链表
线性表链式存储结构的特点是:用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(这组存储单元可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)。 为了表示每个数据元素 a
i与其直接后继数据元素 ai+1之间的逻辑关系,对数据元素 ai 来说,除了其本身的信息之外,还需要存储一个指示其直接后继的信息(直接后继的存储位置)。这两部分信息组成数据元素 a 的存储映像,称为节点 ( node )。 结点包括两个域:其中存储数据元素信息的称为数据域 ;存储直接后继存储位置有域称为指针域。指针域中存储的信息称作指针或链。 n个结点[ a (1< =i <= n )的存储映像]链接成一个链表,即为线性表( ai ,a2,..,an )。
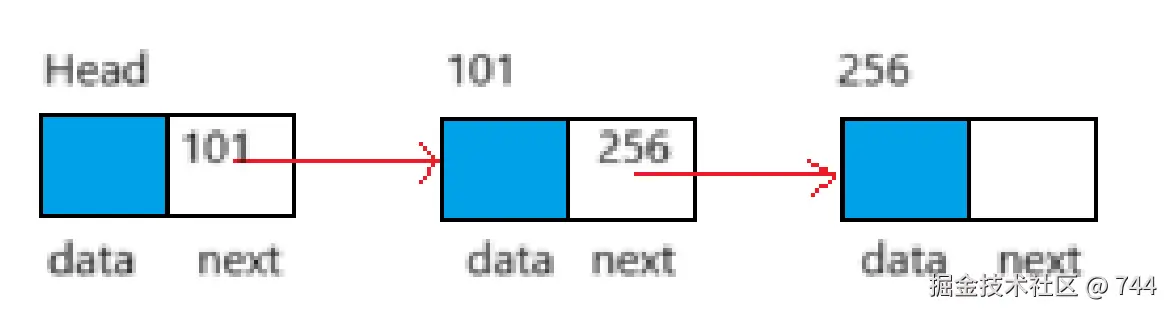
存储结构
- 头节点:可选,在表头前额外添加的空节点(简化边界操作,如删除第一个节点);
- 头指针:指向链表第一个节点(含头节点则指向头节点);
- 尾节点:最后一个节点,指针域为
NULL(循环链表指向头节点); - 空链表:头指针为
NULL(或头节点指针域为NULL)。
c
typedef int ElemType;
// 单链表节点结构体
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;// 数据域:存储元素值
struct node* next;// 指针域:指向下一个节点
}Node;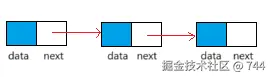
单链表
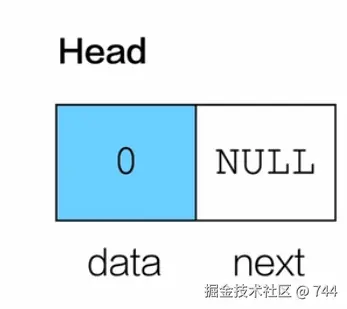
初始化
c
Node* initList()
{
Node* head =(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
遍历
c
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}插入数据
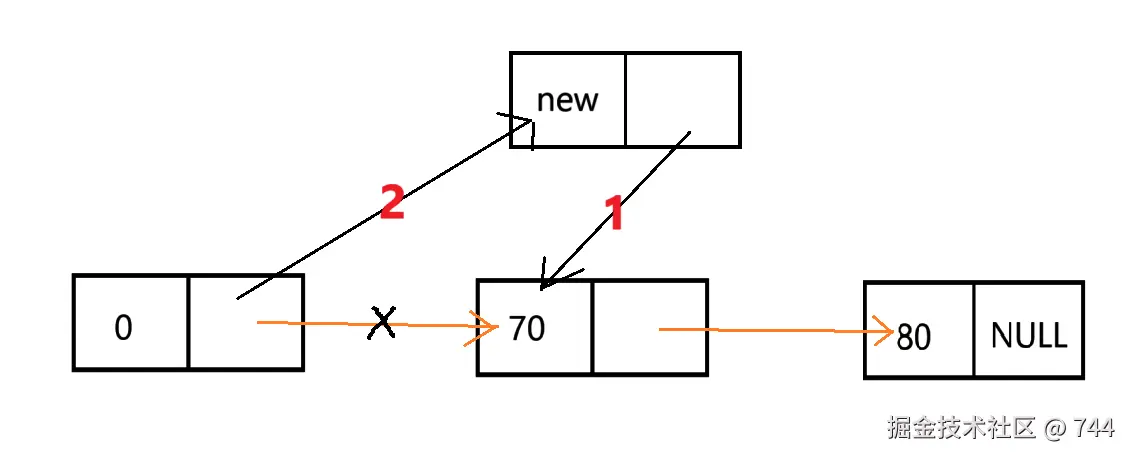
头插法
从表头插入节点
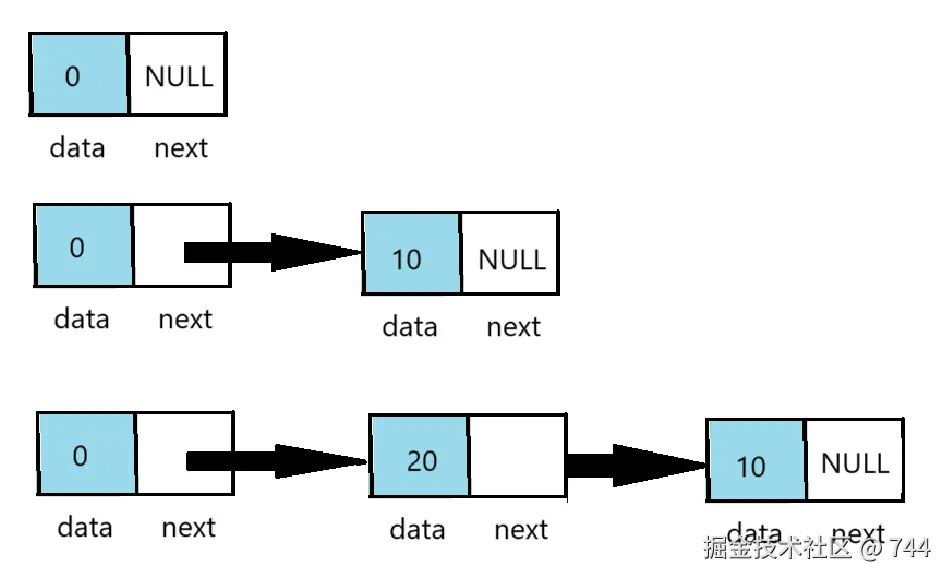
c
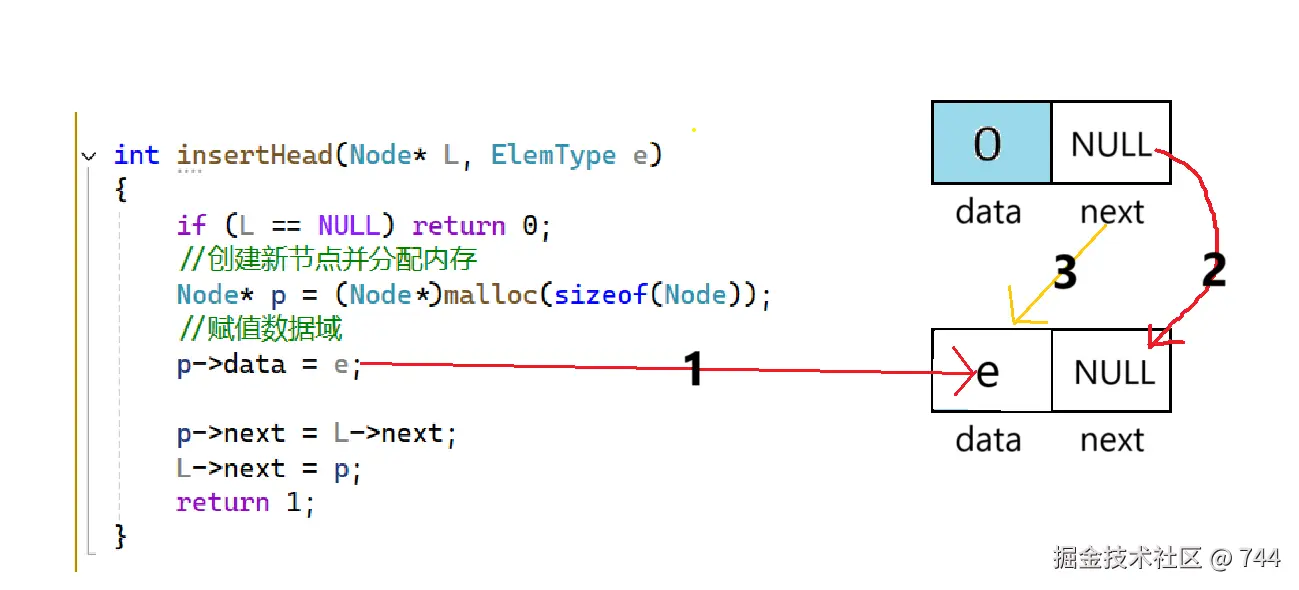
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
//创建新节点并分配内存
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值数据域
p->data = e;
p->next = L->next;// 新节点指向原表头有效节点
L->next = p;// 头节点指向新节点,完成插入
return 1;
}
头插法遍历
完整代码:
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//头插法
int insertHead(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
//创建新节点并分配内存
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值数据域
