文章目录
继承简介
继承是面向对象程序设计代码复用的重要手段,使得程序员可以在保持原类的基础上扩展,新扩展的类叫派生类,体现类的层级结构,之前的重载是函数复用,继承是类的复用。
定义
c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class person
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << _name << " " << _sex << " " << _age << endl;;
}
protected:
string _name ="Jack";
string _sex ="man";
int _age=18;
};
class student : public person
{
protected:
int _number;
};
int main()
{
person p1;
student s1;
p1.print();
s1.print();
return 0;
}可以看到,student是派生类,public是继承方式,person是基类
派生类拥有基类的所有成员
访问限定符和继承方式

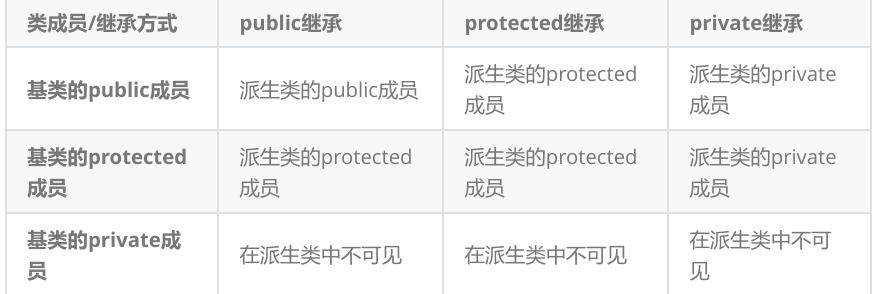
总结:
1,基类的private成员,无论什么继承,派生类都不可见,但是成员还是继承到了派生类中,但是语法限制了派生类访问
2,基类的private在派生类不可见,要想突破限制,就用protected,在类外不可访问,但在派生类可访问,访问限制符protected是为继承准备的
3,观察上面表格,可以发现两个不同限定符,取范围更小的,如protected和private 取private
4,class类默认继承方式private,struct类默认public,一般都写出继承方式的
5,一般都是public继承,几乎很少private/protected,
⭐基类派生类赋值转换
🚩 派生类对象可以赋值基类对象/基类引用/基类指针,这个过程叫切片,意为着把派生类那块基类所有的切给基类,
🚩基类对象不能赋值给派生类
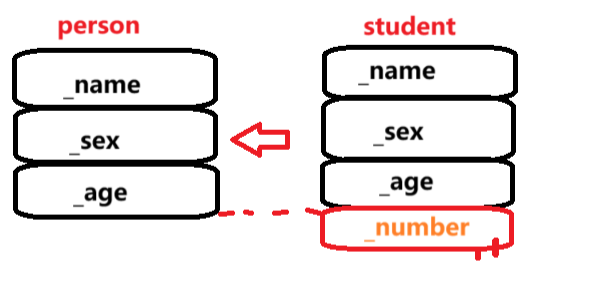
如图,派生可以赋值给基类,只不过 _number消失了
c
int main()
student s2;
person p2 = s2;
person* pp2 = &s2;
person& ppp2 = s2;
student* ss2 = (student*)pp2;//这种强转可以
pp2 = &p2;
//student* ss2 = (student*)pp2;//这种会越界访问
return 0;继承的作用域
c
class person
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "基类" << endl;
}
};
class student : public person
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "派生类" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
student s3;
s3.print();
s3.student::print();
s3.person::print();
return 0;
}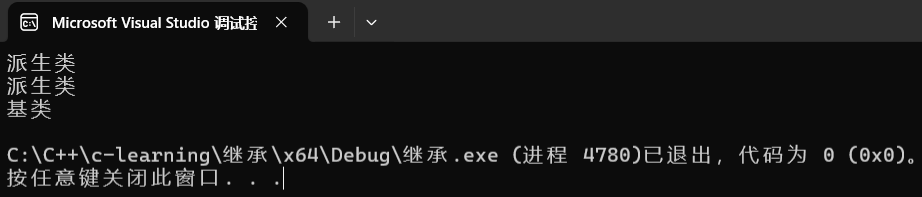
1,基类和派生类都有独立的作用域
🚩2,基类与派生类成员重名时,子类调用会直接跳过父类成员,这叫隐藏,也叫重定义,或者可用 类名::成员 访问
🚩3,在一个作用域的重名叫重载,两个作用域重名叫隐藏
4,继承体系最好不要定义重名成员
派生类的默认成员函数
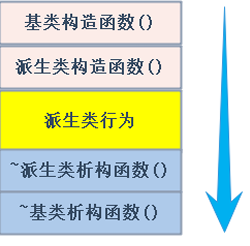
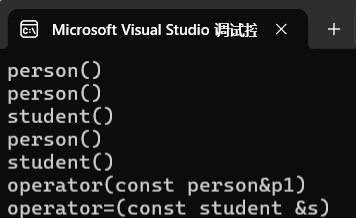
