一.实验目的
- 熟悉线性回归算法的应用。
- 熟悉多项式回归算法的应用。
- 熟悉岭回归算法的应用。
二.实验内容
1.上机实验题一
房价预测问题可以看作一个线性回归问题,尝试用线性回归算法求解。利用书中图3.7线性回归的正规方程算法建立房价预测的线性模型。实现房价预测问题,实现图3.9中房价预测问题的线性回归算法。
2.上机实验题二
书本中第二章中例2.3用一个10次多项式精确地拟合了平面上的10个点,请用多项式回归算法拟合书本中例2.3的数据,实现图3.12并运行。
3.上机实验题三
书本中第二章中例2.3用一个10次多项式精确地拟合了平面上的10个点,请用岭回归算法拟合书本中例2.3的数据,实现图3.16并运行。
4.上机实验题四
糖尿病预测。
糖尿病数据集是Sklearn提供的一个标准数据集。它从442例糖尿病患者的资料中选取了10个特征----年龄、性别、体重、血压和6个血清测量值,以及这些患者在一年后疾病发展的病情量化值。糖尿病预测问题的任务是根据上述10个特征预测病情量化值。图3.27是读取糖尿病数据集的程序,其中load_diabetes函数返回特征矩阵X与标签向量y。

请用线性回归算法来完成糖尿病预测任务。
三 . 实验 要求
1.结合上课内容,写出程序,并调试程序,要给出测试数据和实验结果。
2.整理上机步骤,总结经验和体会。
3.完成实验报告和上交源程序
四、运行代码
1.上机实验题一
首先,我们通过正规方程算法建立了一个线性模型,该模型基于房屋的特征来预测其价格。然后,我们对模型进行了训练,并在测试集上进行了预测,最后通过计算均方误差(MSE)和分数来评估模型的性能。
(1)定义线性回归类、MSE、
python
import numpy as np
class LinearRegression:
def fit(self, X, y):
self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
return
def predict(self, X):
return X.dot(self.w)
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):
return np.average((y_true - y_pred)**2, axis=0)
def r2_score(y_true, y_pred):
numerator = (y_true - y_pred)**2
denominator = (y_true - np.average(y_true, axis=0))**2
return 1- numerator.sum(axis=0) / denominator.sum(axis=0)(2)房价预测
python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import linear_regression.lib.linear_regression as lib
def process_features(X):
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
m, n = X.shape
X = np.c_[np.ones((m,1)), X]
return X
housing = fetch_california_housing()
X = housing.data
y = housing.target.reshape(-1,1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
X_train = process_features(X_train)
X_test = process_features(X_test)
model = lib.LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
mse = lib.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
r2 = lib.r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
print("mse = {}, r2 = {}".format(mse, r2))
2.上机实验题二
首先生成了一组样本数据,并使用10次多项式来拟合这些数据。
(1)定义线性回归类、MSE、
python
import numpy as np
class LinearRegression:
def fit(self, X, y):
self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
return
def predict(self, X):
return X.dot(self.w)
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):
return np.average((y_true - y_pred)**2, axis=0)
def r2_score(y_true, y_pred):
numerator = (y_true - y_pred)**2
denominator = (y_true - np.average(y_true, axis=0))**2
return 1- numerator.sum(axis=0) / denominator.sum(axis=0)(2)多项式拟合平面上的10个点
python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn import linear_model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def generate_samples(m):
