🔥个人主页: Milestone-里程碑
❄️个人专栏: <<力扣hot100>> <<C++>><<Linux>>
🌟心向往之行必能至
目录
[一. 文件内容操作](#一. 文件内容操作)
[1.1 cat&&tac : 正序/倒序查看文件](#1.1 cat&&tac : 正序/倒序查看文件)
[1.2 nano:简单易用的命令行文本编辑器](#1.2 nano:简单易用的命令行文本编辑器)
[1.3 more&&less指令 查看大文件](#1.3 more&&less指令 查看大文件)
[1.3.1 more:只可前进不可后退地查看](#1.3.1 more:只可前进不可后退地查看)
[1.3.2 less:可前进后退,推荐](#1.3.2 less:可前进后退,推荐)
[1.4 head&&tail指令:查看开头或结尾的文字区块](#1.4 head&&tail指令:查看开头或结尾的文字区块)
[1.4.1 head:查看开头的文字区块(可指定区域)](#1.4.1 head:查看开头的文字区块(可指定区域))
[1.4.2 tail:查看结尾的文字区块](#1.4.2 tail:查看结尾的文字区块)
[1.4.3 head与tail组合使用,查找中间区域](#1.4.3 head与tail组合使用,查找中间区域)
[1.4.4 |(管道)使head tail等指令可以灵活搭配使用](#1.4.4 |(管道)使head tail等指令可以灵活搭配使用)
[二. 时间与日历](#二. 时间与日历)
[1.1 date:查看时间](#1.1 date:查看时间)
[1.2 cal 查找日历](#1.2 cal 查找日历)
[三. 搜索指令:高效准确地查找位置](#三. 搜索指令:高效准确地查找位置)
[1.1 find :在目录中准确查找文件](#1.1 find :在目录中准确查找文件)
[1.2 whereis:查找二进制文件](#1.2 whereis:查找二进制文件)
[1.3 grep:查找字符串文件](#1.3 grep:查找字符串文件)
一. 文件内容操作
1.1 cat&&tac : 正序/倒序查看文件
cat
语法: cat [ 选项 ] [ ⽂件 ] (tac即逆序查找,跟cat用法相似,此处不多讲)
功能: 查看⽬标⽂件的内容
常⽤选项:
-b 对⾮空输出⾏编号,空⾏不做编号
-n 对输出的所有⾏编号
-s 不输出多⾏空⾏
bash
# 命令⾏构建多⾏⽂本
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -le 20 ]; do echo "hello Milestone"; let cnt++; done > temp.txt
# 测试cat基本命令
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat temp.txt
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
# cat 输出携带⾏号
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat -n temp.txt
1 hello Milestone
2 hello Milestone
3 hello Milestone
4 hello Milestone
5 hello Milestone
6 hello Milestone
7 hello Milestone
8 hello Milestone
9 hello Milestone
10 hello Milestone
11 hello Milestone
12 hello Milestone
13 hello Milestone
14 hello Milestone
15 hello Milestone
16 hello Milestone
17 hello Milestone
18 hello Milestone
19 hello Milestone
20 hello Milestone
21 hello Milestone
# 修改temp.txt,使其携带多⾏空⾏(后面nano会讲用法)
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# nano temp.txt
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat temp.txt
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
# 测试 -b 对⾮空输出⾏编号
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat -b temp.txt
1 hello Milestone
2 hello Milestone
3 hello Milestone
4 hello Milestone
5 hello Milestone
6 hello Milestone
7 hello Milestone
8 hello Milestone
9 hello Milestone
10 hello Milestone
11 hello Milestone
12 hello Milestone
13 hello Milestone
14 hello Milestone
15 hello Milestone
16 hello Milestone
17 hello Milestone
18 hello Milestone
19 hello Milestone
20 hello Milestone
21 hello Milestone