p->data = e;
p->next = L->next;
L->next = p;
return 1;
}
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertHead(list, 10);
insertHead(list, 20);
insertHead(list, 30);
PrintNode(list);
return 0;
}运行结果:
30 20 10
尾插法
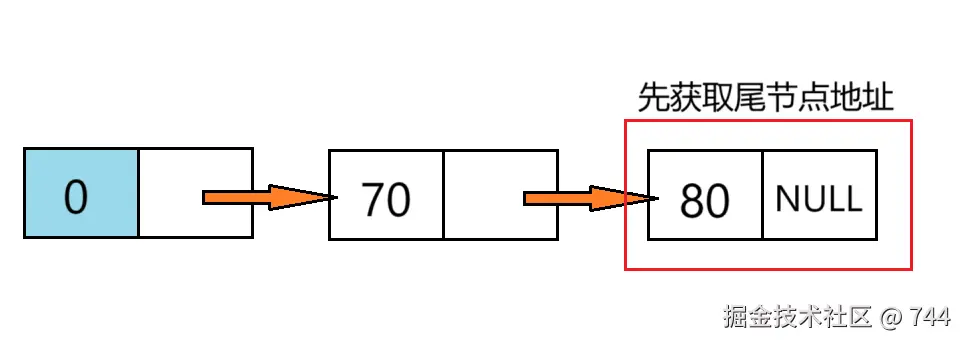
c
//找到尾节点
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}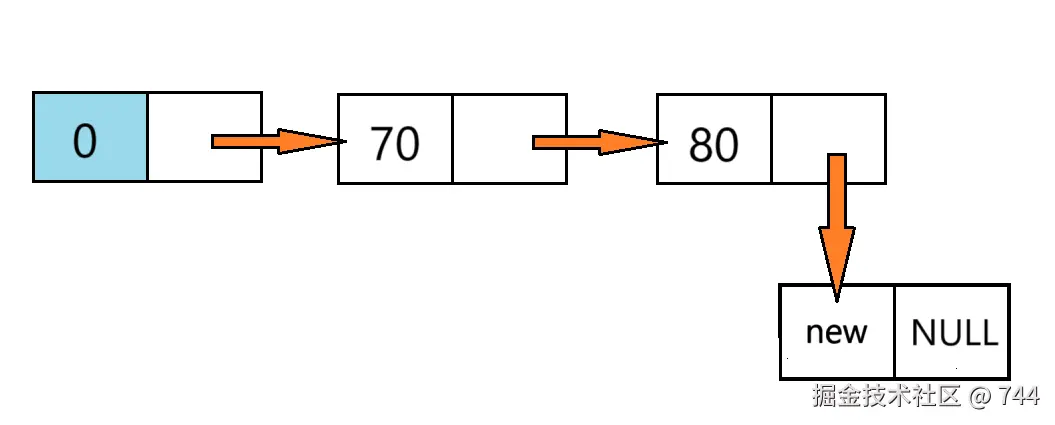
c
//插入
//(1)返回尾节点---完整代码1
Node* insertTail(Node* tail, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;//尾节点的next指向新创建的节点p
p->next = NULL;//节点p变成尾节点
return p;
}
//(2)插入函数中调用get_tail---完整代码2
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}完整代码1---插入函数返回尾节点
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//尾插法--找到尾节点
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
Node* insertTail(Node* tail, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return p;//返回尾节点
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
Node* tail=get_tail(list);
tail=insertTail(tail, 10);
tail=insertTail(tail, 20);
tail=insertTail(tail, 30);
PrintNode(list);
return 0;
}运行结果:
10 20 30
完整代码2---inertTail中调用get_tail
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
//尾插法--找到尾节点
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
PrintNode(list);
return 0;
}运行结果:
10 20 30
在指定位置插入数据
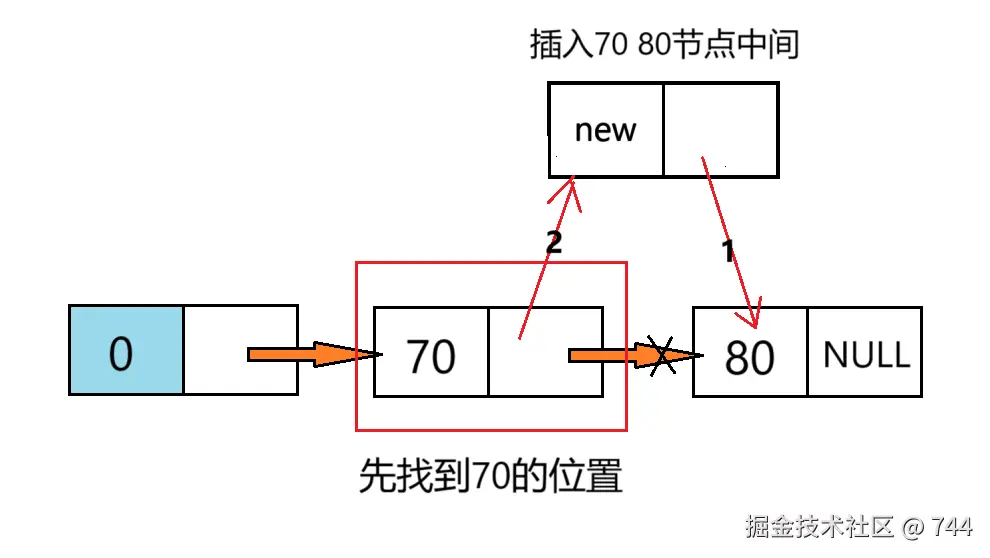
c
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1 新节点指向下一节点
p->next = q;//2 前驱节点指向新节点
return 1;
}完整代码
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 尾插法
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//在指定位置插入数据
