文章目录
双链表循环
头插法
c
void headInsert(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node -> data = data;
node -> next = list -> next;
node -> pre = list;
list -> next ->pre = node;
list -> next = node;
list -> data++;
}注意顺序:
c
list -> next ->pre = node;
list -> next = node;如果是第一次进入函数:
- 此时list -> next为list
- list -> next ->pre = list->pre ,所以list的前一项为node
- 之后才更新list -> next = node;所以list的后一项为node
如果是第n次进入函数:
- 此时list -> next为上一次进入的node,而上面的node -> next = list -> next;把上一次进入的node挤到第二项
- list -> next ->pre = (上一次的)node->pre ,也就是第二项指向第一项
- 之后才更新list -> next = node;
根据1,2步的操作,才成功将新头插进入的函数与原先函数进行连接
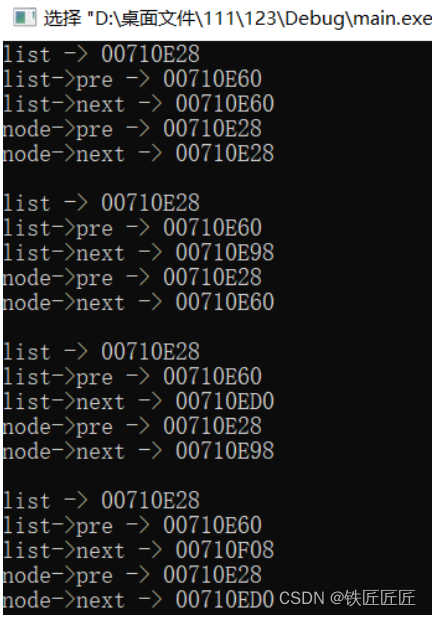
正确插入4个数:1,2,3,3
c
void headInsert(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node -> data = data;
node -> next = list -> next;
node -> pre = list;
list -> next ->pre = node;
list -> next = node;
printf("list -> %p\r\n",list);
printf("list->pre -> %p\r\n",list->pre);
printf("list->next -> %p\r\n",list->next);
printf("node->pre -> %p\r\n",node->pre);
printf("node->next -> %p\r\n",node->next);
printf("\r\n");
list -> data++;
}

但是如果是反过来的话:
c
void headInsert(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node -> data = data;
node -> next = list -> next;
node -> pre = list;
list -> next = node;
list -> next ->pre = node;
printf("list -> %p\r\n",list);
printf("list->pre -> %p\r\n",list->pre);
printf("list->next -> %p\r\n",list->next);
printf("node->pre -> %p\r\n",node->pre);
printf("node->next -> %p\r\n",node->next);
printf("\r\n");
list -> data++;
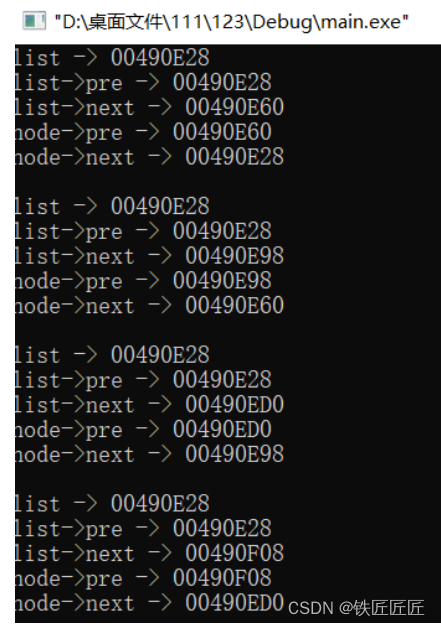
}如果是第一次进入函数:
- 更新list -> next = node
- 此时list -> next = node,而node->pre = node
- 那这样的话就是node指向node了
- 然后因为初始化的时候是list->pre还是指向list,这个并没有改变所以list的上一项还是指向list
如果是第N次进入函数:
- list上一项永远指向list,node的上一项永远指向node
- 只有两条"线"成立,其他两条线是错的
错误插入:
删除操作简化
c
void delete(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = list -> next;
while(node != list)
{
if(node -> data == data)
{
node -> pre -> next = node->next;
node -> next -> pre = node -> pre;
free(node);
list -> data--;
break;
}
node = node -> next;
}
}总代码
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stdlib.h"
typedef struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *pre;
}Node;
Node* InitList()
{
Node* list = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
list -> data = 0;
list -> next = list;
list -> pre = list;
return list;
}
void headInsert(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node -> data = data;
node -> next = list -> next;
node -> pre = list;
list -> next ->pre = node;
list -> next = node;
list -> data++;
}
void tailInsert(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* head = list;
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node -> data = data;
while(list -> next != head)
{
list = list -> next;
}
node -> next = list -> next;
node -> pre = list;
list -> next = node;
head -> pre = node;
head ->data ++;
}
void delete(Node* list, int data)
{
Node* node = list -> next;
printf("node->%p\r\n",node);
while(node != list)
{
if(node -> data == data)
{
node -> pre -> next = node->next;
node -> next -> pre = node -> pre;
free(node);
list -> data--;
break;
}
node = node -> next;
}
}
void printfList(Node* list)
{
Node* head = list;
list = list -> next;
while(list != head)
{
printf("%d->", list -> data);
list = list -> next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
void main()
{
Node* list = InitList();
headInsert(list,1);
headInsert(list,2);
headInsert(list,3);
headInsert(list,3);
tailInsert(list,4);
tailInsert(list,5);
tailInsert(list,6);
printfList(list);
delete(list,3);
delete(list,6);
printfList(list);
}往期回顾
1.【第一章】《线性表与顺序表》
2.【第一章】《单链表》
3.【第一章】《单链表的介绍》
4.【第一章】《单链表的基本操作》
5.【第一章】《单链表循环》
6.【第一章】《双链表》