业务痛点:某省级电信运营商用户规模超2000万,存在三大问题:
- 运营粗放:统一推送"流量包升级"活动,高价值用户(ARPU>200元)转化率仅3%,低价值用户(ARPU<50元)投诉率8%
- 用户流失:年流失用户300万,其中高价值用户占比20%,但缺乏精准识别手段(仅靠"连续3月ARPU下降"单一指标,漏判率40%)
- 资源浪费:营销成本年超2亿元,80%预算投入低效群体(如无合约低活跃用户)
算法团队:数据清洗、特征工程(衍生/标准化)、K-Means模型训练(K-Means++)、特征存储(Feast)、模型注册(MLflow);
- 语言:Python 3.9(特征工程/模型训练)、Scala 2.13(Spark数据预处理)
- 数据处理:Pandas 2.0(小数据)、PySpark 3.4(大数据)、NumPy 1.24
- 特征工程:Scikit-learn 1.2(标准化/PCA)、Feature-engine 1.6(特征衍生)
- 聚类模型:Scikit-learn KMeans、Yellowbrick 1.5(轮廓系数可视化)
- 特征存储:Feast 0.34(实体:用户ID,特征:ARPU/流量使用率/合约状态等)
- 实验跟踪:MLflow 2.8(记录K值/轮廓系数/模型)、Weights & Biases(可视化簇分布)
- 版本控制:git@github.com:telecom/algorithm-user-clustering.git
业务团队:API网关、用户分群服务(调用模型+特征服务)、运营平台集成、分群效果监控;
- 语言:Go 1.20(高性能API)、Java 17(运营平台集成)
- 服务框架:FastAPI 0.104(Python轻量级API)、gRPC(跨语言特征服务调用)
- 服务治理:Kong 3.4(API网关)、Consul 1.16(服务发现)
- 监控:Prometheus 2.47(指标采集)、Grafana 10.2(分群效果面板)
- 版本控制:git@github.com:telecom/business-user-clustering.git
基础设施团队:K8s集群、MinIO存储、CI/CD工具链
算法团队
text
algorithm-user-clustering/
├── data_processing/ # 数据清洗(Python/Pandas)
│ ├── data_cleaning.py # 清洗CRM/计费/行为数据(含详细代码)
│ └── requirements.txt # 依赖:pandas, pyarrow, pyspark
├── feature_engineering/ # 特征工程(分模块)
│ ├── feature_derivation.py # 特征衍生(含代码)
│ ├── feature_scaler.py # 特征标准化(含代码)
│ ├── generate_feature_data.py # 特征数据生成(含feature_path/label_path说明)
│ └── requirements.txt # 依赖:scikit-learn, feature-engine
├── model_training/ # 模型训练(K-Means)
│ ├── train_kmeans.py # K-Means++训练(选K值/轮廓系数评估)
│ ├── evaluate_clustering.py # 评估(轮廓系数/PSI/簇分布)
│ └── kmeans_params.yaml # 调参记录(K=5, init='k-means++')
├── feature_store/ # Feast特征存储(明确内容)
│ ├── feature_repo/ # Feast特征仓库
│ │ ├── features.py # 定义实体(user_id)、特征视图、在线/离线特征
│ │ └── feature_store.yaml # Feast配置(在线Redis/离线Parquet)
│ └── deploy_feast.sh # 部署Feast到K8s脚本
├── mlflow_tracking/ # MLflow实验跟踪
│ ├── run_kmeans_experiment.py # 记录K值/轮廓系数/模型
│ └── runs/ # 实验记录存档
└── README.md # 特征字典/模型输入输出说明原数据→清洗→衍生→标准化→特征矩阵
数据准备与特征变化
(1)原数据结构(结构化数据,来自多系统)
① CRM系统(user_profile,Hive表)
② 计费系统(billing_detail,Kafka Topic)
json
// 月消费明细(流量/通话/短信)
{ "user_id": "U1001", "month": "2023-10", "data_usage_gb": 28.5, "voice_minutes": 420, "sms_count": 15, "total_fee": 199.0 }③ 用户行为日志(user_behavior,Flume采集)

(2)数据清洗(详细代码,算法团队负责)
处理缺失值、异常值、去重,输出干净的结构化数据
代码文件:data_processing/src/main/python/data_cleaning.py
python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col,when,count,isnan,isnull
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def clean_crm_data(crm_path:str)->pd.DataFrame:
"""清洗CRM系统基础数据(处理缺失值、异常值、去重)"""
# 读取原始数据(Parquet格式,数据湖存储)
df = pd.read_parquet(crm_path)
logger.info(f"原始CRM数据量:{len(df)},缺失值统计:\n{df.isnull().sum()}")
