Aho-Corasick 模式搜索算法
给定一个输入文本和一个数组 k 个单词 arr[],找出输入文本中所有单词的所有出现。设n为文本长度,m为所有单词的字符总数,即m = 长度(arr[0]) + length(arr[1]) + ... + 长度(arr[k-1])。这里 k 是输入词的总数。
示例:
Input: text = "ahishers"
arr[] = {"he", "she", "hers", "his"}
Output:
Word his appears from 1 to 3
Word he appears from 4 to 5
Word she appears from 3 to 5
Word hers appears from 4 to 7如果我们使用像KMP这样的线性时间搜索算法,那么我们需要逐个搜索文本中的所有单词。这给出了总时间复杂度为 O(n + 长度(字[0]) + O(n + 长度(字[1]) + O(n + 长度(字[2]) + ...O(n + 长度(word[k-1])。该时间复杂度可写为 O(n*k + m)。
Aho-Corasick算法在O(n + m + z)时间内找到所有单词,其中z为文本中单词出现次数的总数。Aho--Corasick字符串匹配算法构成了最初Unix命令fgrep的基础。
预处理: 构建一个由arr中所有单词组成的自动机[]该自动机主要具有三个功能:
Go To : This function simply follows edges
of Trie of all words in arr[]. It is
represented as 2D array g[][] where
we store next state for current state
and character.
Failure : This function stores all edges that are
followed when current character doesn't
have edge in Trie. It is represented as
1D array f[] where we store next state for
current state.
Output : Stores indexes of all words that end at
current state. It is represented as 1D
array o[] where we store indexes
of all matching words as a bitmap for
current state.匹配:在构建的自动机上遍历给定文本,找到所有匹配的单词。
预处理:
我们首先构建一个所有单词的Trie(或关键词树)。
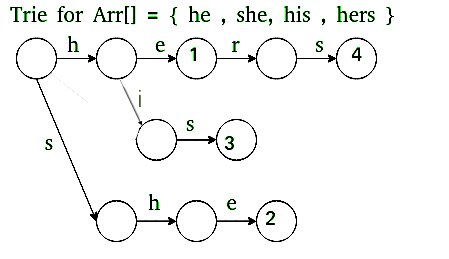
该部分填充 goto g[][] 的条目,输出 o[]。
接下来我们将Trie扩展到自动机中,以支持线性时间匹配。
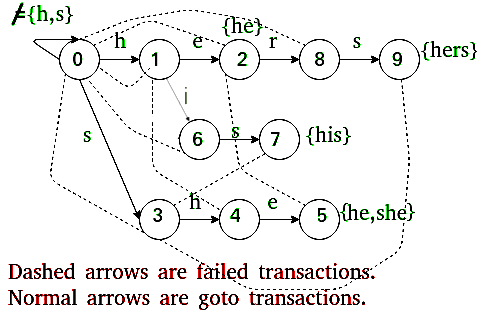
该部分填充失败 f[] 和输出 o[] 的条目。
前往:
我们构建Trie。对于所有没有根边的字符,我们会把边再加回根。
失败:
对于状态s,我们找到最长的真后缀,即某个模式的真前缀。这是通过广度首次遍历Trie实现的。
输出:
对于状态s,存储所有以s结尾的词的索引。这些索引以位映射形式存储(通过对数值进行逐位或对数值进行)。这同样是使用失效广度优先遍历计算。
以下是Aho-Corasick算法的实现
// Java program for implementation of
// Aho Corasick algorithm for String
// matching
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Max number of states in the matching
// machine. Should be equal to the sum
// of the length of all keywords.
static int MAXS = 500;
// Maximum number of characters
// in input alphabet
static int MAXC = 26;
// OUTPUT FUNCTION IS IMPLEMENTED USING out[]
// Bit i in this mask is one if the word with
// index i appears when the machine enters
// this state.
static int []out = new int[MAXS];
// FAILURE FUNCTION IS IMPLEMENTED USING f[]
static int []f = new int[MAXS];
// GOTO FUNCTION (OR TRIE) IS
// IMPLEMENTED USING g[][]
static int [][]g = new int[MAXS][MAXC];
// Builds the String matching machine.
// arr - array of words. The index of each keyword is important:
// "out[state] & (1 << i)" is > 0 if we just found word[i]
// in the text.
// Returns the number of states that the built machine has.
