49风格迁移


读入内容图像:
python
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import liliPytorch as lp
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 读取内容图像
content_img = d2l.Image.open('../limuPytorch/images/rainier.jpg')
plt.imshow(content_img)
plt.show()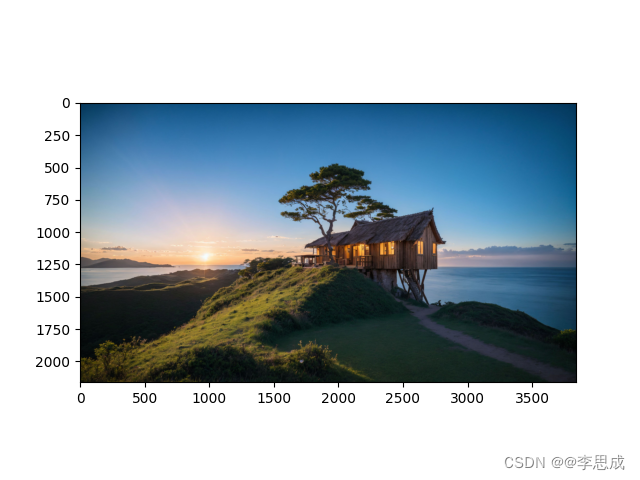
读取风格图像:
python
# 读取风格图像
style_img = d2l.Image.open('../limuPytorch/images/autumn-oak.jpg')
plt.imshow(style_img)
plt.show()
python
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import liliPytorch as lp
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 读取内容图像
content_img = d2l.Image.open('../limuPytorch/images/rainier.jpg')
# plt.imshow(content_img)
# plt.show()
# 读取风格图像
style_img = d2l.Image.open('../limuPytorch/images/autumn-oak.jpg')
# plt.imshow(style_img)
# plt.show()
# 预处理和后处理
rgb_mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
rgb_std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# 函数preprocess对输入图像在RGB三个通道分别做标准化,
# 并将结果变换成卷积神经网络接受的输入格式
def preprocess(img, image_shape):
transforms = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize(image_shape),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=rgb_mean, std=rgb_std)])
return transforms(img).unsqueeze(0) # 增加一个通道
# 后处理函数postprocess则将输出图像中的像素值还原回标准化之前的值。
# 由于图像打印函数要求每个像素的浮点数值在0~1之间,我们对小于0和大于1的值分别取0和1。
def postprocess(img):
# img[0] 表示移除批次维度,从批次中提取出第一个图像
img = img[0].to(rgb_std.device) # 移除批次维度,并将图像张量移动到与 rgb_std 相同的设备
img = torch.clamp(img.permute(1, 2, 0) * rgb_std + rgb_mean, 0, 1) # 反转标准化过程
return torchvision.transforms.ToPILImage()(img.permute(2, 0, 1))
# ToPILImage() 期望的输入是 [C, H, W] 形式,因此需要再次将张量的通道维度移动到第一个位置。
# 抽取图像特征
# 使用基于ImageNet数据集预训练的VGG-19模型
# VGG19包含了19个隐藏层(16个卷积层和3个全连接层)
pretrained_net = torchvision.models.vgg19(pretrained=True)
"""
一般来说,越靠近输入层,越容易抽取图像的细节信息;反之,则越容易抽取图像的全局信息。
为了避免合成图像过多保留内容图像的细节,我们选择VGG较靠近输出的层,即内容层,来输出图像的内容特征。
我们还从VGG中选择不同层的输出来匹配局部和全局的风格,这些图层也称为风格层。
"""
style_layers, content_layers = [0, 5, 10, 19, 28], [25]
# net 模型包含了 VGG-19 从第 0 层到第 28 层的所有层
net = nn.Sequential(*[pretrained_net.features[i] for i in
range(max(content_layers + style_layers) + 1)])
# 由于我们还需要中间层的输出,
# 因此这里我们逐层计算,并保留内容层和风格层的输出
def extract_features(X, content_layers, style_layers):
contents = []
styles = []
for i in range(len(net)):
X = net[i](X)
if i in style_layers:
styles.append(X)
if i in content_layers:
contents.append(X)
return contents, styles
# 对内容图像抽取内容特征
def get_contents(image_shape, device):
content_X = preprocess(content_img, image_shape).to(device)
contents_Y, _ = extract_features(content_X, content_layers, style_layers)
return content_X, contents_Y
# 对风格图像抽取风格特征
def get_styles(image_shape, device):
style_X = preprocess(style_img, image_shape).to(device)
_, styles_Y = extract_features(style_X, content_layers, style_layers)
return style_X, styles_Y
# 定义损失函数
# 由内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失3部分组成
# 内容损失
# 内容损失通过平方误差函数衡量合成图像与内容图像在内容特征上的差异
# 平方误差函数的两个输入均为extract_features函数计算所得到的内容层的输出。
def content_loss(Y_hat, Y):
