本文以YOLOv26为基础,设计研究了基于YOLOv26的道路隐患识别任务(包含道路裂缝、井盖、修补裂缝等8类隐患),自动提取影像中的道路隐患,包含完整数据介绍、训练过程和测试结果全流程。
若需要完整数据集和源代码可以私信。
目录
🌷🌷1.数据集介绍
🍉1.1输入影像
道路病害检测数据集总共包含6000张样本数据,其中训练集5000张,验证集1000张,影像尺寸为1600*1184,部分影像展示如下:
🍉1.2yolo目标检测格式
YOLO(You Only Look Once)目标检测算法使用特定的数据格式进行训练和预测。以下是常见的YOLO数据格式要求:
标注文件格式:
- 每个图像对应一个同名的
.txt文件 - 每行表示一个边界框,格式为:
class_id x_center y_center width height - 所有坐标值都是相对于图像宽度和高度的归一化值(0-1之间)
道路病害识别数据样本类别包含8类。
0:裂缝
1:井盖
2:网状裂缝
3:坑洞
4:修补裂缝
5:修补网状裂缝
6:修补坑洞
7:其他
label为txt格式的yolo目标检测格式,示例txt文件内容为:

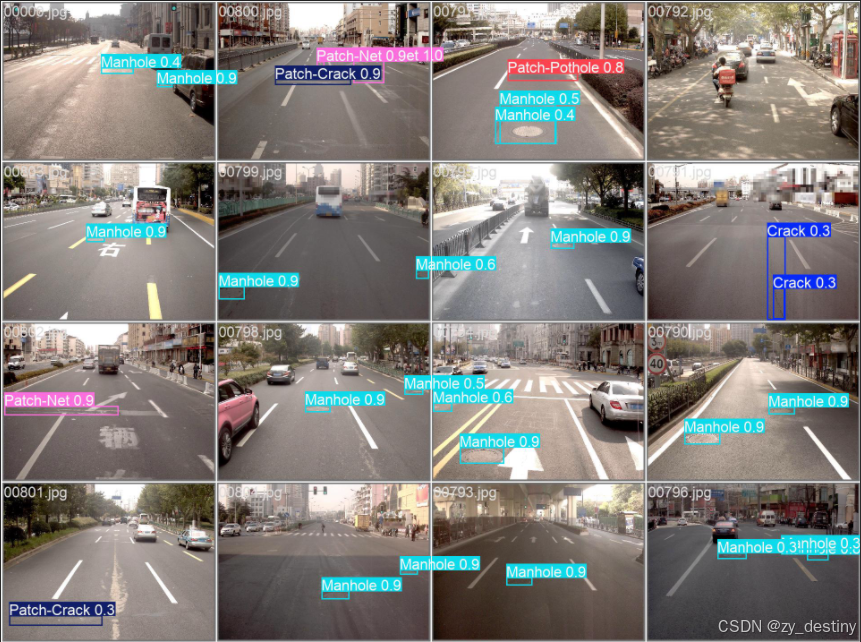
👍👍2.道路病害识别实现效果

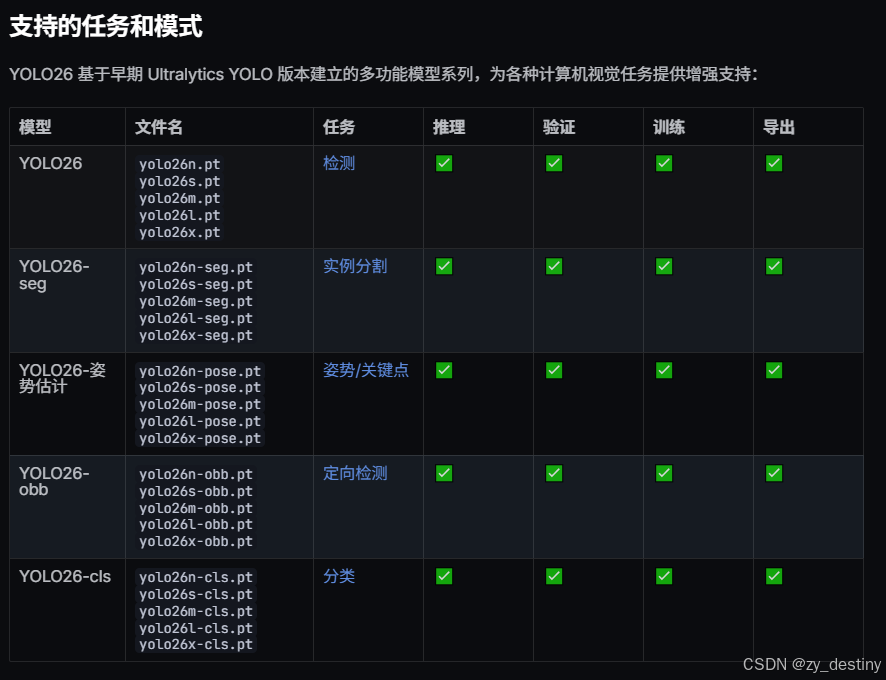
🍎🍎3.YOLOv26识别道路病害算法步骤
通过目标检测方法进行道路病害识别的方法不限,本文以YOLOv26为例进行说明。
🍋3.1数据准备
道路病害检测数据集总共包含6000张样本数据,其中训练集5000张,验证集1000张。
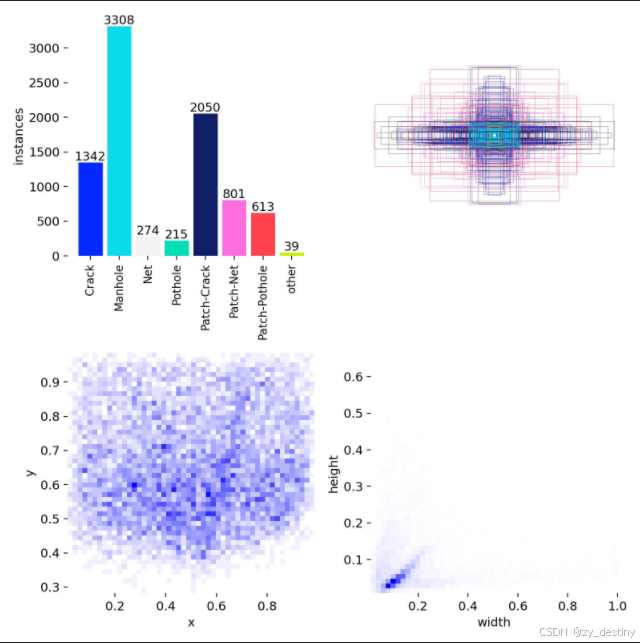
从label.png上来看,样本类别分布并不均匀,裂缝、井盖和修补裂缝样本数量较多,其他几类数据较少,所以这些样本分布势必会对后续的训练产生影响。
数据组织:
bash
dataset/
├── images/
│ ├── train/
│ └── val/
└── labels/
├── train/
└── val/🍋3.2模型选择
images/train文件夹如下:
labels/train文件夹如下:
模型训练label部分采用的是YOLO格式的txt文件,所以如果自己的数据集是xml格式或者json格式需要进行转换哦,转换可移步这里。
具体txt格式内容如1.数据集介绍中所示。
🍋3.3加载预训练模型
以YOLO26n为例,模型选择代码如下:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
#model = YOLO('yolo26n.yaml') # build a new model from YAML
#model = YOLO('yolo26n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolo26n.yaml').load('yolov26n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights其中yolo26.yaml为./ultralytics/cfg/models/26/yolo26.yaml,可根据自己的数据进行模型调整,打开yolo26.yaml显示内容如下:
bash
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
end2end: True # whether to use end-to-end mode
reg_max: 1 # DFL bins