X = 2 * (np.random.rand(m, 1) - 0.5)
y = X + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, (m,1))
return X, y
np.random.seed(100)
X, y = generate_samples(10)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 10)
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
model = linear_model.LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_poly, y)
plt.axis([-1, 1, -2, 2])
plt.scatter(X, y)
W = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100).reshape(100, 1)
W_poly = poly.fit_transform(W)
u = model.predict(W_poly)
plt.plot(W, u)
plt.show()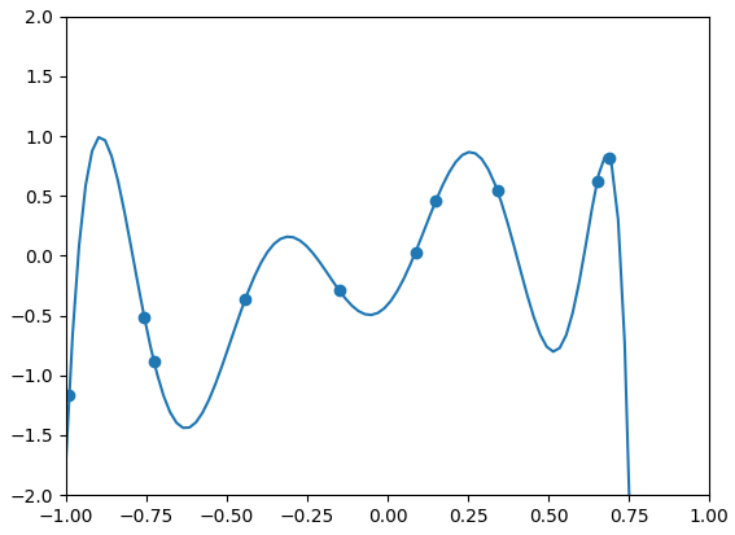
(3)多个数据点并拟合
python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import linear_regression.lib.linear_regression as lib
def generate_samples(m):
X = 2 * np.random.rand(m, 1)
y = X**2 - 2 * X + 1 + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, (m,1))
return X, y
np.random.seed(0)
X, y = generate_samples(100)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
model = lib.LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_poly, y)
plt.figure(0)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.figure(1)
plt.scatter(X, y)
W = np.linspace(0, 2, 100).reshape(100, 1)
W_poly = poly.fit_transform(W)
u = model.predict(W_poly)
plt.plot(W, u)
plt.show()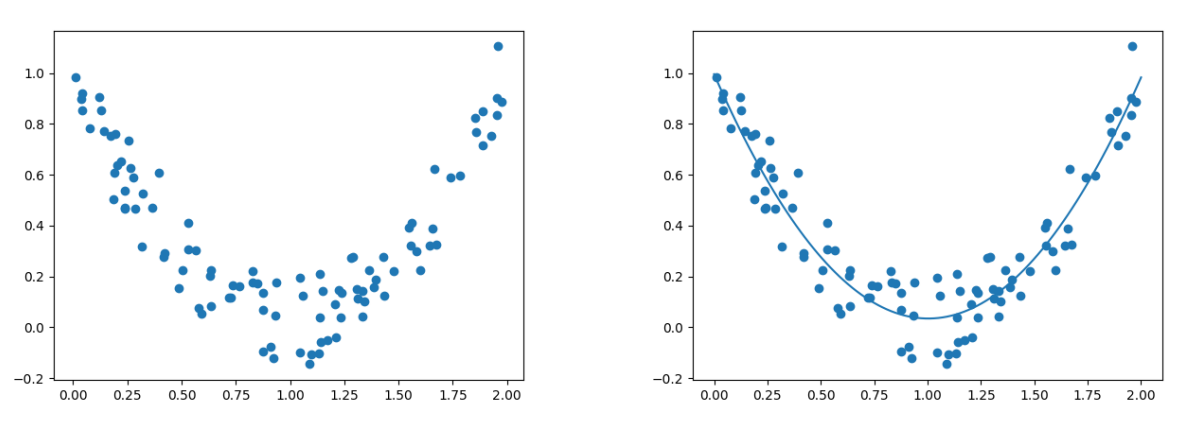
3.上机实验题三
通过添加正则化项来防止过拟合的技术。使用了一个10次多项式来拟合数据,并调整了正则化参数Lambda的值,以观察不同正则化强度下模型在训练集和测试集上的表现。
(1)定义线性回归类、MSE、
python
import numpy as np
class LinearRegression:
def fit(self, X, y):
self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X)).dot(X.T).dot(y)
return
def predict(self, X):
return X.dot(self.w)
def mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred):
return np.average((y_true - y_pred)**2, axis=0)
def r2_score(y_true, y_pred):
numerator = (y_true - y_pred)**2
denominator = (y_true - np.average(y_true, axis=0))**2
return 1- numerator.sum(axis=0) / denominator.sum(axis=0)(2)岭回归
python
import numpy as np
class RidgeRegression:
def __init__(self, Lambda):
self.Lambda = Lambda
def fit(self, X, y):
m, n = X.shape
r = np.diag(self.Lambda * np.ones(n))
self.w = np.linalg.inv(X.T.dot(X) + r).dot(X.T).dot(y)
return
def predict(self, X):
return X.dot(self.w)(3)岭回归拟合
python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from linear_regression.lib.ridge_regression import RidgeRegression
def generate_samples(m):
X = 2 * (np.random.rand(m, 1) - 0.5)
y = X + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, (m,1))
return X, y