1,派生类对象初始化先调用基类构造函数,若基类无默认构造函数,则要在初始化列表显式调用,再调用自己的构造函数
2,构造,赋值,拷贝构造都是先调基类再调子类
3,析构先调子类再基类
c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class person
{
public:
person(string name ="jack")
:_name(name)
{
cout << "person()" << endl;
}
person(const person& p1)
:_name(p1._name)
{
cout << "person(& p1)" << endl;
}
person& operator=(const person& p1)
{
cout << "operator(const person&p1)" << endl;
if(this!=&p1)
{
_name = p1._name;
}
return *this;
}
~person()
{ }
protected:
string _name;
};
class student : public person
{
public:
student(const string name="peter", int number = 110)
:person(name),
_number(number)
{
cout << "student()" << endl;
}
student(const student& s)
:person(s),
_number(s._number)
{
cout << "student(student& s)" << endl;
}
student& operator=(const student& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
person::operator= (s);
_number = s._number;
}
cout << "operator=(const student &s)" << endl;
return *this;
}
~student()
{ }
protected:
int _number;
};
int main()
{
person p1("peter");
student s1("jack", 11);
student s2;
s2 = s1;
return 0;
}
继承与友元
友元不能继承,父类的朋友不是我的朋友
所以父类友元不能访问子类成员,除非子类也声明友元
c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class student;//声明
class person {
public:
friend void Display(const person& p, const student& s);
protected:
string _name = "person";
};
class student : public person {
public:
friend void Display(const person& p, const student& s); // 子类也声明为友元
student(int num = 0) : _number(num) {}
protected:
int _number;
};
void Display(const person& p, const student& s) {
cout << p._name << endl;
cout << s._number << endl; // 现在可以访问(student 的友元)
}
int main() {
person p;
student s(12345);
Display(p, s);
return 0;
}继承与静态成员
🚩基类定义static静态成员,则整个继承体系只有一个这样的成员,无论多少派生多少子类,只有这一个静态成员