# 我们从动态计算梯度的树中分离目标:
# 这是一个规定的值,而不是一个变量。
return torch.square(Y_hat - Y.detach()).mean()
# 风格损失
def gram(X): # 基于风格图像的格拉姆矩阵
num_channels, n = X.shape[1], X.numel() // X.shape[1]
X = X.reshape((num_channels, n))
return torch.matmul(X, X.T) / (num_channels * n)
def style_loss(Y_hat, gram_Y):
return torch.square(gram(Y_hat) - gram_Y.detach()).mean()
# 全变分损失
# 合成图像里面有大量高频噪点,即有特别亮或者特别暗的颗粒像素。
# 一种常见的去噪方法是全变分去噪total variation denoising
def tv_loss(Y_hat):
return 0.5 * (torch.abs(Y_hat[:, :, 1:, :] - Y_hat[:, :, :-1, :]).mean() +
torch.abs(Y_hat[:, :, :, 1:] - Y_hat[:, :, :, :-1]).mean())
"""
风格转移的损失函数是内容损失、风格损失和总变化损失的加权和。
通过调节这些权重超参数,我们可以权衡合成图像在保留内容、迁移风格以及去噪三方面的相对重要性。
"""
content_weight, style_weight, tv_weight = 1, 1e3, 10
def compute_loss(X, contents_Y_hat, styles_Y_hat, contents_Y, styles_Y_gram):
# 分别计算内容损失、风格损失和全变分损失
contents_l = [content_loss(Y_hat, Y) * content_weight for Y_hat, Y in zip(
contents_Y_hat, contents_Y)]
styles_l = [style_loss(Y_hat, Y) * style_weight for Y_hat, Y in zip(
styles_Y_hat, styles_Y_gram)]
tv_l = tv_loss(X) * tv_weight
# 对所有损失求和
l = sum(10 * styles_l + contents_l + [tv_l])
return contents_l, styles_l, tv_l, l
# 初始化合成图像
class SynthesizedImage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, img_shape, **kwargs):
super(SynthesizedImage, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(*img_shape))
def forward(self):
return self.weight
# 函数创建了合成图像的模型实例,并将其初始化为图像X
def get_inits(X, device, lr, styles_Y):
gen_img = SynthesizedImage(X.shape).to(device)
gen_img.weight.data.copy_(X.data)
trainer = torch.optim.Adam(gen_img.parameters(), lr=lr)
styles_Y_gram = [gram(Y) for Y in styles_Y]
return gen_img(), styles_Y_gram, trainer
# 训练模型
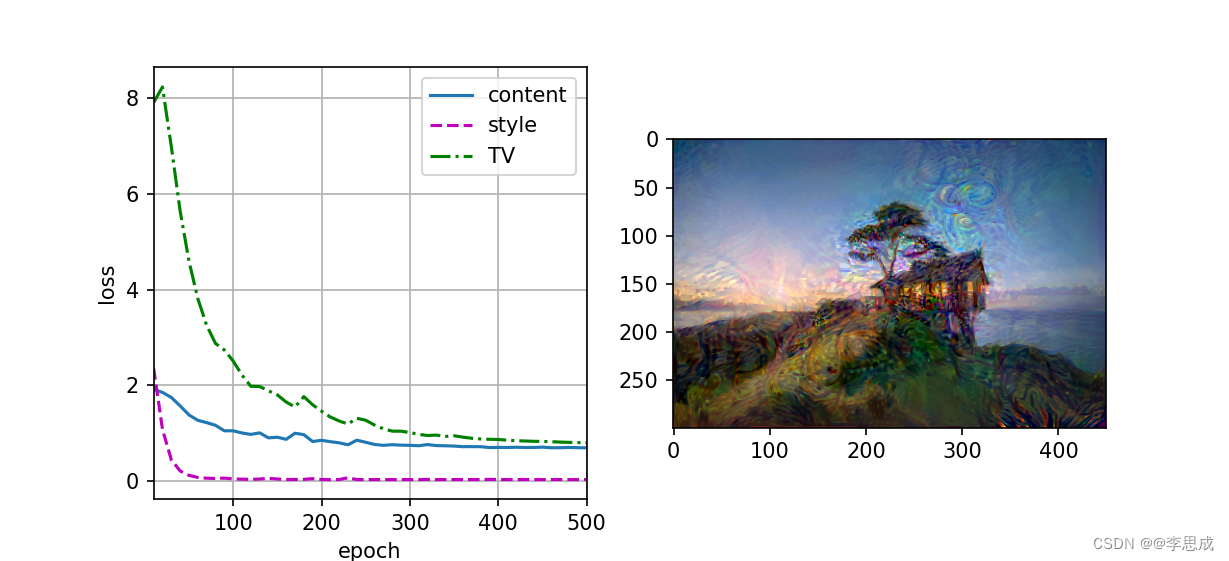
def train(X, contents_Y, styles_Y, device, lr, num_epochs, lr_decay_epoch):
X, styles_Y_gram, trainer = get_inits(X, device, lr, styles_Y) # 初始化合成图像和优化器
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(trainer, lr_decay_epoch, 0.8)
animator = lp.Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss',
xlim=[10, num_epochs],
legend=['content', 'style', 'TV'],
ncols=2, figsize=(7, 2.5))
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
trainer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
contents_Y_hat, styles_Y_hat = extract_features(
X, content_layers, style_layers) # 提取特征
contents_l, styles_l, tv_l, l = compute_loss(
X, contents_Y_hat, styles_Y_hat, contents_Y, styles_Y_gram) # 计算损失
l.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
trainer.step() # 更新模型参数
scheduler.step() # 更新学习率
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
animator.axes[1].imshow(postprocess(X))
animator.add(epoch + 1, [float(sum(contents_l)),
float(sum(styles_l)), float(tv_l)])
return X
device, image_shape = d2l.try_gpu(), (300, 450)
net = net.to(device)
content_X, contents_Y = get_contents(image_shape, device)
_, styles_Y = get_styles(image_shape, device)
output = train(content_X, contents_Y, styles_Y, device, 0.3, 500, 50)
plt.show()运行结果: