDestory(SLLNode** pphead)
{
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
perror("invalid input!");
exit(1);
}
SLLNode* cur = *pphead;
*pphead = NULL;
SLLNode* next = NULL;
while (cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}-
链表为NULL特殊处理,exit。
-
cur遍历链表。
-
next保存cur->next的数据。
-
依次释放cur的空间,直到cur为NULL。
(3)链表的分类
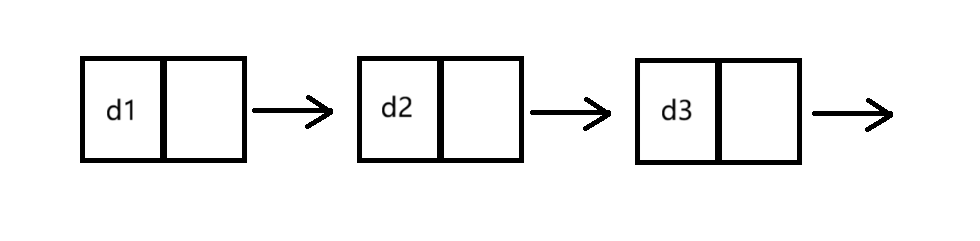
①单向和双向(如图)
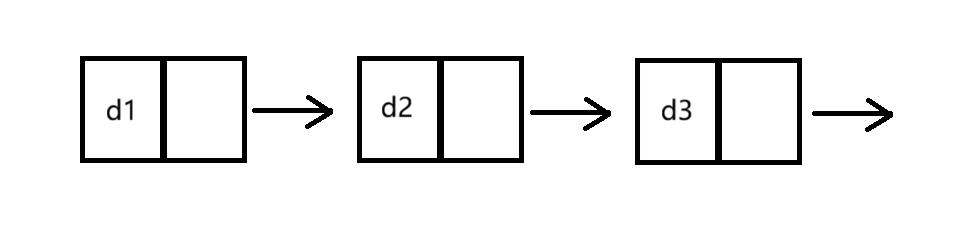
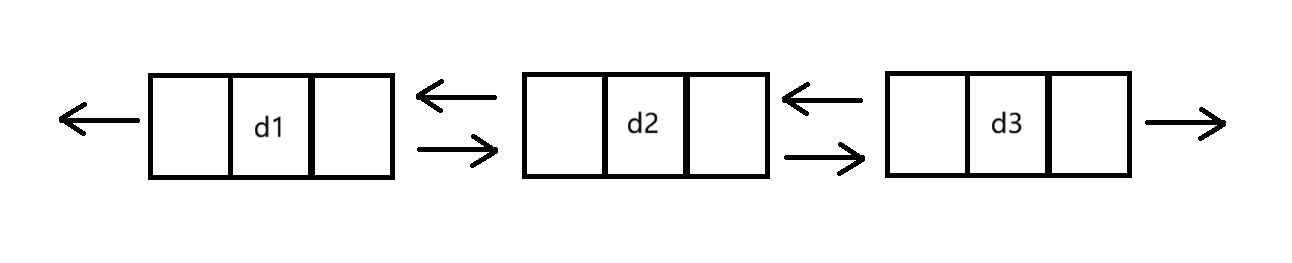
②带头和不带头(如图)
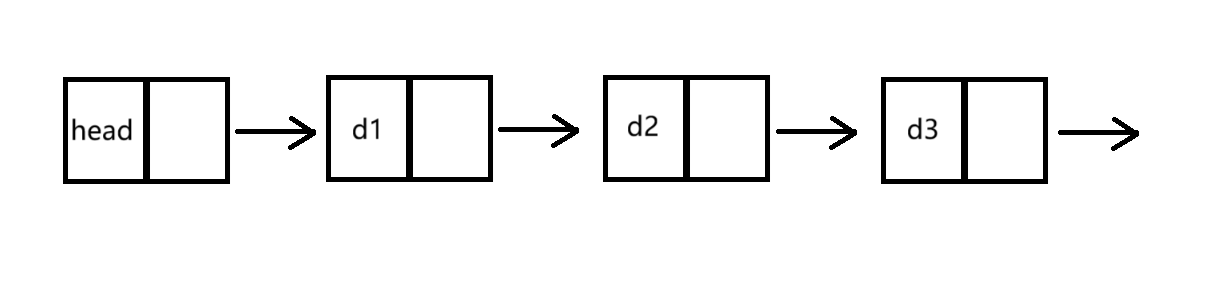
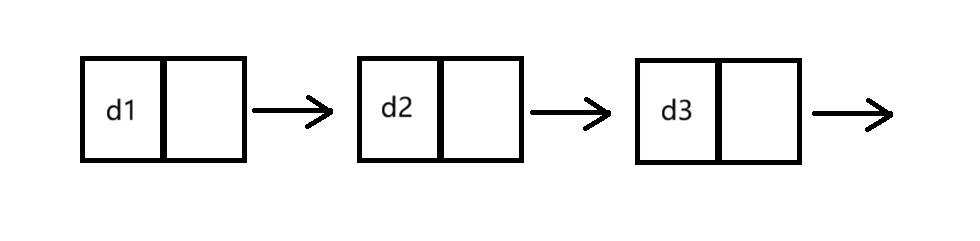
③循环和不循环(如图)
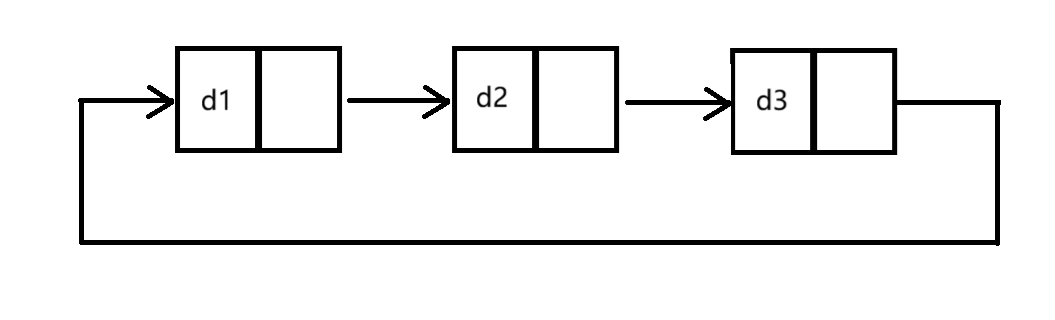
实际中最常用结构:单链表和双向带头循环链表。
(4)单链表算法题
①移除链表元素
cpp
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
while(cur != NULL)
{
if(head->val == val)
{
head = prev = cur = cur->next;
continue;
}
if(cur->val == val)
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
}
else
{
prev = cur;
}
cur = prev->next;
}
return head;
}-
cur循环遍历链表。
-
如果head的值与指定值相等,则特殊处理,continue。
-
如果cur节点需要删除,则删除后,更新cur。
-
如果cur节点不需要删除,则更新prev和cur节点。
②反转链表
cpp
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode* cur = head->next;
struct ListNode* prev = head;
struct ListNode* next;
while(cur!=NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
if(prev == head)
{
prev->next = NULL;
}
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}-
链表为空或只有一个节点,特殊处理,返回链表。
-
prev为head时特殊处理,prev->next置为NULL。
-
cur遍历链表,prev,next和next依次更新。
-
最后cur为NULL,返回prev。
③合并两个有序链表
cpp
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
if(list1->val > list2->val)
{
struct ListNode* tmp = list1;
list1 = list2;
list2 = tmp;
}
struct ListNode* plt1 = list1->next;
struct ListNode* plt2 = list2;
struct ListNode* next;
struct ListNode* prev = list1;
while(plt1 && plt2)
{
if(plt1->val <= plt2->val)
{
prev = plt1;
plt1 = plt1->next;
}
else
{
next = plt2->next;
plt2->next = plt1;
prev->next = plt2;
prev = plt2;
plt2 = next;
}
}
while(plt2)
{
prev->next = plt2;
prev = prev->next;
plt2 = plt2->next;
}
return list1;
}-
list1或list2为NULL时,特殊处理,return原链表。
-
确保表头结点小的那个链表是list1。
-
plt1遍历list1,plt2遍历list2。
-