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1
p->next = q;//2
return 1;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
PrintNode(list);
insertNode(list, 2, 15);
PrintNode(list);
return 0;
}运行结果:
10 20 30 10 15 20 30
删除节点
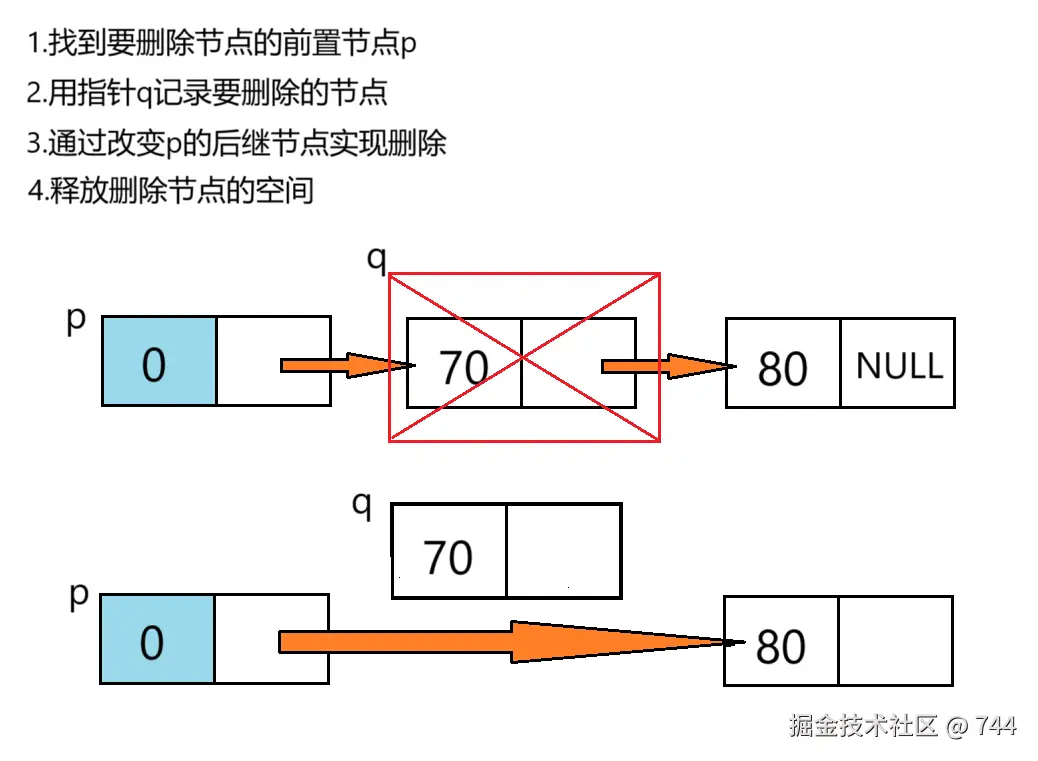
c
//删除节点
int delectNode(Node* L, int pos) {
//要删除节点的前驱
Node* p = L;
//遍历找到要删除节点的前驱
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("要删除的位置错误\n");
return 0;
}
Node* q = p->next; //记录被删除的节点q
p->next = q->next; //(将被删除的节点的前驱)p指向被删除结点的后继
free(q);//释放被删除节点的内存空间
return 1;
}完整代码:
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 尾插法
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//在指定位置插入数据
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1
p->next = q;//2
return 1;
}
//删除节点
int delectNode(Node* L, int pos) {
//要删除节点的前驱
Node* p = L;
//遍历找到要删除节点的前驱
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("要删除的位置错误\n");
return 0;
}
Node* q = p->next; //记录被删除的节点q
p->next = q->next; //(将被删除的节点的前驱)p指向被删除结点的后继
free(q);//释放被删除节点的内存空间
return 1;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
printf("原链表:");
PrintNode(list);
insertNode(list, 2, 15);
printf("插入后");
PrintNode(list);
delectNode(list, 2);
printf("删除后:");
PrintNode(list);
return 0;
}运行结果:
原链表:10 20 30 插入后10 15 20 30 删除后:10 20 30
按值查找
c
Node* findByValue(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
if (L == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* p = L;
while (p != NULL) {
p = p->next;
if (p->data == e)
