题目链接
思路
核心思路是通过「虚拟头节点 + 节点删除 / 插入」的方式实现两两交换:
- 先创建一个虚拟头节点(dummy) 指向原链表头节点,避免处理头节点交换的特殊情况;
- 遍历链表时,每次定位到需要交换的两个相邻节点(记为 first、second);
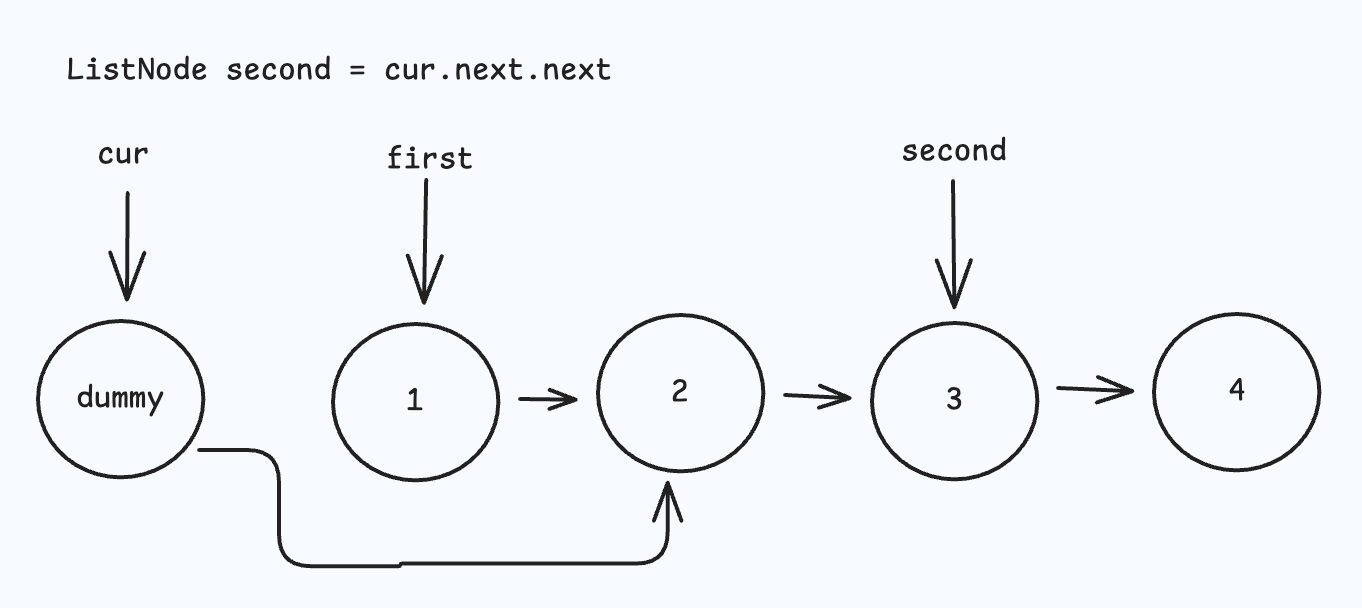
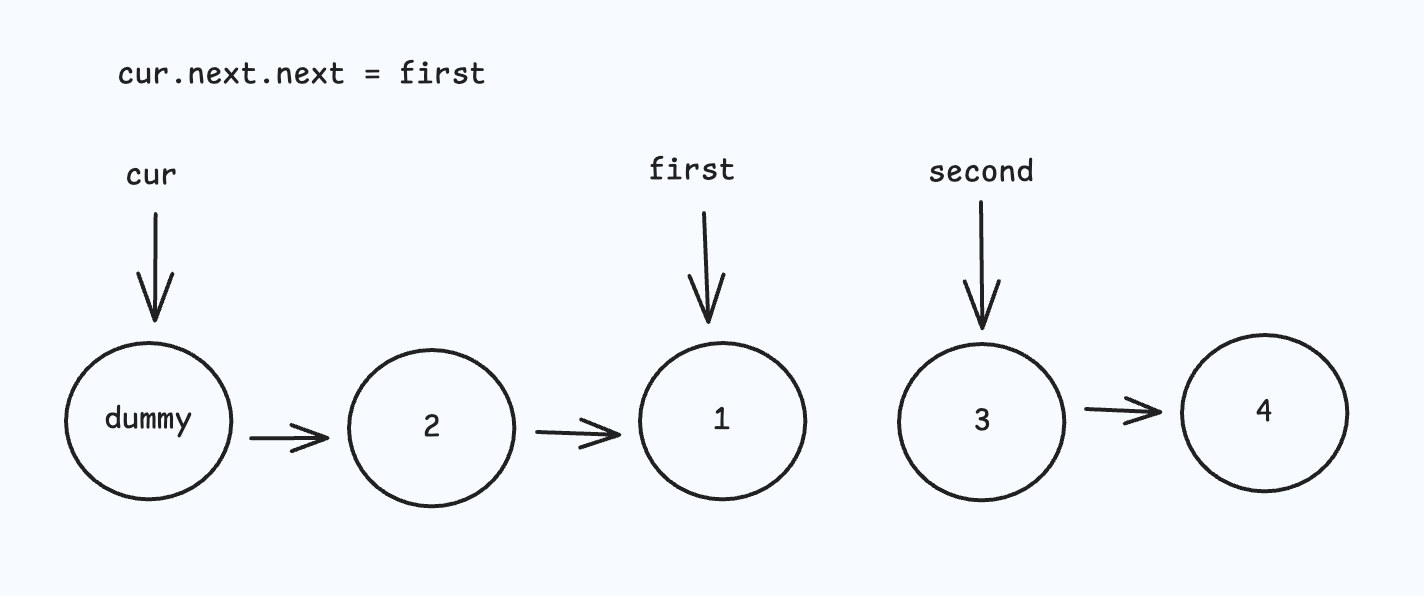
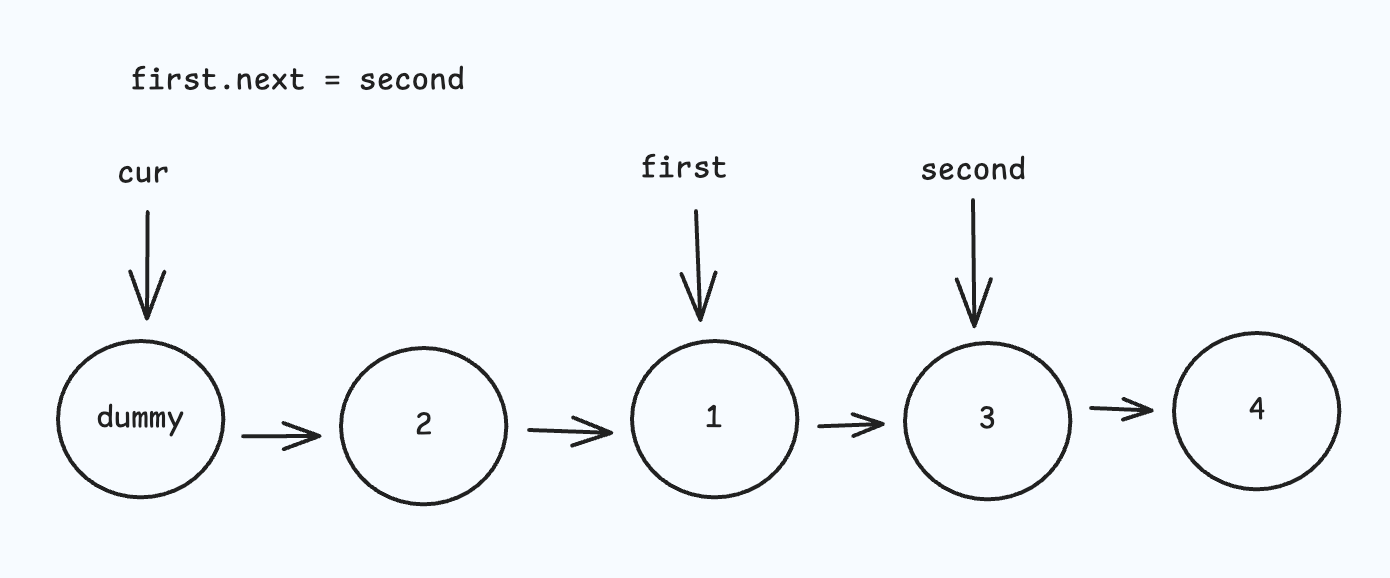
- 先将 first 节点从原位置 "删除",再将 first 节点插入到 second 节点的后面;