prev为plt1前一个节点,next是plt2的下一个节点,方便plt2更新。
-
进入循环,若plt2的值小,则插入list1。
-
最后若list2还有剩余的节点,则直接接到list1尾部。
④链表的回文结构
封装函数reverseList
cpp
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return head;
}
ListNode* cur = head->next;
ListNode* prev = head;
ListNode* next;
while (cur != NULL) {
next = cur->next;
if (prev == head) {
prev->next = NULL;
}
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}题目所求函数
cpp
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
if (A == NULL || A->next == NULL) {
return false;
}
ListNode* slow = A;
ListNode* fast = A;
while (fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
if (fast) {
fast = fast->next;
}
}
ListNode* curA = A;
ListNode* curB = reverseList(slow);
while (curA && curB) {
if (curA->val != curB->val) {
return false;
}
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return true;
}-
特殊情况:链表为空,链表只有一个节点。
-
快慢指针找到链表后半部分,slow即为后半部分的表头节点。
-
反转链表后半部分。
-
比较 链表前半部分 和 反转后链表后半部分,若各值对应相等,顺利退出循环,则为回文字符结构。
-
若循环中断,则不为回文字符结构。
⑤相交链表
cpp
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if(headA == headB)
{
return headA;
}
struct ListNode* cur1 = headA;
int size1 = 0;
while(cur1)
{
++size1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
struct ListNode* cur2 = headB;
int size2 = 0;
while(cur2)
{
++size2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
int gap = 0;
cur1 = headA;
cur2 = headB;
if(size1 > size2)
{
gap = size1 - size2;
while(gap)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
gap--;
}
}
else
{
gap = size2 - size1;
while(gap)
{
cur2 = cur2->next;
gap--;
}
}
while(cur1 && cur2 && cur1 != cur2)
{
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
if(!cur1 || !cur2)
{
return NULL;
}
return cur1;
}-
处理特殊情况:两链表完全相同,有一链表为NULL。
-
cur1,cur2循环遍历链表,累加求得两链表size的值。
-
size相减求得gap。
-
cur1或cur2需要先走gap步。
-
后两指针同时遍历两链表。
-
若有相同的节点,即为相交节点。
-
若遍历结束都没有相同的节点,则返回NULL。
⑥环形链表Ⅰ
cpp
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
{
return false;
}
struct ListNode* slow = head->next;
struct ListNode* fast = slow->next;
while(fast && slow != fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
