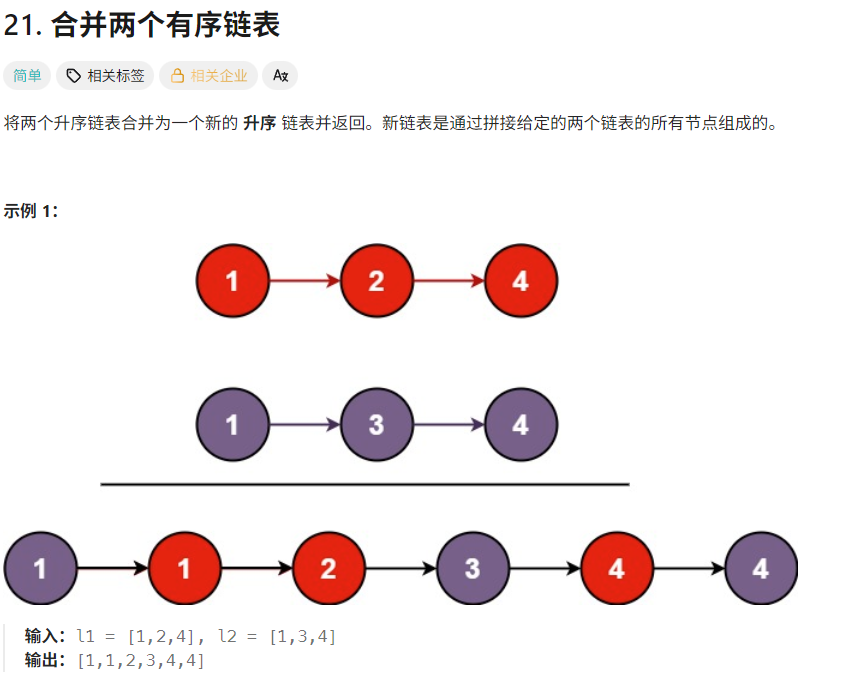
题目
分析
思路一
用一个multiset来存储<int,ListNode*>类型的多射数据,以此来存储这些节点的信息。然后遍历这个multiset来重建链表。
代码
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 使用 multiset,让 std::less 自动处理 pair<int, ListNode*> 的比较
multiset<pair<int, ListNode*>> nodes;
// 遍历 list1
ListNode* curr = list1;
while (curr != nullptr) {
nodes.insert({curr->val, curr});
curr = curr->next;
}
// 遍历 list2
curr = list2;
while (curr != nullptr) {
nodes.insert({curr->val, curr});
curr = curr->next;
}
if (nodes.empty()) {
return nullptr;
}
// 构建新链表
auto it = nodes.begin();
ListNode* head = it->second;
ListNode* tail = head;
++it;
for (; it != nodes.end(); ++it) {
tail->next = it->second;
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = nullptr; // 最后一个节点的 next 设置为空
return head;
}
};结果
思路二
利用两个指针,分别指向list1和list2的节点,然后继续比较,将两者之中较小的接到后面,然后移动指针,直到两条链都被遍历完。
代码
cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
// 创建一个虚拟头节点,简化边界处理
ListNode dummy;
ListNode* tail = &dummy; // 尾指针,用于构建新链表
// 当两个链表都还有节点时,比较节点值,将较小的接到结果链表后面
while(list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr) {
if(list1->val <= list2->val) {
tail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
tail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
tail = tail->next; // 移动尾指针
}
// 将剩余的非空链表直接接到结果链表末尾
if(list1 != nullptr) {
tail->next = list1;
} else {
tail->next = list2;
}
// 返回真正的头节点
return dummy.next;
}
};结果