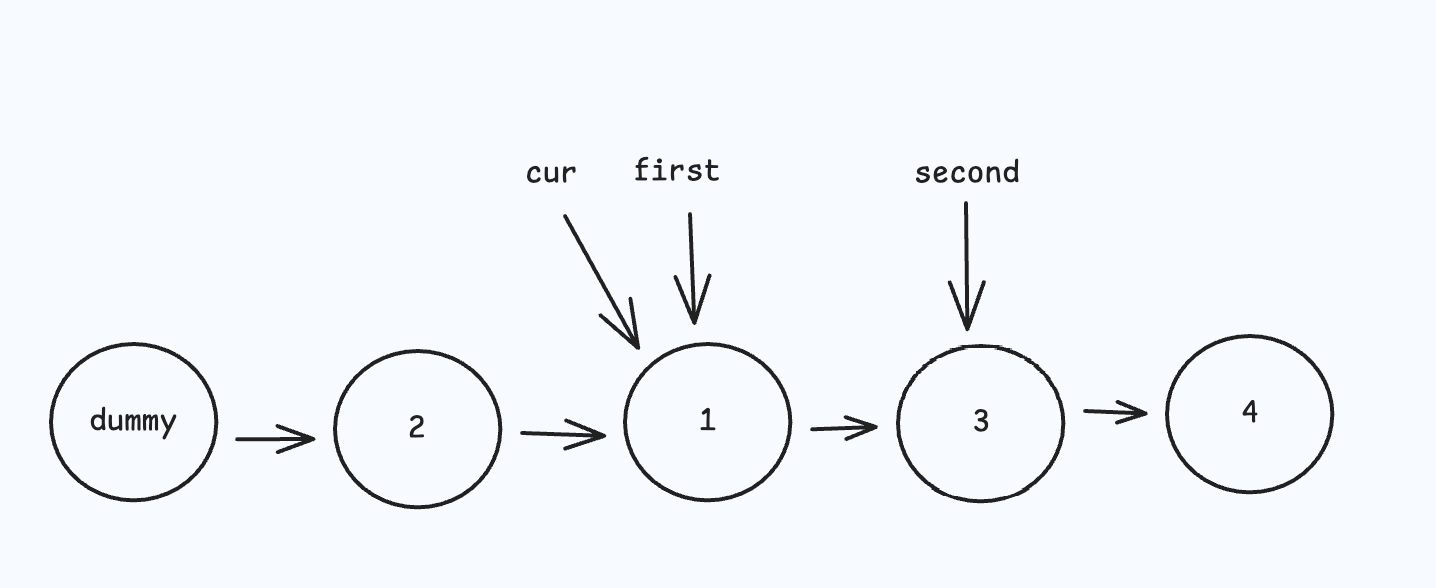
- 移动遍历指针,重复上述过程直到所有两两节点交换完成。
图解过程
plain
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
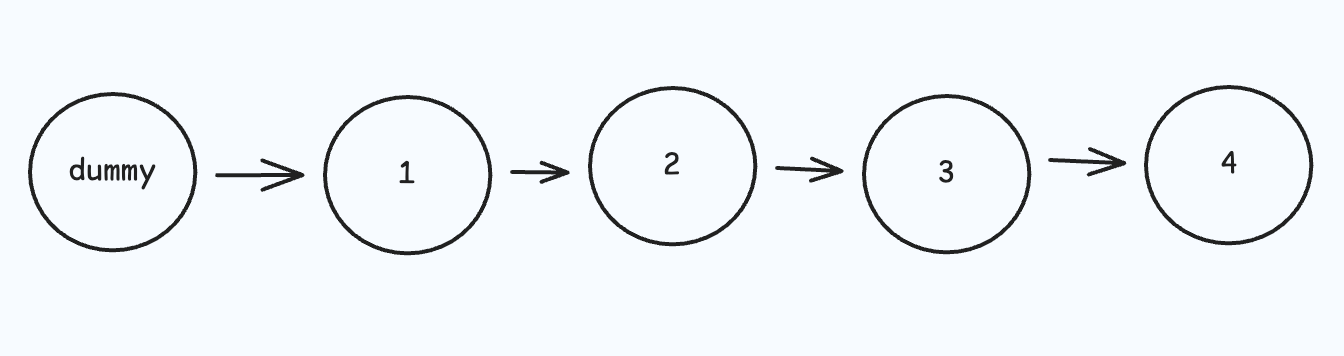
输出:[2,1,4,3]1.初始化链表
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
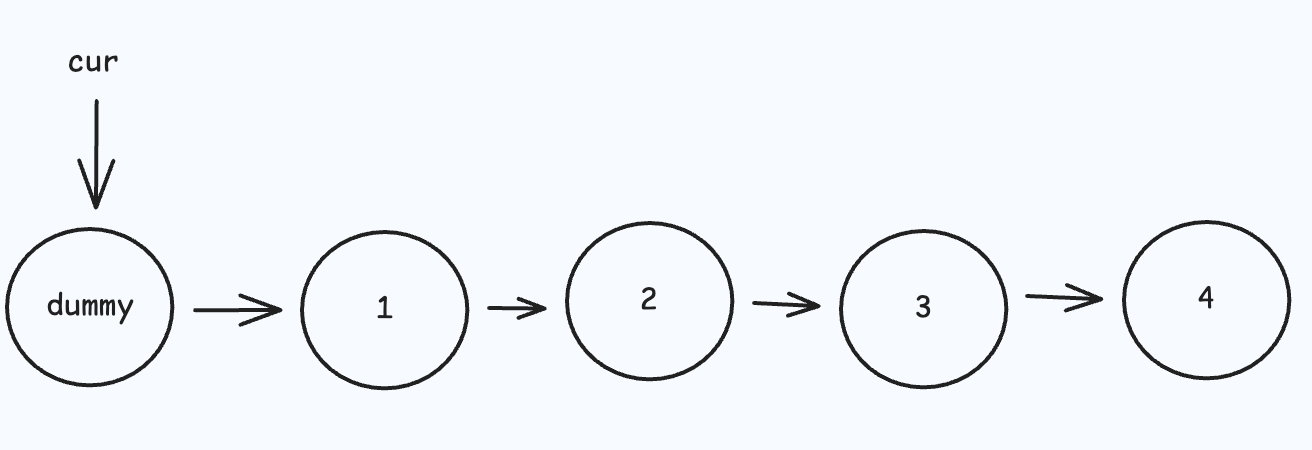
ListNode cur = dummy;
