今天把代码随想录的链表部分看完了,还开了点哈希表部分。
142. 环形链表 II
这道题写起来不难,但理解起来有一定难度。这道题可以使用双指针的办法,设置快慢指针,如果有环的话,它们一定会相遇。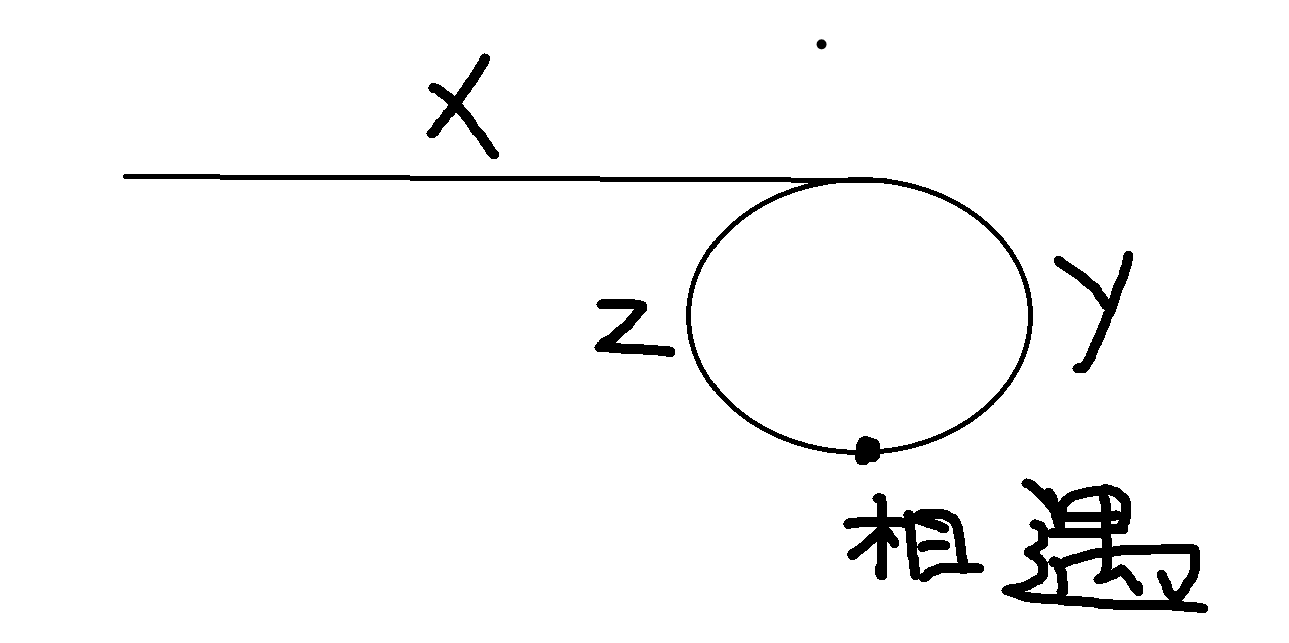
slow走的路程为slow=x+y,fast=x+y+n(y+z),2*slow=fast,fast在环内走n圈后一定会与slow相遇,以入口处为一圈始终,走了n(y+z),最后又走了y与slow相遇,因为fast时slow的二倍,所以无论如何,slow在走完一圈之前就会与fast相遇。最终化简完就是x=(n-1)(y+z)+z。那假如n=1,则x=y。另index1为相遇点,index2为起始点,则相遇点就是入口,那要是n不为1呢?
我们可以把相遇点作为圆的始终,index1走了n-1圈后,再走z就会与index2相遇。代码如下。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
ListNode index1=slow;
ListNode index2=head;
while(index1!=index2){
index1=index1.next;
index2=index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}242. 有效的字母异位词
这个题比较简单,一开始的思路就是创建俩数组,一一对比,但还有更简单的方法。创建一个数组,第一串出现的字母加1,第二串出现的字母减1,如果有不为0的,就返回false。代码如下。
java
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int[] hash=new int[26];
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
hash[s.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}
for(int i=0;i<t.length();i++){
hash[t.charAt(i)-'a']--;
}
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
if(hash[i]!=0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
}创建一个hash数组,里面存26个字母,a代表0,z代表25,用s.charAt(i)-'a'不用知道a的阿斯克吗也可以写。
349. 两个数组的交集
这题对于我来说上强度了,因为不太了解哈希,后续了解了一下,可以看我上个文章https://blog.csdn.net/mingxunwwww/article/details/157403159?spm=1011.2415.3001.10575&sharefrom=mp_manage_link
这道题给了
1 <= nums1.length, nums2.length <= 1000
0 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 1000
那么我们可以用数组来写,代码如下。
java
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> result=new HashSet<>();
int[] hash=new int[1005];
for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
hash[nums1[i]]=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums2.length;i++){
if(hash[nums2[i]]==1){
result.add(nums2[i]);
}
}
int[] res = new int[result.size()];
int index = 0;
for (int num : result) {
res[index++] = num;
}
return res;
}
}我们先将nums1中出现的数字存到hash中,并置为1,之后在遍历nums2时判断hash中的这些数字有没有为1,如果置为1,则存入result数组中,因为它是hashset,所以会自动去重。函数返回int[]类型数组,所以在最后把result中的数存入res数组中。
如果没有给出范围,那么我们可以用hashset解决,代码如下。
java
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> result = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> numSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int n : nums1) {
numSet.add(n);
}
for (int n : nums2) {
if (numSet.contains(n)) {
result.add(n);
}
}
int[] res = new int[result.size()];
int i = 0;
for (int n : result) {
res[i++] = n;
}
return res;
}
}思路是一样的,不再赘述。