c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class person
{
public:
person()
{
++_count;
}
string _name;
static int _count;
};
int person ::_count = 0;
class student:public person
{
public:
student()
:person()
{
++_count;
}
};
int main()
{
student s;
cout << person::_count<<endl;
return 0;
}2
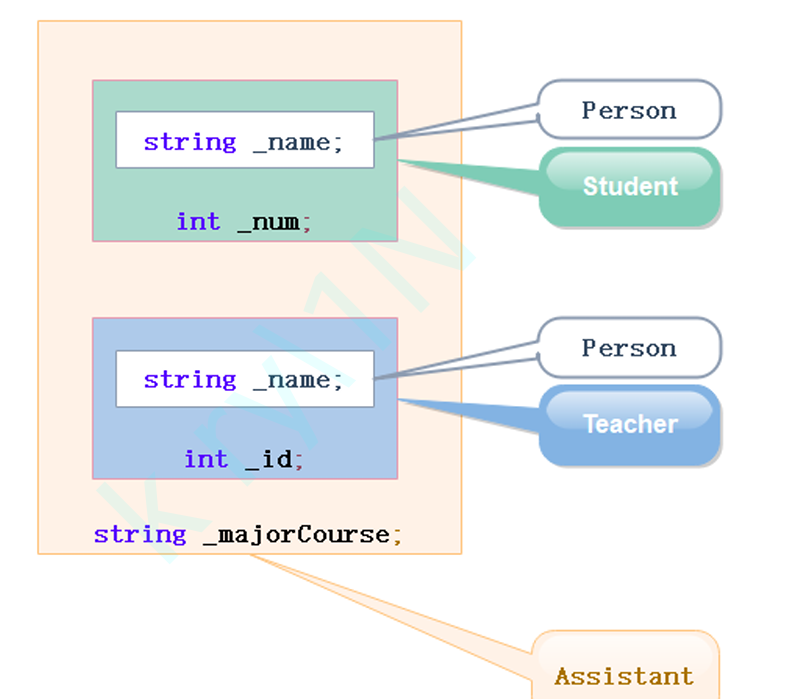
⭐复杂的菱形继承
单继承:一个子类只有一个父类
多继承:一个子类有两个及以上的父类
菱形继承:多继承的一种
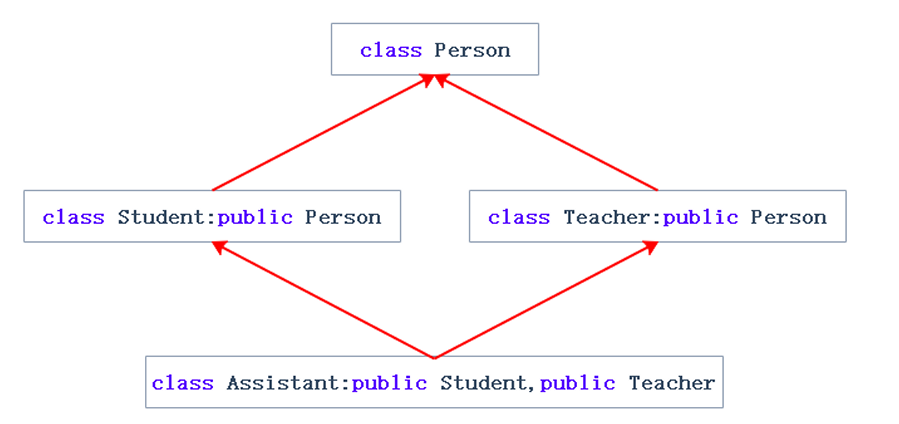
下图,可看出菱形继承数据冗余和二义性问题,有两份person值
c
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class person
{
public:
string _name;
};
class student :public person
{
public:
string _num;
};
class teacher :public person
{
public:
string _id;
};
class assistant :public student, public teacher
{
public:
string _majorcourse;
};
int main()
{
assistant a;
//a._name = "peter";//❌不明确
a.student::_name = "peter";//可以指明访问,
a.teacher::_name = "jack";
return 0;
}指明访问解决了二义性,但数据冗余还是没解决,
虚拟继承
虚拟继承解决了二义性和数据冗余问题,
c
class person
{
public:
string _name;
};
class student :virtual public person
{
public:
string _num;
};
class teacher :virtual public person
{
public:
string _id;
};
class assistant :virtual public student, virtual public teacher
{
public:
string _majorcourse;
};原理:
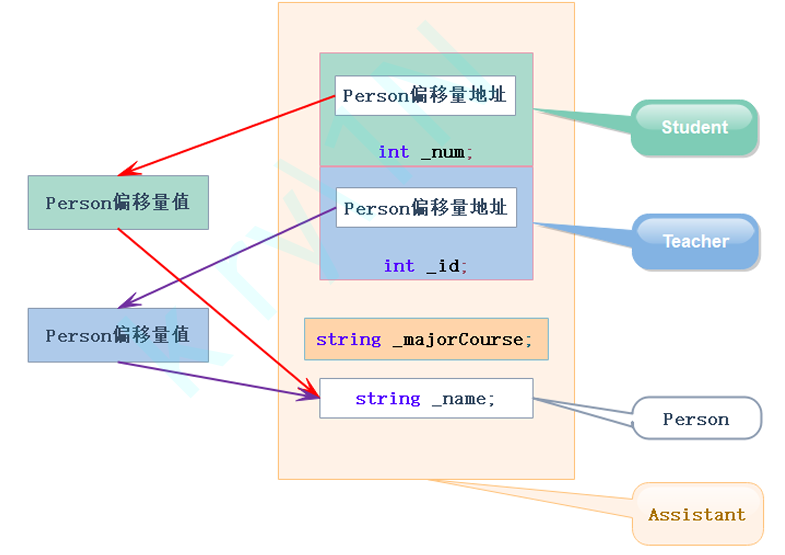
只存一个person,student和teacher中的person 存到assistant的地址偏移量,用时再跳过去找
注意:
菱形虚拟继承底层复杂,一般不设计多继承,更不能设计菱形继承
组合
继承是 is-a关系
组合是 has-a关系
- 继承复用 基类对子类公布了成员细节,俗称白箱复用,一定程度上破坏了封装,且基类 改动对子类影响较大,子类和基类关联性强,耦合度高
- 组合复用 被组合对象要求有良好接口,基类成员细节不可见,俗称黑箱复用,不破坏封装,关联性低,耦合度低
实战中能用组合就用组合,耦合度低,代码便于维护,不过有些情况就适合继承,多态也需要继承实现,可以用继承和组合就用组合
c
class car
{
protected:
string _colour;
string _num;
};
class Benz :public car
{
public:
void Drive()
{
cout << "奢华" << endl;
}
};继承关系
c
class tire
{
public:
string _brand;
int _size;
};
class car {
string _colour;
string _num;//车牌
tire _t;//轮胎
};组合关系