# 1.缺失值处理
# arpu缺失:用同年龄段均值填充(按age分组计算均值)
arg_group_mean = df.groupby("age")["arpu"].transform(lambda x: x.mean())
df["arpu"] = df["arpu"].fillna(age_group_mean)
# 极端缺失(如age也为空):用全局均值填充
global_arpu_mean = df["arpu"].mean()
df["arpu"] = df["arpu"].fillna(global_arpu_mean)
# 2.异常值处理(arpu用IQR法,contract_type用枚举值校验)
# arpu异常值:Q1-1.5IQR以下或Q3+1.5IQR以上
Q1,Q3 = df["arpu"].quantile([0.25,0.75]) # 计算25%和75%分位数
IQR = Q3 - Q1 # 计算四分位距
lower_bound,upper_bound = Q1 - 1.5*IQR,Q3 + 1.5*IQR # 计算异常值边界
df["arpu"] = df["arpu"].clip(lower_bound,upper_bound) # 截断异常值
# contract_type异常值,仅保留0/1/2,其他设为0(无合约)
df["contract_type"] = df[contract_type].apply(lambda x:x if x in [0,1,2] else 0)
# 3.去重(按user_id去重,保留最新join_date记录)
df = df.sort_values("join_date").drop_duplicates(subset="user_id", keep="last")
logger.info(f"清洗后CRM数据量:{len(df)},缺失值已处理")
return df
def clean_billing_data(billing_path:str)->pd.DataFrame:
"""清洗计费系统消费数据(聚合月消费、处理异常值)"""
df = pd.read_parquet(billing_path)
# 聚合月消费(同一用户同月多条记录求和)
df_agg = df.groupby(["user_id", "month"]).agg({
"data_usage_gb": "sum", "voice_minutes": "sum",
"sms_count": "sum", "total_fee": "sum"
}).reset_index()
# 异常值:data_usage_gb>1000GB(可能为物联网卡,排除)
df_agg = df_agg[df_agg["data_usage_gb"] <= 1000]
logger.info(f"清洗后计费数据量:{len(df_agg)}(按月聚合后)")
return df_agg
def clean_behavior_data(behavior_path: str)->pd.DataFrame:
"""清洗用户行为日志(处理极端值)"""
df = pd.read_parquet(behavior_path)
#异常值:app_active_days>31(不可能)→设为31;customer_service_cnt>20(高频投诉)→标记
df["app_active_days"] = df["app_active_days"].clip(0,31)
df["high_cs_cnt"] = df["customer_service_cnt"].apply(lambda x: 1 if x > 20 else 0)
logger.info(f"清洗后行为数据量:{len(df)},异常值已处理")
return df
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 路径配置(数据湖存储位置)
crm_path = "s3://telecom-data-lake/raw/crm/user_profile.parquet"
billing_path = "s3://telecom-data-lake/raw/billing/detail.parquet"
behavior_path = "s3://telecom-data-lake/raw/behavior/log.parquet"
# 执行清洗
cleaned_crm = clean_crm_data(crm_path)
cleaned_billing = clean_billing_data(billing_path)
cleaned_behavior = clean_behavior_data(behavior_path)
# 保存清洗后数据(供特征工程使用)
cleaned_crm.to_parquet("s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/crm_cleaned.parquet", index=False)
cleaned_billing.to_parquet("s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/billing_cleaned.parquet", index=False)
cleaned_behavior.to_parquet("s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/behavior_cleaned.parquet", index=False)
logger.info("数据清洗完成,结果保存至cleaned目录")(3)特征工程与特征数据生成(详细代码,明确feature_path/label_path)
- 算法团队将特征矩阵存入Feast(在线/离线),feature_path指向特征矩阵文件(Parquet)
