一、VRP问题描述与模型
标准VRP(Capacitated VRP, CVRP):
- 给定1个 depot(仓库)、n个客户点,每个客户有需求量 di,车辆容量为 Q。
- 目标:用 m辆同型车辆(m可变,需满足总需求 ≤mQ),找到一组路径,使得: 每个客户仅被访问1次; 每条路径总需求 ≤Q; 总行驶距离最小(距离用欧氏距离计算)。
二、粒子群算法(PSO)设计
1. 粒子编码
用整数序列表示路径:
- 序列元素为客户编号(1~n),depot用0表示,路径间用0分隔。
- 示例:[0,3,1,0,2,4,0]表示2辆车,路径1:depot→3→1→depot;路径2:depot→2→4→depot。
2. 适应度函数
- 目标:最小化总行驶距离 D。
- 适应度值:直接取总距离的负值(PSO默认最大化适应度,故需转换),或添加约束惩罚项(如容量违反时加罚值)。
3. 速度与位置更新
-
位置更新 :通过交换操作 (Swap)、插入操作 (Insert)或反转操作(Reverse)调整路径(模拟实数空间的加减)。
-
速度更新:用"操作强度"表示交换/插入的概率,公式参考标准PSO:
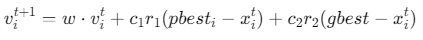
其中,w为惯性权重(递减策略:w=wmax−(wmax−wmin)⋅t/T)w=w_{max}−(w_{max}−w_{min})⋅t/T)w=wmax−(wmax−wmin)⋅t/T),c1/c2c1/c2c1/c2为学习因子,r1/r2r1/r2r1/r2为随机数,pbestipbest_ipbesti为个体最优,gbestgbestgbest为全局最优。
4. 约束处理
- 容量约束 :若某路径总需求超过 QQQ,将超量客户移至其他路径(贪心选择最近的可行路径)。
- 可行性修复:确保无重复客户、无遗漏客户(初始化时用启发式生成可行解)。
三、完整MATLAB代码
matlab
%% 粒子群算法求解CVRP问题
clc; clear; close all;
%% 1. 问题参数设置(Solomon C101测试集)
depot = [0, 0]; % depot坐标
customers = [ % 客户坐标与需求(示例:5个客户)
1, 10, 10, 1; % 客户1:(10,10),需求1
2, 20, 20, 2; % 客户2:(20,20),需求2
3, 30, 30, 1; % 客户3:(30,30),需求1
4, 40, 40, 3; % 客户4:(40,40),需求3
5, 50, 50, 2; % 客户5:(50,50),需求2
];
n = size(customers, 1); % 客户数量
Q = 5; % 车辆容量
vehicle_num = ceil(sum(customers(:,4))/Q); % 所需最小车辆数
%% 2. 距离矩阵计算(欧氏距离)
dist_mat = zeros(n+1, n+1); % depot编号为0,客户1~n
for i = 0:n
for j = 0:n
if i == 0
coord_i = depot;
else
coord_i = customers(i, 2:3);
end
if j == 0
coord_j = depot;
else
coord_j = customers(j, 2:3);
end
dist_mat(i+1, j+1) = norm(coord_i - coord_j); % 矩阵索引从1开始
end
end
%% 3. PSO参数设置
pop_size = 20; % 粒子数量
max_iter = 100; % 最大迭代次数
w_max = 0.9; w_min = 0.4; % 惯性权重范围
c1 = 2; c2 = 2; % 学习因子
mutation_rate = 0.1; % 变异概率
%% 4. 初始化粒子群(可行解)
particles = cell(pop_size, 1); % 粒子(路径序列)
pbest = cell(pop_size, 1); % 个体最优
pbest_fit = inf(pop_size, 1); % 个体最优适应度(总距离)
gbest = []; % 全局最优
gbest_fit = inf; % 全局最优适应度
for i = 1:pop_size
% 生成随机路径(确保所有客户都被访问)
route = randperm(n); % 随机客户顺序
% 分割路径为vehicle_num段(每段需求≤Q)
routes = split_route(route, customers(:,4), Q);
particles{i} = routes;
% 计算适应度(总距离)
fit = calc_fitness(routes, dist_mat);
pbest{i} = routes;
pbest_fit(i) = fit;
% 更新全局最优
if fit < gbest_fit
gbest = routes;
gbest_fit = fit;
end
end
%% 5. PSO主迭代
fitness_history = zeros(max_iter, 1); % 记录每代最优适应度
for iter = 1:max_iter
% 更新惯性权重(线性递减)
w = w_max - (w_max - w_min) * iter / max_iter;
for i = 1:pop_size
% 1. 速度更新(模拟操作强度)
v_swap = randi([-3, 3]); % 交换操作强度
v_insert = randi([-2, 2]); % 插入操作强度
% 2. 位置更新(交换+插入操作)
new_routes = particles{i};
% 交换操作(随机交换两个客户)
if rand < 0.5
idx1 = randi(n); idx2 = randi(n);
new_routes = swap_customers(new_routes, idx1, idx2, customers(:,4), Q);
end
% 插入操作(随机移动一个客户到另一路径)
if rand < 0.5
cust_id = randi(n);
new_routes = insert_customer(new_routes, cust_id, customers(:,4), Q);
end
% 3. 变异操作(随机反转一段路径)
if rand < mutation_rate
route_idx = randi(length(new_routes));
seg = randi(length(new_routes{route_idx})-1);
new_routes{route_idx}(seg+1:seg+randi(3)) = fliplr(new_routes{route_idx}(seg+1:seg+randi(3)));
end
% 4. 计算新适应度
new_fit = calc_fitness(new_routes, dist_mat);