# 测试-n 对输出的所有⾏编号
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat -n temp.txt
1 hello Milestone
2
3 hello Milestone
4 hello Milestone
5
6
7 hello Milestone
8 hello Milestone
9 hello Milestone
10
11
12
13 hello Milestone
14
15 hello Milestone
16 hello Milestone
17 hello Milestone
18 hello Milestone
19 hello Milestone
20 hello Milestone
21 hello Milestone
22 hello Milestone
23 hello Milestone
24 hello Milestone
25 hello Milestone
26 hello Milestone
27 hello Milestone
28 hello Milestone
# 测试 -s 不输出多⾏空⾏,多⾏空⾏压缩成为⼀⾏
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:/dir# cat -s temp.txt
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone
hello Milestone1.2 nano:简单易用的命令行文本编辑器
功能:支持基本编辑操作,足以应付日常使用
语法: nano 文件名
1.2.1常用快捷键
Nano 的快捷键以 ^(代表 Ctrl)或 M-(代表 Alt)开头,显示在屏幕底部。
- 保存文件 :
Ctrl + O,按Enter确认文件名。 - 退出 Nano :
Ctrl + X,如果文件未保存会提示保存。 - 搜索文本 :
Ctrl + W,输入搜索词后按Enter。 - 替换文本 :
Ctrl + \,输入搜索词和替换词,按Enter逐个替换或A全部替换。
1.2.2高级功能
- 剪切/粘贴行 :
- 剪切当前行:
Ctrl + K - 粘贴:
Ctrl + U
- 剪切当前行:
- 跳转到行号 :
Ctrl + _,输入行号后按Enter。 - 语法高亮:Nano 支持部分语言的语法高亮
1.2.3适用场景:
- 快速修改系统配置文件(如 /etc/ 目录下的配置)。
- 在服务器终1.端中编写简单的脚本(如 Shell 脚本)。
- 初学者入门命令行文本编辑,避免因 Vim 的复杂性而劝退。
1.3 more&&less指令 查看大文件
1.3.1 more:只可前进不可后退地查看
语法: more [ 选项 ]
功能:more命令,功能类似 cat
常⽤选项:
• -n 指定输出⾏数
• q 退出more
使用
bash
# 命令行输出多行文本
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -le 2000 ]; do echo "mp.txt"
# -n 指定输出行数
[root@VM-4-4-centos lesson4]# more -10 temp.txt
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
hello Lotso
--More--(0%)如果还要查看剩下的文件代码,则需要按enter键,每按一下更新一次
1.3.2 less:可前进后退,推荐
语法: less [参数] ⽂件
功能:less与more类似,但使⽤less可以随意浏览⽂件,⽽more仅能向前移动,却不能向后移动,⽽且less在查看之前不会加载整个⽂件。
选项:
• -i 忽略搜索时的⼤⼩写
• -N 显⽰每⾏的⾏号
• /字符串:向下搜索"字符串"的功能
• ?字符串:向上搜索"字符串"的功能
• n:重复前⼀个搜索(与 / 或 ? 有关)
• N:反向重复前⼀个搜索(与 / 或 ? 有关)
• q:quit
bash
# 命令⾏输出多⾏⽂本
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ cnt=0; while [ $cnt -le 2000 ]; do echo "hello
$cnt"; let cnt++; done > temp.txt
# 测试搜索和-N等功能
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ less -N temp.txt
1 hello 0
2 hello 1
3 hello 2
4 hello 3
5 hello 4
6 hello 5
7 hello 6
8 hello 7
9 hello 8
10 hello 9
11 hello 10
12 hello 11
13 hello 12
14 hello 13
...补充
• less ⼯具也是对⽂件或其它输出进⾏分⻚显⽰的⼯具,应该说是linux正统查看⽂件内容的⼯具,功能极其强⼤
• less 的⽤法⽐起 more 更加的有弹性,在 more 的时候,我们并没有办法向前⾯翻, 只能往后⾯看
• 但若使⽤了 less 时,就可以使⽤ [pageup] [pagedown] 等按键的功能来往前往后翻看⽂件,更容易⽤来查看⼀个⽂件的内容
• 除此之外,在 less ⾥头可以拥有更多的搜索功能,不⽌可以向下搜,也可以向上搜
1.4 head&&tail指令:查看开头或结尾的文字区块
1.4.1 head:查看开头的文字区块(可指定区域)
语法:head [参数]... [⽂件]...