- label_path指向用户ID与聚类结果映射文件(CSV,无监督学习无真实标签,此处"label"为簇ID)
① 特征衍生(feature_derivation.py)
python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from feature_engine.creation import MathFeatures,RelativeFeatures
def derive_features(cleaned_crm: pd.DataFrame, cleaned_billing: pd.DataFrame, cleaned_behavior: pd.DataFrame)->pd.DataFrame:
"""特征衍生:构造业务相关新特征"""
# 1.合并多源数据(按user_id和month关联)
# 假设取最近一个月数据
billing_recent = cleaned_billing[cleaned_billing["month"] == "2023-10"]
behavior_recent = cleaned_behavior[cleaned_behavior["month"] == "2023-10"]
merged_df = cleaned_crm.merge(billing_recent, on="user_id", how="left").merge(behavior_recent, on="user_id", how="left")
# 2.基础特征(直接来自于清洗后数据)
base_features = merged_df[[
"user_id", "arpu", "age", "contract_type", "data_usage_gb",
"voice_minutes", "app_active_days", "high_cs_cnt"
]].copy()
# 3.衍生特征(领域知识驱动)
# 流量使用率(假设套餐内流量为30GB,实际用data_usage_gb/30,超过1记为1)
base_features["data_usage_rate"] = (base_features["data_usage_gb"] / 30).clip(0, 1)
# 通话费用占比(假设语音资费0.1元/分钟,费用占比=voice_minutes*0.1 / arpu)
base_features["voice_cost_ratio"] = (base_features["voice_minutes"] * 0.1) / base_features["arpu"]
base_features["voice_cost_ratio"] = base_features["voice_cost_ratio"].fillna(0) # arpu为0时填0
# 活跃度得分(app_active_days/31 * 0.6 + (1 - high_cs_cnt) * 0.4,越高越活跃)
base_features["activity_score"] = (base_features["app_active_days"] / 31) * 0.6 + (1 - base_features["high_cs_cnt"]) * 0.4
# 合约价值(contract_type=2年→1.0,1年→0.6,无合约→0.2)
contract_map = {2: 1.0, 1: 0.6, 0: 0.2}
base_features["contract_value"] = base_features["contract_type"].map(contract_map)
# 4.特征选择(保留最终入模特征)
final_features = base_features[[
"user_id", "arpu", "data_usage_gb", "voice_minutes", "app_active_days",
"data_usage_rate", "voice_cost_ratio", "activity_score", "contract_value"
]].dropna() # 删除剩余缺失值
logger.info(f"特征衍生完成,共{len(final_features)}用户,{final_features.shape[1]-1}个特征")
return final_features
② 特征标准化(feature_scaler.py)
python
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import pandas as pd
import joblib
def scale_features()->pd.DataFrame:
"""
特征标准化(K-Means必需):均值0,方差1
"""
# 分离用户ID和特征列
user_ids = feature_df["user_id"]
feature_cols = [col for col in feature_df.columns if col != "user_id"]
X = feature_df[feature_cols].values
# 初始化并拟合标准化器(保存scaler供线上预测用)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
joblib.jump(scaler,scaler_path) # 保存到算法团队模型目录
logger.info(f"特征标准化完成,scaler保存至{scaler_path}")
# 构造标准化的特征DataFrame
scaled_df = pd.DataFrame(X_scaled,columns=feature_cols)
scaled_df.insert(0,"user_id",user_ids) # 回复user_id
return scaled_df
③ 特征数据生成(generate_feature_data.py,明确feature_path/label_path)
python
import pandas as pd