{
return p;
}
}
printf("查找失败:未找到元素%d\n", e);
return NULL;
}完整代码:
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 尾插法
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//在指定位置插入数据
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1
p->next = q;//2
return 1;
}
//删除节点
int delectNode(Node* L, int pos) {
//要删除节点的前驱
Node* p = L;
//遍历找到要删除节点的前驱
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("要删除的位置错误\n");
return 0;
}
Node* q = p->next; //记录被删除的节点q
p->next = q->next; //(将被删除的节点的前驱)p指向被删除结点的后继
free(q);//释放被删除节点的内存空间
return 1;
}
//按值查找
Node* findByValue(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
if (L == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* p = L;
while (p != NULL) {
p = p->next;
if (p->data == e)
{
return p;
}
}
printf("查找失败:未找到元素%d\n", e);
return NULL;
}
//获取节点长度
int NodeLength(Node*L)
{
Node* p = L;
int len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//释放链表
void freeList(Node* L) {
Node* p = L->next;
Node* q;
while (p != NULL) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
L->next = NULL;
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
printf("原链表:");
PrintNode(list);
insertNode(list, 2, 15);
printf("插入后");
PrintNode(list);
delectNode(list, 2);
printf("删除后:");
PrintNode(list);
Node*find_node=findByValue(list, 20);
if (find_node != NULL) {
printf("找到元素:%d\n", find_node->data);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
原链表:10 20 30 插入后10 15 20 30 删除后:10 20 30 找到元素:20
获取链表长度
c
//获取节点长度
int LinklistLength(Node*L)