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolo26n.yaml' will call yolo26.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.50, 0.25, 1024] # summary: 260 layers, 2,572,280 parameters, 2,572,280 gradients, 6.1 GFLOPs
s: [0.50, 0.50, 1024] # summary: 260 layers, 10,009,784 parameters, 10,009,784 gradients, 22.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.50, 1.00, 512] # summary: 280 layers, 21,896,248 parameters, 21,896,248 gradients, 75.4 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # summary: 392 layers, 26,299,704 parameters, 26,299,704 gradients, 93.8 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.50, 512] # summary: 392 layers, 58,993,368 parameters, 58,993,368 gradients, 209.5 GFLOPs
# YOLO26n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, False, 0.25]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5, 3, True]] # 9
- [-1, 2, C2PSA, [1024]] # 10
# YOLO26n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [256, True]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 2, C3k2, [512, True]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 1, C3k2, [1024, True, 0.5, True]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)主要需要修改的地方为nc,也就是num_class,此处数据集类别为8类,所以nc=8。
如果其他的模型参数不变的话,就默认保持原版yolo26,需要改造模型结构的大佬请绕行。
加载预训练模型yolo26-obb.pt,可以在第一次运行时自动下载,如果受到下载速度限制,也可以自行下载好(下载链接),放在对应目录下即可。
🍋3.4输入数据组织
yolo26还是以yolo格式的数据为例,./ultralytics/cfg/datasets/data.yaml的内容示例如下:
bash
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: ../datasets/coco8 # dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