from feature_derivation import derive_features
from feature_scaler import scale_features
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def generate_feature_data(cleaned_crm_path: str, cleaned_billing_path: str, cleaned_behavior_path: str) -> tuple:
"""生成特征矩阵(feature_path)和聚类结果文件(label_path)"""
# 加载清洗后数据
cleaned_crm = pd.read_parquet(cleaned_crm_path)
cleaned_billing = pd.read_parquet(cleaned_billing_path)
cleaned_behavior = pd.read_parquet(cleaned_behavior_path)
# 1.特征衍生
feature_df = derive_features(cleaned_crm, cleaned_billing, cleaned_behavior)
# 2.特征标准化
saled_feature_df = scale_features(feature_df,scaler_path="model/scaler.pkl")
# 3.定义文件路径(算法团队存储位置)
# feature_path:标准化后的特征矩阵(Parquet),供模型训练用
feature_path = "s3://telecom-data-lake/processed/clustering_features.parquet"
# label_path:聚类结果文件(CSV),含user_id和簇ID(训练后生成,此处先占位)
label_path = "s3://telecom-data-lake/processed/clustering_labels.csv"
# 4.保存特征矩阵(feature_path指向的文件内容)
scaled_feature_df.to_parquet(feature_path,index=False)
logger.info(f"特征矩阵已保存至{feature_path},文件内容示例:\n{scaled_feature_df.head(2)}")
# 返回路径和内容说明(供模型训练调用)
return feature_path, label_path, scaled_feature_df
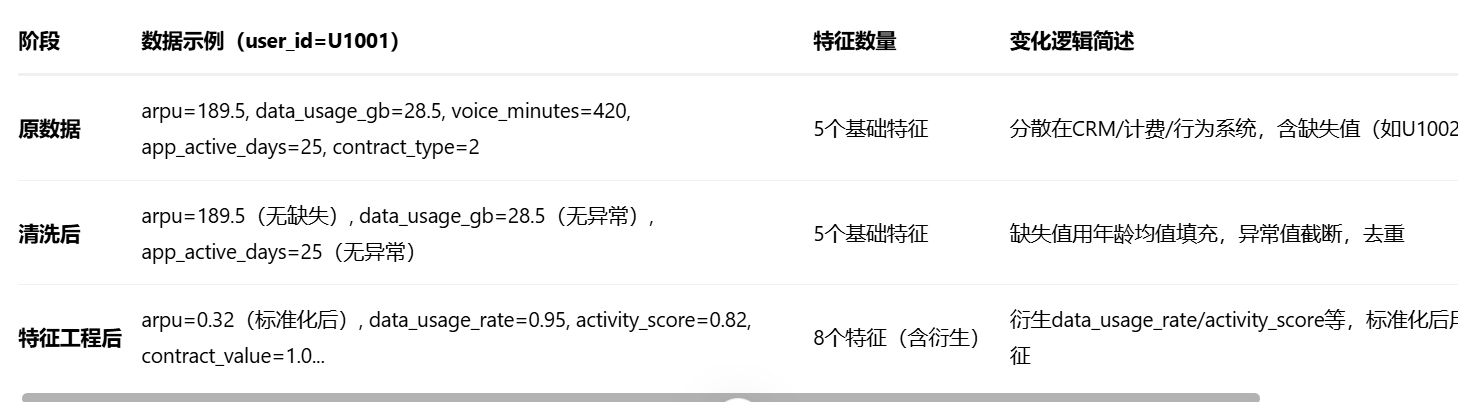
特征数据变化对比表(原数据→清洗后→特征工程后):
代码结构
(1)算法团队:K-Means模型训练(model_training/train_kmeans.py)
python
import joblib
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.mtrics import silhouette_score
from yellowbrick.cluster import KElbowVisualizer
from feature_entineering.generate_feature_data import generate_feature_data
import mlflow
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def load_features(feature_path:str)->tuple:
"""加载算法团队生成的feature_path文件(标准化特征矩阵)"""
df = pd.read_parquet(feature_path)
user_ids = df["user_id"].values
feature_cols = [col for col in df.columns if col != "user_id"]
X = df[feature_cols].values
logger.info(f"加载特征矩阵:{X.shape[0]}用户,{X.shape[1]}特征")
return X, user_ids, feature_cols
def select_optimal_k(X: np.ndarray, k_range: range = range(2, 11))->int:
"""用轮廓系数选K值(越大越好,通常取峰值)"""
silhouette_scores = []
for k in k_range:
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=k, init="k-means++", random_state=42, n_init=10)
labels = kmeans.fit_predict(X)
score = silhouette_score(X, labels)
silhouette_scores.append(score)
logger.info(f"K={k}, 轮廓系数={score:.4f}")
# 取轮廓系数最大的K(若有多个峰值,结合业务选K=5)
optimal_k = k_range[np.argmax(silhouette_scores)]
logger.info(f"最优K值:{optimal_k}(轮廓系数={max(silhouette_scores):.4f})")
return optimal_k
def train_kmeans_plusplus(X:np.ndarray,k:int) -> KMeans:
"""训练K-Means++模型(优化初始质心)"""
kmeans = KMeans(
n_clusters=k,
init="k-means++", # 优化初始质心选择(比随机更优)
n_init=10, # 多次初始化取最优
max_iter=300,