功能:head ⽤来显⽰档案的开头⾄标准输出中,默认head命令打印其相应⽂件的开头10⾏。
选项: -n<⾏数> 显⽰的⾏数
bash
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ head temp.txt
hello 0
hello 1
hello 2
hello 3
hello 4
hello 5
hello 6
hello 7
hello 8
hello 9
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ head -5 temp.txt
hello 0
hello 1
hello 2
hello 3
hello 41.4.2 tail:查看结尾的文字区块
语法: tail 必要参数 [ ⽂件 ]
功能:⽤于显⽰指定⽂件末尾内容,不指定⽂件时,作为输⼊信息进⾏处理。常⽤查看⽇志⽂件
选项: -f 循环读取
-n<⾏数> 显⽰⾏数
bash
# 基本功能演⽰
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ tail temp.txt
hello 1991
hello 1992
hello 1993
hello 1994
hello 1995
hello 1996
hello 1997
hello 1998
hello 1999
hello 2000
[whb@bite-alicloud test]$ tail -3 temp.txt
hello 1998
hello 1999
hello 20001.4.3 head与tail组合使用,查找中间区域
此处以模拟查找日志为例
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# head -200 temp.txt | tail -20
hello 180
hello 181
hello 182
hello 183
hello 184
hello 185
hello 186
hello 187
hello 188
hello 189
hello 190
hello 191
hello 192
hello 193
hello 194
hello 195
hello 196
hello 197
hello 198
hello 1991.4.4 |(管道)使head tail等指令可以灵活搭配使用
管道是一种用于在进程间传递数据的通信机制,通常用于单向数据传输。在Unix/Linux系统中,管道分为匿名管道和命名管道两种类型。
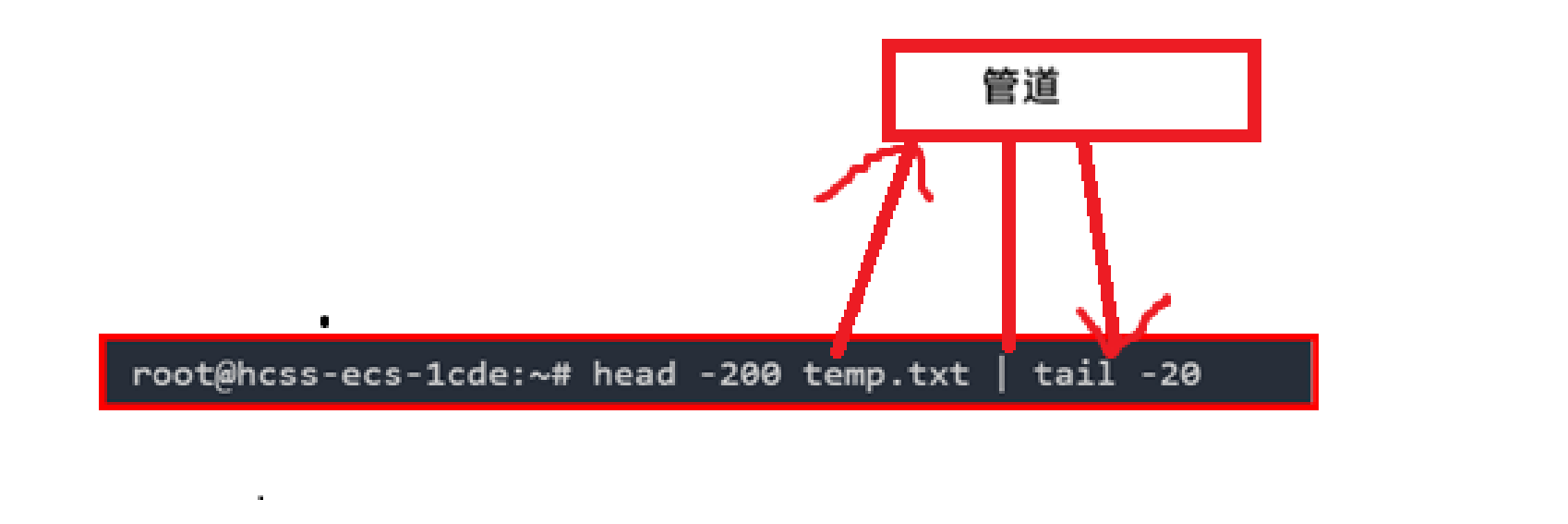
上面head先从temp.txt读取数据,然后给|,最后tail再从|这个管道读取数据
注:一行命令中有多个管道也是可以
二. 时间与日历
1.1 date:查看时间
指定格式显⽰时间: date +%Y:%m:%d
⽤法: date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]
- 在显⽰⽅⾯,使⽤者可以设定欲显⽰的格式,格式设定为⼀个加号后接数个标记,其中常⽤的标记列表如下
• %H : ⼩时(00..23)
• %M : 分钟(00..59)
• %S : 秒(00..61)
• %X : 相当于 %H:%M:%S
• %d : ⽇ (01..31)
• %m : ⽉份 (01..12)
• %Y : 完整年份 (0000..9999)
• %F : 相当于 %Y-%m-%d
- 在设定时间⽅⾯
date -s //设置当前时间,只有root权限才能设置,其他只能查看。
date -s 20080523 //设置成20080523,这样会把具体时间设置成空00:00:00
date -s 01:01:01 //设置具体时间,不会对⽇期做更改
date -s "01:01:01 2008-05-23″ //这样可以设置全部时间
date -s "01:01:01 20080523″ //这样可以设置全部时间
date -s "2008-05-23 01:01:01″ //这样可以设置全部时间
date -s "20080523 01:01:01″ //这样可以设置全部时间
3.时间戳
时间->时间戳:date +%s
时间戳->时间:date -d@1508749502
Unix时间戳(英⽂为Unix epoch, Unix time, POSIX time 或 Unix timestamp)是从1970年1⽉1⽇(UTC/GMT的午夜)开始所经过的秒数,不考虑闰秒
时间戳非常重要,可以转换为时间,而大型文件都是需要日志记录的,日志包含时间\
bash
# 显⽰常规时间
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# date +%Y/%m/%d
2025/12/10
# 显⽰时间戳
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# date +%Y/%m/%d
2025/12/10
# 时间戳转成可视时间
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# date +%Y/%m/%d-%H:%M:%S -d@0
1970/01/01-08:00:001.1.1小知识:电脑时间总是是准确的
当我们电脑哪怕关机或者断网后,一段时间却电脑时间却依旧准确,原因就是电脑有一个小的纽扣电池,用来记录时间
1.2 cal 查找日历
命令格式: cal 参数 [ 年份 ]
功能:⽤于查看⽇历等时间信息,如只有⼀个参数,则表⽰年份(1-9999),如有两个参数,则表⽰⽉份 和年份
常⽤选项:
• -3 显⽰系统前⼀个⽉,当前⽉,下⼀个⽉的⽉历
• - j 显⽰在当年中的第⼏天(⼀年⽇期按天算,从1⽉1号算起,默认显⽰当前⽉在⼀年中的天数)
• -y 显⽰当前年份的⽇历
bash
# 常规样例
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# cal
December 2025