{
Node* p = L;//包含头节点
//计算有效节点长度
//Node* p = L->next; //跳过头节点,指向第一个有效节点
int len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}完整代码:
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 尾插法
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//在指定位置插入数据
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1
p->next = q;//2
return 1;
}
//删除节点
int delectNode(Node* L, int pos) {
//要删除节点的前驱
Node* p = L;
//遍历找到要删除节点的前驱
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("要删除的位置错误\n");
return 0;
}
Node* q = p->next; //记录被删除的节点q
p->next = q->next; //(将被删除的节点的前驱)p指向被删除结点的后继
free(q);//释放被删除节点的内存空间
return 1;
}
//按值查找
Node* findByValue(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
if (L == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* p = L;
while (p != NULL) {
p = p->next;
if (p->data == e)
{
return p;
}
}
printf("查找失败:未找到元素%d\n", e);
return NULL;
}
//获取节点长度
int LinklistLength(Node*L)
{
Node* p = L;//未跳过头节点
int len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
printf("原链表:");
PrintNode(list);
insertNode(list, 2, 15);
printf("插入后");
PrintNode(list);
delectNode(list, 2);
printf("删除后:");
PrintNode(list);
Node*find_node=findByValue(list, 20);
if (find_node != NULL) {
printf("找到元素:%d\n", find_node->data);
}
printf("链表长度为%d\n", LinklistLength(list));
return 0;
}运行结果:
原链表:10 20 30 插入后10 15 20 30 删除后:10 20 30 找到元素:20 链表长度为4
释放链表
需逐个释放节点,避免内存泄漏。
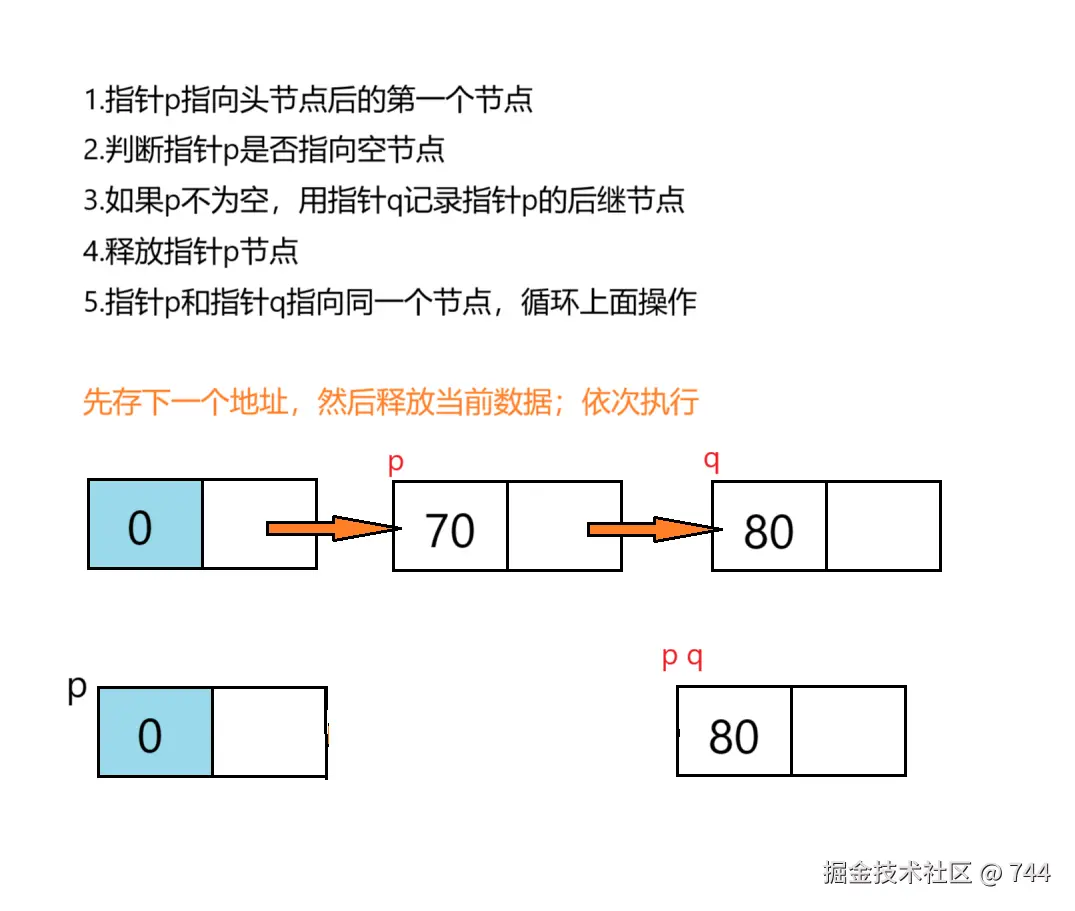
c
//释放链表--头节点保留
void freeList(Node* L) {
Node* p = L->next;
Node* q;
