lc3509
暴力出奇迹 子集dfs
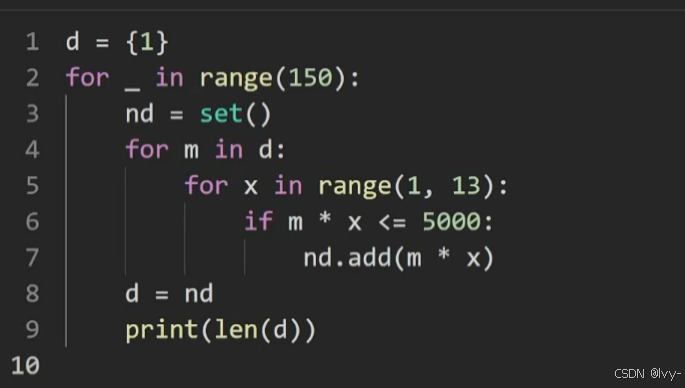
如何分析状态个数 (打一下表观察 就知道了
可以缩小数据范围 然后dfs暴力就行
=k <limit max
参数设计:遍历位 i 、和 s 、积 m 、符号标记 odd 、空序列标记 empty
提前终止:答案达上限或积超限制且有有效解时直接返回,剪枝无效递归;
递归出口:遍历完所有元素 i==n ,校验非空、和为 k 、积≤limit后更新最大积答案;
记忆去重:将所有状态打包为掩码,++已访问的状态直接跳过++,避免重复计算;
状态转移:分不选(状态不变递归下一位)、选(更新和/积/符号/空标记后递归下一位)两个分支
很灵性的vis
++if (!vis.insert(mask).second)++
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums, int k, int limit) {
int total = reduce(nums.begin(), nums.end());
if (total < abs(k)) // |k| 太大 cut
return -1;
int n = nums.size(), ans = -1;
unordered_set<long long> vis;
auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i, int s, int m, bool odd, bool empty) -> void {
if (ans == limit || m > limit && ans >= 0) // 无法让 ans 变得更大
return;
if (i == n) {
if (!empty && s == k && m <= limit) { // 合法子序列
ans = max(ans, m);
}
return;
}
long long mask = (long long) i << 32 | (s + total) << 15 | m << 2 | odd << 1 | empty;
++if (!vis.insert(mask).second)++ { // mask 在 vis 中
return;
}
// 不选 x
dfs(i + 1, s, m, odd, empty);
// 选 x
int x = nums[i];
//灵性优雅的 状态转移设计
++dfs(i + 1, s + (odd ? -x : x), min(m * x, limit + 1), !odd, false);++
};
dfs(0, 0, 1, false, true);
return ans;
}
};
lc3510
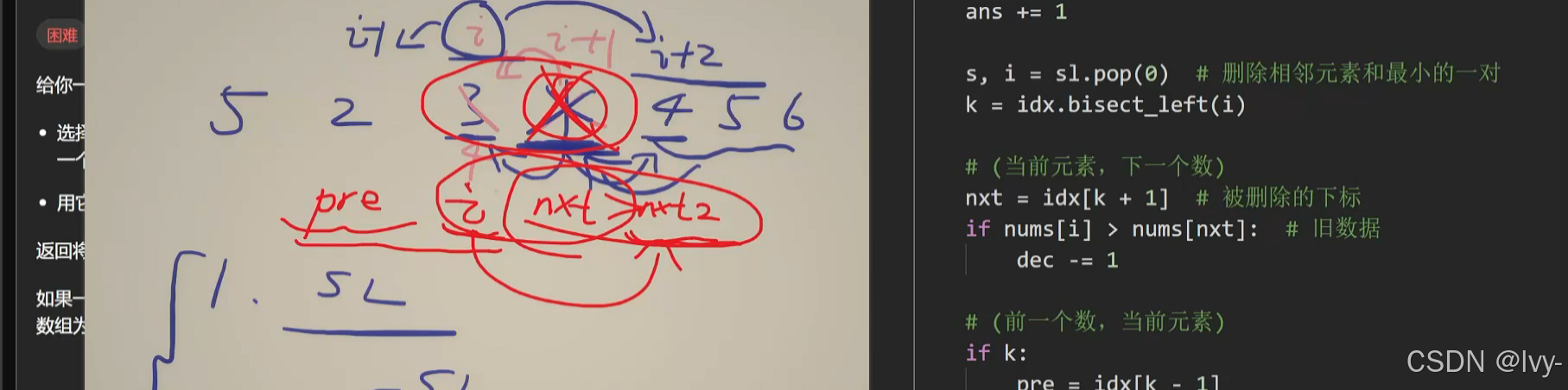
两个set表 ++sum_min(x+y, i) & idx_i++
pre i nxt nnxt 维护四个指针状态
更新dec
贪心策略,++每次移除和最小的递减相邻数对并将两数合并++,持续消除所有递减相邻对
统计移除操作次数即为最少移除对数
实现数组非递减的最小相邻数对移除求解

class Solution {
public:
int minimumPairRemoval(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
set<pair<long long, int>> pairs; // (相邻元素和,左边那个数的下标)
int dec = 0;
// 递减的相邻对的个数-need op
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < n; i++) {
int x = nums[i], y = nums[i + 1];
++if (x > y)
dec++;++
pairs.emplace(x + y, i);
}
set<int> idx; // 剩余下标