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28 29 30 31
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# cal -3
November 2025 December 2025 January 2026
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
16 17 18 19 20 21 22 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
23 24 25 26 27 28 29 28 29 30 31 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
30
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# cal 2025
2025
January February March
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 1 1
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
30 31
April May June
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
27 28 29 30 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 29 30
July August September
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
27 28 29 30 31 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 28 29 30
31
October November December
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 5 6
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
26 27 28 29 30 31 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 28 29 30 31
30 三. 搜索指令:高效准确地查找位置
1.1 find :在目录中准确查找文件
语法: find pathname -options
功能:⽤于在⽂件树中查找⽂件,并作出相应的处理(可能访问磁盘)
常⽤选项
• -name 按照⽂件名查找⽂件
• 其他选项需要在查,这个命令其实⽐较复杂
bash
# 在指定路径下搜索执⾏名称的⽂件
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~# find ~-name *txt
find: '~-name': No such file or directory
a.txt
modify.txt
mp.txt
my-backup.txt
temp.txt补充
Linux下find命令在⽬录结构中搜索⽂件,并执⾏指定的操作。
Linux下find命令提供了相当多的查找条件,功能很强⼤。由于find具有强⼤的功能,所以它的选项也很多,其中⼤部分选项都值得我们花时间来了解⼀下。
即使系统中含有⽹络⽂件系统( NFS),find命令在该⽂件系统中同样有效,只你具有相应的权
限。
在运⾏⼀个⾮常消耗资源的find命令时,很多⼈都倾向于把它放在后台执⾏,因为遍历⼀个⼤的 ⽂件系统可能会花费很⻓的时间(这⾥是指30G字节以上的⽂件系统)。
1.2 whereis:查找二进制文件
功能:⽤于找到程序的源、⼆进制⽂件或⼿册
bash
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# whereis ls
ls: /usr/bin/ls /usr/share/man/man1/ls.1.gz1.3 grep:查找字符串文件
语法: grep [ 选项 ] 搜寻字符串 ⽂件
功能:在⽂件中搜索字符串,将找到的⾏打印出来
常⽤选项:
-i :忽略⼤⼩写的不同,所以⼤⼩写视为相同
-n :顺便输出⾏号
-v :反向选择,亦即显⽰出没有 '搜寻字符串' 内容的那⼀⾏
bash
# ⽂件内容
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# cat temp.txt
aabb
ccdd
ffgg
1234
AABB
#基本查找
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep 'aabb' temp.txt
aabb
# 忽略⼤⼩写的不同,所以⼤⼩写视为相同
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep -i 'aabb' temp.txt
aabb
AABB
# 顺便输出⾏号
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep -in 'aabb' temp.txt
1:aabb
5:AABB
# 反向选择,亦即显⽰出没有 '搜寻字符串' 内容的那⼀⾏
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep -v 'aabb' temp.txt
ccdd
ffgg
1234
AABB
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep -vn 'aabb' temp.txt
2:ccdd
3:ffgg
4:1234
5:AABB
root@hcss-ecs-1cde:~/dir# grep -vni 'aabb' temp.txt
2:ccdd
3:ffgg
4:1234总结:
灵活使用管道与其他指令搭配,明白data的来历就初始值0