# ...
77: teddy bear
78: hair drier这个是官方的标准coco数据集,需要换成自己的数据集格式,此处建议根据自己的数据集设置新建一个road_hazards.yaml文件,放在./ultralytics/cfg/datasets/目录下,最后数据集设置就可以直接用自己的road_hazards.yaml文件了。以我的road_hazards.yaml文件为例:
bash
path: /home/datasets/road_hazards# dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
test: images/test # test images (optional)
names:
0: Crack
1: Manhole
2: Net
3: Pothole
4: Patch-Crack
5: Patch-Net
6: Patch-Pothole
7: other🍭🍭4.目标检测训练代码
准备好数据和模型之后,就可以开始训练了,train.py的内容显示为:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("yolo26n-obb.pt")
results = model.train(data="road_hazards.yaml", epochs=300, imgsz=1024, device="0", batch = 8)通常我会选择在基础YOLO模型上进行transfer微调,不会从头开始训练,如果想自己从头开始,可以自行选择第一种方式。这里建议选择第三种。
⭐4.1训练过程
训练的过程忘记截图了,贴上result.csv吧
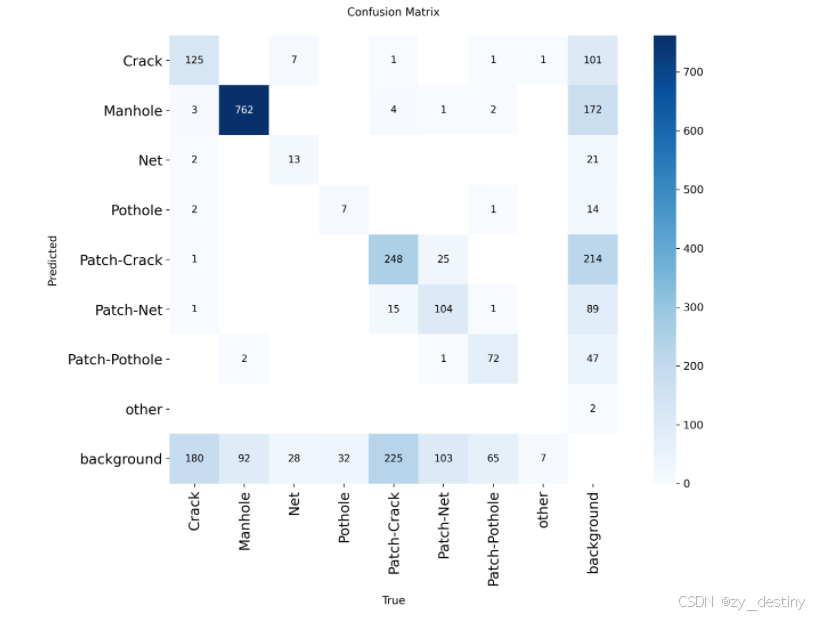
⭐4.2训练结果
训练完成后会在/runs/detect/目录下生成train或者train+数字的文件夹,存放你的训练结果。
训练完成后的结果如下:
其中weights文件夹内会包含2个模型,一个best.pth,一个last.pth。
至此就可以使用best.pth进行推理检测道路隐患了。
🏆🏆5.目标检测推理代码
批量推理python代码如下:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
from PIL import Image
import cv2
import os
model = YOLO('/yolov8/runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt') # load a custom model
path = '/home/dataset/images/test/' #test_image_path_dir
img_list = os.listdir(path)
for img_path in img_list:
### =============detect=====================
im1 = Image.open(os.path.join(path,img_path))
results = model.predict(source=im1, save=True,save_txt=True)若需要完整数据集和源代码可以私信。
整理不易,欢迎一键三连!!!
送你们一条美丽的--分割线--
🌷🌷🍀🍀🌾🌾🍓🍓🍂🍂🙋🙋🐸🐸🙋🙋💖💖🍌🍌🔔🔔🍉🍉🍭🍭🍋🍋🍇🍇🏆🏆📸📸⛵⛵⭐⭐🍎🍎👍👍🌷🌷