while (p != NULL) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
L->next = NULL;
}完整代码:
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct node {
ElemType data;
struct node* next;
}Node;
//初始化
Node* initList()
{
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->data = 0;
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// 尾插法
Node* get_tail(Node* L) {
Node* p = L;
while (p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
int insertTail(Node* L, ElemType e) {
Node* tail=get_tail(L);
Node* p = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
//赋值并连接节点
p->data = e;
tail->next = p;
p->next = NULL;
return 1;
}
//在指定位置插入数据
int insertNode(Node* L, int pos, ElemType e)
{
Node* p = L;//用来保存插入位置的前驱节点
//遍历找到插入位置的前驱节点
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;// 先移动节点
if (p == NULL)// 移动后检查是否越界
{
return 0;// pos 超出链表长度,返回失败
}
}
Node* q = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//创建一个要插入的新节点
q->data = e;//赋值
q->next = p->next;//1
p->next = q;//2
return 1;
}
//删除节点
int delectNode(Node* L, int pos) {
//要删除节点的前驱
Node* p = L;
//遍历找到要删除节点的前驱
for (int i = 0; i < pos - 1; i++)
{
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("要删除的位置错误\n");
return 0;
}
Node* q = p->next; //记录被删除的节点q
p->next = q->next; //(将被删除的节点的前驱)p指向被删除结点的后继
free(q);//释放被删除节点的内存空间
return 1;
}
//按值查找
Node* findByValue(Node* L, ElemType e)
{
if (L == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
Node* p = L;
while (p != NULL) {
p = p->next;
if (p->data == e)
{
return p;
}
}