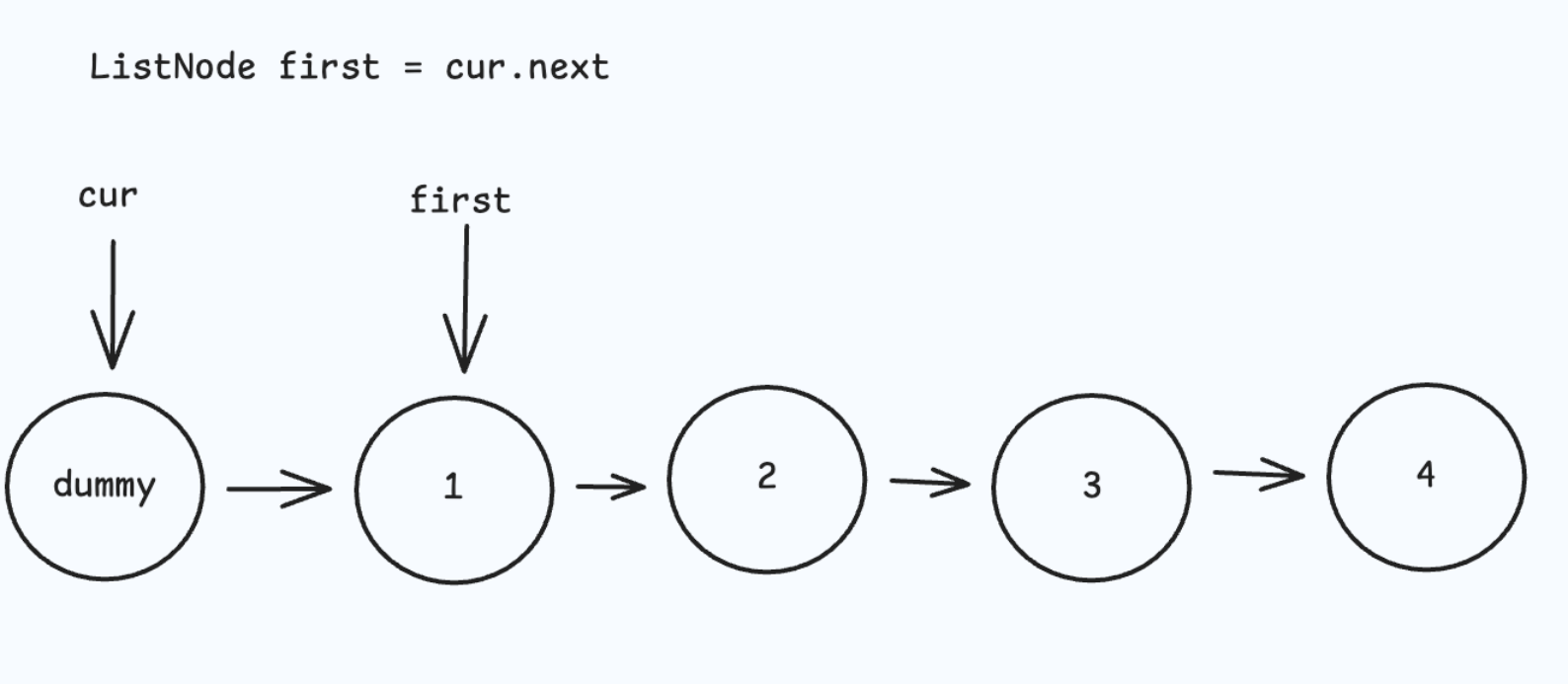
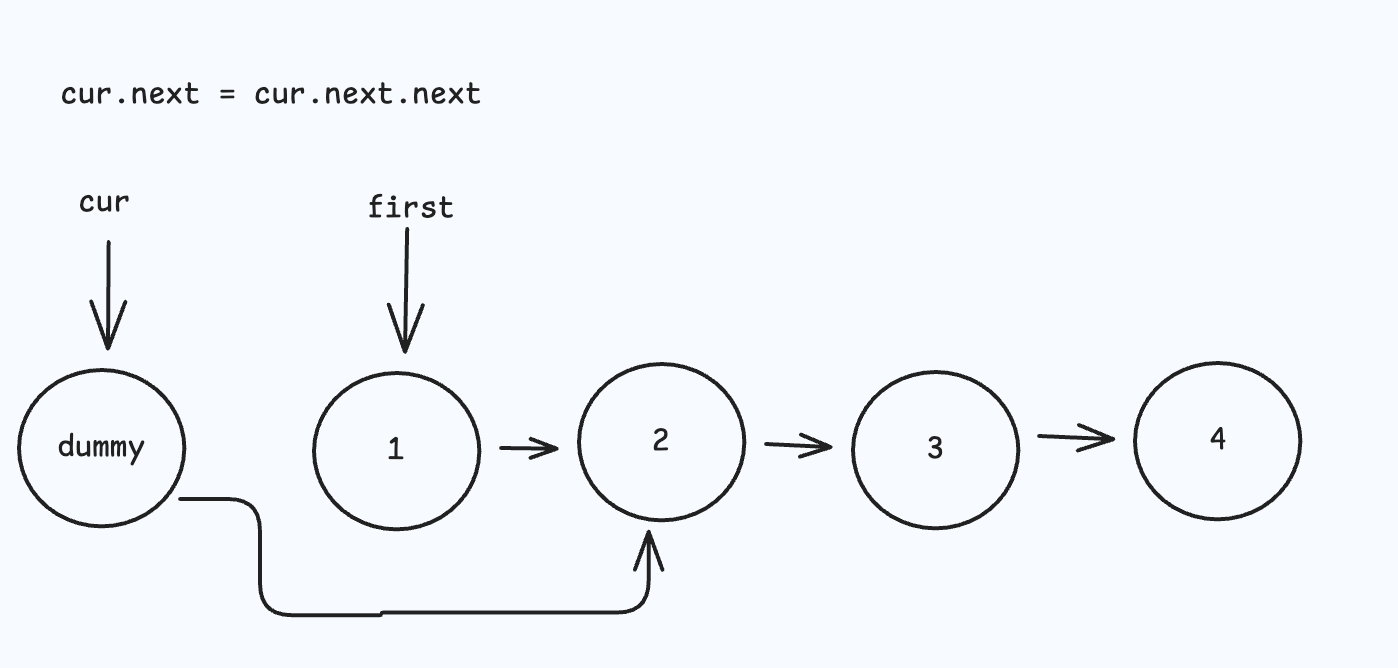
重复上面过程
代码
java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class 两两交换链表中的节点 {
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
static BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");
ListNode head = new ListNode(Integer.parseInt(s[0]));
ListNode cur = head;
// 1 2 3
for (int i = 1; i < s.length; i++) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(Integer.parseInt(s[i]));
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode newHead = swapPairs(head);
cur = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
// 思路 删除第一个节点 并记录 然后放到第二个节点后面
public static ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
// 记录第一个节点
ListNode first = cur.next;
// 删除第一个节点
cur.next = cur.next.next;
// 记录后面的节点
ListNode second = cur.next.next;
cur.next.next = first;
first.next = second;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}