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
idx.insert(i);
vector<long long> a(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int ans = 0;
while (dec > 0) {
ans++;
// 删除相邻元素和最小的一对
++auto [s, i] = *pairs.begin();++
pairs.erase(pairs.begin());
++auto it = idx.lower_bound(i);++
// (当前元素,下一个数)
auto nxt_it = next(it);
int nxt = *nxt_it;
++dec -= a[i] > a[nxt]; // 旧数据++
// (前一个数,当前元素)
if (it != idx.begin()) {
int pre = *prev(it);
++dec -= a[pre] > a[i]; // 旧数据++
dec += a[pre] > s; // 新数据
pairs.erase({a[pre] + a[i], pre});
++pairs.emplace(a[pre] + s, pre);++
}
// (下一个数,下下一个数)
auto nxt2_it = next(nxt_it);
if (nxt2_it != idx.end()) {
int nxt2 = *nxt2_it;
++dec -= a[nxt] > a[nxt2]; // 旧数据
dec += s > a[nxt2]; // 新数据++ (当前元素,下下一个数)
pairs.erase({a[nxt] + a[nxt2], nxt});
pairs.emplace(s + a[nxt2], i);
}
++a[i] = s; // 把 a[nxt] 加到 a[i] 中
idx.erase(nxt); // 删除 nxt++
}
return ans;
}
};

也可以通过并查集 merge 模拟删除😋
lc1634
链表多项式 老老实实
// 逐个拼接剩余节点,避免直接接上整个链表
while (poly1) {
ret->next = poly1;
ret = ret->next;
poly1 = poly1->next;
}
class Solution {
public:
PolyNode* addPoly(PolyNode* poly1, PolyNode* poly2)
{
PolyNode dummy;
PolyNode* ret = &dummy;
while(poly1 && poly2)
{
int a=poly1->power,b=poly2->power;
if(a==b)
{
int coe = poly1->coefficient + poly2->coefficient;
if(coe != 0)
{
PolyNode* t=new PolyNode(coe,poly1->power);
ret->next=t;
ret=ret->next;
}
poly1=poly1->next;
poly2=poly2->next;
}
else if(a<b)
{
ret->next=poly2;
ret=ret->next;
poly2=poly2->next;
}
else
{
ret->next=poly1;
ret=ret->next;
poly1=poly1->next;
}
}
// 逐个拼接剩余节点,避免直接接上整个链表
while (poly1) {
ret->next = poly1;
ret = ret->next;
poly1 = poly1->next;
}
while (poly2) {
ret->next = poly2;
ret = ret->next;
poly2 = poly2->next;
}
ret->next = nullptr;
return dummy.next;
}
};