printf("查找失败:未找到元素%d\n", e);
return NULL;
}
//获取节点长度
int LinklistLength(Node*L)
{
Node* p = L;
int len = 0;
while (p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//遍历
void PrintNode(Node* L)
{
Node* p = L->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//释放链表
void freeList(Node* L) {
Node* p = L->next;
Node* q;
while (p != NULL) {
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
L->next = NULL;
}
int main()
{
Node* list = initList();
insertTail(list, 10);
insertTail(list, 20);
insertTail(list, 30);
printf("原链表:");
PrintNode(list);
insertNode(list, 2, 15);
printf("插入后");
PrintNode(list);
delectNode(list, 2);
printf("删除后:");
PrintNode(list);
Node*find_node=findByValue(list, 20);
if (find_node != NULL) {
printf("找到元素:%d\n", find_node->data);
}
printf("链表长度为%d\n", LinklistLength(list));
freeList(list);
printf("释放后链表长度为%d\n", NodeLength(list));
return 0;
}运行结果:
原链表:10 20 30 插入后10 15 20 30 删除后:10 20 30 找到元素:20 链表长度为4 释放后链表长度为1
单链表 vs 顺序表 核心对比
| 特性 | 单链表 | 顺序表 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储方式 | 非连续,节点 + 指针 | 连续数组 |
| 随机访问 | 不支持(O(n)) |
支持(O(1)) |
| 插入 / 删除 | 无需移动元素(O(1)) |
需移动元素(O(n)) |
| 内存利用率 | 按需分配(无浪费) | 可能浪费(静态表)或扩容 |
| 缓存友好性 | 差(内存分散) | 好(连续存储) |
| 实现复杂度 | 较高(指针操作) | 较低(数组操作) |
拓展
循环单链表
- 尾节点的
next指向头节点(而非NULL); - 优势:遍历可从任意节点开始,无需回到头指针;
- 判空:
head->next == head(带头节点)。
2. 双向链表
-
节点新增
prev指针(指向前驱节点); -
优势:可双向遍历,删除节点无需找前驱(
O(1)); -
结构体定义:
ctypedef struct DNode { ElemType data; struct DNode *prev; // 前驱指针 struct DNode *next; // 后继指针 } DNode, *DLinkList;