// States are numbered 0 up to the return value - 1, inclusive.
static int buildMatchingMachine(String arr[], int k)
{
// Initialize all values in output function as 0.
Arrays.fill(out, 0);
// Initialize all values in goto function as -1.
for(int i = 0; i < MAXS; i++)
Arrays.fill(g[i], -1);
// Initially, we just have the 0 state
int states = 1;
// Convalues for goto function, i.e., fill g[][]
// This is same as building a Trie for arr[]
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
String word = arr[i];
int currentState = 0;
// Insert all characters of current
// word in arr[]
for(int j = 0; j < word.length(); ++j)
{
int ch = word.charAt(j) - 'a';
// Allocate a new node (create a new state)
// if a node for ch doesn't exist.
if (g[currentState][ch] == -1)
g[currentState][ch] = states++;
currentState = g[currentState][ch];
}
// Add current word in output function
out[currentState] |= (1 << i);
}
// For all characters which don't have
// an edge from root (or state 0) in Trie,
// add a goto edge to state 0 itself
for(int ch = 0; ch < MAXC; ++ch)
if (g[0][ch] == -1)
g[0][ch] = 0;
// Now, let's build the failure function
// Initialize values in fail function
Arrays.fill(f, -1);
// Failure function is computed in
// breadth first order
// using a queue
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Iterate over every possible input
for(int ch = 0; ch < MAXC; ++ch)
{
// All nodes of depth 1 have failure
// function value as 0. For example,
// in above diagram we move to 0
// from states 1 and 3.
if (g[0][ch] != 0)
{
f[g[0][ch]] = 0;
q.add(g[0][ch]);
}
}
// Now queue has states 1 and 3
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Remove the front state from queue
int state = q.peek();
q.remove();
// For the removed state, find failure
// function for all those characters
// for which goto function is
// not defined.
for(int ch = 0; ch < MAXC; ++ch)
{
// If goto function is defined for
// character 'ch' and 'state'
if (g[state][ch] != -1)
{
// Find failure state of removed state
int failure = f[state];
// Find the deepest node labeled by proper
// suffix of String from root to current
// state.
while (g[failure][ch] == -1)
failure = f[failure];
failure = g[failure][ch];
f[g[state][ch]] = failure;
// Merge output values
out[g[state][ch]] |= out[failure];
// Insert the next level node
// (of Trie) in Queue
q.add(g[state][ch]);
}
}
}
return states;
}
// Returns the next state the machine will transition to using goto
// and failure functions.
// currentState - The current state of the machine. Must be between
// 0 and the number of states - 1, inclusive.
// nextInput - The next character that enters into the machine.
static int findNextState(int currentState, char nextInput)
{
int answer = currentState;
int ch = nextInput - 'a';
// If goto is not defined, use
// failure function
while (g[answer][ch] == -1)
answer = f[answer];
return g[answer][ch];
}
// This function finds all occurrences of
// all array words in text.
static void searchWords(String arr[], int k,
String text)
{
// Preprocess patterns.
// Build machine with goto, failure
// and output functions
buildMatchingMachine(arr, k);
// Initialize current state
int currentState = 0;
// Traverse the text through the
// built machine to find all
// occurrences of words in arr[]
for(int i = 0; i < text.length(); ++i)
{
currentState = findNextState(currentState,
text.charAt(i));
// If match not found, move to next state
if (out[currentState] == 0)
continue;
// Match found, print all matching
// words of arr[]
// using output function.
for(int j = 0; j < k; ++j)
{
if ((out[currentState] & (1 << j)) > 0)
{
System.out.print("Word " + arr[j] +
" appears from " +
(i - arr[j].length() + 1) +
" to " + i + "\n");
}
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String arr[] = { "he", "she", "hers", "his" };
String text = "ahishers";
int k = arr.length;
searchWords(arr, k, text);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh输出
Word his appears from 1 to 3
Word he appears from 4 to 5
Word she appears from 3 to 5
Word hers appears from 4 to 7时间复杂性:O(n + l + z),其中"n"为文本长度,"l"为关键词长度,"z"为匹配数。
辅助空间: O(l * q),其中"q"是字母表的长度,因为这是节点最多可拥有的子节点数。
应用:
抄袭检测
文本挖掘
生物信息学
入侵检测
编程资源
https://pan.quark.cn/s/7f7c83756948
更多资源
https://pan.quark.cn/s/bda57957c548