目录
(一)栈
(1)概念与结构
-
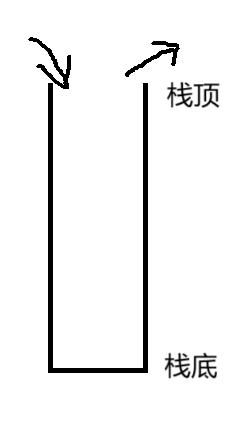
特殊的线性表,只允许在固定的一端插入和删除。
-
数据插入删除的一端为栈顶,另一端为栈底。
-
栈中元素遵循 先进后出(Last In First Out) 原则。
-
++压栈++:或称 进栈/入栈,插入数据。
-
++出栈++:删除数据。
-
底层结构:推荐数组。
(2)栈的实现
①初始化栈等
cpp
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(10 * sizeof(STDataType));
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 10;
}②入栈/出栈
函数STPush
cpp
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
checkbefore(ps);
if (ps->top == 10)
{
printf("full stack,operation invalid\n");
return;
}
ps->a[ps->top++] = x;
}函数STPop
cpp
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
checkbefore(ps);
if (STEmpty(ps))
{
printf("empty stack,the operation is invalid\n");
return;
}
ps->top--;
}③获取栈顶元素
cpp
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
if (STEmpty(ps))
{
printf("empty stack,the operation is invalid\n");
return;
}
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}④获取栈元素数量
cpp
int STSize(ST* ps)
{
checkbefore(ps);
if (STEmpty(ps))
{
return 0;
}
return ps->top;
}⑤判断栈是否为空
cpp
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
checkbefore(ps);
if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}(二)队列
(1)概念与结构
-
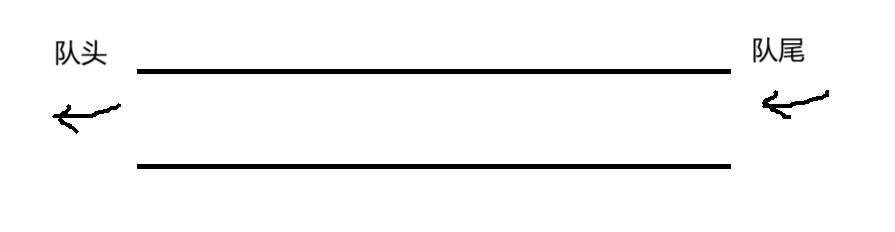
特殊线性表。
-
只允许在一端插入,另一端删除数据。
-
遵循 先进先出(First In First Out)原则。
-
底层结构:推荐链表。
(2)队列的实现
①初始化队列等
cpp
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}②入队/出队
函数QueuePush
cpp
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
checkBefore(pq);
QNode* newNode = buyNode(x);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
pq->phead = newNode;
pq->ptail = newNode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newNode;
pq->ptail = newNode;
}
pq->size++;
}函数QueuePop
cpp
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QNode* phead = pq->phead;
pq->phead = phead->next;
if (pq->ptail == phead)
{
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
free(phead);
phead = NULL;
pq->size--;
}③取队头/队尾元素
函数QueueFront
cpp
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
if (QueueEmpty(pq))
{
perror("the queue is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
return pq->phead->val;
}函数QueueBack
cpp
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
if (QueueEmpty(pq))
{
perror("the queue is empty\n");
exit(1);
}
return pq->ptail->val;
}④队列判空
函数QueueEmpty
cpp
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
checkBefore(pq);
if (pq->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}⑤队列有效元素
函数QueueSize
cpp
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
checkBefore(pq);
return pq->size;
}(三)栈和队列算法题
(1)有效的括号
栈的结构上面已经实现过,以下是函数isValid的实现:
cpp
bool isValid(char* s) {
ST st;
STInit(&st);
char* pc = s;
while(*pc != '\0')
{
if(*pc == '('||*pc == '['||*pc == '{')
{
STPush(&st,*pc);
}else
{
if(STEmpty(&st))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char topVal = STTop(&st);
if((*pc == ')' && topVal != '(')
|| (*pc == ']' && topVal != '[')
|| (*pc == '}' && topVal != '{'))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
STPop(&st);
}
pc++;
}
bool ret = STEmpty(&st);
STDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}(2)用队列实现栈
队列的结构我们已经实现过,以下是新的栈结构设计:
cpp
typedef struct {
Queue A;
Queue B;
} MyStack;①初始化栈
cpp
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* ps = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&ps->A);
QueueInit(&ps->B);
return ps;
}②入栈
cpp
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->A))
{
QueuePush(&obj->B, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->A, x);
}
}③出栈
函数OneQueuePop
cpp
int OneQueuePop(Queue** A, Queue** B)
{
while (QueueSize(*B) != 1)
{
QueuePush(*A, QueueFront(*B));
QueuePop(*B);
}
int val = QueueFront(*B);
QueuePop(*B);
return val;
}这里第一次写的时候没用二级指针传址,报错了。
函数myStackPop
cpp
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* A = &obj->A;
Queue* B = &obj->B;
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->A))
{
return OneQueuePop(&A, &B);
}
else
{
return OneQueuePop(&B, &A);
}
}④取栈顶元素
cpp
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if (QueueEmpty(&obj->A))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->B);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->A);
}
}⑤判断栈是否为空
cpp
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->A) && QueueEmpty(&obj->B);
}⑥栈的销毁
cpp
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->A);
QueueDestroy(&obj->B);
free(obj);
obj = NULL;
}(3)用栈实现队列
cpp
typedef struct MyQueue{
ST pushS;
ST popS;
}MyQueue;①初始化
cpp
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* pq = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&pq->pushS);
STInit(&pq->popS);
return pq;
}②入队
cpp
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
STPush(&obj->pushS,x);
}③出队
cpp
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(STEmpty(&obj->popS)&&STEmpty(&obj->pushS))
{
perror("these two stacks are empty");
exit(1);
}
if(STEmpty(&obj->popS))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushS))
{
STPush(&obj->popS,STTop(&obj->pushS));
STPop(&obj->pushS);
}
}
int topVal = STTop(&obj->popS);
STPop(&obj->popS);
return topVal;
}④获取栈顶元素
cpp
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(STEmpty(&obj->popS)&&STEmpty(&obj->pushS))
{
perror("these two stacks are empty");
exit(1);
}
if(STEmpty(&obj->popS))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushS))
{
STPush(&obj->popS,STTop(&obj->pushS));
STPop(&obj->pushS);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popS);
}⑤判断栈是否为空
cpp
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return STEmpty(&obj->popS) && STEmpty(&obj->pushS);
}⑥销毁栈
cpp
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
STDestroy(&obj->popS);
STDestroy(&obj->pushS);
free(obj);
obj = NULL;
}