(本文只介绍算法及实现,关于Gamma的具体原理需要大家自行去了解)
目录
一.计算公式
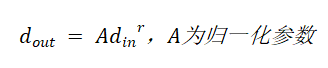
将像素扩展到0-255,上述计算公式进一步变形如下:
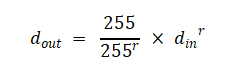
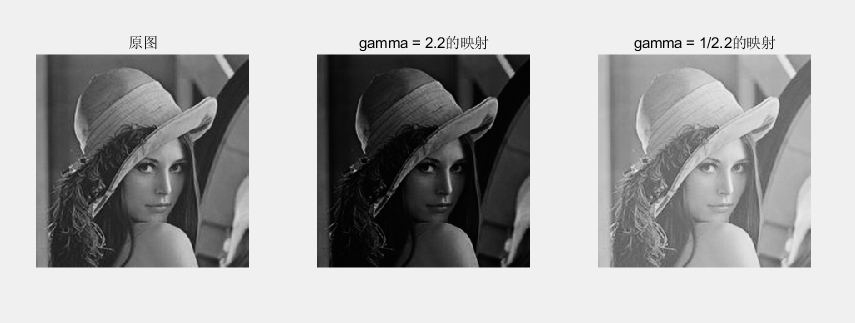
当r<1时,增强暗部细节,压缩亮部,用于处理过暗的图像;
当r>1时,增强亮部细节,压缩暗部,用于处理过亮的图像。
二.MATLAB的实现
Matlab
clc;
clear all;
img = imread('D:\matlab file\image_gamma\yu.bmp');
img = rgb2gray(img);
[h,w] = size(img);
figure('Position', [700,200, 1000, 800]); %设置figure的大小
subplot(1,3,1);imshow(img);title('原图');
img = double(img);
image1 = zeros(h,w);
for i = 1 : h
for j = 1 : w
image1(i,j) = (255/(255.^2.2)) * img(i,j).^2.2; %gamma取2.2
end
end
image1 = uint8(image1);
subplot(1,3,2);imshow(image1);title('gamma = 2.2的映射');
image2 = zeros(h,w);
for m = 1 : h
for n = 1 : w
image2(m,n) = (255/(255.^(1/2.2))) * img(m,n).^(1/2.2); %gamma取1/2.2
end
end
image2 = uint8(image2);
subplot(1,3,3);imshow(image2);title('gamma = 1/2.2的映射');显示效果如下所示
参考自《基于MATLAB与FPGA的图像处理教程》。
内容仅供学习使用,请勿转载。
如有问题,欢迎指正。