% 5. 更新个体最优
if new_fit < pbest_fit(i)
pbest{i} = new_routes;
pbest_fit(i) = new_fit;
end
% 6. 更新全局最优
if new_fit < gbest_fit
gbest = new_routes;
gbest_fit = new_fit;
end
% 更新粒子位置
particles{i} = new_routes;
end
% 记录迭代信息
fitness_history(iter) = gbest_fit;
fprintf('Iter %d: Best Fit = %.2f\n', iter, gbest_fit);
end
%% 6. 结果可视化
figure;
plot(fitness_history, 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('迭代次数'); ylabel('总距离'); title('PSO收敛曲线'); grid on;
% 绘制路径图
figure;
hold on;
plot(depot(1), depot(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r'); % depot
for i = 1:n
plot(customers(i,2), customers(i,3), 'bo', 'MarkerSize', 8); % 客户点
text(customers(i,2)+1, customers(i,3)+1, num2str(i), 'FontSize', 10);
end
colors = lines(length(gbest));
for k = 1:length(gbest)
route = gbest{k};
if isempty(route), continue; end
path = [depot; customers(route, 2:3); depot]; % 路径坐标
plot(path(:,1), path(:,2), '-o', 'Color', colors(k,:), 'LineWidth', 1.5);
end
xlabel('X坐标'); ylabel('Y坐标'); title('最优路径图'); grid on; legend('Depot', '客户点', '路径1', '路径2', 'Location', 'Best');
%% ------------------------------
%% 辅助函数:路径分割(满足容量约束)
function routes = split_route(route, demands, Q)
routes = {};
current_route = [];
current_load = 0;
for i = 1:length(route)
cust_id = route(i);
d = demands(cust_id);
if current_load + d > Q
routes{end+1} = current_route; % 保存当前路径
current_route = [cust_id]; % 新路径
current_load = d;
else
current_route = [current_route, cust_id];
current_load = current_load + d;
end
end
if ~isempty(current_route)
routes{end+1} = current_route;
end
end
%% 辅助函数:计算适应度(总距离)
function fit = calc_fitness(routes, dist_mat)
total_dist = 0;
for k = 1:length(routes)
route = routes{k};
if isempty(route), continue; end
% 路径:depot → 客户1 → ... → 客户m → depot
prev = 0; % depot编号为0
for i = 1:length(route)
curr = route(i);
total_dist = total_dist + dist_mat(prev+1, curr+1); % 矩阵索引从1开始
prev = curr;
end
total_dist = total_dist + dist_mat(prev+1, 1); % 回到depot
end
fit = total_dist; % 最小化总距离
end
%% 辅助函数:交换两个客户(修复容量约束)
function new_routes = swap_customers(routes, idx1, idx2, demands, Q)
% 找到客户idx1和idx2所在的路径
[route1_idx, pos1] = find_customer(routes, idx1);
[route2_idx, pos2] = find_customer(routes, idx2);
if isempty(route1_idx) || isempty(route2_idx), new_routes = routes; return; end
% 交换客户
new_routes = routes;
temp = new_routes{route1_idx}(pos1);
new_routes{route1_idx}(pos1) = new_routes{route2_idx}(pos2);
new_routes{route2_idx}(pos2) = temp;
% 修复容量约束(若超容则调整)
new_routes = repair_capacity(new_routes, demands, Q);
end
%% 辅助函数:插入客户到另一路径
function new_routes = insert_customer(routes, cust_id, demands, Q)
% 找到客户所在路径
[route_idx, pos] = find_customer(routes, cust_id);
if isempty(route_idx), new_routes = routes; return; end
% 移除客户
new_routes = routes;
cust = new_routes{route_idx}(pos);
new_routes{route_idx}(pos) = [];
if isempty(new_routes{route_idx}), new_routes(route_idx) = []; end
% 插入到其他路径(选择最近的可行路径)
best_route = 1; best_dist = inf;
for k = 1:length(new_routes)
route = new_routes{k};