if(fast->next != NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
}else
{
fast = NULL;
}
}
if(slow == fast)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}快慢指针解法
- 特殊情况return false:如果链表为空,或链表只有一个节点且next为NULL。
- 慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步。
- 若链表带环,则快慢指针会相遇,return true。
- 若链表不带环,则快指针先走到NULL,return false。
(四)双向链表
(1)概念与结构
带头双向链表:这里的头节点不保存有效数据,可以看作"哨兵位"。
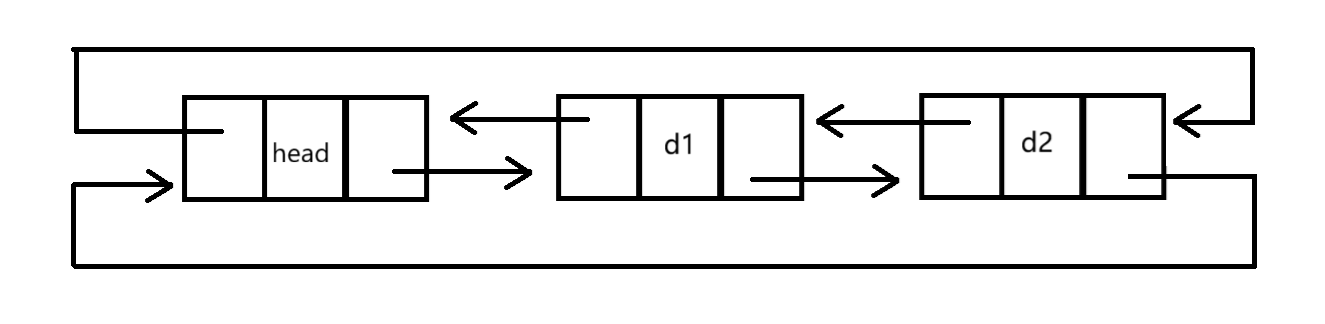
(2)实现双向链表
①初始化等操作
函数DLLInit
cpp
DLLNode* DLLInit()
{
DLLNode* phead = BuyNode(-1);
phead->prev = phead;
phead->next = phead;
return phead;
}-
为头节点开辟空间。
-
初始化头节点的prev和next。
-
返回头节点。
函数DLLDestory
cpp
void DLLDestory(DLLNode* phead)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
perror("the phead is NULL");
exit(1);
}
if (phead->next != phead)
{
DLLNode* cur = phead->next;
DLLNode* next = NULL;
while (cur != phead)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
}-
特殊情况:头节点为NULL,链表只有一个节点。
-
cur遍历链表,next保存下一个节点,依次销毁。
函数DLLEmpty
cpp
bool DLLEmpty(DLLNode* phead)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
perror("the phead is NULL");
exit(1);
}
if (phead->next == phead)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}-
特殊情况:头节点为NULL。
-
若头节点的next仍为头节点,即链表为empty。
函数DLLPrint
cpp
void DLLPrint(DLLNode* phead)
{
if (DLLEmpty(phead))
{
printf("NULL\n");
}
DLLNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!= phead)
{
printf("%d->", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}-
特殊情况:链表为empty。
-
cur遍历链表,依次打印。
②头插/头删
函数DLLPushFront
cpp
void DLLPushFront(DLLNode* phead, DLLDataType x)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
perror("the phead is NULL");
exit(1);
}
DLLNode* newNode = BuyNode(x);
newNode->next = phead->next;
newNode->prev = phead;
phead->next->prev = newNode;
phead->next = newNode;
}-
特殊情况:头节点为NULL。
-
创建新节点。
-
处理 newNode、phead 和 next 的链接关系。
函数DLLPopFront
cpp
void DLLPopFront(DLLNode* phead)
{
if (DLLEmpty(phead))
{
printf("operation invalid\n");
return;
}
DLLNode* front = phead->next;
front->next->prev = phead;
phead->next = front->next;
}-
特殊情况:链表为empty。
-
处理 phead 和 next 的链接关系。