np.random.seed(100)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 10)
X, y = generate_samples(10)
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
model = RidgeRegression(Lambda = 0.01)
model.fit(X_poly, y)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.axis([-1, 1, -2, 2])
W = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100).reshape(100, 1)
W_poly = poly.fit_transform(W)
u = model.predict(W_poly)
plt.plot(W, u)
plt.show()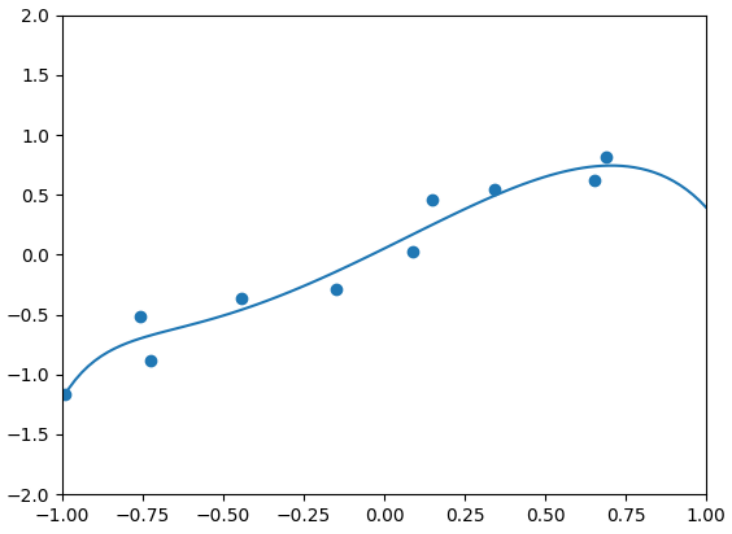 (4)岭回归在不同正则化强度下对训练集和测试集的拟合效果
(4)岭回归在不同正则化强度下对训练集和测试集的拟合效果
python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import linear_regression.lib.linear_regression as lib
from linear_regression.lib.ridge_regression import RidgeRegression
def generate_samples(m):
X = 2 * (np.random.rand(m, 1) - 0.5)
y = X + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, (m,1))
return X,y
np.random.seed(100)
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree = 10)
X_train, y_train = generate_samples(30)
X_train = poly.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test, y_test = generate_samples(100)
X_test = poly.fit_transform(X_test)
Lambdas, train_r2s, test_r2s = [], [], []
for i in range(1, 200):
Lambda = 0.01 * i
Lambdas.append(Lambda)
ridge = RidgeRegression(Lambda)
ridge.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = ridge.predict(X_train)
y_test_pred = ridge.predict(X_test)
train_r2s.append(lib.r2_score(y_train, y_train_pred))
test_r2s.append(lib.r2_score(y_test, y_test_pred))
plt.figure(0)
plt.plot(Lambdas, train_r2s)
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(Lambdas, test_r2s)
plt.show()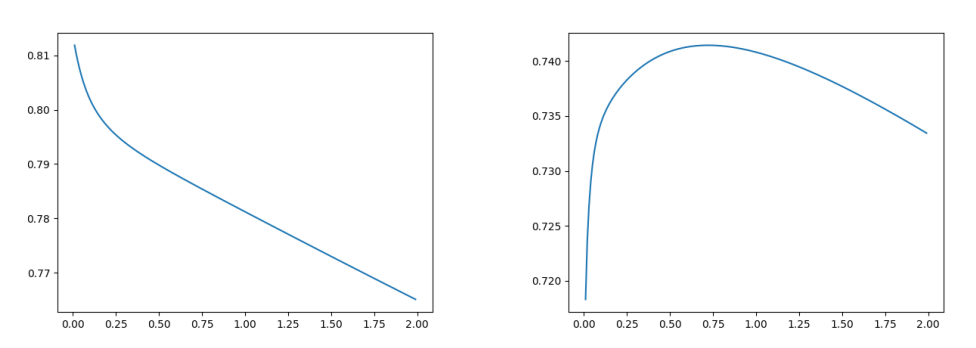
4. 上机实验题四 ------ 糖尿病预测
首先加载了糖尿病数据集,并将数据集分为训练集和测试集。接着,创建了一个线性回归模型并用训练集数据进行训练。训练完成后,模型对测试集进行了预测。然后,计算了预测结果的均方误差(MSE)以评估模型性能。此外,还提取了模型的系数和截距,并将它们打印出来。最后,根据这些系数和截距,构建并打印出了线性回归方程,该方程描述了各个特征与目标变量之间的关系。
python
# 导入所需的库
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 加载糖尿病数据集
X, y = load_diabetes(return_X_y=True)
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 创建线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
# 训练模型
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 获取模型的系数和截距
coefficients = model.coef_
intercept = model.intercept_
# 计算预测的均方误差
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'Mean Squared Error: {mse}')
# 打印模型的系数和截距
print(f'Coefficients: {model.coef_}')
print(f'Intercept: {model.intercept_}')
# 打印线性回归方程
print(f'Linear Regression Equation: y = {intercept:.4f} + ')
for i, coef in enumerate(coefficients):
print(f'{coef:.4f} * x{i+1} + ', end='')