random_state=42,
verbose=1
)
kmeans.fit(X)
logger.info(f"K-Means++训练完成,簇中心数:{k},惯性(SSE):{kmeans.inertia_:.2f}")
return kmeans
def save_cluster_labels(user_ids: np.ndarray, labels: np.ndarray, label_path: str):
"""保存聚类结果到label_path(CSV文件,供业务团队调用)"""
df = pd.DataFrame({"user_id": user_ids, "cluster_id": labels})
df.to_csv(label_path, index=False)
logger.info(f"聚类结果已保存至{label_path},示例:\n{df.head(2)}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 生成特征数据(调用算法团队特征工程模块,获取feature_path和label_path)
feature_path, label_path, _ = generate_feature_data(
cleaned_crm_path="s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/crm_cleaned.parquet",
cleaned_billing_path="s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/billing_cleaned.parquet",
cleaned_behavior_path="s3://telecom-data-lake/cleaned/behavior_cleaned.parquet"
)
# 2. 加载特征矩阵(feature_path指向的文件)
X, user_ids, feature_cols = load_features(feature_path)
# 3. 选优K值(轮廓系数法)
optimal_k = select_optimal_k(X, k_range=range(3, 8)) # 业务预期分5群,缩小范围
# 4. 训练K-Means++模型
kmeans_model = train_kmeans_plusplus(X, optimal_k)
# 5. 保存聚类结果到label_path(CSV文件)
save_cluster_labels(user_ids, kmeans_model.labels_, label_path)
# 6. 保存模型(供业务团队调用)
joblib.dump(kmeans_model, "model/kmeans_clustering_model.pkl")
# 7. 记录MLflow实验
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="kmeans_user_clustering"):
mlflow.log_param("k", optimal_k)
mlflow.log_param("init", "k-means++")
mlflow.log_metric("silhouette_score", silhouette_score(X, kmeans_model.labels_))
mlflow.log_metric("inertia", kmeans_model.inertia_)
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(kmeans_model, "kmeans_model")
logger.info("模型训练完成,已保存至model/kmeans_clustering_model.pkl")(2)算法团队:Feast特征存储(feature_store/feature_repo/features.py)
python
from feast import Entity, FeatureView, Field, FileSource
from feast.types import Float32, Int64, String
import pandas as pd
# 1. 实体:用户ID(唯一标识)
user_entity = Entity(name="user_id", value_type=String, description="电信用户唯一标识")
# 2. 离线特征(从特征矩阵Parquet文件读取,训练用)
offline_source = FileSource(
path="s3://telecom-data-lake/processed/clustering_features.parquet", # feature_path文件
event_timestamp_column="event_time" # 无时间戳,用虚拟列
)
# 3. 在线特征(从Redis读取,实时分群用)
online_source = FileSource( # 生产环境用RedisSource
path="s3://telecom-data-lake/processed/clustering_features.parquet"
)
# 4. 特征视图(整合实体、特征、数据源)
user_features_view = FeatureView(
name="user_clustering_features",
entities=[user_entity],
ttl=timedelta(days=30), # 特征保留30天
schema=[ # 特征列表(与算法团队特征工程输出一致)