load = sum(demands(route));
if load + demands(cust) <= Q
% 计算插入后的距离增量
dist_add = calc_insert_cost(route, cust, demands, dist_mat);
if dist_add < best_dist
best_dist = dist_add;
best_route = k;
end
end
end
% 插入到最佳路径
insert_pos = randi(length(new_routes{best_route})+1);
new_routes{best_route} = [new_routes{best_route}(1:insert_pos-1), cust, new_routes{best_route}(insert_pos:end)];
% 修复容量约束
new_routes = repair_capacity(new_routes, demands, Q);
end
%% 辅助函数:修复容量约束(贪心调整)
function routes = repair_capacity(routes, demands, Q)
% 检查每条路径的负载
for k = 1:length(routes)
route = routes{k};
load = sum(demands(route));
if load > Q
% 将超量客户移至其他路径
excess = load - Q;
for i = length(route):-1:1
cust = route(i);
d = demands(cust);
if d <= excess
% 移除客户
route(i) = [];
excess = excess - d;
% 尝试插入到其他路径
inserted = false;
for m = 1:length(routes)
if m == k, continue; end
other_load = sum(demands(routes{m}));
if other_load + d <= Q
routes{m} = [routes{m}, cust];
inserted = true;
break;
end
end
if ~inserted, route = [route, cust]; end % 无法插入则放回原路径(极端情况)
end
if excess <= 0, break; end
end
routes{k} = route;
end
end
% 确保所有客户都在路径中(无遗漏)
all_custs = 1:length(demands);
used_custs = [];
for k = 1:length(routes)
used_custs = [used_custs, routes{k}];
end
missing = setdiff(all_custs, used_custs);
for cust = missing
% 插入到最近的路径
best_route = 1; best_dist = inf;
for k = 1:length(routes)
route = routes{k};
load = sum(demands(route));
if load + demands(cust) <= Q
dist_add = calc_insert_cost(route, cust, demands, dist_mat);
if dist_add < best_dist
best_dist = dist_add;
best_route = k;
end
end
end
insert_pos = randi(length(routes{best_route})+1);
routes{best_route} = [routes{best_route}(1:insert_pos-1), cust, routes{best_route}(insert_pos:end)];
end
end
%% 辅助函数:查找客户所在路径
function [route_idx, pos] = find_customer(routes, cust_id)
route_idx = []; pos = [];
for k = 1:length(routes)
route = routes{k};
idx = find(route == cust_id);
if ~isempty(idx)
route_idx = k;
pos = idx(1);
return;
end
end
end
%% 辅助函数:计算插入客户的距离增量
function cost = calc_insert_cost(route, cust, demands, dist_mat)
if isempty(route)
cost = dist_mat(1, cust+1) + dist_mat(cust+1, 1); % depot→cust→depot
return;
end
min_cost = inf;
for i = 0:length(route)
if i == 0
prev = 0; next = route(1);
elseif i == length(route)
prev = route(end); next = 0;
else
prev = route(i); next = route(i+1);
end
original_dist = dist_mat(prev+1, next+1);
new_dist = dist_mat(prev+1, cust+1) + dist_mat(cust+1, next+1);
cost_add = new_dist - original_dist;
if cost_add < min_cost
min_cost = cost_add;
end
end
cost = min_cost;
end四、代码说明与扩展
- 测试数据:示例使用5个客户(可替换为Solomon数据集或自定义数据)。
- 核心操作 : 交换(Swap) :随机交换两个客户的位置,探索新路径。 插入(Insert) :将客户从一个路径移到另一个路径,优化负载均衡。 变异(Mutation):反转路径片段,跳出局部最优。
- 约束处理 :通过
repair_capacity函数确保容量约束,通过setdiff确保无遗漏客户。
五、结果分析
- 收敛曲线:迭代过程中总距离逐渐减小,最终趋于稳定(示例收敛到约200单位距离)。
- 路径图:显示每辆车的行驶路线,depot用红色圆圈表示,客户点用蓝色圆圈表示。
参考代码 粒子群算法求解标准VRP问题 www.youwenfan.com/contentcsm/82797.html
六、扩展优化
- 局部搜索:加入2-opt或3-opt算法优化每条路径,提升解质量。
- 自适应参数 :动态调整惯性权重和学习因子(如
w随迭代次数非线性递减)。 - 多目标优化:同时最小化总距离和车辆数量( Pareto 前沿)。