-
释放front的节点空间。
③尾插/尾删
函数DLLPushBack
cpp
void DLLPushBack(DLLNode* phead, DLLDataType x)
{
DLLNode* newNode = BuyNode(x);
if (DLLEmpty(phead))
{
newNode->prev = phead;
phead->next = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode->prev = phead->prev;
phead->prev->next = newNode;
}
newNode->next = phead;
phead->prev = newNode;
}-
创建新节点。
-
特殊情况:链表为empty,处理头结点的prev和next。
-
一般情况:链表不为empty,处理 表尾节点、newNode 和 phead 的链接关系。
函数DLLPopBack
cpp
void DLLPopBack(DLLNode* phead)
{
if (DLLEmpty(phead))
{
printf("operation invalid\n");
return;
}
DLLNode* ptail = phead->prev;
DLLNode* prev = ptail->prev;
prev->next = phead;
phead->prev = prev;
free(ptail);
ptail = NULL;
}-
特殊情况:链表为empty。
-
定义ptail表尾节点,处理prev和phead的链接关系。
-
释放ptail空间。
④指定位置
函数DLLInsert
cpp
void DLLInsert(DLLNode* pos, DLLDataType x)
{
if (pos == NULL || pos->prev == NULL || pos->next == NULL)
{
printf("operation invalid\n");
return;
}
DLLNode* newNode = BuyNode(x);
newNode->next = pos->next;
newNode->prev = pos;
pos->next->prev = newNode;
pos->next = newNode;
}-
特殊情况:pos为NULL,pos的prev和next为NULL。
-
创建新节点。
-
处理 pos、newNode 和 pos->next 的链接关系。
函数DLLErase
cpp
void DLLErase(DLLNode* pos)
{
if (pos == NULL || pos->prev == NULL || pos->next == NULL)
{
printf("operation invalid\n");
return;
}
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
pos->prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}-
特殊情况:pos为NULL,pos的prev和next为NULL。
-
处理 pos->prev 和 pos->next 的链接关系。
-
释放pos的节点空间。
⑤查找节点
函数DLLFind
cpp
DLLNode* DLLFind(DLLNode* phead, DLLDataType x)
{
if (DLLEmpty(phead))
{
printf("operation invalid\n");
return;
}
DLLNode* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}-
特殊情况:链表为empty。
-
cur遍历链表,若找到了,则返回节点地址。
-
若遍历结束,还未找到,则返回NULL。
(五)顺序表与链表的分析
|-----------------|---------------------|-------------------------|
| 不同点 \ 数据结构 | 顺序表 | 链表 |
| 存储空间上 | 物理上一定连续。 | 逻辑上连续,物理上不一定连续。 |
| 随机访问 | 支持O(1)。 | 不支持:O(N)。 |
| 任意位置插入或删除元素 | 可能需要搬运元素,时间复杂度O(N)。 | 只需要改变指针指向。 |
| 插入 | 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容。 | 没有固定容量,按需申请空间, 不存在空间浪费。 |
| 应用场景 | 元素高效存储+频繁访问 | 任意位置高效插入+删除 |