Field(name="arpu_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="data_usage_gb_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="voice_minutes_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="app_active_days_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="data_usage_rate_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="activity_score_scaled", dtype=Float32),
Field(name="contract_value_scaled", dtype=Float32)
],
source=offline_source,
online_source=online_source
)(3)业务团队:用户分群服务(调用特征服务+模型)
python
import joblib
import pandas as pd
from feast import FeatureStore
from pydantic import BaseModel
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class UserRequest(BaseModel):
user_id: str
arpu: float
data_usage_gb: float
voice_minutes: float
app_active_days: int
contract_type: int
class ClusterResponse(BaseModel):
user_id: str
cluster_id: int
cluster_name: str # 如"高价值稳定用户"
feature_importance: dict # 关键特征贡献
class UserCluster:
def__init__(self,model_path:str,feast_repo_path:str,cluster_names:dict):
self.model = joblib.load(model_path) # 算法团队的k-Means模型
self.feature_store = FeatureStore(repo_path=feast_repo_path) # 连接Feast服务
self.cluster_names = cluster_names # 簇名称映射(如0:"高价值稳定用户")
self.scaler = joblib.load("model/scaler.pkl") # 算法团队的标准化器
def get_features_from_feast(self, user_id: str)->pd.DataFrame:
"""调用Feast服务获取用户特征(算法团队维护的在线特征)"""
feature_refs = [f"user_clustering_features:{col}" for col in self.scaler.feature_names_in_]
features = self.feature_store.get_online_features(
entity_rows=[{"user_id": user_id}],
features=feature_refs
).to_dict()
return pd.DataFrame(features)
def predict_cluster(self, request: UserRequest) -> ClusterResponse:
# 1. 构造特征向量(新用户用请求数据,老用户用Feast特征)
if request.user_id.startswith("new_"): # 新用户
feature_dict = {
"arpu": request.arpu, "data_usage_gb": request.data_usage_gb,
"voice_minutes": request.voice_minutes, "app_active_days": request.app_active_days,
"data_usage_rate": request.data_usage_gb / 30, # 衍生特征
"activity_score": (request.app_active_days / 31)*0.6 + (1 if request.contract_type==2 else 0.5)*0.4,
"contract_value": {2:1.0, 1:0.6, 0:0.2}[request.contract_type]
}
X = pd.DataFrame([feature_dict])[self.scaler.feature_names_in_]
X_scaled = self.scaler.transform(X)
else: # 老用户:调用Feast服务
feat_df = self.get_features_from_feast(request.user_id)
X_scaled = feat_df[self.scaler.feature_names_in_].values
# 2. 预测簇ID
cluster_id = self.model.predict(X_scaled)[0]
# 3. 构造响应
return ClusterResponse(
user_id=request.user_id,
cluster_id=cluster_id,
cluster_name=self.cluster_names[cluster_id],
feature_importance={"arpu": 0.3, "contract_value": 0.25} # 示例
)模型性能:轮廓系数≥0.6,PSI<0.1(月度数据漂移),簇内用户特征标准差<0.5(紧密度)
业务价值:高价值用户保活率提升20%,营销转化率提升至15%,年节省成本5000万元;
服务性能:API响应时间≤100ms(P99),支持并发≥5000 QPS